Autonomic Nervous System Chart
Autonomic Nervous System Chart - The autonomic nervous system is a complex network of cells that. Web the autonomic nervous system (ans) is a functional division of the nervous system, with its structural parts in both the central nervous system (cns) and the peripheral nervous system (pns). Web introduction to the autonomic nervous system | anatomy. The autonomic nervous system receives input from parts of the central nervous system (cns) that process and integrate stimuli from the body and external environment. Web the autonomic system is the part of the peripheral nervous system responsible for regulating involuntary body functions, such as heartbeat, blood flow, breathing, and digestion. The ans controls subconscious effectors such as visceral muscle tissue, cardiac muscle tissue, and glandular tissue. Web the somatic involves parts of the body a person can command at will, and the autonomic helps run involuntary functions such as pumping blood. The autonomic nervous system has two divisions: Web the autonomic nervous system is a component of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary physiologic processes including heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, digestion, and sexual arousal. Your nervous system helps you regulate your voluntary and involuntary actions, as well as thinking, communicating, and memory. The ans controls subconscious effectors such as visceral muscle tissue, cardiac muscle tissue, and glandular tissue. Information conveyed through the nervous system. It consists of two subsystems: The ans can be subdivided into the parasympathetic nervous system (psns) and. Identify the anatomical and functional divisions of the nervous system. The ans can be subdivided into the parasympathetic nervous system (psns) and. It controls the glands and smooth muscle of all the internal organs (viscera) unconsciously. The autonomic nervous system (ans) is made up of pathways of neurons that control various organ systems inside the body, using many diverse chemicals and signals to maintain homeostasis. It contains three anatomically distinct. Web the autonomic system is the part of the peripheral nervous system responsible for regulating involuntary body functions, such as heartbeat, blood flow, breathing, and digestion. Web the autonomic nervous system (ans) is a division of the pns that includes all of the involuntary efferent neurons. What affects how it works? These are processes you don’t think about and that. The autonomic nervous system (ans) is made up of pathways of neurons that control various organ systems inside the body, using many diverse chemicals and signals to maintain homeostasis. Information conveyed through the nervous system. List the basic functions of the nervous system. Web the autonomic nervous system (ans) is the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls visceral. Because of this, the autonomic nervous system is also sometimes known by another name: List the basic functions of the nervous system. Relate the functional and structural differences between gray matter and white matter structures of the nervous system to the structure of neurons. The sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. Web the autonomic nervous system controls cardiac. The sympathetic nervous system for fight or flight responses, and the parasympathetic nervous system for rest and digestion. Web the autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, its force of contraction, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. The ans controls subconscious effectors such as. Web your autonomic nervous system is a part of your overall nervous system that controls the automatic functions of your body that you need to survive. Because of this, the autonomic nervous system is also sometimes known by another name: Differentiate between the structures of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions in the autonomic nervous system. It divides into the sympathetic. Web the autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, its force of contraction, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. This is why it’s also called the visceral nervous. What affects how it works? Web your autonomic nervous system is a part of your overall. Web the autonomic nervous system, a part of our overall nervous system, regulates smooth muscle cells, cardiac muscle, and gland cells autonomously. Web the autonomic nervous system is the part of the nervous system that supplies the internal organs, including the blood vessels, stomach, intestine, liver, kidneys, bladder, genitals, lungs, pupils, heart, and sweat, salivary, and digestive glands. The ans. Complex neural pathways interconnect and relay information between the hypothalamus and the autonomic nervous system. The ans controls subconscious effectors such as visceral muscle tissue, cardiac muscle tissue, and glandular tissue. It consists of two subsystems: The motor outflow of both systems is formed by two serially connected sets of neurons. Web the autonomic system is the part of the. Differentiate between the structures of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions in the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system (ans) is made up of pathways of neurons that control various organ systems inside the body, using many diverse chemicals and signals to maintain homeostasis. The sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. Information conveyed through the nervous system. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Nervous system (anterior view) the nervous system is a network of neurons whose main feature is to generate, modulate and transmit information between all the different parts of the human body. It consists of two subsystems: The autonomic nervous system is a complex network of cells that. Web introduction to the autonomic nervous system | anatomy. The ans can be subdivided into the parasympathetic nervous system (psns) and. The autonomic nervous system receives input from parts of the central nervous system (cns) that process and integrate stimuli from the body and external environment. These parts include the hypothalamus, nucleus of the solitary tract, reticular formation, amygdala, hippocampus, and olfactory cortex. Web the autonomic nervous system controls cardiac and smooth muscle, as well as glandular tissue. The sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. Because of this, the autonomic nervous system is also sometimes known by another name: What affects how it works?
The Autonomic Nervous System Explained
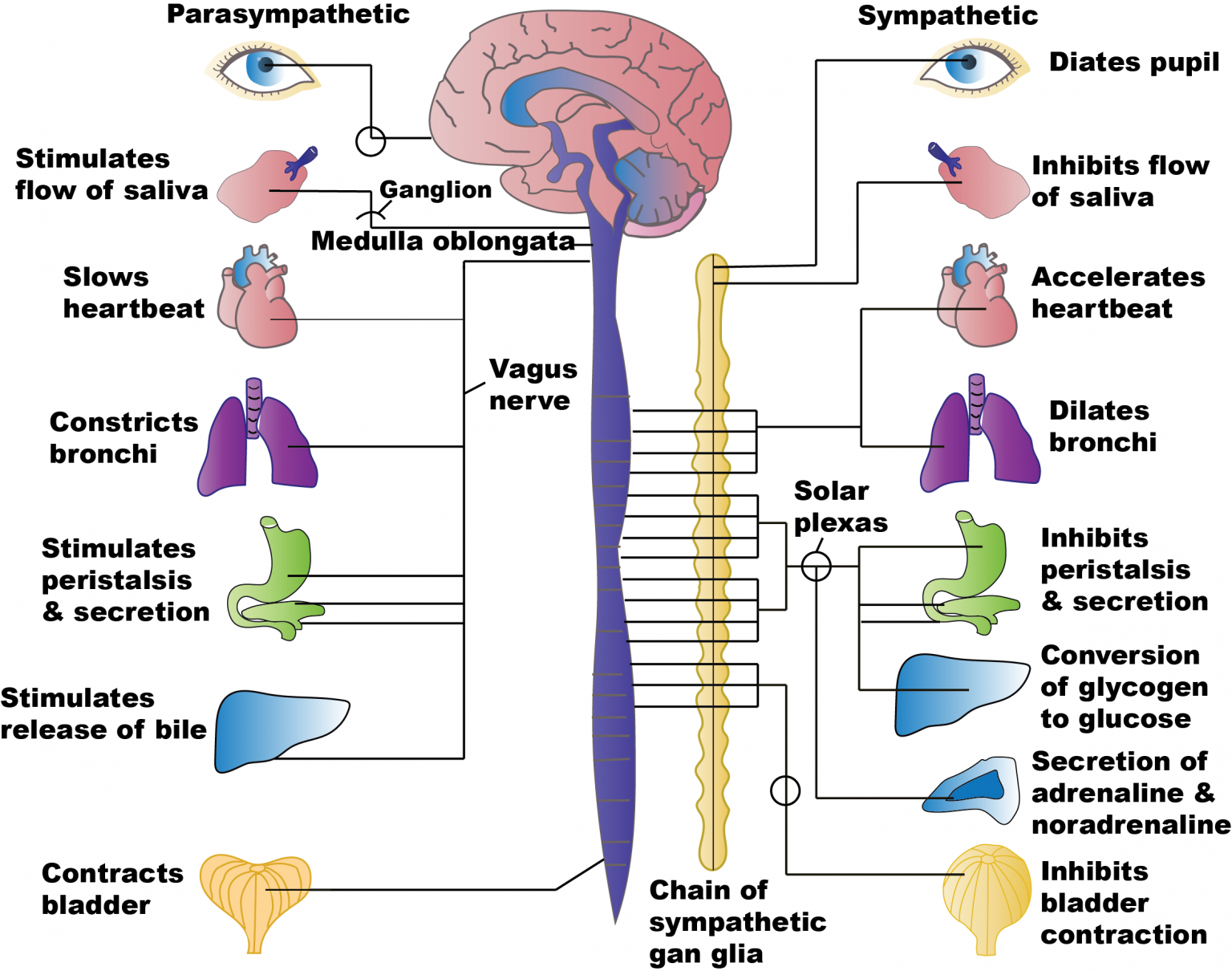
4.2 Autonomic Nervous System Basics Nursing Pharmacology
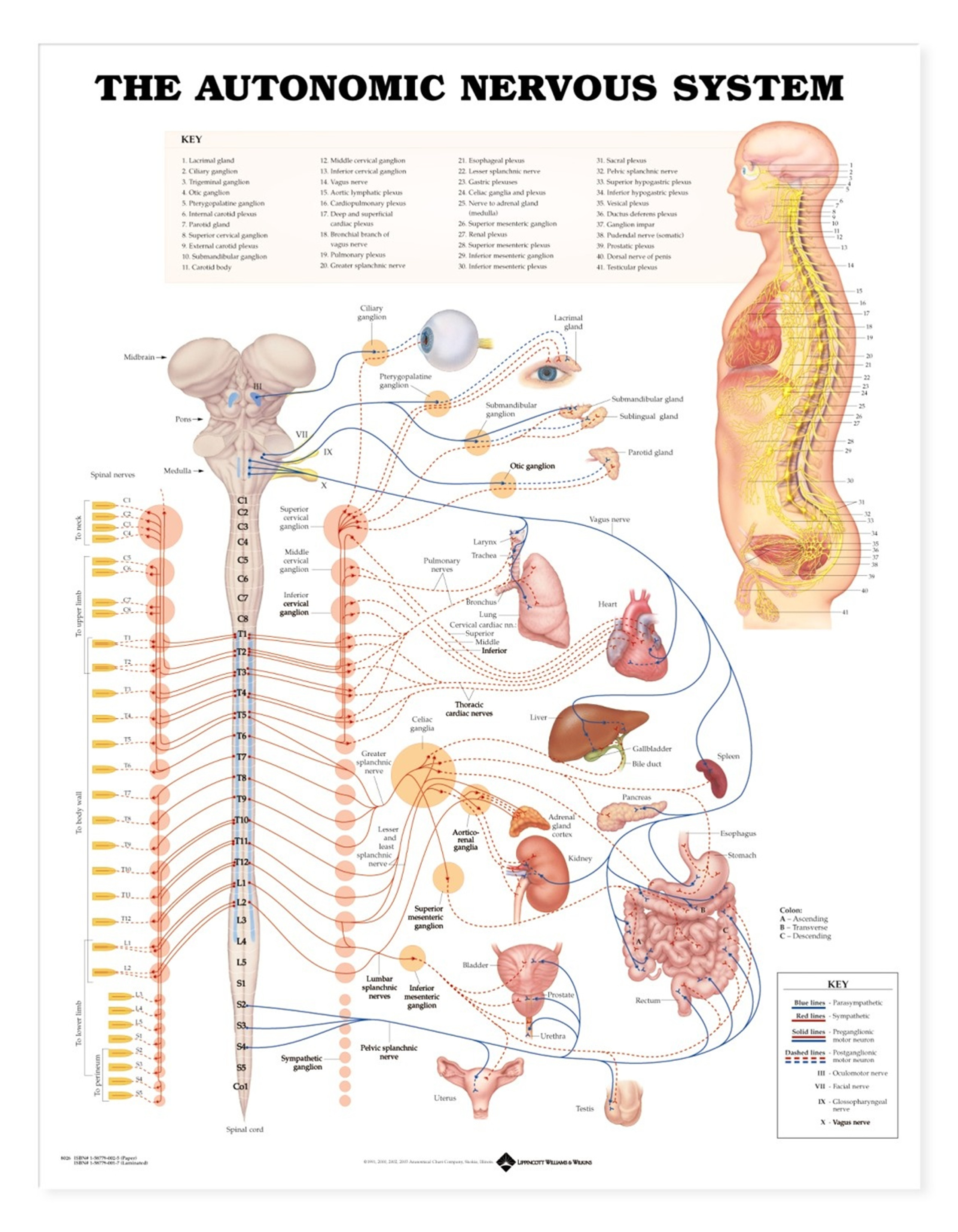
Autonomic Nervous System Chart Autonomic Nerves Poster 9781587790010

FUNCTIONING OF THE AUTONIMOC NERVOUS SYSTEM Diagram Quizlet

Autonomic nervous system disorders causes, symptoms, diagnosis

Anatomy Charts Posters The Autonomic Nervous System Anatomical Chart

Erwecke unser autonomes Nervensystem zum Leben! von Bence Balaton More

diagram of the human body with labels
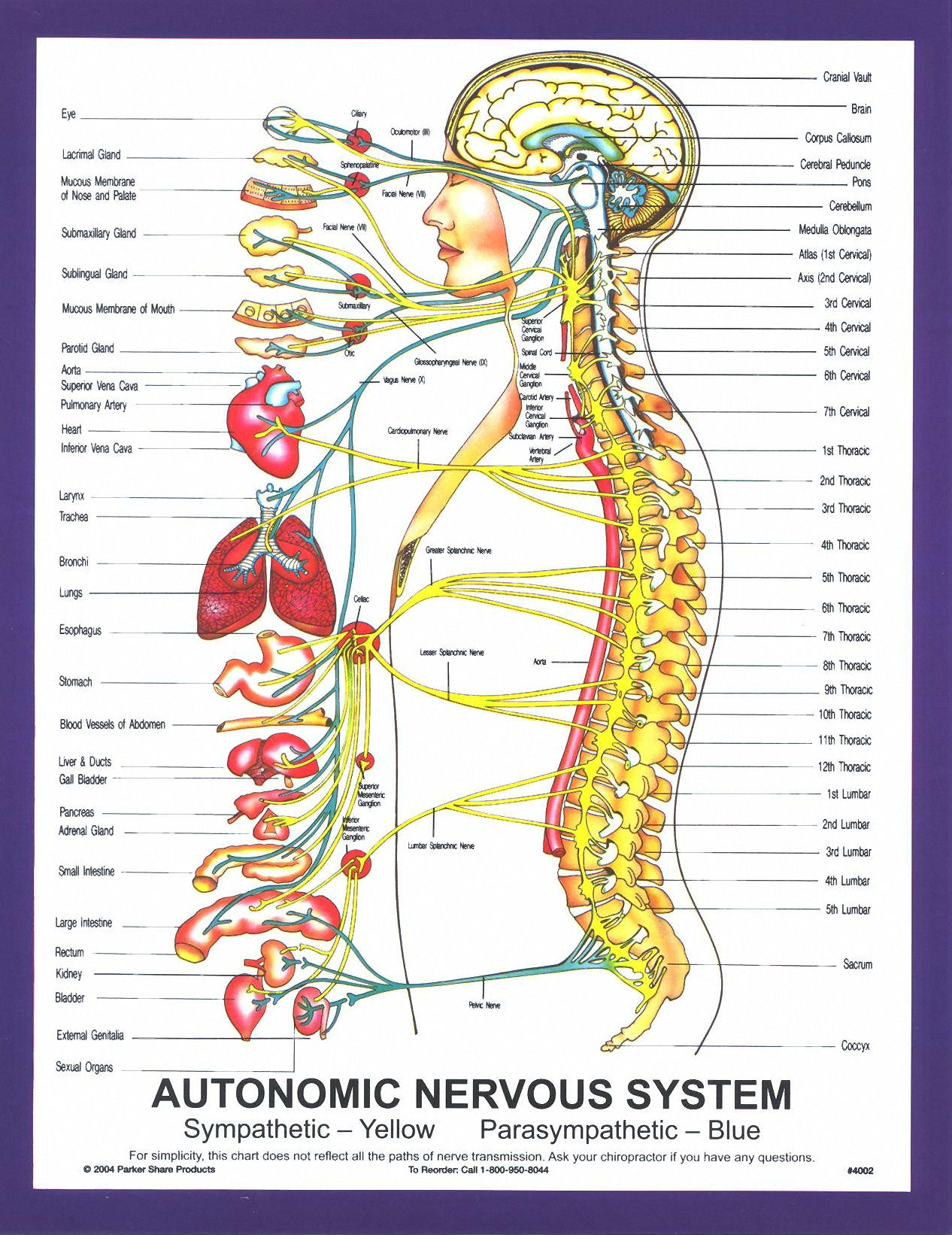
New The Autonomic Nervous System Anatomical Diagram Chart My XXX Hot Girl

BodyPartChart Autonomic Nervous System
It Controls The Glands And Smooth Muscle Of All The Internal Organs (Viscera) Unconsciously.
Web The Autonomic Nervous System (Ans) Is A Functional Division Of The Nervous System, With Its Structural Parts In Both The Central Nervous System (Cns) And The Peripheral Nervous System (Pns).
The Somatic Nervous System Is Associated With Voluntary Responses (Though Many Can Happen Without Conscious Awareness, Like Breathing), And The Autonomic Nervous System Is Associated With Involuntary Responses, Such As Those Related To Homeostasis.
Web The Autonomic Nervous System (Ans) Is The Part Of The Peripheral Nervous System That Controls Visceral Functions That Occur Below The Level Of Consciousness.
Related Post: