Atomic Radius Chart Periodic Table
Atomic Radius Chart Periodic Table - As there are no physical existence of orbital in atoms, it is difficult to measure the atomic radius. Web the atomic radius is the size of the atom, typically measured by the distance from the nucleus of the atom to the electron clouds around the nucleus. Web interactive periodic table showing names, electrons, and oxidation states. Web atomic radius trends on periodic table. Web major periodic trends include: The atomic radius of atoms generally increases from top to. Web how atomic radius is defined, and trends across a period and down a group. Web in the periodic table, atomic radii decrease from left to right across a row and increase from top to bottom down a column. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius. Because of these two trends, the largest atoms are found in the lower left corner of the periodic table, and the smallest are found in the upper right corner (figure \(\pageindex{4}\)). The atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period. Web atomic radius of all the elements are mentioned in the chart below. Web the atomic radius of a chemical element is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost shell of an electron. Pdf without crop marks | pdf with crop marks.. Why going down a group makes a bigger radius? Web atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Web the periodic table is a graphic description of the periodic law, which states that the properties and atomic structures of the chemical elements are a periodic function of their atomic number. Web the periodic table of the elements (including atomic radius) element. Periodic trends, arising from the arrangement of the periodic table, provide chemists with an invaluable tool to. Electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius, melting point, and metallic character. Web atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Web atomic radius trends on periodic table. Ionic radii are also available. Look up chemical element names, symbols, atomic masses and other properties, visualize trends, or even test your elements knowledge by playing a periodic table game! Going across a period, the main group elements tend to decrease in atomic radius due to the increased nuclear charge. Web atomic radii decrease, however, as one moves from left to right, across the periodic. Web the periodic table contains nist’s latest critically evaluated data for atomic properties of the elements. Web interactive periodic table showing names, electrons, and oxidation states. The atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period. Ionic radii are also available. Web the atomic radius is the size of the atom, typically measured by the distance. Look up chemical element names, symbols, atomic masses and other properties, visualize trends, or even test your elements knowledge by playing a periodic table game! Web the atomic radius is the size of the atom, typically measured by the distance from the nucleus of the atom to the electron clouds around the nucleus. This is due to the way electrons. Web atomic radius trends on periodic table. Web major periodic trends include: Atomic radii (empirical) atomic radii (absolute) atomic radii (density cutoff) covalent radii revisited (2008 values) covalent radii (molecular single bond) Although more electrons are being added to atoms, they are at similar distances to the nucleus; Web interactive periodic table showing names, electrons, and oxidation states. Look up chemical element names, symbols, atomic masses and other properties, visualize trends, or even test your elements knowledge by playing a periodic table game! First and second ionization energy. Below mentioned radii are the van der waals radius in picometer (pm)). Although more electrons are being added to atoms, they are at similar distances to the nucleus; Atoms decrease. Web the atomic radius is the size of the atom, typically measured by the distance from the nucleus of the atom to the electron clouds around the nucleus. Why going down a group makes a bigger radius? Ionic radii are also available. Web this table shows how the atom size, and atomic radius values change as you move horizontally and. Web explore how atomic radius changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Pdf without crop marks | pdf with crop marks. Web atomic radius is determined as half the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together. Web atomic radius (ionic radius) atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus to the. Web atomic radius is determined as half the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together. Web atomic radii decrease, however, as one moves from left to right, across the periodic table. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atom, usually the mean or typical distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost isolated electron. Periodic trends, arising from the arrangement of the periodic table, provide chemists with an invaluable tool to. Web explore how atomic radius changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web how atomic radius is defined, and trends across a period and down a group. Web in the periodic table, atomic radii decrease from left to right across a row and increase from top to bottom down a column. Web the atomic radius is the size of the atom, typically measured by the distance from the nucleus of the atom to the electron clouds around the nucleus. Web atomic radius trends on periodic table. Web the atomic radius of a chemical element is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost shell of an electron. First and second ionization energy. Although more electrons are being added to atoms, they are at similar distances to the nucleus; Want to join the conversation? Ionic radii are also available. Web the periodic table of the elements (including atomic radius) element name. Web major periodic trends include:
Atomic Radius of Elements The Periodic Table
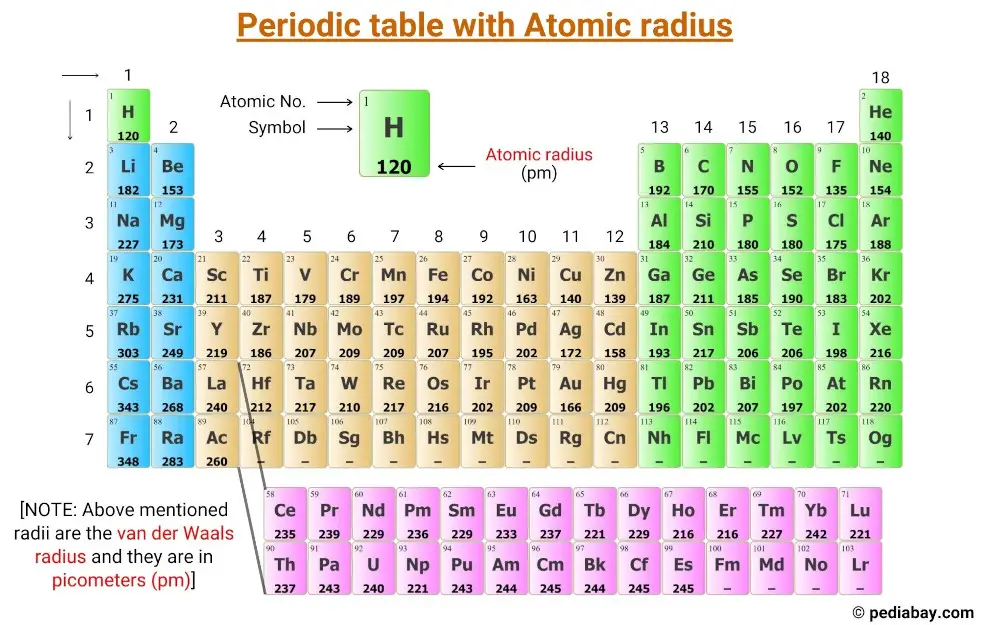
Atomic Radius of Elements (With Periodic table Chart) Pediabay
.png)
Periodic Table Of The Elements Atomic Radius vrogue.co
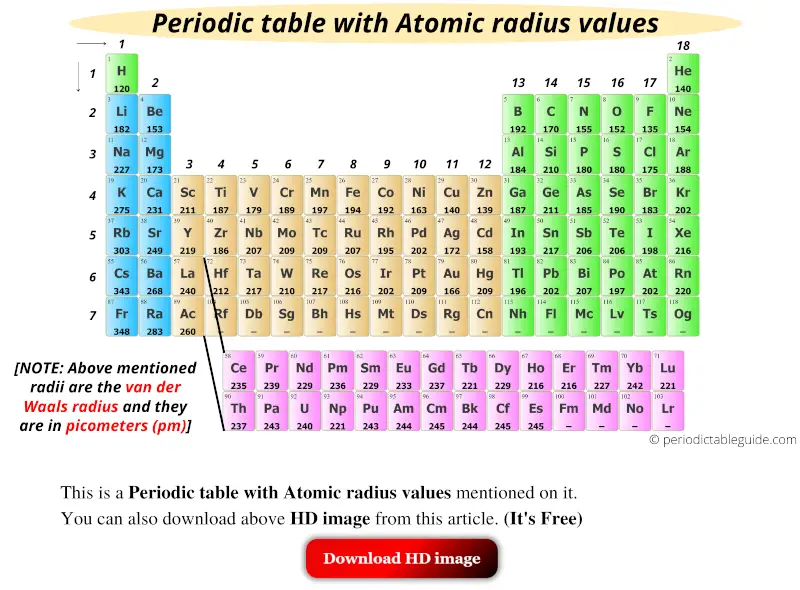
Get the Periodic table with Atomic radius values (Img+Chart)
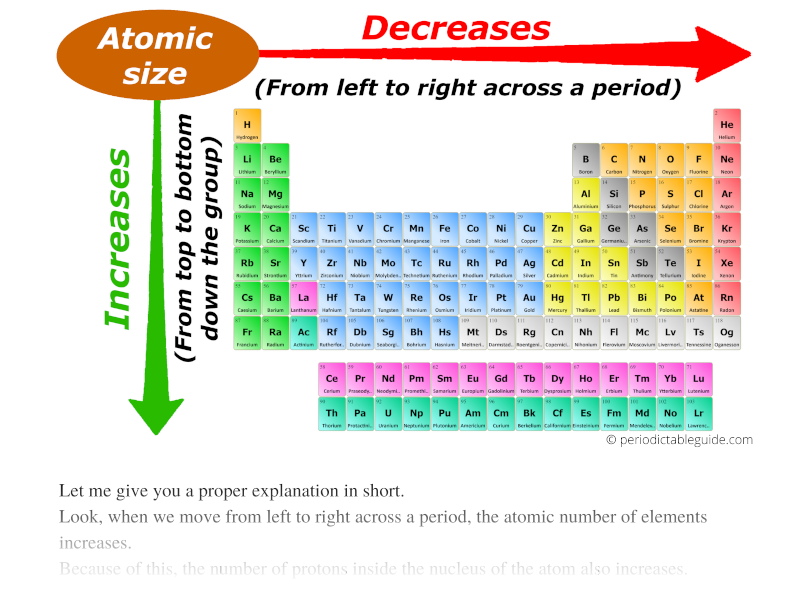
Atomic radius chart mindsstorm

Atomic Radius of Elements
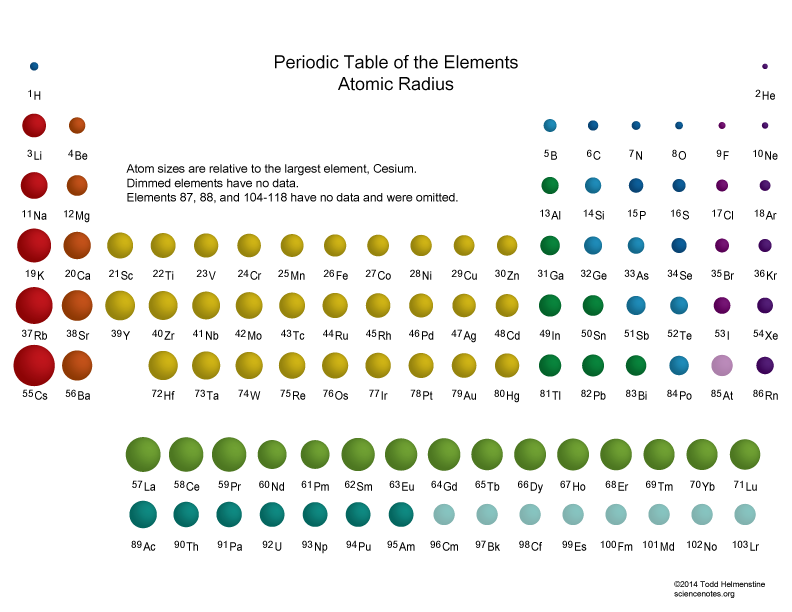
Atomic Radius Trends of the Periodic Table
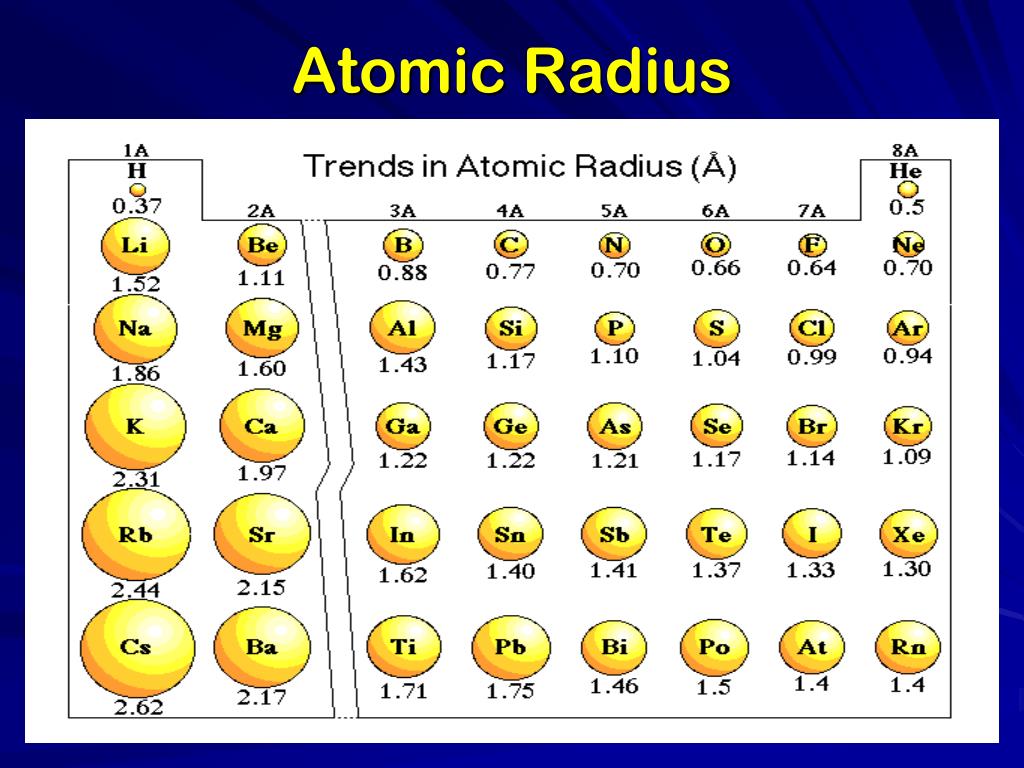
PPT Periodic Table PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2617702
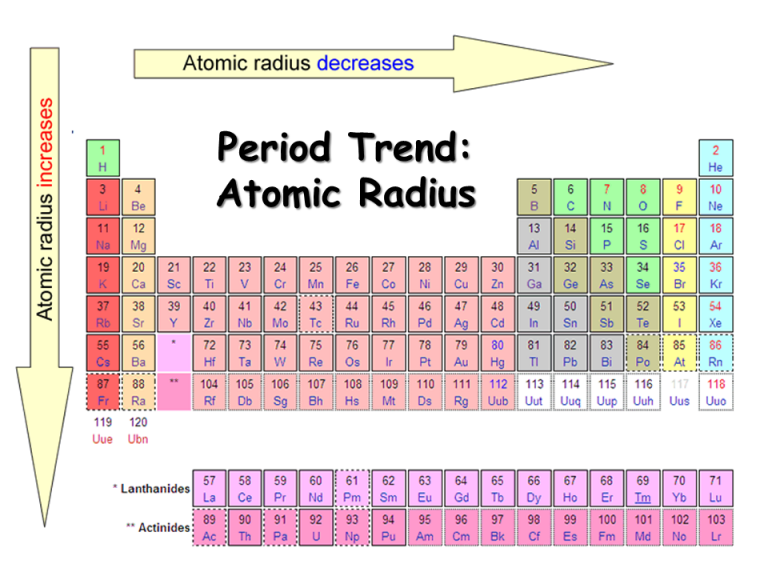
Atomic Radius NEETLab
/accurate-illustration-of-the-periodic-table-82020791-57cc76f23df78c71b66efbd7.jpg)
Atomic Radius Table Pdf Elcho Table
Going Across A Period, The Main Group Elements Tend To Decrease In Atomic Radius Due To The Increased Nuclear Charge.
Web The Periodic Table Is A Graphic Description Of The Periodic Law, Which States That The Properties And Atomic Structures Of The Chemical Elements Are A Periodic Function Of Their Atomic Number.
Atomic Radii (Empirical) Atomic Radii (Absolute) Atomic Radii (Density Cutoff) Covalent Radii Revisited (2008 Values) Covalent Radii (Molecular Single Bond)
In General, Atomic Radius Or Atom Size Decreases As You Move From Left To Right.
Related Post: