Biogeochemical Cycles Drawing
Biogeochemical Cycles Drawing - Water, which contains hydrogen and oxygen, is essential to all living processes. Web biogeochemical cycles the carbon cycle google classroom learn how carbon moves through earth's ecosystems and how human activities are altering the carbon cycle. Sulfur initially enters the biogeochemical cycle via volcanic activity and continental erosion. In biology, conserved matter refers to the finite amount of matter, in the form of atoms, that is present within the earth. Water contains hydrogen and oxygen, which is essential to all living processes. The sun warms the ocean surface and other surface water, causing liquid water to evaporate and ice to sublime—turn directly from a solid to a gas. Key points carbon is an essential element in the bodies of living organisms. Biogeochemical cycles important to living organisms include the water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur cycles. Web a biogeochemical cycle, or more generally a cycle of matter, is the movement and transformation of chemical elements and compounds between living organisms, the atmosphere, and the earth's crust. Ask them to make a diagram that includes all the cycles. Web biogeochemical cycles the carbon cycle google classroom learn how carbon moves through earth's ecosystems and how human activities are altering the carbon cycle. Web because geology and chemistry have major roles in the study of these processes, the recycling of inorganic matter between living organisms and their nonliving environment are called biogeochemical cycles. Web biogeochemical cycle, any of the. Web the ways in which an element—or compound such as water—moves between its various living and nonliving forms and locations in the biosphere is called a biogeochemical cycle. The sun warms the ocean surface and other surface water, causing liquid water to evaporate and ice to sublime—turn directly from a solid to a gas. Web because geology and chemistry have. In biology, conserved matter refers to the finite amount of matter, in the form of atoms, that is present within the earth. Web because geology and chemistry have major roles in the study of this process, the recycling of inorganic matter between living organisms and their nonliving environment is called a biogeochemical cycle. Web this manuscript is a synthesis on. In biology, conserved matter refers to the finite amount of matter, in the form of atoms, that is present within the earth. Biogeochemical cycles important to living organisms include the water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur cycles. Below is a sample diagram template that is included in my biogeochemical cycles lesson. Define and describe the importance of microorganisms in the. The sun warms the ocean surface and other surface water, causing liquid water to evaporate and ice to sublime—turn directly from a solid to a gas. Water, which contains hydrogen and oxygen, is essential to all living processes. All of the atoms that are building blocks of living things are a part of biogeochemical cycles. Web because geology and chemistry. It is also economically important to modern humans, in the form of fossil fuels. The term biogeochemical is a contraction that incorporates the biological, geological, and chemical aspects of each cycle. Web some of the major biogeochemical cycles are as follows: Biogeochemical cycles important to living organisms include the water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur cycles. The most common of. Web the ways in which an element—or compound such as water—moves between its various living and nonliving forms and locations in the biosphere is called a biogeochemical cycle. These materials get transformed into the bio mass of the producers. The global nitrogen cycle is characterized by a relatively small biogeochemical cycle with rapid turnover (50 yrs) that is coupled to. Web types of biogeochemical cycles. Biogeochemical cycles are basically divided into two types: Sulfur initially enters the biogeochemical cycle via volcanic activity and continental erosion. Water contains hydrogen and oxygen, which is essential to all living processes. Web a biogeochemical cycle, or more generally a cycle of matter, is the movement and transformation of chemical elements and compounds between living. The term biogeochemical is a contraction that incorporates the biological, geological, and chemical aspects of each cycle. Web the ways in which an element—or compound such as water—moves between its various living and nonliving forms and locations in the biosphere is called a biogeochemical cycle. Web some of the major biogeochemical cycles are as follows: Water, which contains hydrogen and. Water, which contains hydrogen and oxygen, is essential to all living processes. Major biogeochemical cycles include the carbon cycle , the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. Web types of biogeochemical cycles. It is also economically important to modern humans, in the form of fossil fuels. The term biogeochemical is a contraction that incorporates the biological, geological, and chemical aspects. Web because geology and chemistry have major roles in the study of this process, the recycling of inorganic matter between living organisms and their nonliving environment is called a biogeochemical cycle. Let us have a look at each of these biogeochemical cycles in brief: Biogeochemical cycles important to living organisms include the water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur cycles. Web collectively, these microbial reactions drive the global cycle of nitrogen. Web the water cycle, or hydrologic cycle, is driven by the sun’s energy. Sulfur initially enters the biogeochemical cycle via volcanic activity and continental erosion. Web the ways in which an element—or compound such as water—moves between its various living and nonliving forms and locations in the biosphere is called a biogeochemical cycle. Web types of biogeochemical cycles. It is also economically important to modern humans, in the form of fossil fuels. Below is a sample diagram template that is included in my biogeochemical cycles lesson. The most common of these are the carbon and nitrogen cycles. In biology, conserved matter refers to the finite amount of matter, in the form of atoms, that is present within the earth. Web biogeochemical cycles the carbon cycle google classroom learn how carbon moves through earth's ecosystems and how human activities are altering the carbon cycle. Web a biogeochemical cycle is one of several natural cycles, in which conserved matter moves through the biotic and abiotic parts of an ecosystem. Hopefully by the end of the activity students will see that multiple nutrients cycle through organisms. Water contains hydrogen and oxygen, which is essential to all living processes.
Biogeochemical cycles as natural substance circulation pathway outline

How to Draw Biogeochemical Cycles Diagram Easy Way to Draw Ecosystem

What is a Biogeochemical Cycle in Ecology? Definition and Examples
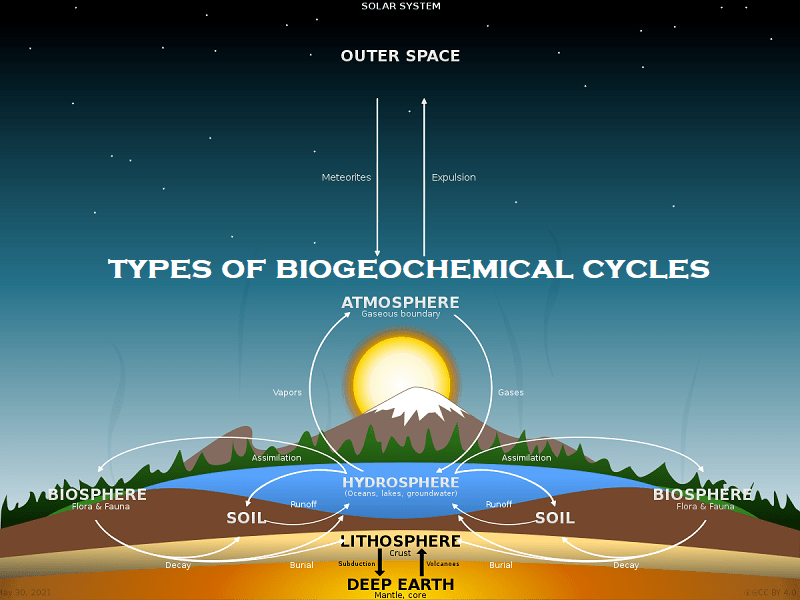
Basic 6 types of biogeochemical cycles with examples Basic
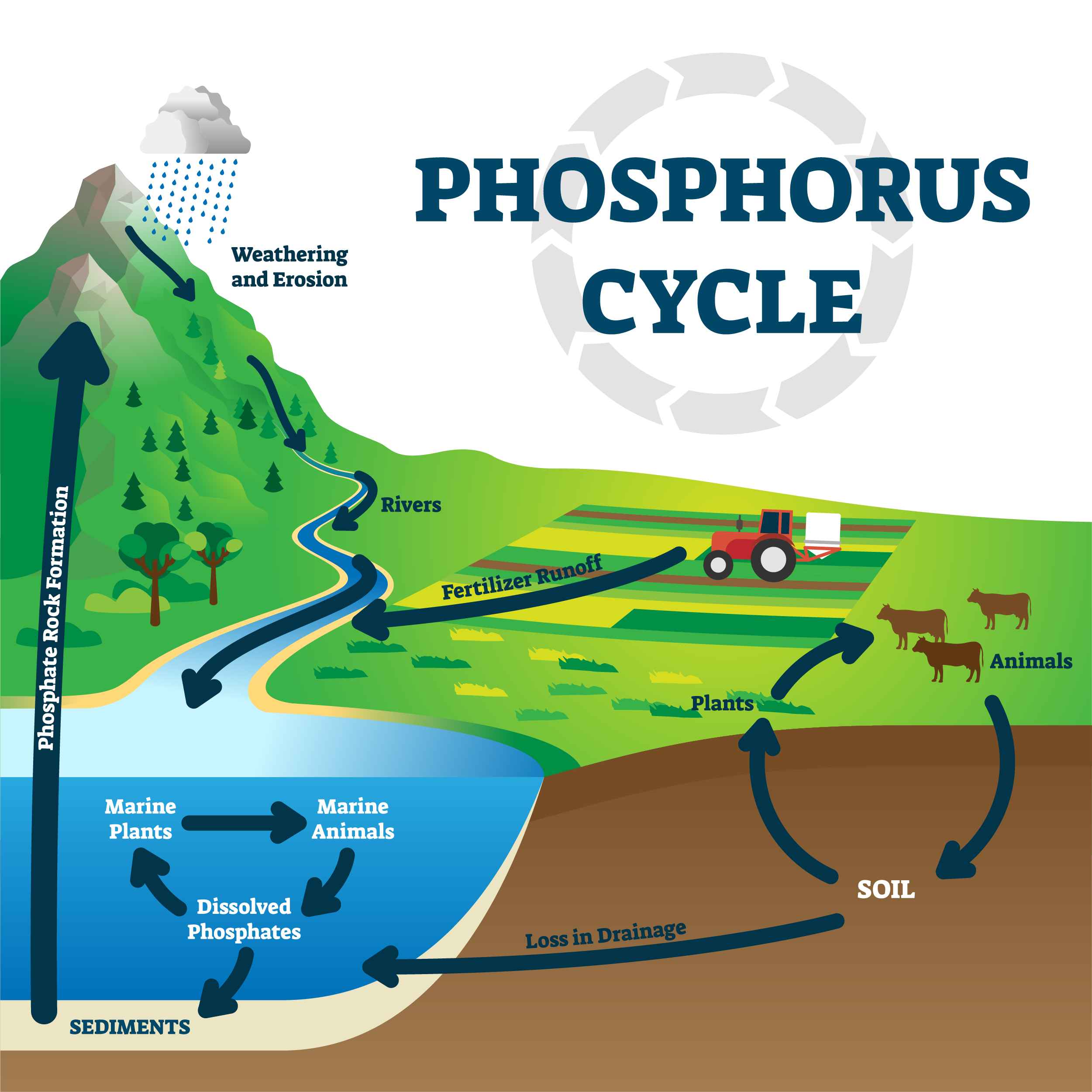
Grade 7 Biogeochemical Transformations Made in Science

Teaching Resources for the Biogeochemical Cycles Science Lessons That

8.7 Biogeochemical Cycles Biology LibreTexts
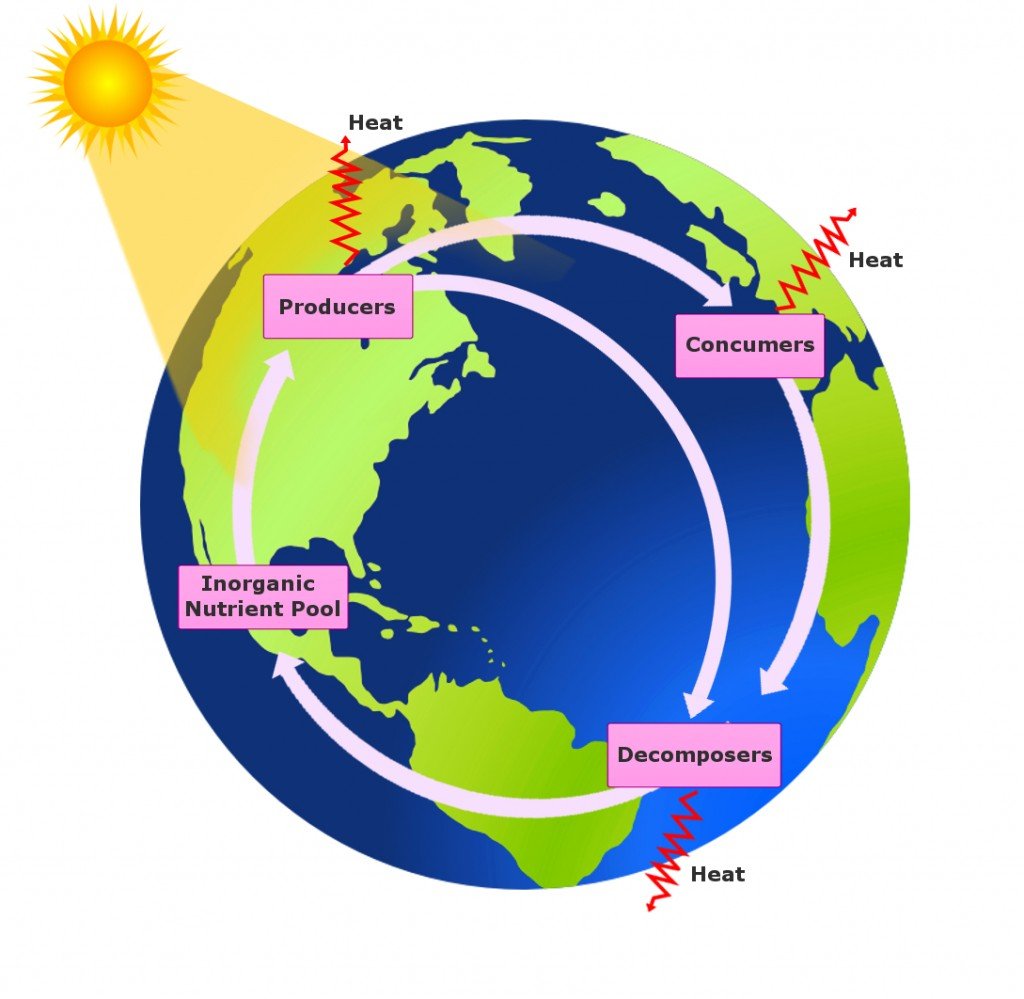
Biogeochemical Cycle Definition, Types And Importance

What Do Biogeochemical Cycles Connect? Biology Dictionary
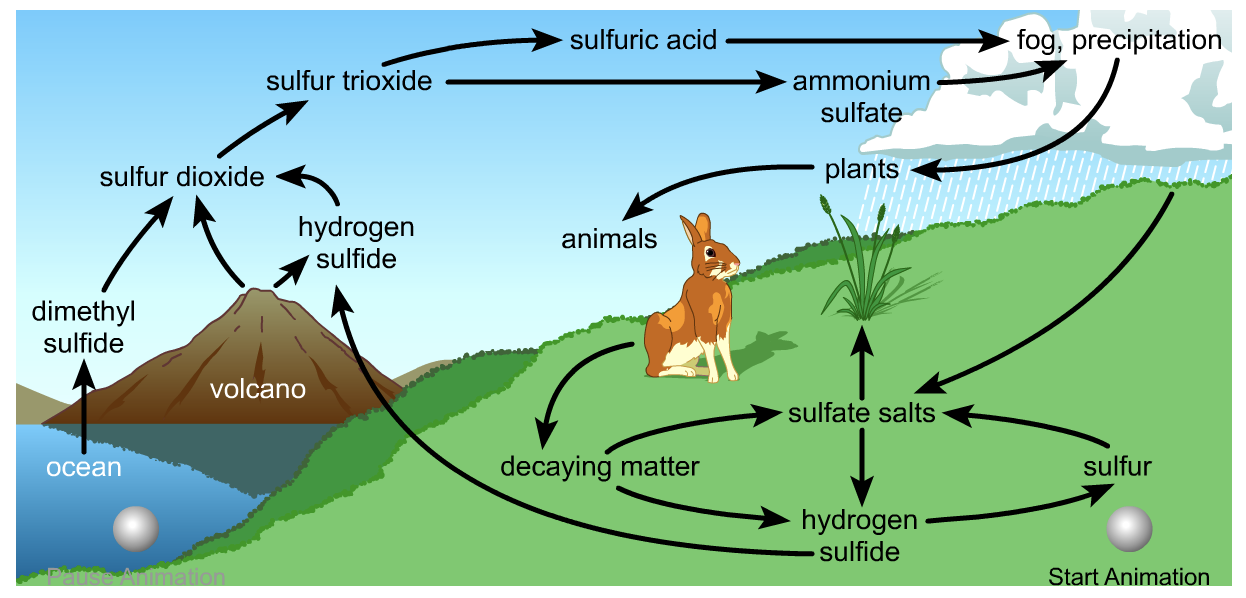
Biogeochemical Cycles Jonathan's Classroom
Web In This Drawing I Show You How To Draw Biogeochemical Cycle Diagram In Easy Way Which Shows Ecosystem Cycles Of Earth Where Chemical Substance Is Turned Over Or Moves Through The Biotic.
Biogeochemical Cycles Are Basically Divided Into Two Types:
Web This Manuscript Is A Synthesis On The Effects Of Human Activities Associated With Urbanization Which Directly And Indirectly Alter Biogeochemical Cycles With A Focus On C And N.
Web A Biogeochemical Cycle, Or More Generally A Cycle Of Matter, Is The Movement And Transformation Of Chemical Elements And Compounds Between Living Organisms, The Atmosphere, And The Earth's Crust.
Related Post: