Base Strength Chart
Base Strength Chart - The exact strength of a given. Web the relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. Web the greater the ability of a species to accept a h+ from another species, the greater its base strength. Web assess the relative strengths of acids and bases according to their ionization constants; A weak base yields a small. Web a strong base yields 100% (or very nearly so) of oh − and hb + when it reacts with water; Web determine at a glance the relative strengths of a host of acids and bases. If the ionization reaction is essentially complete, the acid or. Figure \(\pageindex{1}\) lists several strong bases. Chart or notebook size available. Chart or notebook size available. Web stronger acids, such as hcl, react almost completely with water, whereas weaker acids, such as acetic acid (ch 3 co 2 h), react only slightly. If the ionization reaction is essentially complete, the acid or. If the ionization reaction is essentially complete, the acid or base is termed. Web the greater the ability of. Stronger acids form weaker conjugate. Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid. Web the relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. Web assess the relative strengths of acids and bases according to their ionization constants; Web determine at a glance the relative strengths of a host of acids and. Web the relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. Web the relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. Web stronger acids, such as hcl, react almost completely with water, whereas weaker acids, such as acetic acid (ch 3. Web stronger acids, such as hcl, react almost completely with water, whereas weaker acids, such as acetic acid (ch 3 co 2 h), react only slightly. Organic chemists customarily compare the strength of bases using the. The strong bases are listed at the bottom right of the table and get weaker. Chart or notebook size available. The exact strength of. Chart or notebook size available. Figure 2 lists a series of acids and bases. Web use this acids and bases chart to find the relative strength of the most common acids and bases. Web the relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. Stronger acids form weaker conjugate. Web stronger acids, such as hcl, react almost completely with water, whereas weaker acids, such as acetic acid (ch 3 co 2 h), react only slightly. A weak base yields a small. Web use this acids and bases chart to find the relative strength of the most common acids and bases. Web the relative strength of an acid or base. Web the relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. Stronger acids form weaker conjugate. Web a strong base yields 100% (or very nearly so) of oh − and hb + when it reacts with water; A weak base yields a small. Web use this acids and bases chart to. A weak base yields a small. Web a strong base yields 100% (or very nearly so) of oh − and hb + when it reacts with water; Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid. Web assess the relative strengths of acids and bases according to their ionization constants; Web use this acids and bases chart to find the relative strength. Web assess the relative strengths of acids and bases according to their ionization constants; Web use this acids and bases chart to find the relative strength of the most common acids and bases. Organic chemists customarily compare the strength of bases using the. Web use this acids and bases chart to find the relative strength of the most common acids. Web use this acids and bases chart to find the relative strength of the most common acids and bases. Web use this acids and bases chart to find the relative strength of the most common acids and bases. Web the relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. Web assess. The exact strength of a given. If the ionization reaction is essentially complete, the acid or base is termed. Web a strong base yields 100% (or very nearly so) of oh − and hb + when it reacts with water; Figure \(\pageindex{1}\) lists several strong bases. Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid. Web stronger acids, such as hcl, react almost completely with water, whereas weaker acids, such as acetic acid (ch 3 co 2 h), react only slightly. If the ionization reaction is essentially complete, the acid or. The strong bases are listed at the bottom right of the table and get weaker. Web the relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. Stronger acids form weaker conjugate. Web use this acids and bases chart to find the relative strength of the most common acids and bases. A weak base yields a small. Web use this acids and bases chart to find the relative strength of the most common acids and bases. Web assess the relative strengths of acids and bases according to their ionization constants; Web the relative strength of an acid or base is the extent to which it ionizes when dissolved in water. Web determine at a glance the relative strengths of a host of acids and bases.
Acid Base Strength Chart
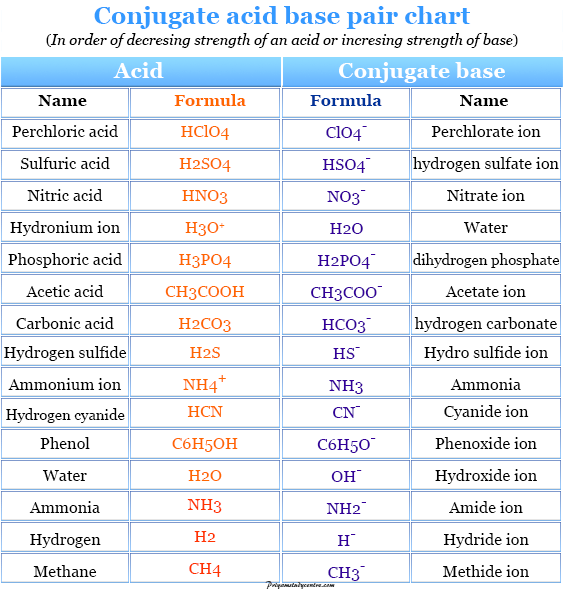
Acids and Bases Definition, Concept, Theory, Examples
Acid And Base Strength Chart
Acids And Bases List Strength
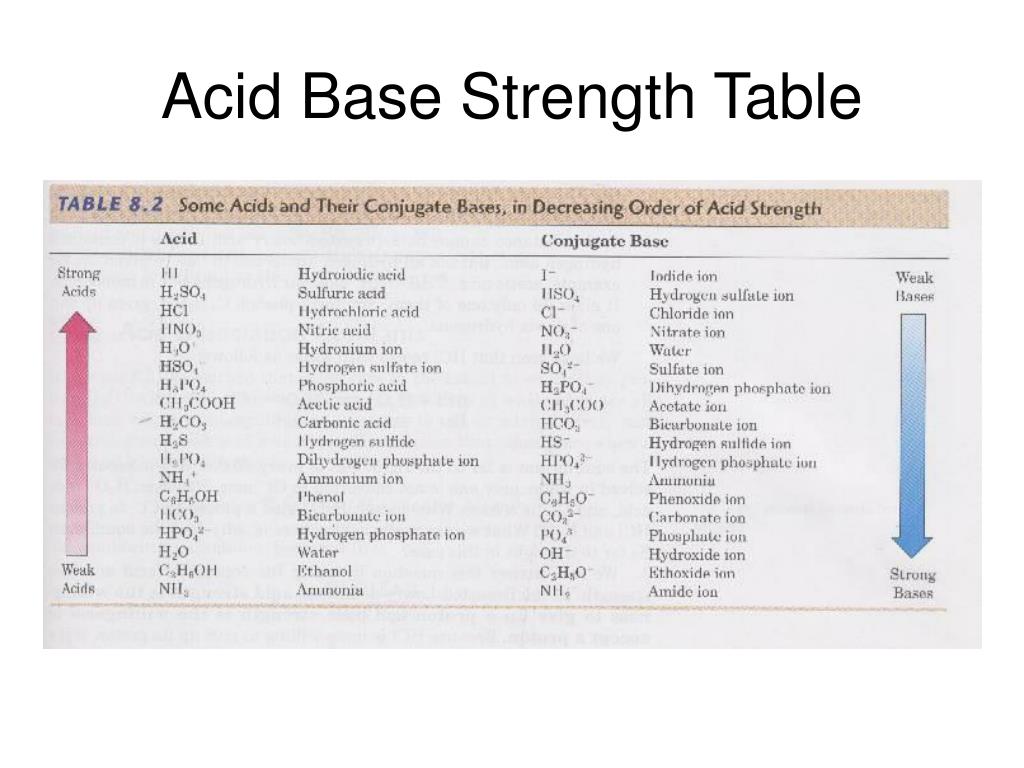
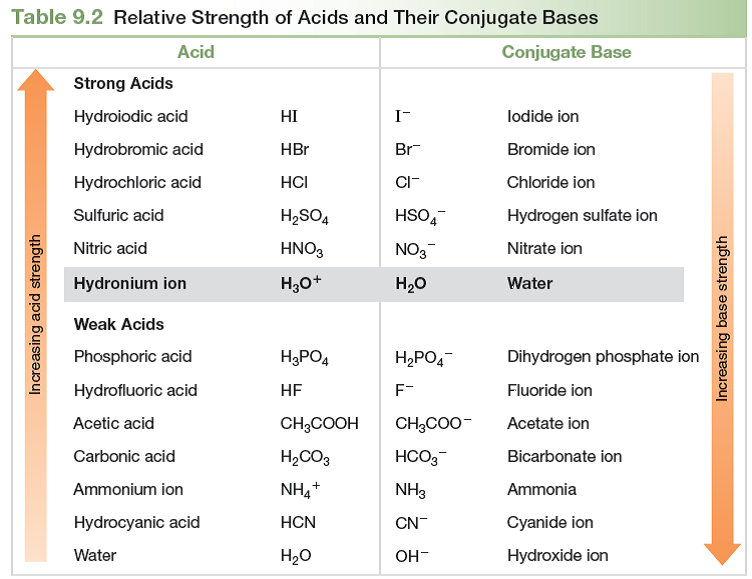
Acid Base Strength Chart
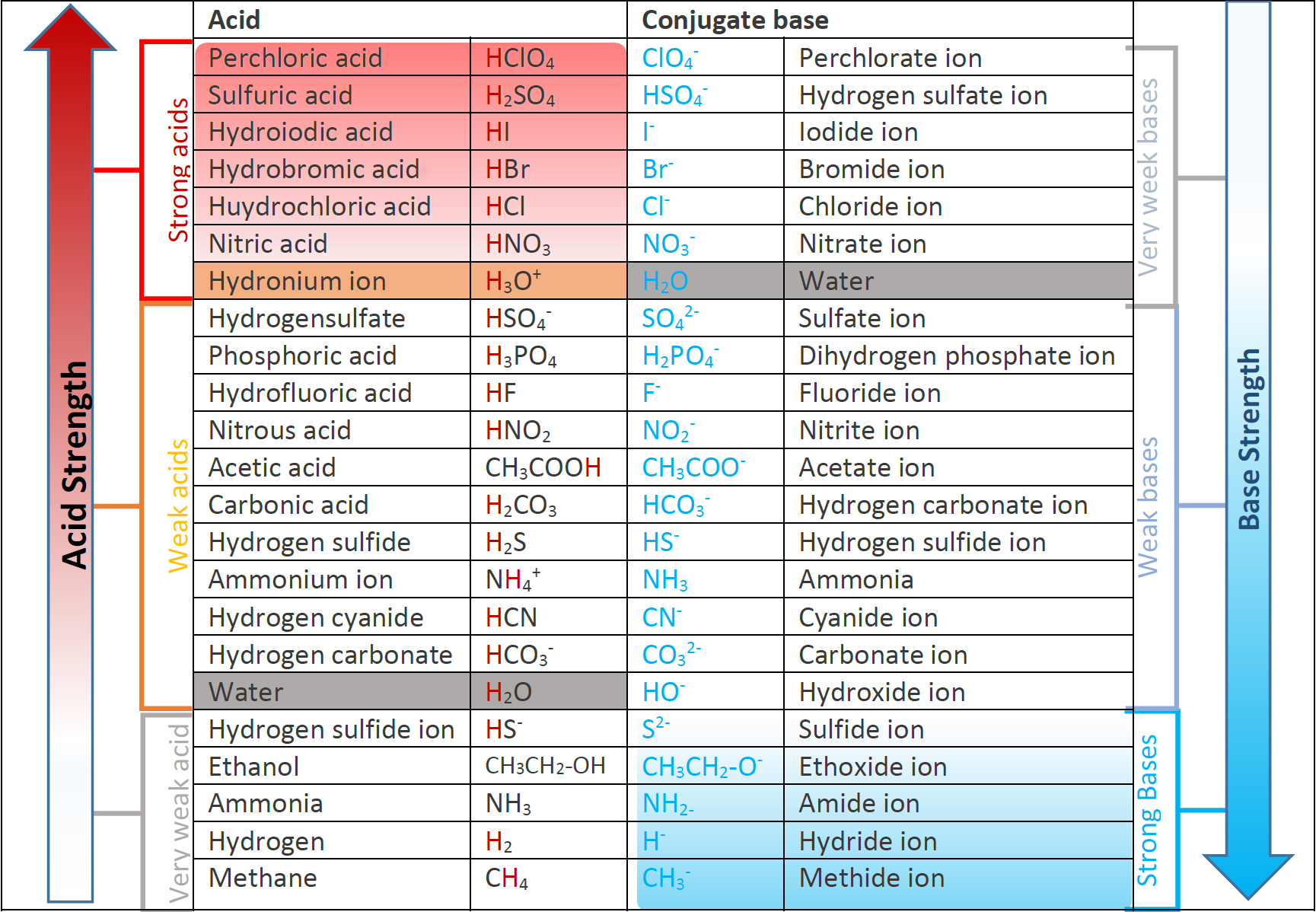
6.3 Strength of acids and bases Chemistry LibreTexts
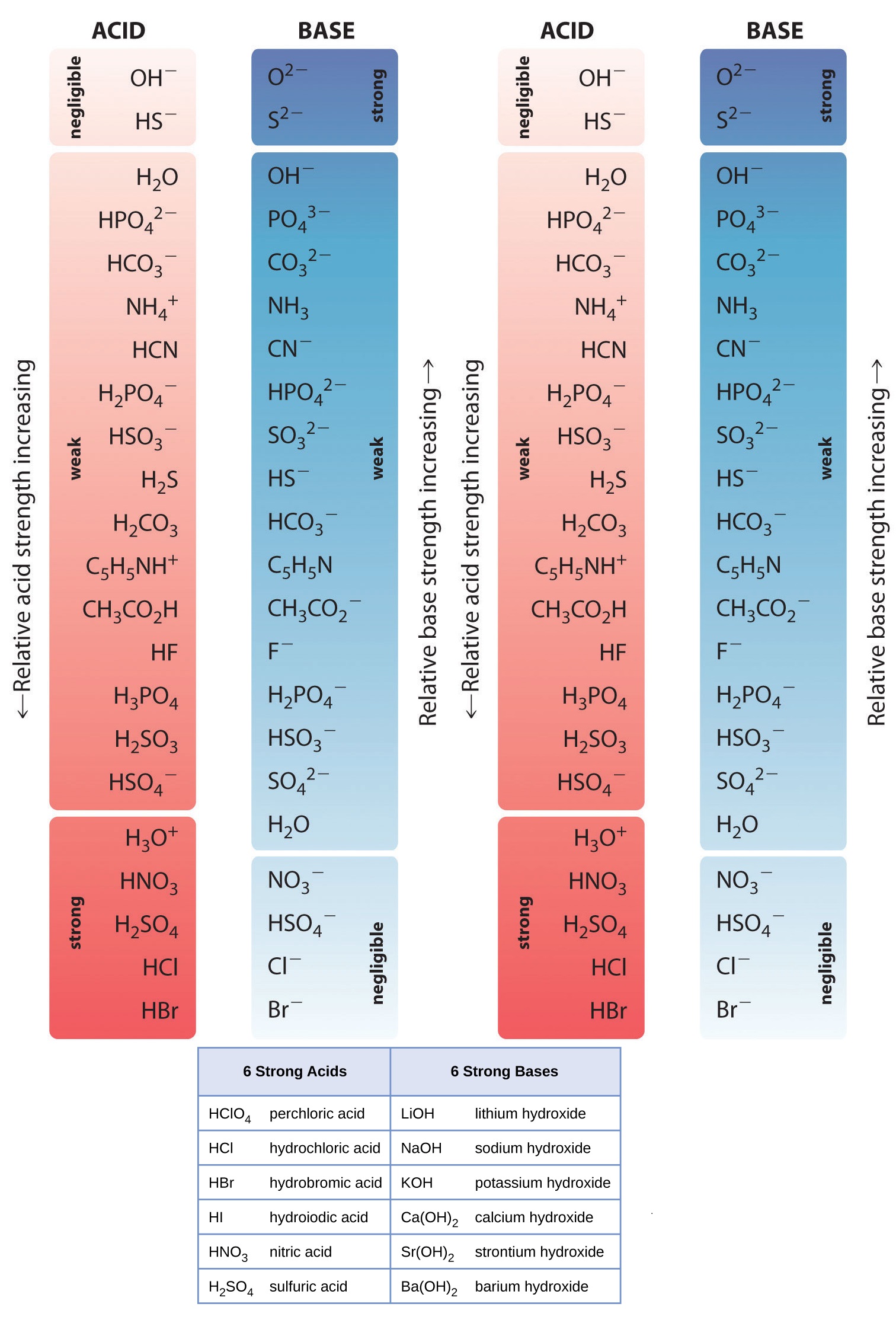
List of Strong Acids & Bases in Order StudyPK
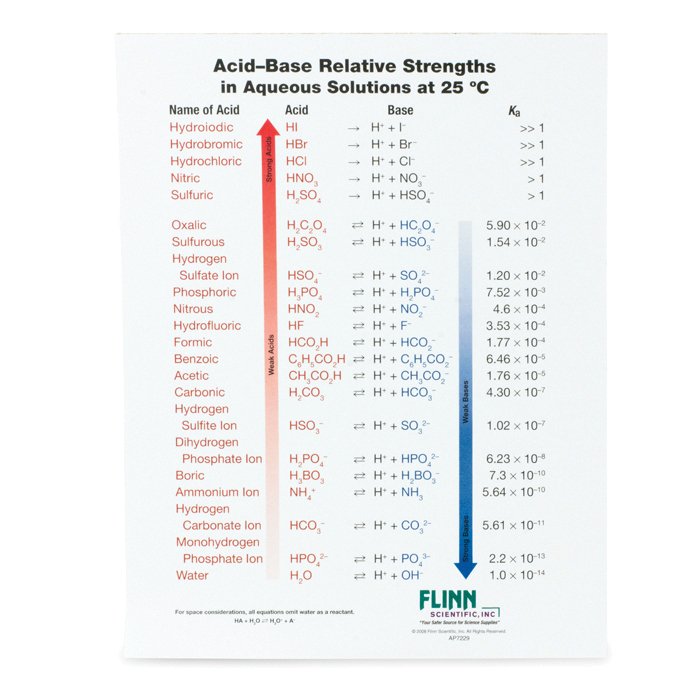
AcidBase Strength Charts for Chemistry
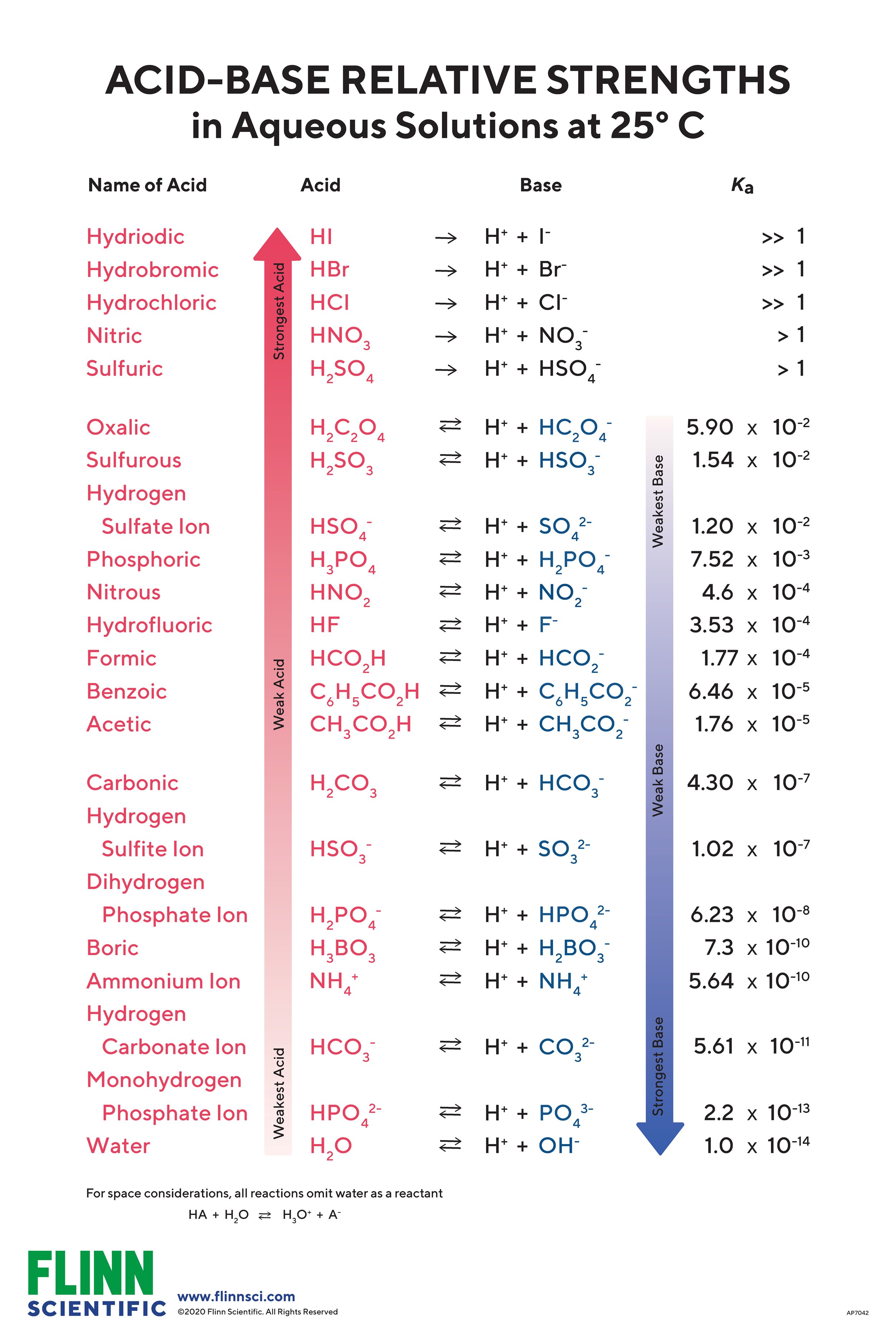
AcidBase Strength Chart
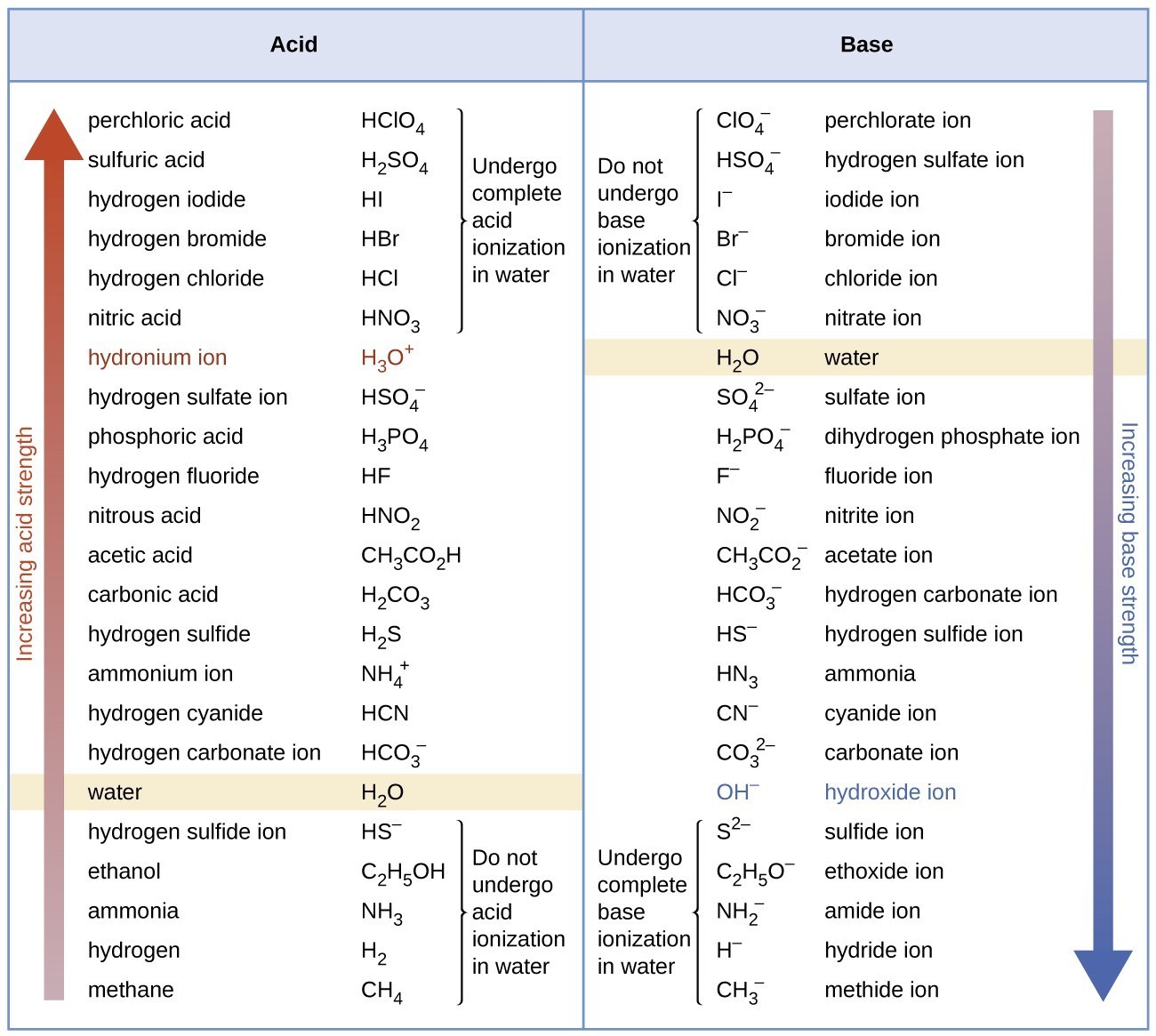
Relative Strengths of Acids and Bases General Chemistry
Web Assess The Relative Strengths Of Acids And Bases According To Their Ionization Constants.
Web 34 Rows Use This Acids And Bases Chart To Find The Relative Strength Of The Most Common Acids And Bases.
Organic Chemists Customarily Compare The Strength Of Bases Using The.
Web The Greater The Ability Of A Species To Accept A H+ From Another Species, The Greater Its Base Strength.
Related Post:
