Acid And Base Strength Chart
Acid And Base Strength Chart - By the end of this section, you will be able to: Define the ph scale and use it to describe acids and bases. Describe how a chemical reaction reaches chemical equilibrium. Pka = −log ka p k a = − log k a. Web acid strengths are normally expressed using p ka values rather than ka values, where the pka is the negative common logarithm of the ka: This chart is ideal for use in the lab or in the classroom. Web describe the difference between strong and weak acids and bases. Table 1 lists several strong acids. Chart or notebook size available. Web 34 rows table of acid and base strength; Web use this acids and bases chart to find the relative strength of the most common acids and bases. This chart is ideal for use in the lab or in the classroom. The acid and base chart is a reference table designed to make determining the strength of acids and bases simpler. Define the ph scale and use it to. Web acid strengths are normally expressed using p ka values rather than ka values, where the pka is the negative common logarithm of the ka: Web 34 rows table of acid and base strength; Web describe the difference between strong and weak acids and bases. Web (top) measures of acid strength. Weakest 3.2 * 10 9: Table 1 lists several strong acids. Assess the relative strengths of acids and bases according to their ionization constants. The extent to which a base forms hydroxide ion in aqueous solution depends on the strength of the base relative to that of the hydroxide ion, as shown in the last column in figure \(\pageindex{2}\). Acid and base ionization constants. Web. A stronger acid (larger ka) has a smaller p ka, and a. Web acid strengths are normally expressed using p ka values rather than ka values, where the pka is the negative common logarithm of the ka: Figure 15.3.3 lists a series of acids and bases in order of the decreasing strengths of the acids and the corresponding increasing strengths. Pka = −log ka p k a = − log k a. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Weakest 3.2 * 10 9: Web 34 rows table of acid and base strength; Describe how a chemical reaction reaches chemical equilibrium. Pka = −log ka p k a = − log k a. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Web a strong acid yields 100% (or very nearly so) of [latex] {\text {h}}_ {3} {\text {o}}^ {+} [/latex] and a − when the acid ionizes in water; The extent to which a base forms hydroxide ion. In solutions of the same concentration, stronger acids ionize to a greater extent, and so yield higher concentrations of hydronium ions than do weaker acids. (select option to see volume pricing availability) 8½ × 11, pad of 30 (ap7229) $24.50. Web 34 rows table of acid and base strength; Describe how a chemical reaction reaches chemical equilibrium. This chart is. Figure 14.3.3 lists a series of acids and bases in order of the decreasing strengths of the acids and the corresponding increasing strengths of the bases. This chart is ideal for use in the lab or in the classroom. Acid and base ionization constants. Web the most common strong acids and bases are listed in table 1. In solutions of. Acid and base ionization constants. Chart or notebook size available. This chart is ideal for use in the lab or in the classroom. Web the relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. Define the ph scale and use it to describe acids and bases. If the ionization reaction is essentially complete, the acid or base is termed strong; Define the ph scale and use it to describe acids and bases. Acid and base ionization constants. Web a strong acid yields 100% (or very nearly so) of [latex] {\text {h}}_ {3} {\text {o}}^ {+} [/latex] and a − when the acid ionizes in water; The. The acid and base chart is a reference table designed to make determining the strength of acids and bases simpler. Describe how a chemical reaction reaches chemical equilibrium. Pka = −log ka p k a = − log k a. Table 1 lists several strong acids. This chart is ideal for use in the lab or in the classroom. Web acid strengths are normally expressed using p ka values rather than ka values, where the pka is the negative common logarithm of the ka: This chart is ideal for use in the lab or in the classroom. A weak acid gives small amounts of [latex] {\text {h}}_ {3} {\text {o}}^ {+} [/latex] and a −. In solutions of the same concentration, stronger acids ionize to a greater extent, and so yield higher concentrations of hydronium ions than do weaker acids. The extent to which a base forms hydroxide ion in aqueous solution depends on the strength of the base relative to that of the hydroxide ion, as shown in the last column in figure \(\pageindex{2}\). If the ionization reaction is essentially complete, the acid or base is termed strong; Chart or notebook size available. (select option to see volume pricing availability) 8½ × 11, pad of 30 (ap7229) $24.50. Weakest 3.2 * 10 9: Assess the relative strengths of acids and bases according to their ionization constants. Web (top) measures of acid strength.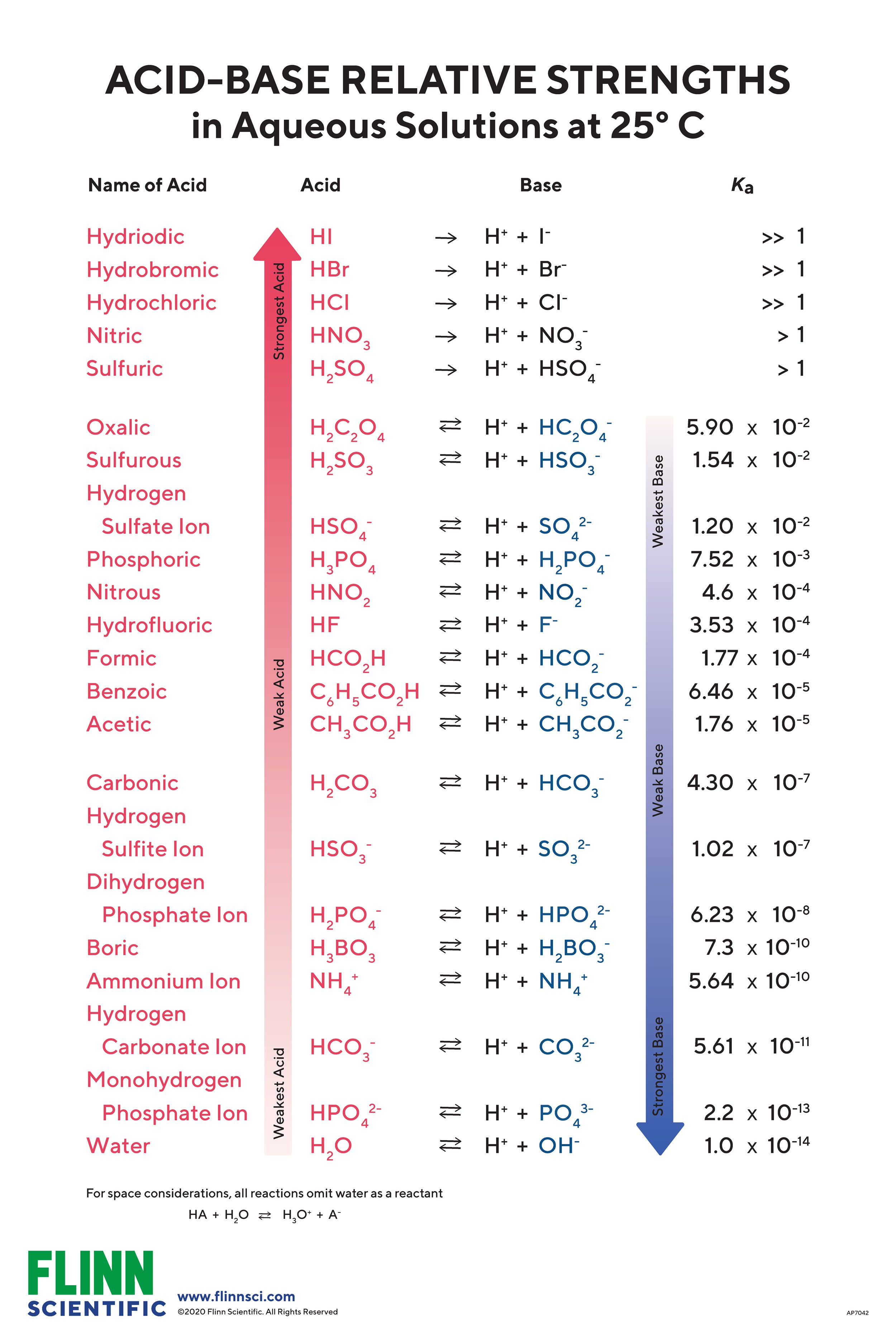
AcidBase Strength Charts for Chemistry
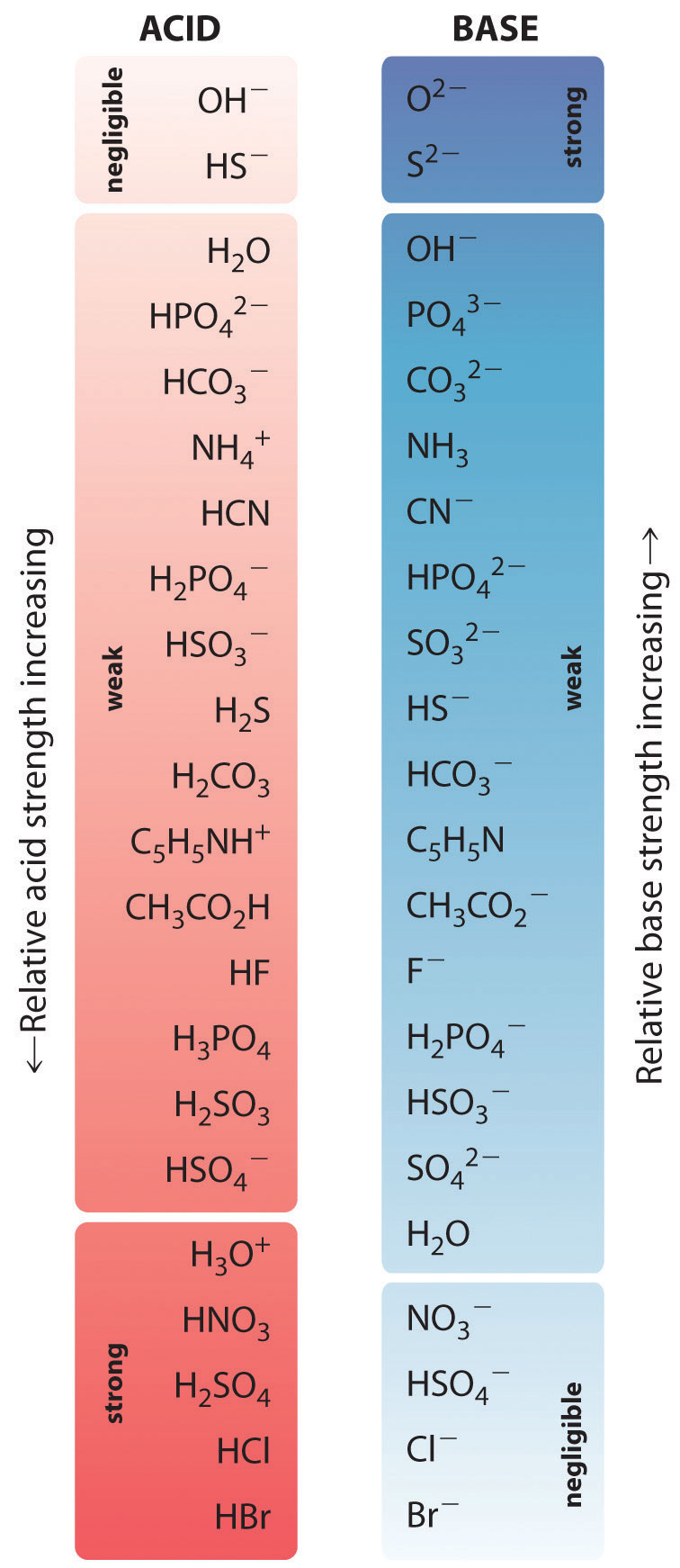
Acid Strengths Table
pKa Values and strengths of Acids and Bases
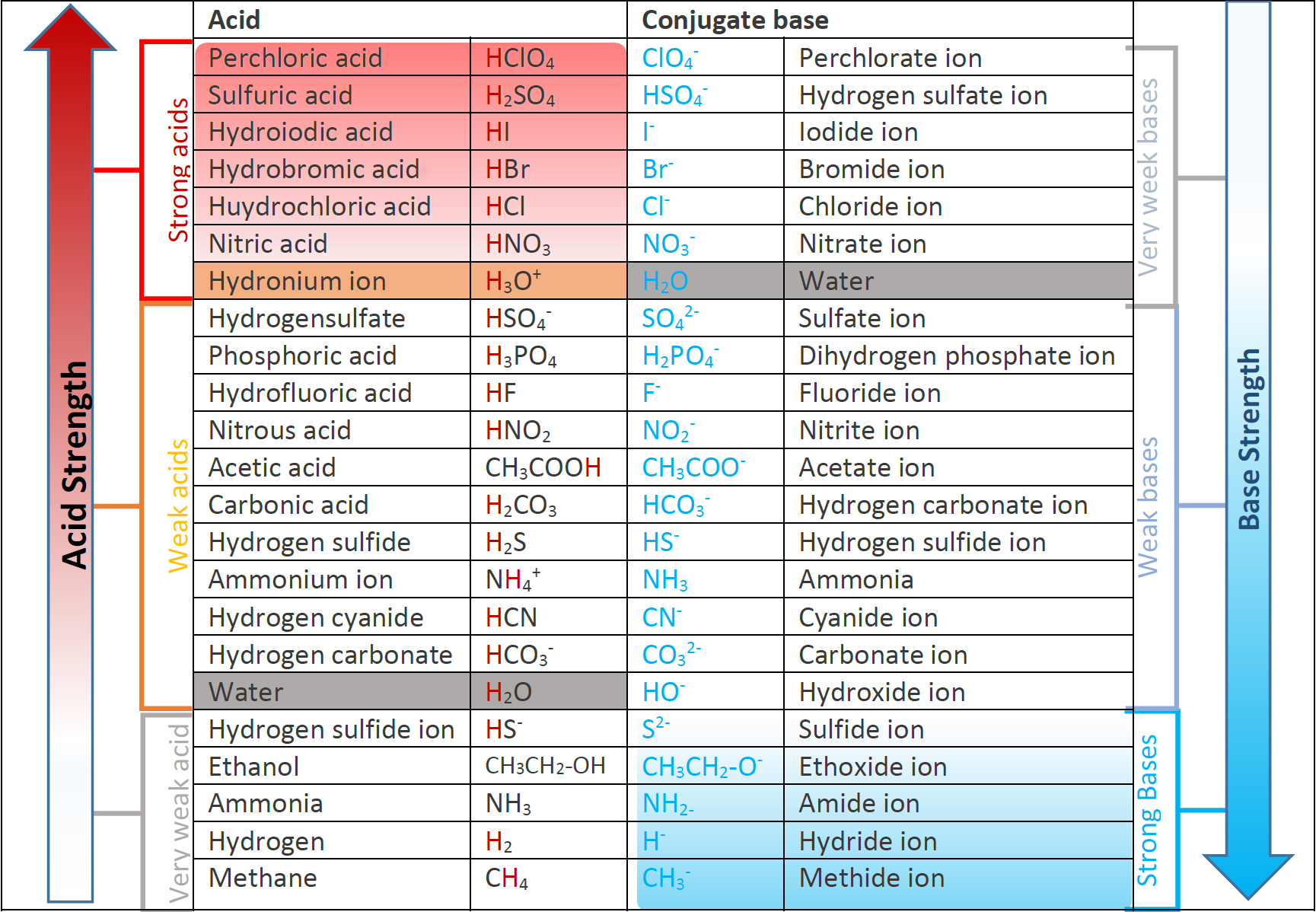
6.3 Strength of acids and bases Chemistry LibreTexts
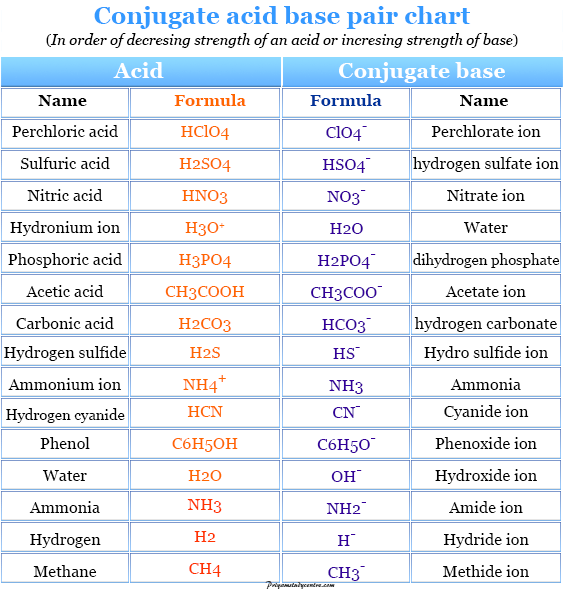
Acids and Bases Definition, Concept, Theory, Examples
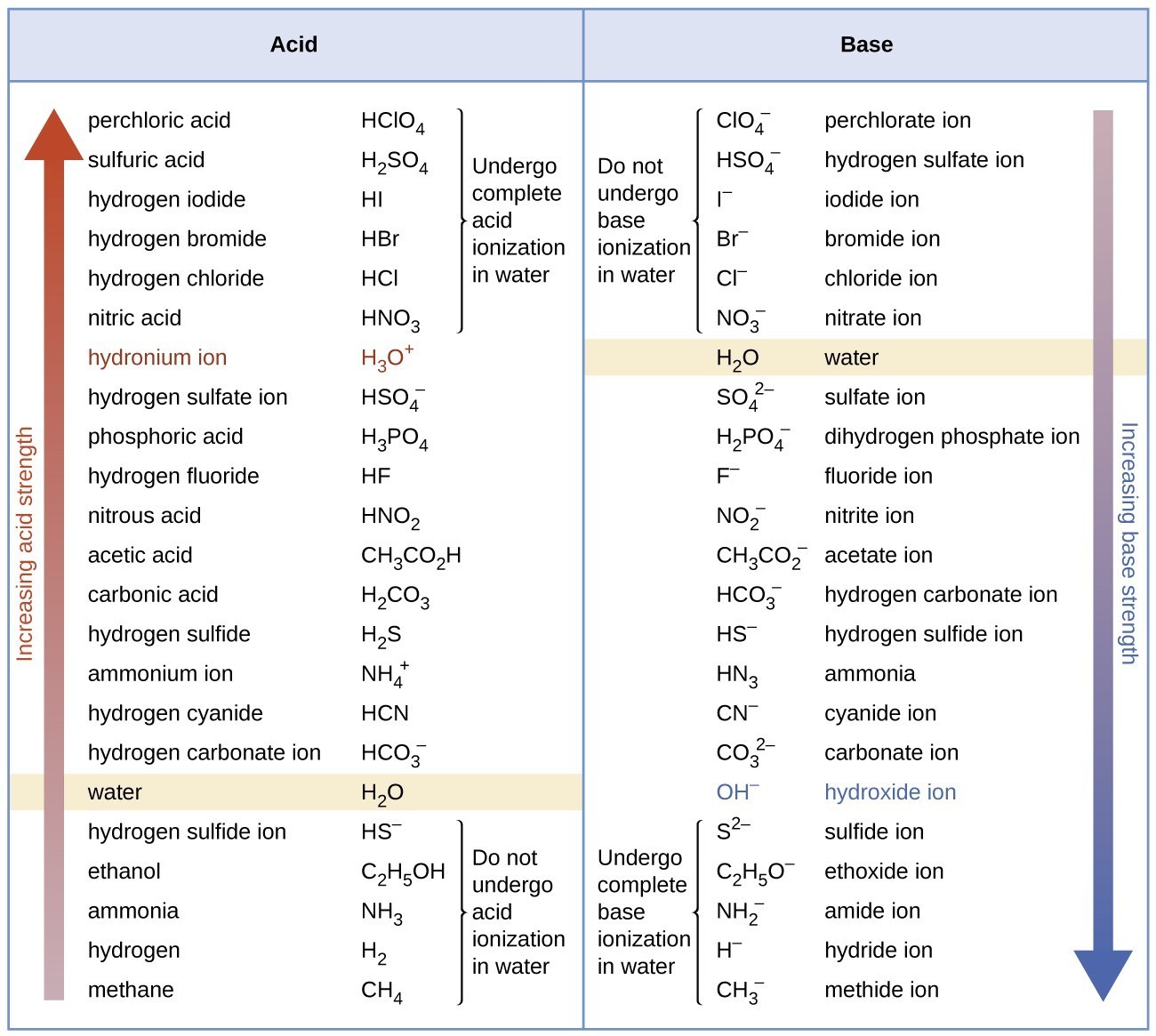
Relative Strengths of Acids and Bases Chemistry Atoms First
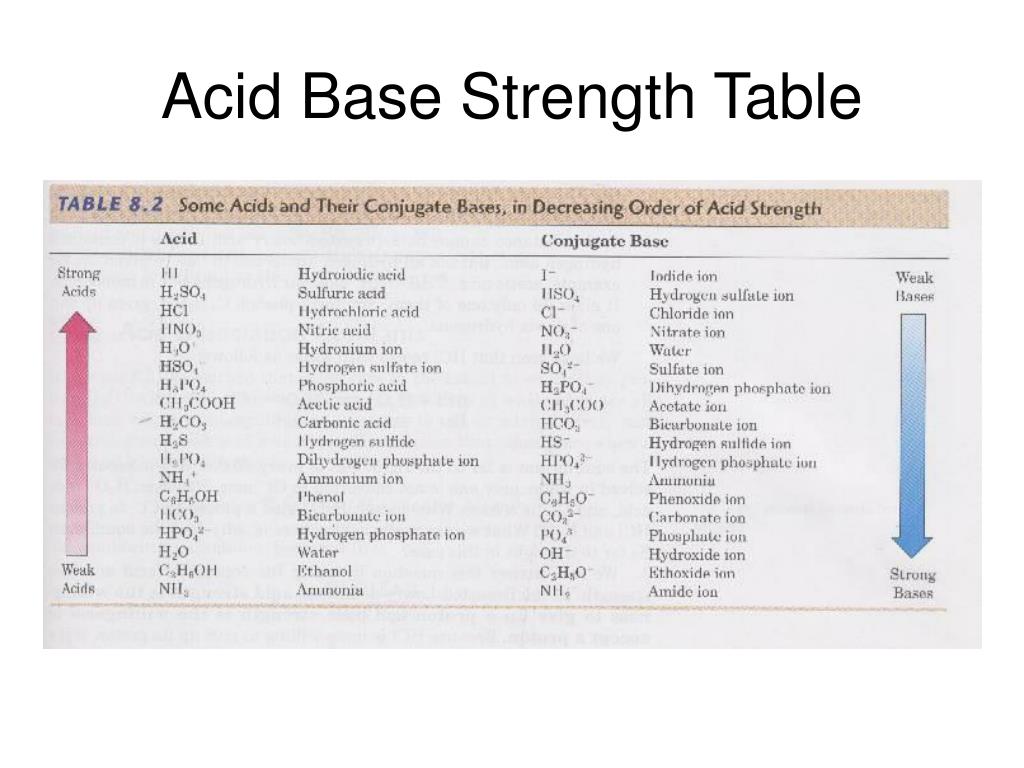
Acid Base Strength Chart
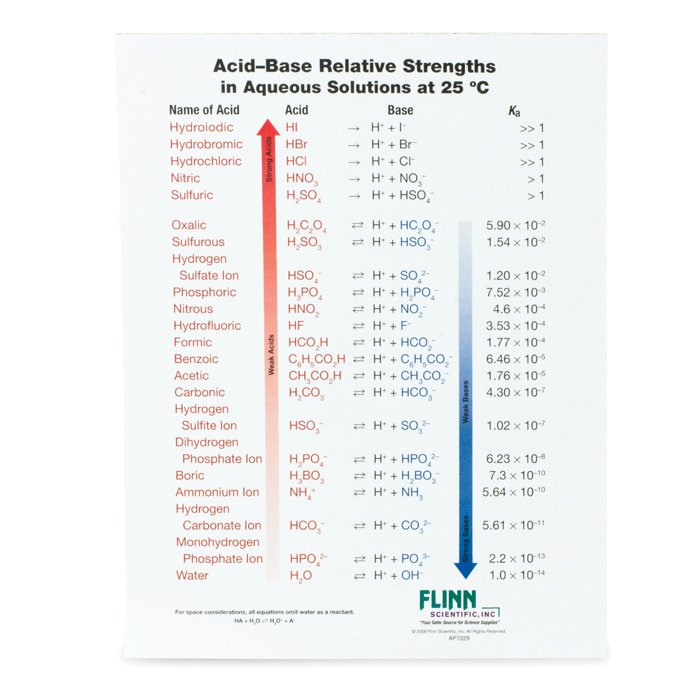
AcidBase Strength Charts for Chemistry
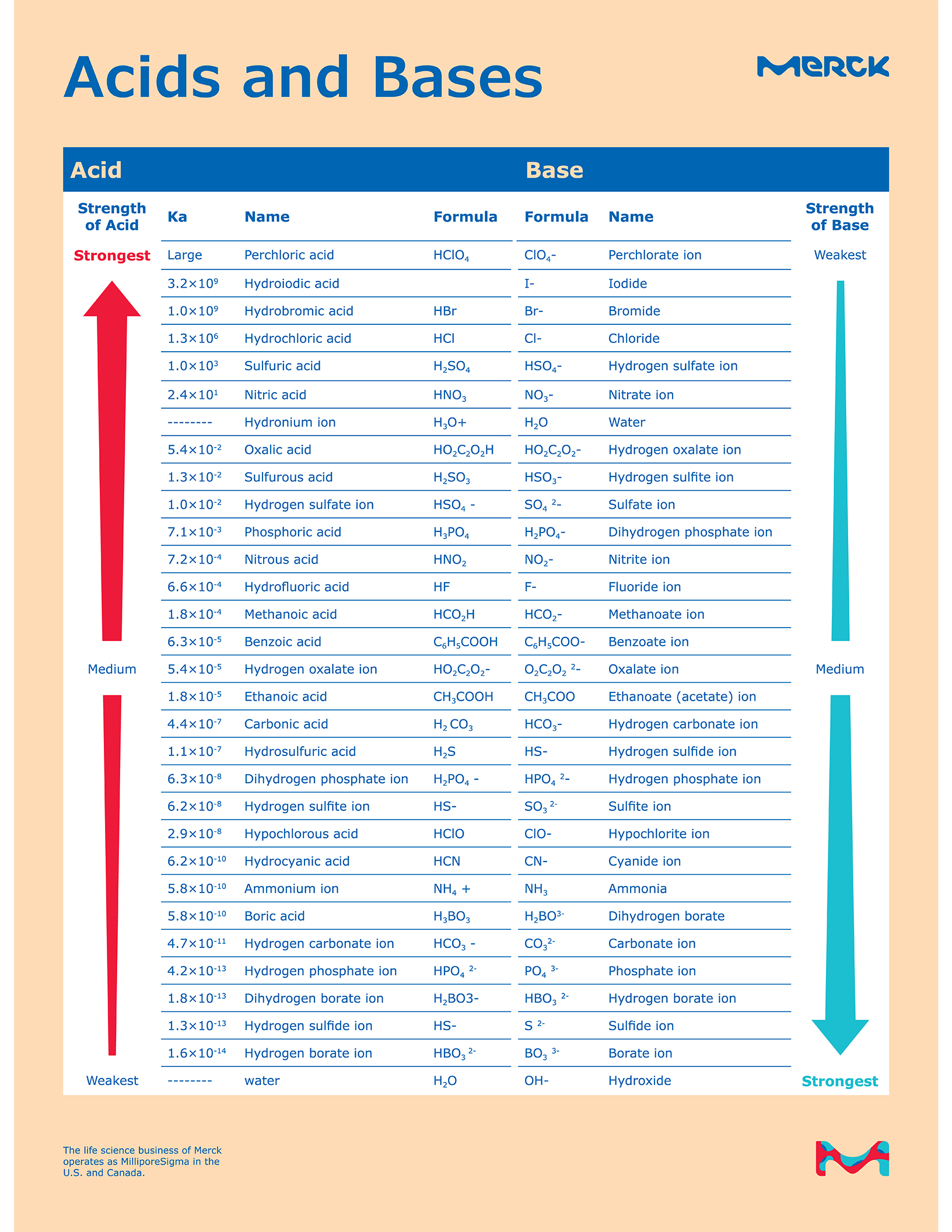
Acid and Base Chart — Table of Acids & Bases
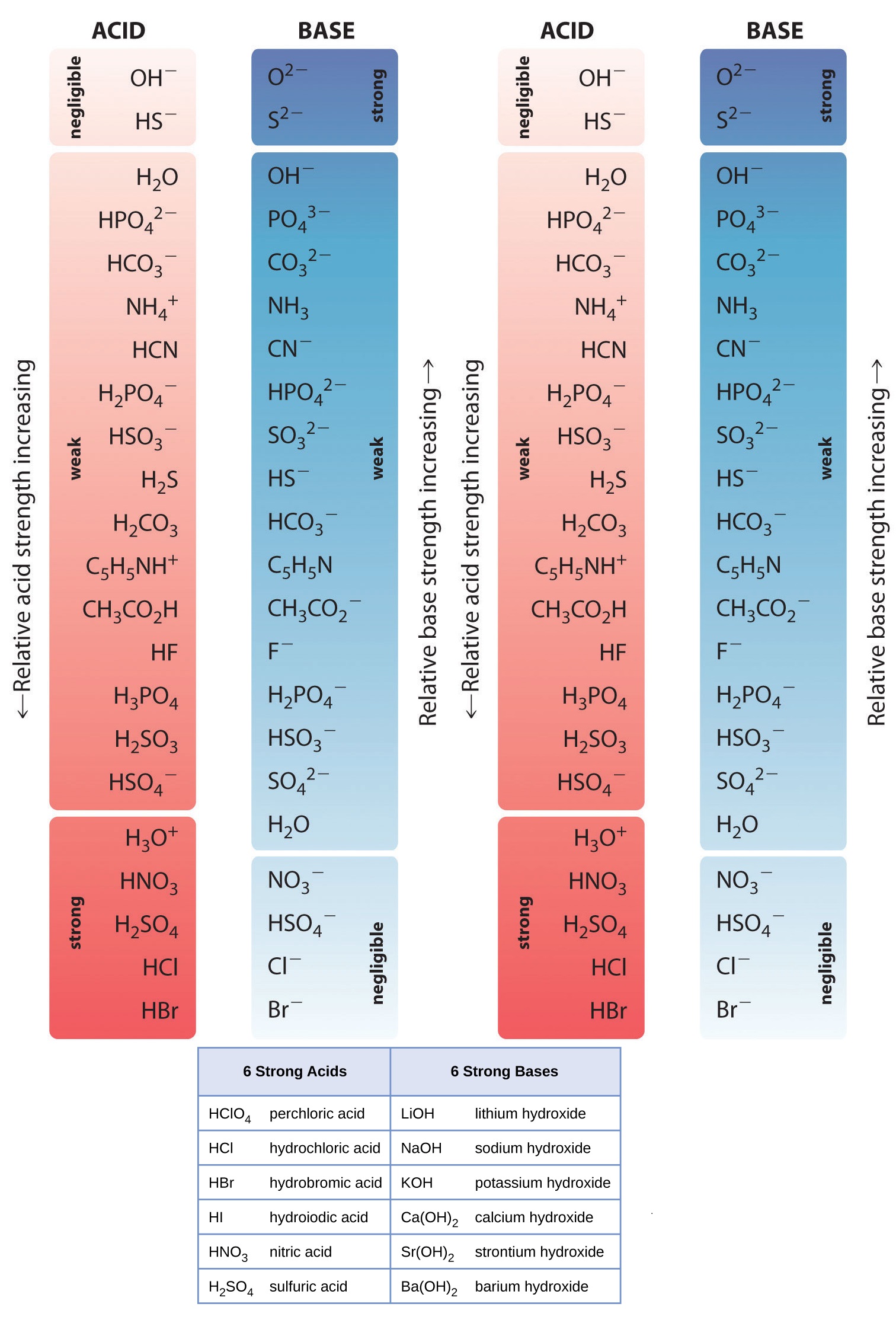
List of Strong Acids & Bases in Order StudyPK
The Acid And Base Chart Is A Reference Table Designed To Make Determining The Strength Of Acids And Bases Simpler.
Web The Relative Strength Of An Acid Or Base Is The Extent To Which It Ionizes When Dissolved In Water.
A Stronger Acid (Larger Ka) Has A Smaller P Ka, And A.
The Relative Strengths Of Acids May Be Quantified By Measuring Their Equilibrium Constants In Aqueous Solutions.
Related Post:
