Bar Chart And Histogram
Bar Chart And Histogram - When choosing between a histogram and a bar graph, consider the type of data you have and the insights you want to present: Each bin is plotted as a bar whose height corresponds to how many data points are in that bin. Web bar graph allows you to compare and contrast metrics (averages, sums, etc.) across different categories while histogram allows you to view the distribution, or relative frequencies, of values in a dataset. A histogram represents the frequency distribution of continuous variables. A histogram displays the shape and spread of continuous sample data. A bar graph is a plot of a single data point (a sum, average, or other value) for each category while a histogram is a plot of a range of data. The histogram refers to a graphical representation that shows data by way of bars to display the frequency of numerical data whereas the bar graph is a graphical representation of data that uses bars to compare different categories of data. For continuous data and distribution analysis, use a histogram. Web a histogram is a graphical display of data using bars of different heights. Taller bars show that more data falls in that range. If there is any post helps, then please consider accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly. Web histograms are graphs that display the distribution of your continuous data. Web a histogram is a graphical display of data using bars of different heights. It is particularly effective in illustrating the frequency distribution of continuous. Understanding when and how to use each can dramatically enhance your data presentation skills. The histogram refers to a graphical representation that shows data by way of bars to display the frequency of numerical data whereas the bar graph is a graphical representation of data that uses bars to compare different categories of data. Web a bar graph is a. Web a histogram is a chart that plots the distribution of a numeric variable’s values as a series of bars. For instance, while the mean and standard deviation can numerically summarize your data, histograms bring your sample data to life. Web here's how we make a histogram: Web bar graph allows you to compare and contrast metrics (averages, sums, etc.). Web here's how we make a histogram: Web a bar graph is a pictorial representation of data that uses bars to compare different categories of data. It is also called a bar chart. Web histograms are graphs that display the distribution of your continuous data. In a histogram, data is grouped into ranges (known as bins), representing each bin by. The major difference is that a histogram is only used to plot the frequency of score occurrences in a continuous data set that has been divided into classes, called bins. Both bar graphs and histograms are useful tools for summarizing and visualizing data. Web a bar graph is a pictorial representation using vertical and horizontal bars in a graph. And. Each bar typically covers a range of numeric values called a bin or class; Web histograms are graphs that display the distribution of your continuous data. Understanding when and how to use each can dramatically enhance your data presentation skills. Web what is the difference between a bar chart and a histogram? When to use a histogram versus a bar. Conversely, a bar graph is a diagrammatic comparison of discrete variables. Web a histogram is a type of graph used in statistics to represent the distribution of numerical data. A bar graph is a plot of a single data point (a sum, average, or other value) for each category while a histogram is a plot of a range of data.. Web histogram vs bar graph: From a bar chart, we can see which groups are highest or most common, and how other groups compare against the. Web as bar charts vs. A histogram is also a pictorial representation of data using rectangular bars, that are adjacent to. Want to join the conversation? Each bin is plotted as a bar whose height corresponds to how many data points are in that bin. For categorical data and group comparisons, use a bar graph. Web with bar charts, each column represents a group defined by a categorical variable; Count the number of data points that fall within each bin. The histogram refers to a graphical. Web here's how we make a histogram: As always, the complete code is…read more › a simple, yet effective way to set your colour palette in r using ggplot library. A histogram displays the shape and spread of continuous sample data. The length of the bar is proportional to the measure of data. They are fantastic exploratory tools because they. Web the key difference between the two is that the bars in a bar graph represent individual categories, while the bars in a histogram represent ranges of values. In a histogram, data is grouped into ranges (known as bins), representing each bin by a bar. A bar’s height indicates the frequency of data points with a value within the corresponding bin. Collect your data and decide on the number and size of bins (categories) you want to divide your data into. Web a bar graph is a pictorial representation of data that uses bars to compare different categories of data. The major difference is that a histogram is only used to plot the frequency of score occurrences in a continuous data set that has been divided into classes, called bins. For categorical data and group comparisons, use a bar graph. They are fantastic exploratory tools because they reveal properties about your sample data in ways that summary statistics cannot. It is particularly effective in illustrating the frequency distribution of continuous data sets. Taller bars show that more data falls in that range. Web a histogram is a graphical display of data using bars of different heights. From histograms and heatmaps to word clouds and network diagrams, here's how to take full advantage of this powerful capability. After that, we can start “chaining” ggplot graphs. It is also called a bar chart. While one shines in comparing categories, the other excels in showing data distributions. Web histograms and bar graphs are two popular chart types that nearly all tools support.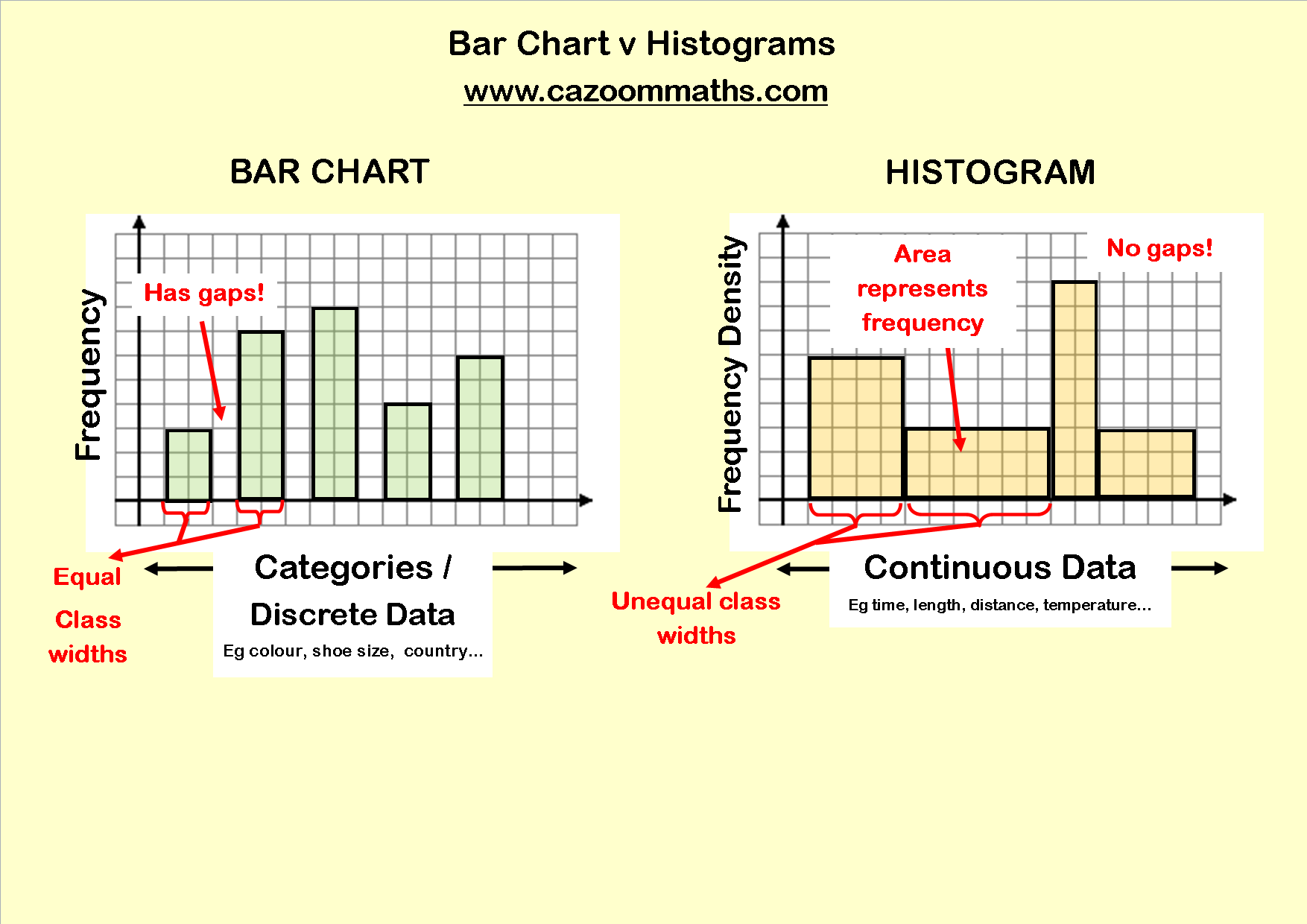
Histograms and Frequency Polygons

Histogram Graph, Definition, Properties, Examples

Aggregating Data using Bar Charts And Histograms Data Science Blog
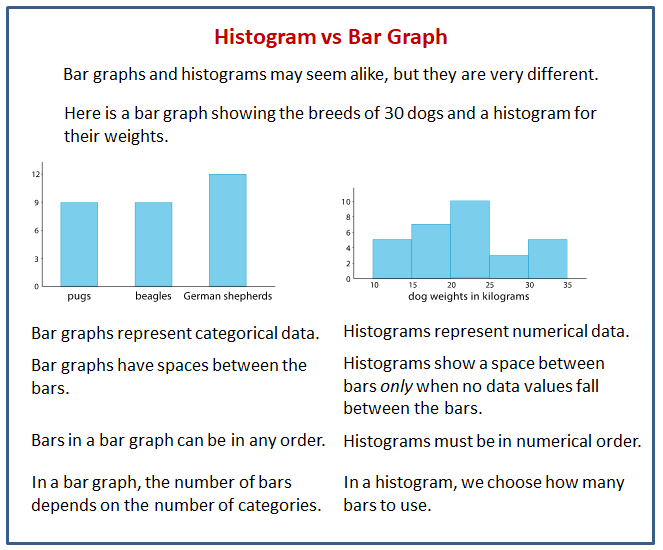
Describing Distributions on Histograms
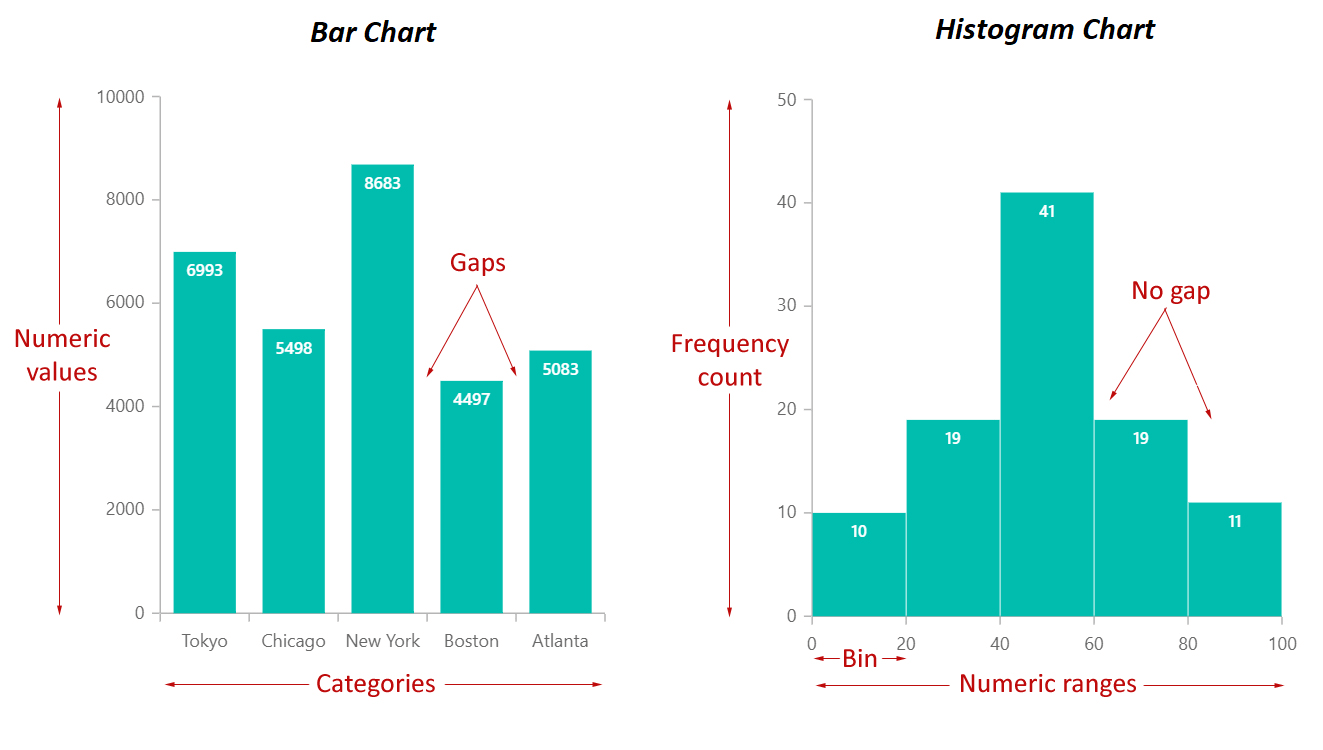
8 key differences between Bar graph and Histogram chart Syncfusion
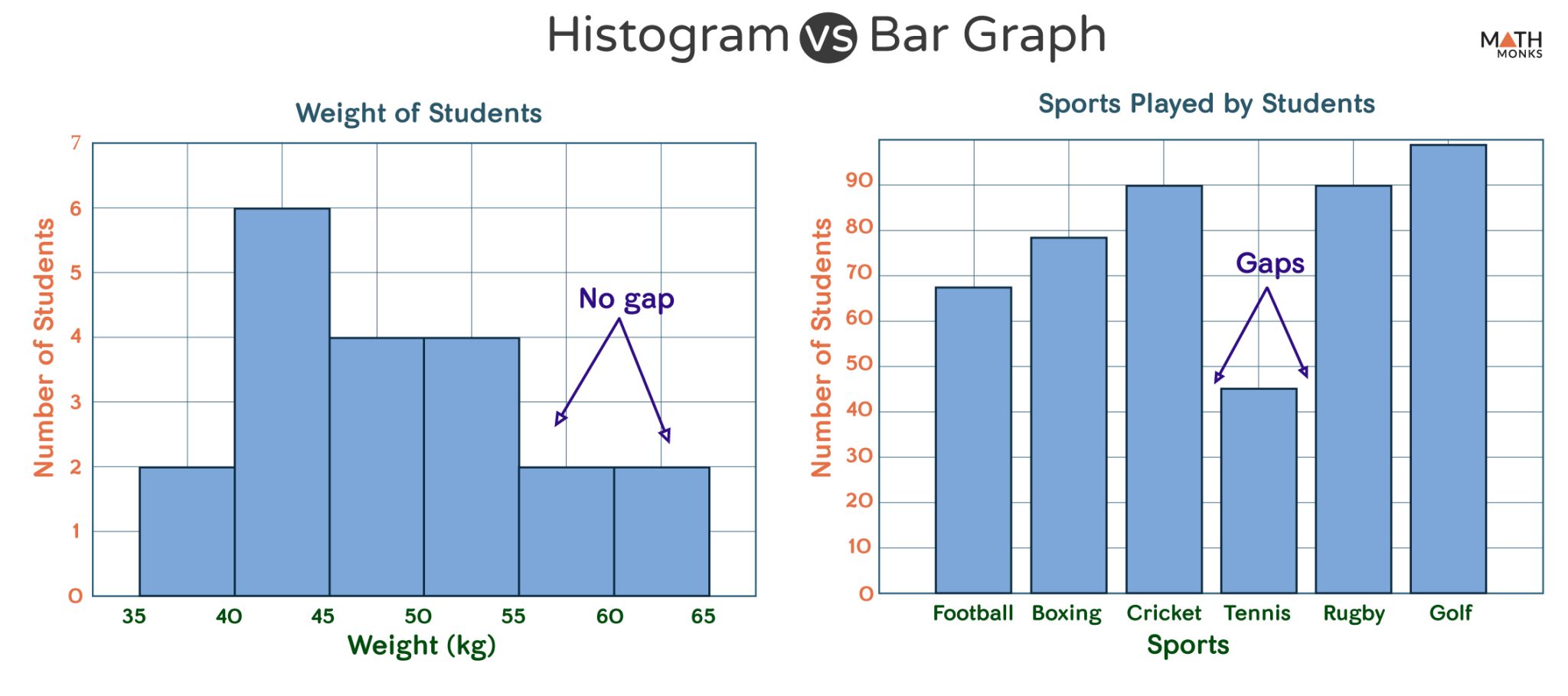
Histogram vs. Bar Graph Differences and Examples

What is the difference between a histogram and a bar graph? Teachoo

Bar Chart vs. Histogram BioRender Science Templates
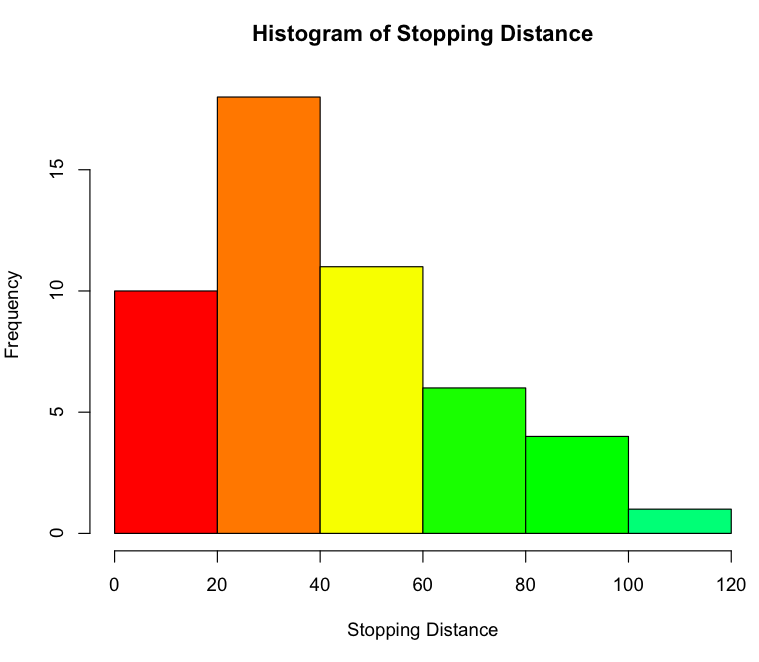
Differences Between Bar Chart And Histogram In 2021 Histogram Data Images
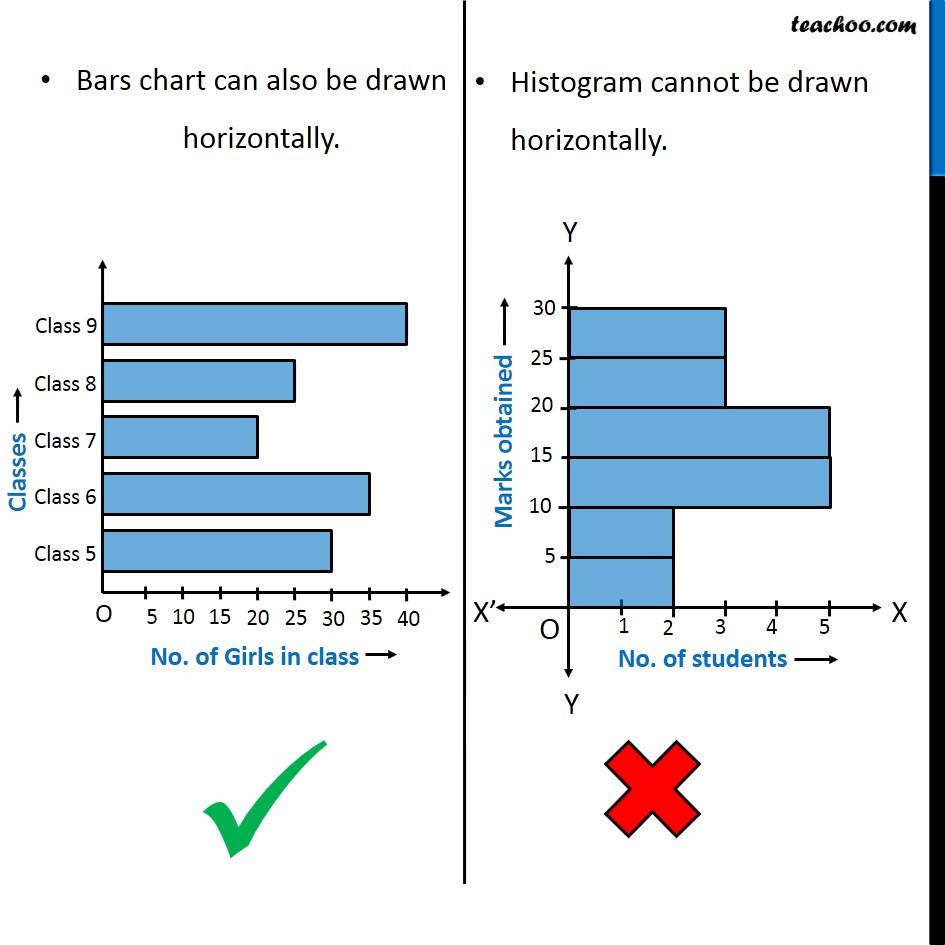
What is the difference between a histogram and a bar graph? Teachoo
A Histogram Displays The Shape And Spread Of Continuous Sample Data.
Web Two Key Types Of Graphical Representation Of Data Are Bar Charts And Histograms, Which Look Similar But Are Actually Very Different.
Scatter Plot Barchart / Histogram Boxplot 3.14 Chart Finally Custom Colours!
In A Histogram, Each Bar Groups Numbers Into Ranges.
Related Post: