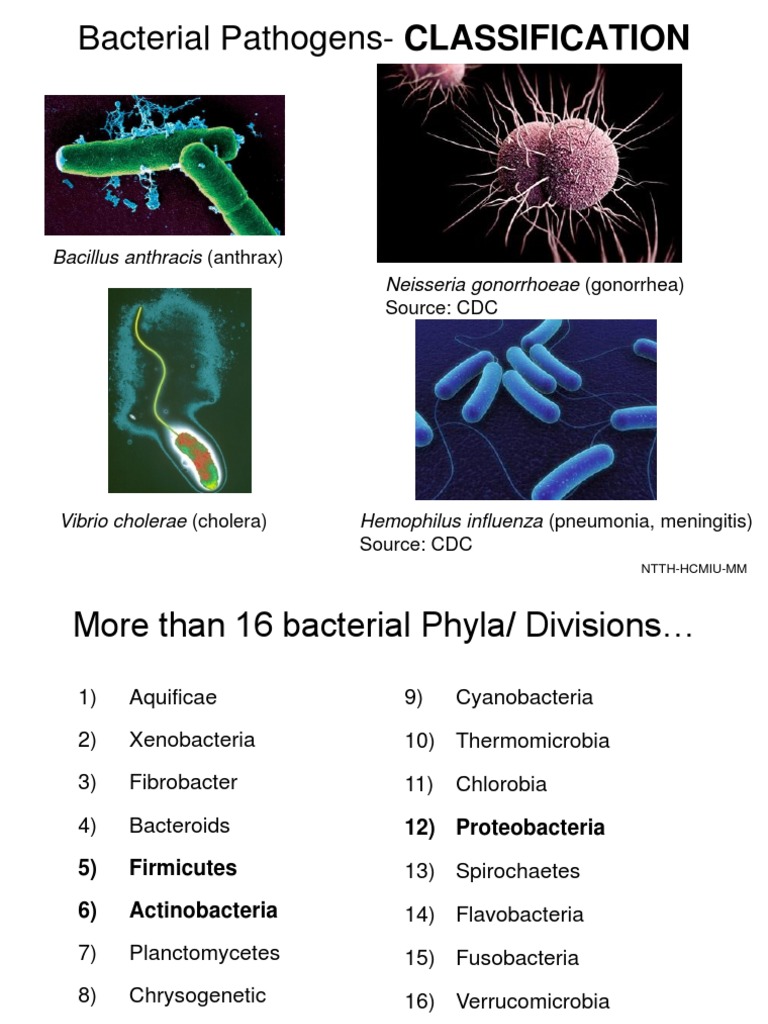
Bacteria Identification Chart
Bacteria Identification Chart - There is a chart at the end of these lecture notes on the general phenotypic classification of many of the clinically important bacteria. Web discuss the characterization of microbes based on phenotypic and genotypic methods. Web biochemical reactions are significant in the identification of bacterial isolates and in the identification of different bacterial species. Treatment of m ethicillin s ensitive staphylococcus aureus ( mssa) penicillins. Taxonomy is the classification, nomenclature and identification of microbes (algae, protozoa, slime moulds, fungi, bacteria, archaea and viruses). Use this tool to view properties of individual pseudomonads. Introduction to bacterial identification using genotypic methods; Web although bacterial and fungi colonies have many characteristics and some can be rare, there are a few basic elements that you can identify for all colonies: Web this paper reviewed core concepts of interpreting bacterial culture results, including timing of cultures, common culture sites, potential for contamination, interpreting the gram stain, role of rapid diagnostic tests, conventional antibiotic susceptibility testing, and automated testing. Carefully document results of microbiological tests. Web in this blog post, i am sharing information about the standard, conventional biochemical tests and their primary uses in the microbiology laboratory for identifying pathogens of interest. Bacteria are identified in laboratories by various methods, including microscopy ( fresh state, after staining ), observation of growth characteristics ( list of culture media ), determination of reactions to organic and. Taxonomy is the classification, nomenclature and identification of microbes (algae, protozoa, slime moulds, fungi, bacteria, archaea and viruses). Introduction to bacterial identification using genotypic methods; Treatment of m ethicillin s ensitive staphylococcus aureus ( mssa) penicillins. By the end of the course you will be able to recognize most of these microorganisms. Though basic identification can be carried out using. Web this interactive, modular lab explores the techniques used to identify different types of bacteria based on their dna sequences. Newer molecular techniques permit species to be identified by their genetic sequences, sometimes directly from the clinical specimen. With improved coloring and contrast, the dyes overcome these problems by facilitating the cellular structure identification. Pharmig’s latest publication is a guide. Web although bacterial and fungi colonies have many characteristics and some can be rare, there are a few basic elements that you can identify for all colonies: Introduction to bacterial identification using genotypic methods; Taxonomy is the classification, nomenclature and identification of microbes (algae, protozoa, slime moulds, fungi, bacteria, archaea and viruses). Introduction to bacterial identification using enterotube test; Web. Selection of appropriate antibiotics depends on diagnosis! Web accurate identification of bacterial isolates is essential in a clinical microbiology laboratory because the results often inform decisions about treatment that directly affect patient outcomes. Web in this section, we will discuss a few methods that use biochemical characteristics to identify microorganisms. Effectively collaborate with a classmate. By the end of the. Newer molecular techniques permit species to be identified by their genetic sequences, sometimes directly from the clinical specimen. Introduction to bacterial identification using culture media; Pharmig’s latest publication is a guide to bacterial identification. Use this tool to view properties of individual pseudomonads. Bacterial identification with culture media one of the common methods to identify bacteria is through the use. Introduction to bacterial identification using genotypic methods; These tests depend on the presence of certain enzymes, such as catalase, oxidase, urease, gelatinase, etc., produced by the bacteria. Web biochemical reactions are significant in the identification of bacterial isolates and in the identification of different bacterial species. Some of the biochemical tests mentioned here, for example, catalase test, and oxidase test,. Taxonomy is the classification, nomenclature and identification of microbes (algae, protozoa, slime moulds, fungi, bacteria, archaea and viruses). Introduction to bacterial identification using culture media; For example, circular, filamentous, etc. Bacteria are identified routinely by morphological and biochemical tests, supplemented as needed by specialized tests such as serotyping and antibiotic inhibition patterns. Web learn how to identify and classify bacteria. Bacterial identification with culture media one of the common methods to identify bacteria is through the use of specialized media. Treatment of m ethicillin s ensitive staphylococcus aureus ( mssa) penicillins. Web this paper reviewed core concepts of interpreting bacterial culture results, including timing of cultures, common culture sites, potential for contamination, interpreting the gram stain, role of rapid diagnostic. Web although bacterial and fungi colonies have many characteristics and some can be rare, there are a few basic elements that you can identify for all colonies: Web discuss the characterization of microbes based on phenotypic and genotypic methods. Some microorganisms store certain compounds as granules within their cytoplasm, and the contents of these. Bacteria are identified routinely by morphological. Introduction to bacterial identification using enterotube test; Web the enzymes produced by an organism helps in the identification of bacteria by observing their enzymatic activities using a specific media with the inoculation of a pure culture of the organism where under suitable incubation period releases their respective enzymes. Web in this blog post, i am sharing information about the standard, conventional biochemical tests and their primary uses in the microbiology laboratory for identifying pathogens of interest. These tests depend on the presence of certain enzymes, such as catalase, oxidase, urease, gelatinase, etc., produced by the bacteria. Web in this section, we will discuss a few methods that use biochemical characteristics to identify microorganisms. Newer molecular techniques permit species to be identified by their genetic sequences, sometimes directly from the clinical specimen. In this lab, students prepare and analyze a virtual bacterial dna sample. Introduction to bacterial identification using genotypic methods; Bacterial identification with culture media one of the common methods to identify bacteria is through the use of specialized media. Web learn how to identify and classify bacteria based on their morphology, physiology, genetics, and ecology. Pharmig’s latest publication is a guide to bacterial identification. By the end of the course you will be able to recognize most of these microorganisms. Web this interactive, modular lab explores the techniques used to identify different types of bacteria based on their dna sequences. Bacteria are identified routinely by morphological and biochemical tests, supplemented as needed by specialized tests such as serotyping and antibiotic inhibition patterns. Some of the biochemical tests mentioned here, for example, catalase test, and oxidase test, assist us in many ways apart from the primary purpose. Some microorganisms store certain compounds as granules within their cytoplasm, and the contents of these.
Types of bacteria Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock

72 best images about Microbiology on Pinterest Image search, Public
Bacterial Classification Bacteria Gram Negative Bacteria

Bacteria Identification Chart

Flow chart for the identification of bacteria in clinical solid waste
Frontiers Metabolomic Diversity and Identification of Antibacterial
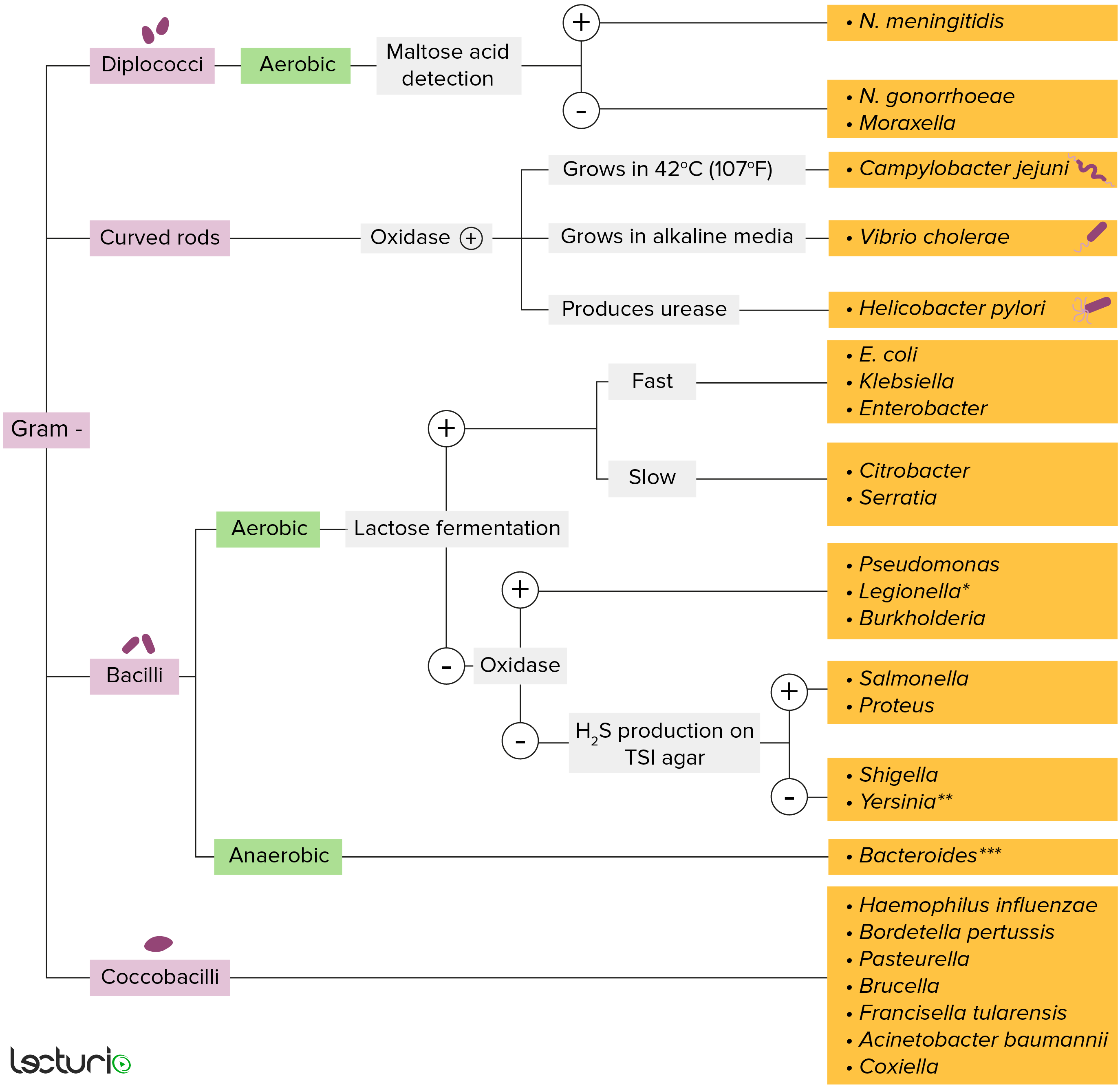
Bacteroides Concise Medical Knowledge

Identifying Bacteria Through Look, Growth, Stain and Strain

Flow Chart For Bacterial Identification My XXX Hot Girl

Bacteria Identification Chart
Web Accurate Identification Of Bacterial Isolates Is Essential In A Clinical Microbiology Laboratory Because The Results Often Inform Decisions About Treatment That Directly Affect Patient Outcomes.
Though Basic Identification Can Be Carried Out Using A Light Microscope, Without Staining, Bacteria Look Colorless, Transparent, And Are Very Difficult To See.
Bacteria Are Identified In Laboratories By Various Methods, Including Microscopy ( Fresh State, After Staining ), Observation Of Growth Characteristics ( List Of Culture Media ), Determination Of Reactions To Organic And Inorganic Compounds ( Api Gallery , Microbiological Techniques) And Molecular Techniques.
Web This Paper Reviewed Core Concepts Of Interpreting Bacterial Culture Results, Including Timing Of Cultures, Common Culture Sites, Potential For Contamination, Interpreting The Gram Stain, Role Of Rapid Diagnostic Tests, Conventional Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing, And Automated Testing.
Related Post: