Biology Macromolecules Chart
Biology Macromolecules Chart - As we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: Within all cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form larger molecules. Define the term “macromolecule” distinguish between the 4 classes of macromolecules. Carbohydrates (such as sugars), lipids (such as fats), proteins, and nucleic acids (such as dna and rna). There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Living systems are organized in a hierarchy of structural levels that interact. Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Web the four major types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Synthetic fibers and experimental materials such as carbon nanotubes [2] [3] are also examples of macromolecules. Web carbohydrates are a major class of biological macromolecules that are an essential part of our diet and provide energy to the body. Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. These biological macromolecules are essential for life and include proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates,. Polymers of nucleotides) let’s take a closer look at the differences between the difference classes. Amino acids share a basic structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group ( nh 2 ), a carboxyl group ( cooh ), and a hydrogen atom. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.. Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the four macromolecules?, the monomer of carbohydrates, the monomer of proteins and more. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates,. Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic. Proteins (polymers of amino acids) carbohydrates (polymers of sugars) lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) nucleic acids (dna and rna; Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. All living things are made up of four. Web biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. Among biomolecules, nucleic acids, namely dna and rna, have the unique function of storing an organism’s genetic code —the sequence of nucleotides that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins, which are of critical importance to life.. Web level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 400 mastery points! Which of the following best describes the role that water plays in the reaction depicted above? Carbohydrates (such as sugars), lipids (such as fats), proteins, and nucleic acids (such as dna and rna). Polymers of nucleotides) let’s take a closer look at the. Which of the following best describes the role that water plays in the reaction depicted above? Web biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. Synthetic fibers and experimental materials such as carbon. Web distinguish between the four classes of macromolecules carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell, provide structural support to many organisms, and can be found on the surface of the cell as receptors or. Synthetic fibers and experimental materials such as carbon nanotubes [2] [3] are also examples of macromolecules. This composition. Amino acids share a basic structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group ( nh 2 ), a carboxyl group ( cooh ), and a hydrogen atom. Web carbohydrates are a major class of biological macromolecules that are an essential part of our diet and provide energy to. All living things are made up of four main classes of macromolecules: Web there are four major biological macromolecule classes (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). As we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: The four major classes of biological macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and. These biological macromolecules are essential for life and include proteins, nucleic. Synthetic fibers and experimental materials such as carbon nanotubes [2] [3] are also examples of macromolecules. Explain how a change in the subunits of a polymer may lead to changes in structure or function of the macromolecule. The polymer is more than the sum of. This composition gives carbohydrates their name: Among biomolecules, nucleic acids, namely dna and rna, have the unique function of storing an organism’s genetic code —the sequence of nucleotides that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins, which are of critical importance to life. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); Define the term “macromolecule” distinguish between the 4 classes of macromolecules. Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Web carbohydrates are a major class of biological macromolecules that are an essential part of our diet and provide energy to the body. Web level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 400 mastery points! This unit is part of the biology library. Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. These biological macromolecules are essential for life and include proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. Openstax college [cc by 3.0], via wikimedia commons. Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. Proteins (polymers of amino acids) carbohydrates (polymers of sugars) lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) nucleic acids (dna and rna;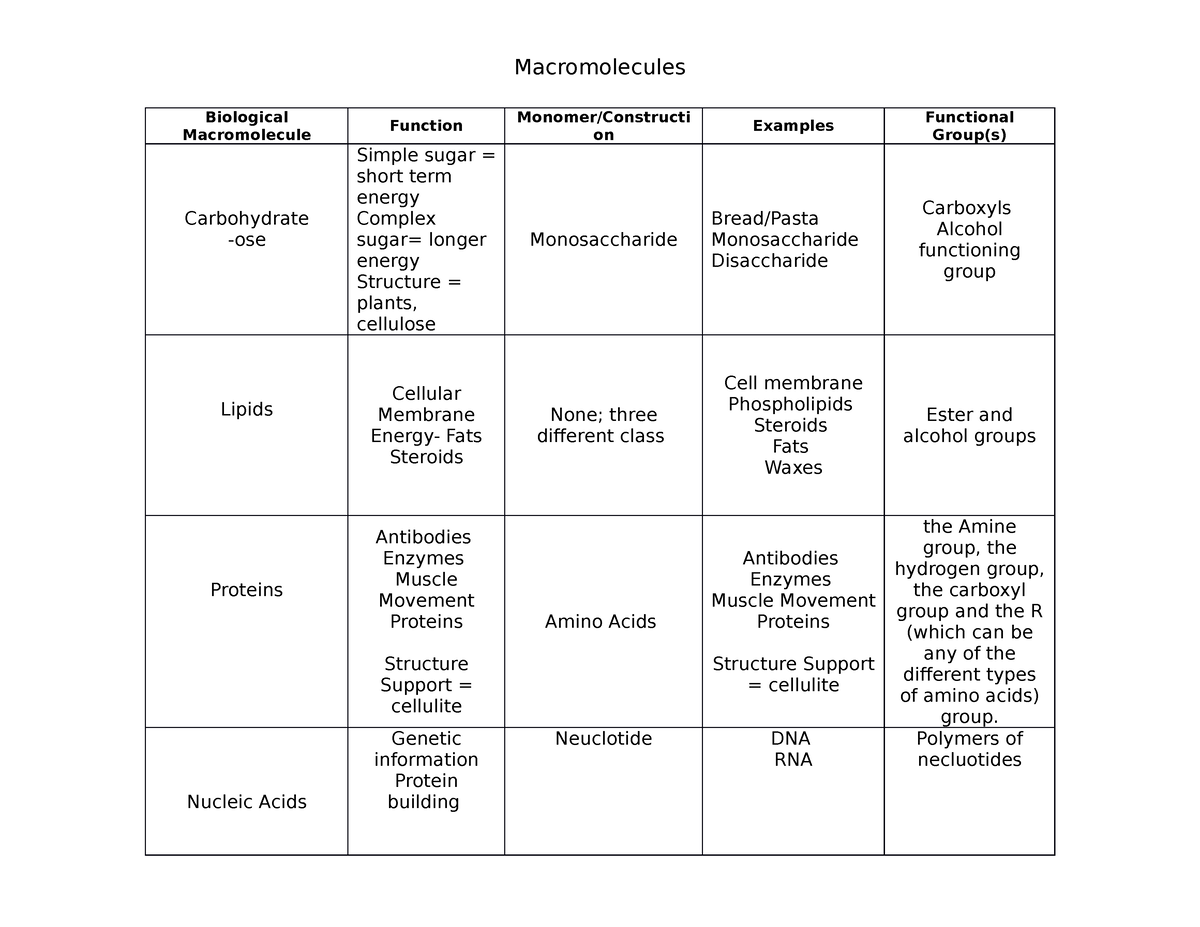
Macromolecules chartM Macromolecules Biological

Pre IB/GT Biology 1 Macromolecules Chart Diagram Quizlet
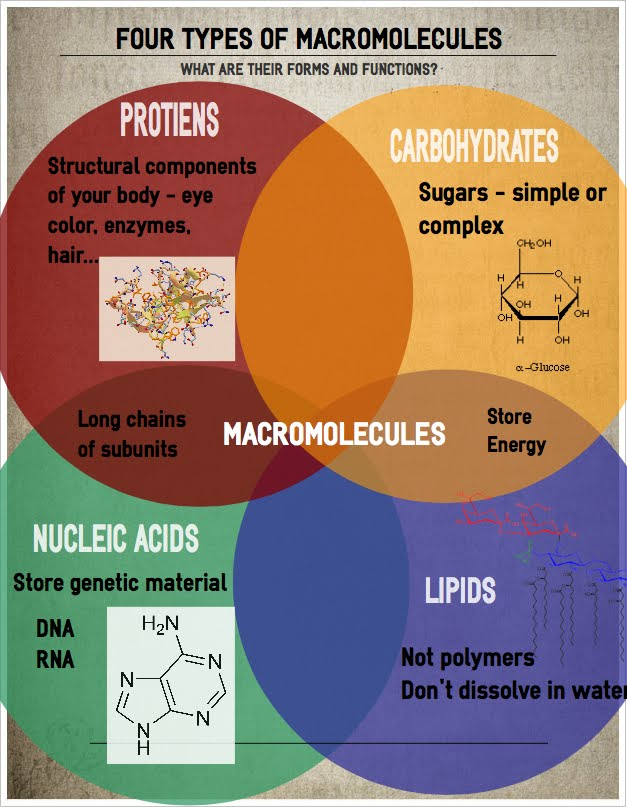
Properties of Biological Macromolecules Study Guide Inspirit
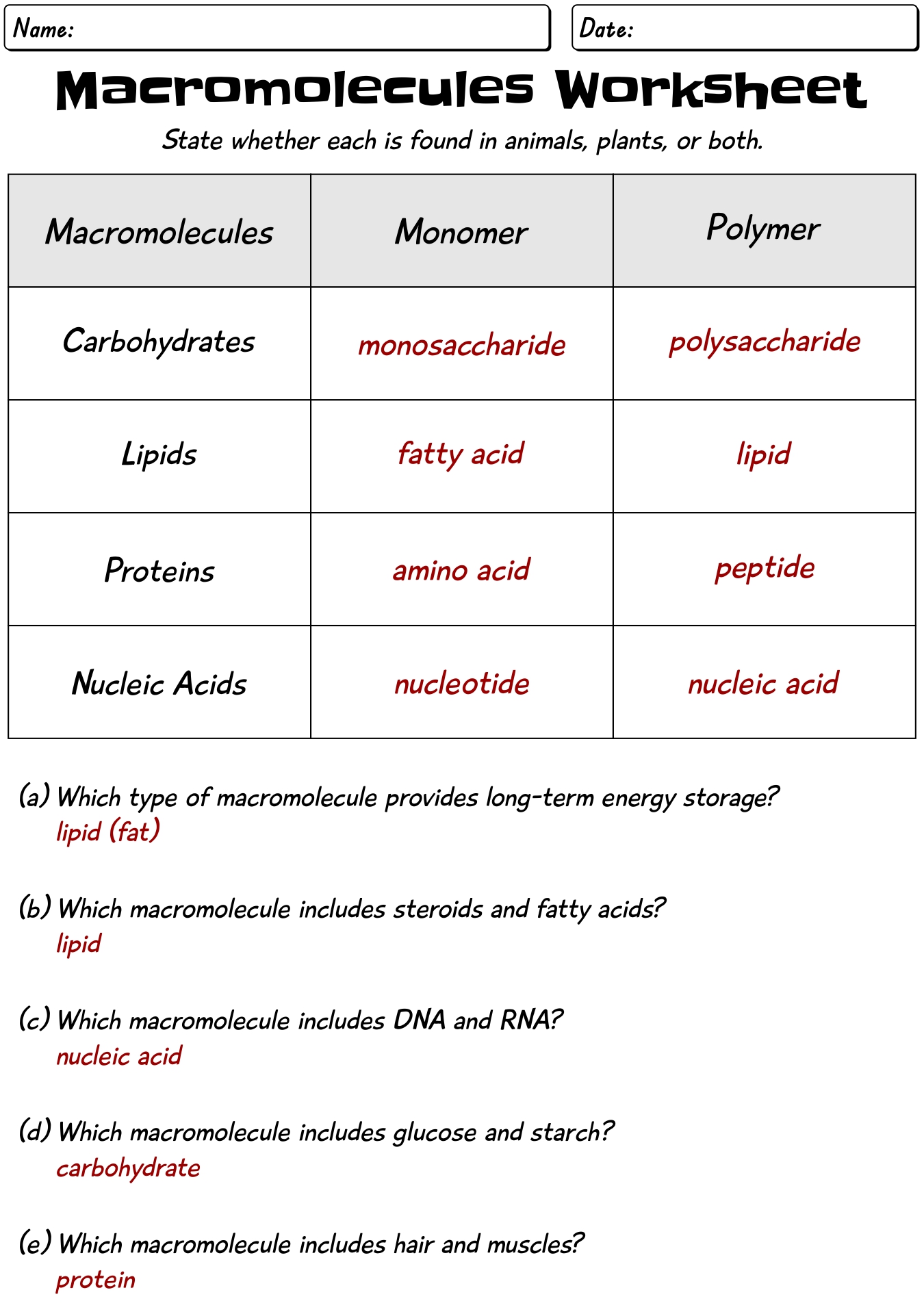
14 Biology Macromolecules Worksheets And Answers /
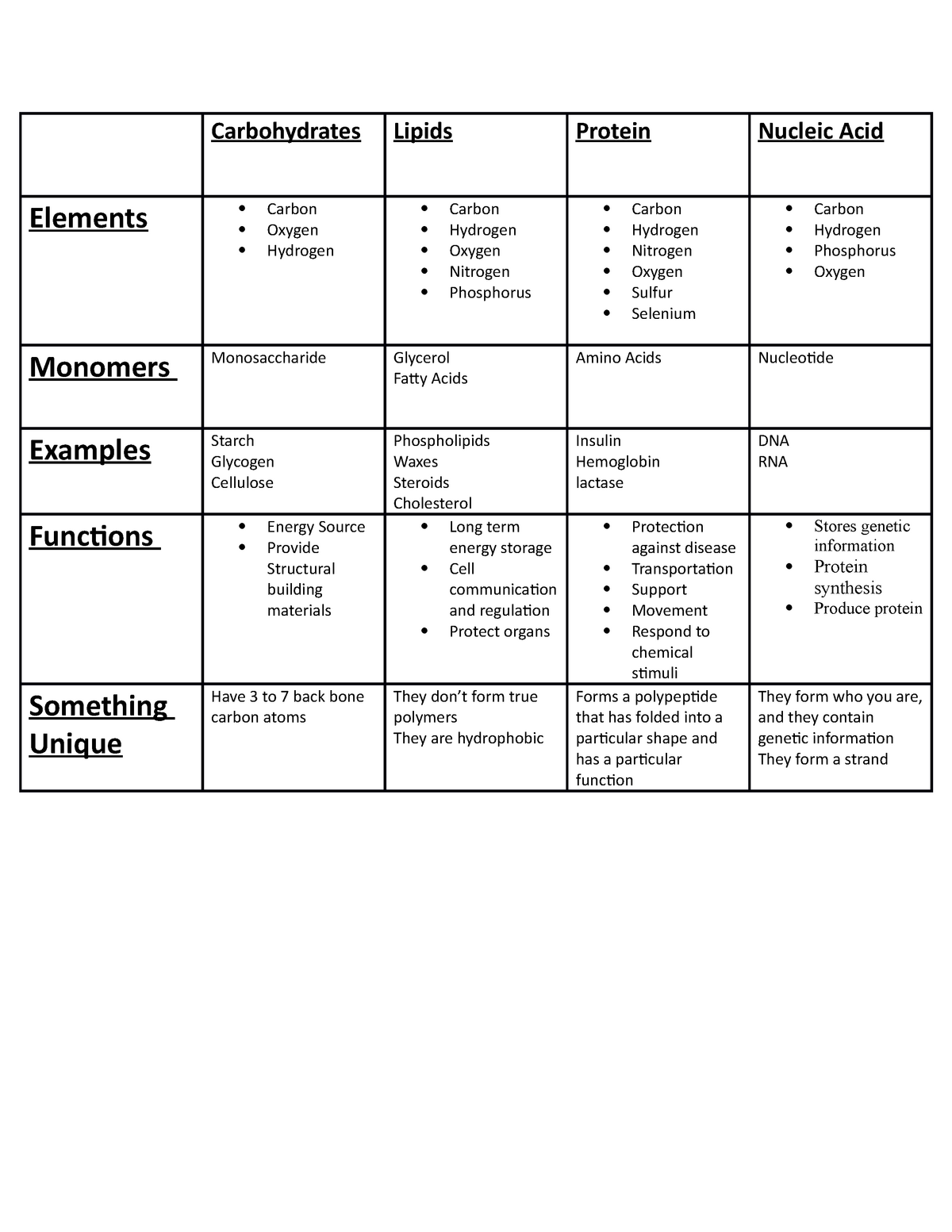
Macromolecules chart Lecture notes A Carbohydrates Elements Carbon
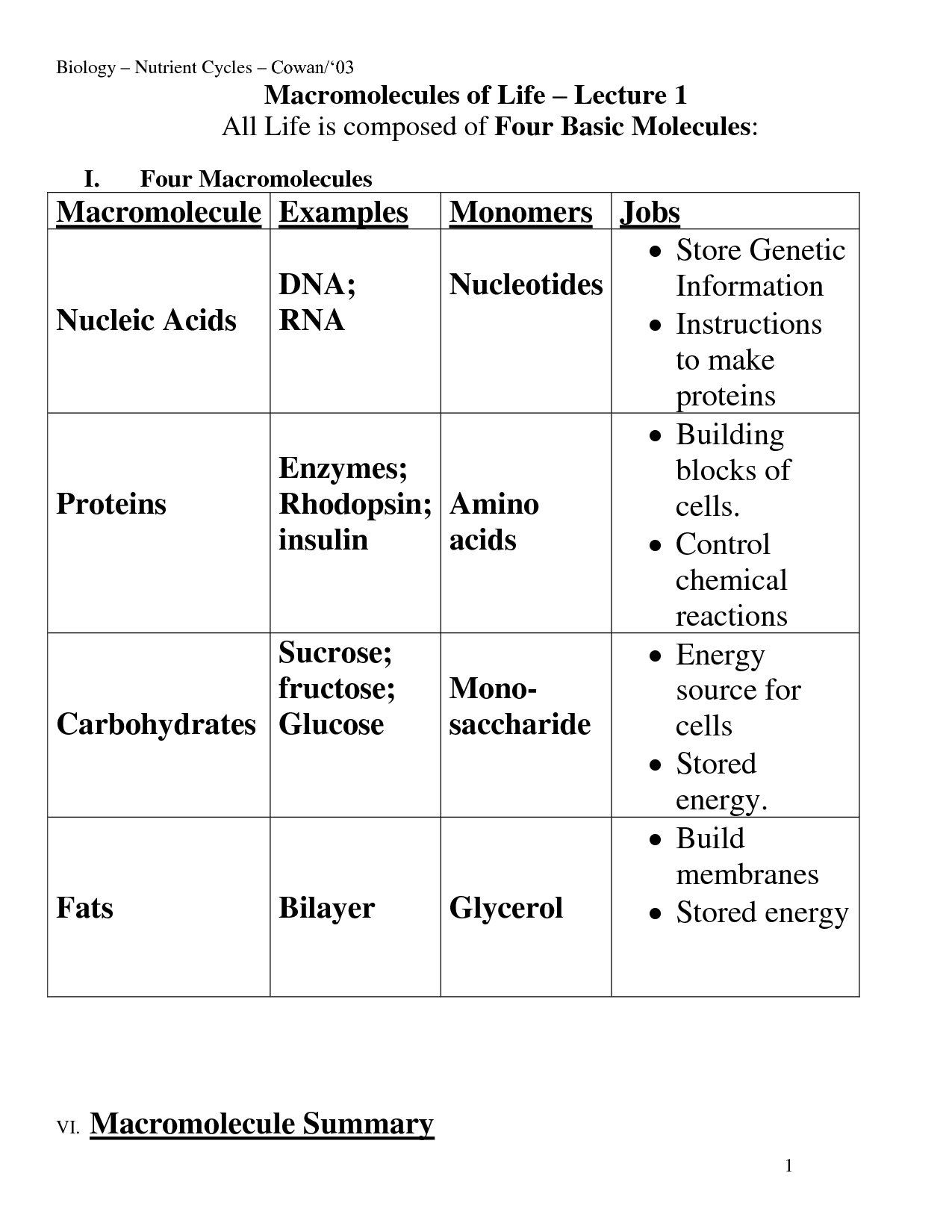
12 Biology Macromolecules Worksheets /

2.3 Biologically Important Macromolecules Biology LibreTexts
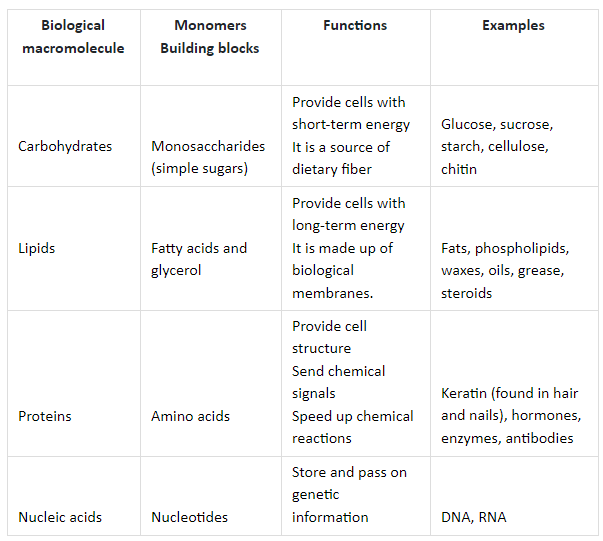
Structure and Function of Biological Macromolecules Study Guide
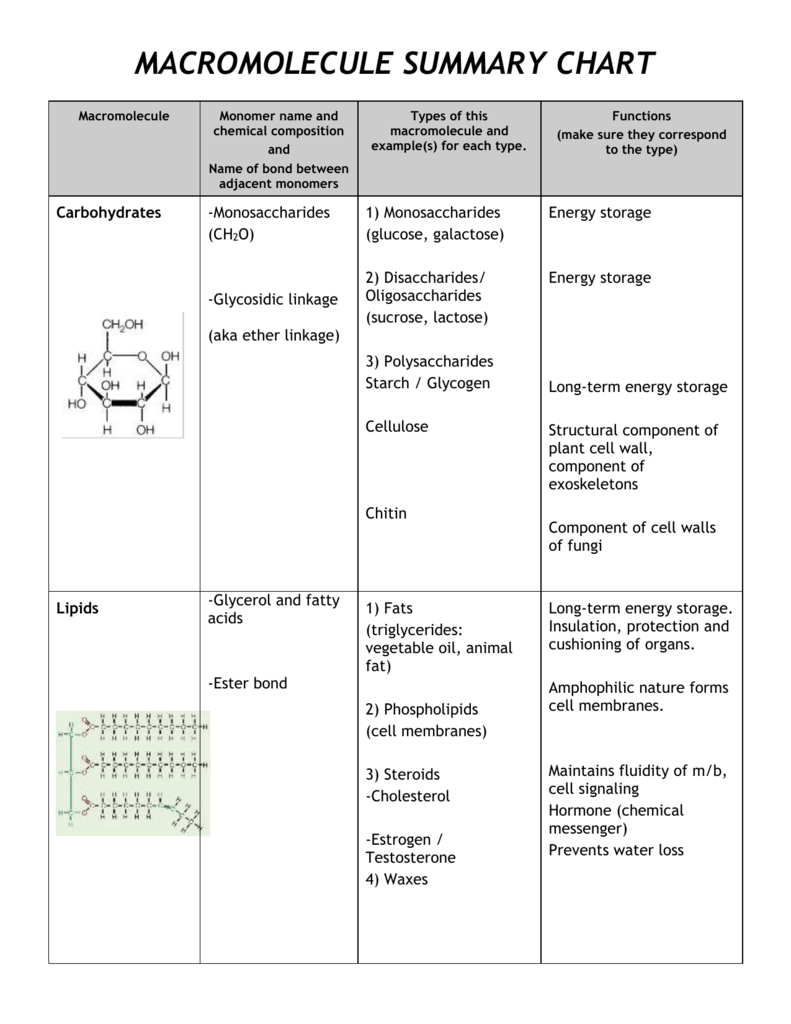
Four Macromolecules Chart
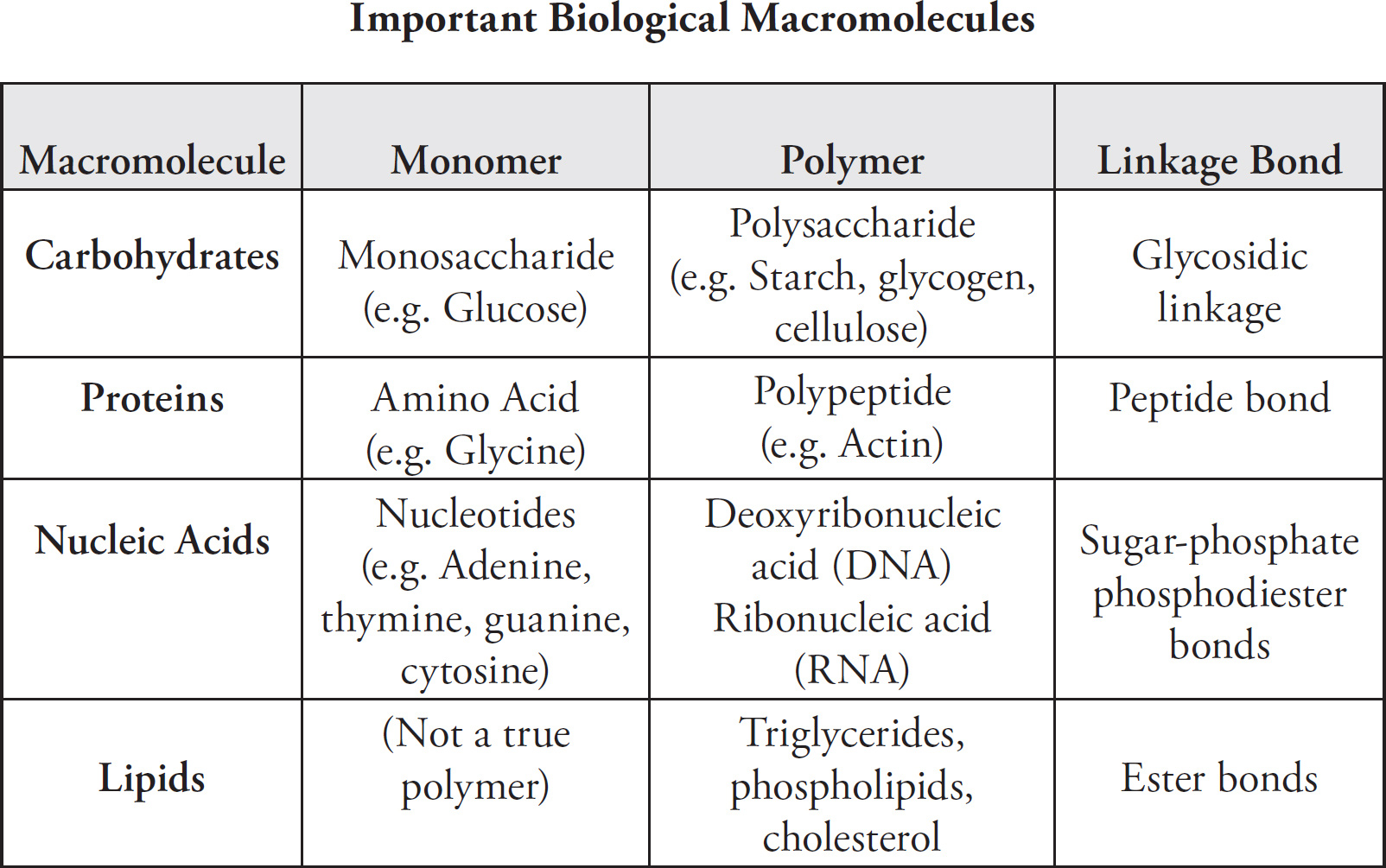
Biological macromolecules
Dna Separates During Meiosis, Or Sex Cell Formation.
Within All Cells, Small Organic Molecules Are Joined Together To Form Larger Molecules.
Each Is An Important Cell Component And Performs A Wide Array Of Functions.
As We’ve Learned, There Are Four Major Classes Of Biological Macromolecules:
Related Post: