Blood Clotting Flow Chart
Blood Clotting Flow Chart - A picture showing clotting of blood cells. This capability is essential to keep you alive, particularly with significant injuries. These types of blood clots can block the flow of blood and can cause swelling, pain, and red or purplish discoloration. Web create a flow chart showing the major systemic veins through which blood travels from the feet to the right atrium of the heart. The process of blood coagulation leads to haemostasis, i.e. Web blood clotting, or coagulation, is an important process that prevents excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. Platelets (a type of blood cell) and proteins in your plasma (the liquid part of blood) work together to stop the bleeding by forming a clot over the injury. The coagulation cascade is a series of reactions, catalysed by protein enzymes known as coagulation ‘factors’. The human body protects against loss of blood through the clotting mechanism. Web the flowchart in the question outlines the steps and the factors involved in the process of blood clotting. The human body protects against loss of blood through the clotting mechanism. The type of blood clot a person has will typically depend on where they affect a person’s body. As such, the proteins required for such clotting to take place are part of the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. If a dvt is not treated, it can move or. Web blood clotting (technically “blood coagulation”) is the process by which (liquid) blood is transformed into a solid state. Each protein circulates in the blood in an active form. Tissue factor (factor iii) is released by damaged cells outside the circulation. As such, the proteins required for such clotting to take place are part of the intrinsic pathway of blood. Web blood clotting (technically “blood coagulation”) is the process by which (liquid) blood is transformed into a solid state. Web when blood vessels are cut or damaged, the loss of blood from the system must be stopped before shock and possible death occur. The coagulation cascade is a series of reactions, catalysed by protein enzymes known as coagulation ‘factors’. A. As such, the proteins required for such clotting to take place are part of the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. These types of blood clots can block the flow of blood and can cause swelling, pain, and red or purplish discoloration. Virtually every cell, tissue, organ, and system in the body is impacted by the circulatory system. Platelets (a type. Web the coagulation cascade, or secondary hemostasis, is a series of steps in response to bleeding caused by tissue injury, where each step activates the next and ultimately produces a blood clot. The coagulation cascade is a series of reactions, catalysed by protein enzymes known as coagulation ‘factors’. Web when blood comes into contact with negatively charged surfaces, a series. This blood clotting is a complex process involving many clotting factors (incl. This reaction stops bleeding and allows your body to start repairs on the injury. This damage is known as coronary artery disease. This is accomplished by solidification of the blood, a process called coagulation or clotting. Web blood clotting, or coagulation, is an important process that prevents excessive. The type of blood clot a person has will typically depend on where they affect a person’s body. The human body protects against loss of blood through the clotting mechanism. This is accomplished by solidification of the blood, a process called coagulation or clotting. Web blood clotting, or coagulation, is an important process that prevents excessive bleeding when a blood. All the components necessary for the clotting process to proceed are found in the blood. Prevention of bleeding or haemorrhage. This reaction stops bleeding and allows your body to start repairs on the injury. Damage to the blood vessel means that factor vii exits the circulation into surrounding tissues. As such, the proteins required for such clotting to take place. Web when blood vessels are cut or damaged, the loss of blood from the system must be stopped before shock and possible death occur. Web blood clotting, or coagulation, is an important process that prevents excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. Web blood clotting (technically “blood coagulation”) is the process by which (liquid) blood is transformed into a. Platelets (a type of blood cell) and proteins in your plasma (the liquid part of blood) work together to stop the bleeding by forming a clot over the injury. If a dvt is not treated, it can move or break off and travel to the lungs, which can cause a pe. Hemostasis is how your body plugs and repairs a. Platelets (a type of blood cell) and proteins in your plasma (the liquid part of blood) work together to stop the bleeding by forming a clot over the injury. Hemostasis is your body’s normal reaction to an injury that causes bleeding. This damage is known as coronary artery disease. The type of blood clot a person has will typically depend on where they affect a person’s body. Each protein circulates in the blood in an active form. Calcium ions, enzymes, platelets, damaged tissues) activating each other. Although they have different causes and symptoms, blood clots can. Damage to the blood vessel means that factor vii exits the circulation into surrounding tissues. Web the coagulation cascade, or secondary hemostasis, is a series of steps in response to bleeding caused by tissue injury, where each step activates the next and ultimately produces a blood clot. Tissue factor (factor iii) is released by damaged cells outside the circulation. Web blood clotting (technically “blood coagulation”) is the process by which (liquid) blood is transformed into a solid state. Or it can lead to a heart attack. Web when blood comes into contact with negatively charged surfaces, a series of proteolytic reactions are initiated that result in the activation of the plasma proteases factor (f)xii, prekallikrein (pk), and fxi, and the cleavage of high molecular weight kininogen (hk; The human body protects against loss of blood through the clotting mechanism. A blood clot consists of a plug of platelets enmeshed in a network of insoluble fibrin molecules. It can lead to irregular heart rhythms, called arrhythmias.
The Clotting Cascade Made Easy! Nurse Your Own Way
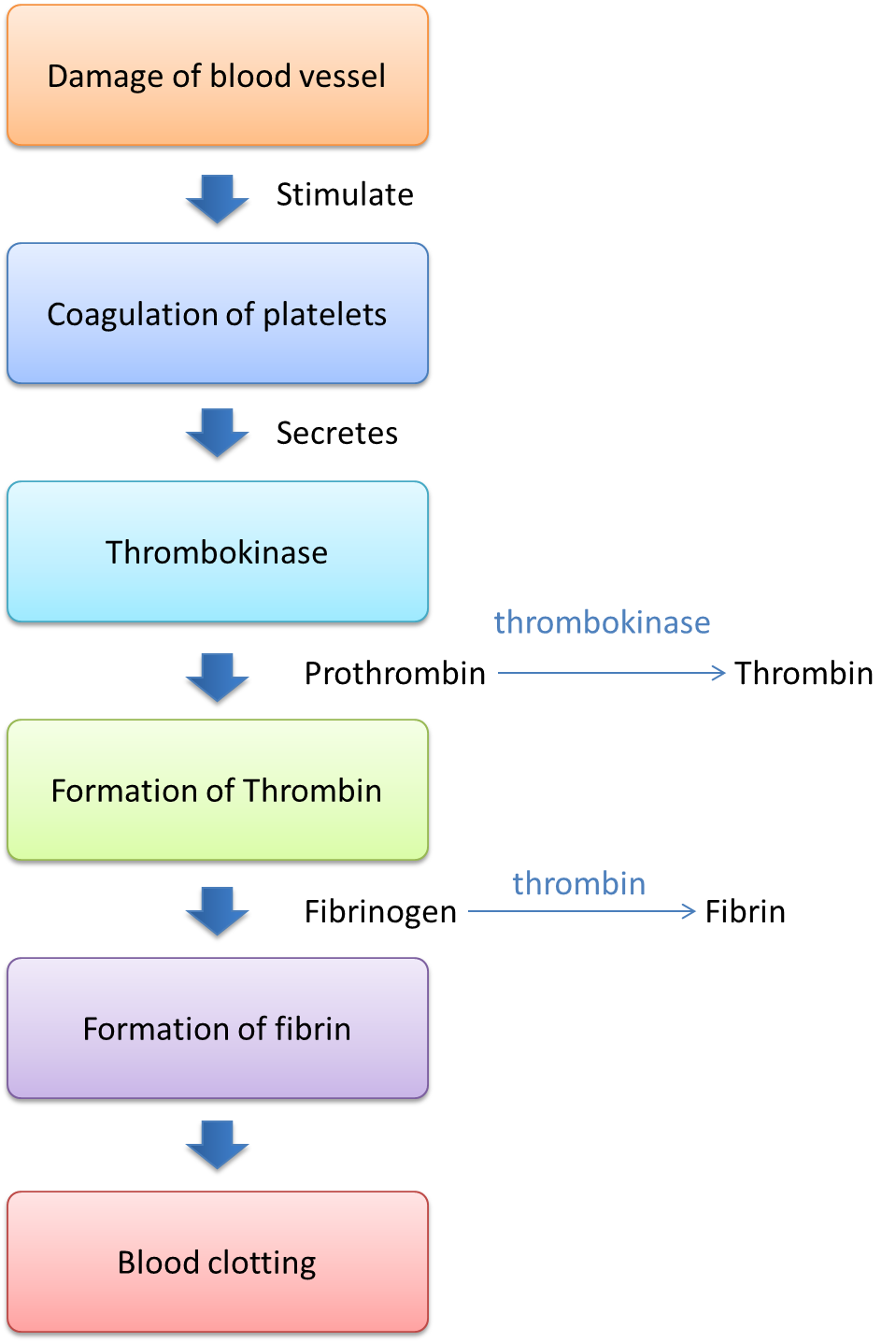
1.3.1 Mechanism of Blood Clotting SPM Biology

Blood Clotting Cascade Diagram

Coagulation Theory & Clotting A Level Biology Revision
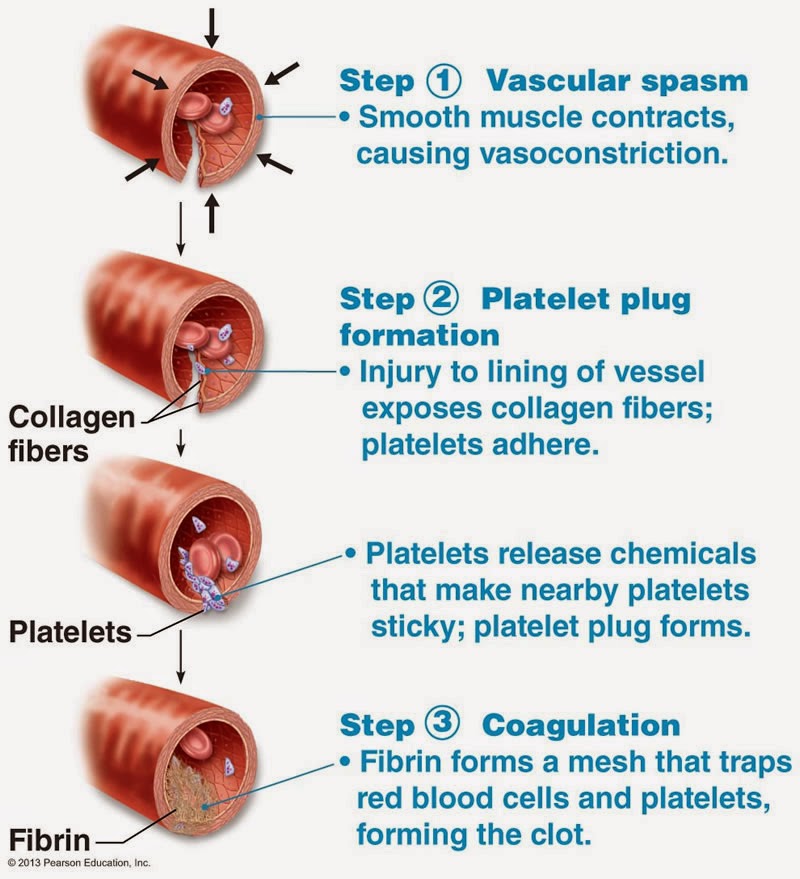
Bio Geo Nerd Blood Clotting
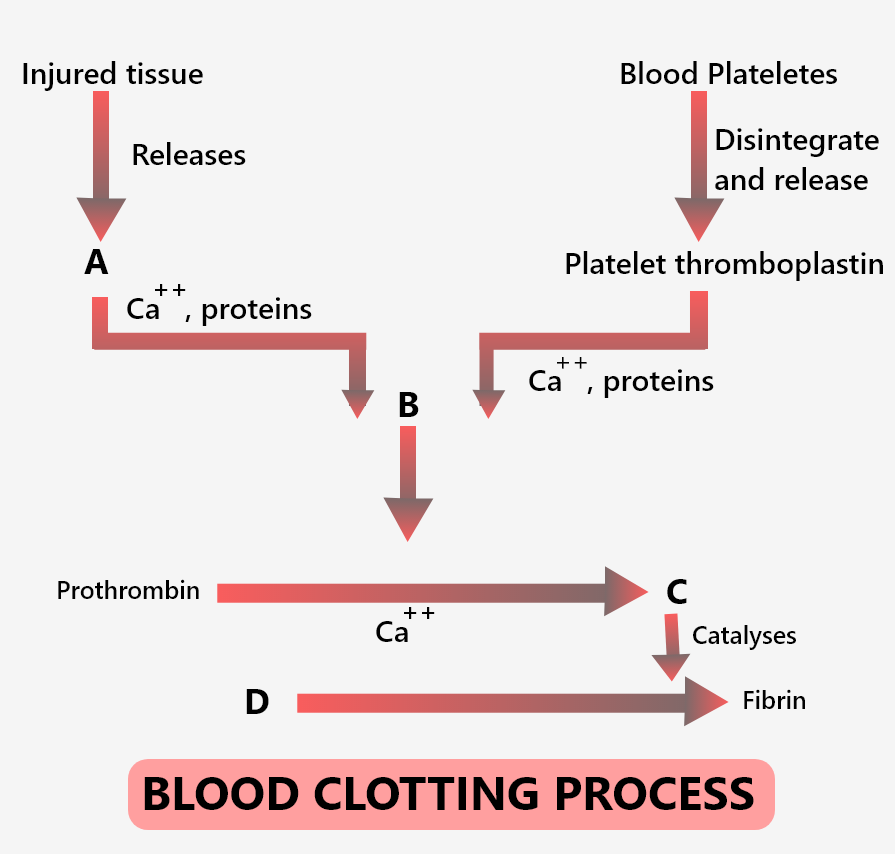
In the extrinsic clotting pathway, the active factor VII activates

Mechanism Of Blood Clotting
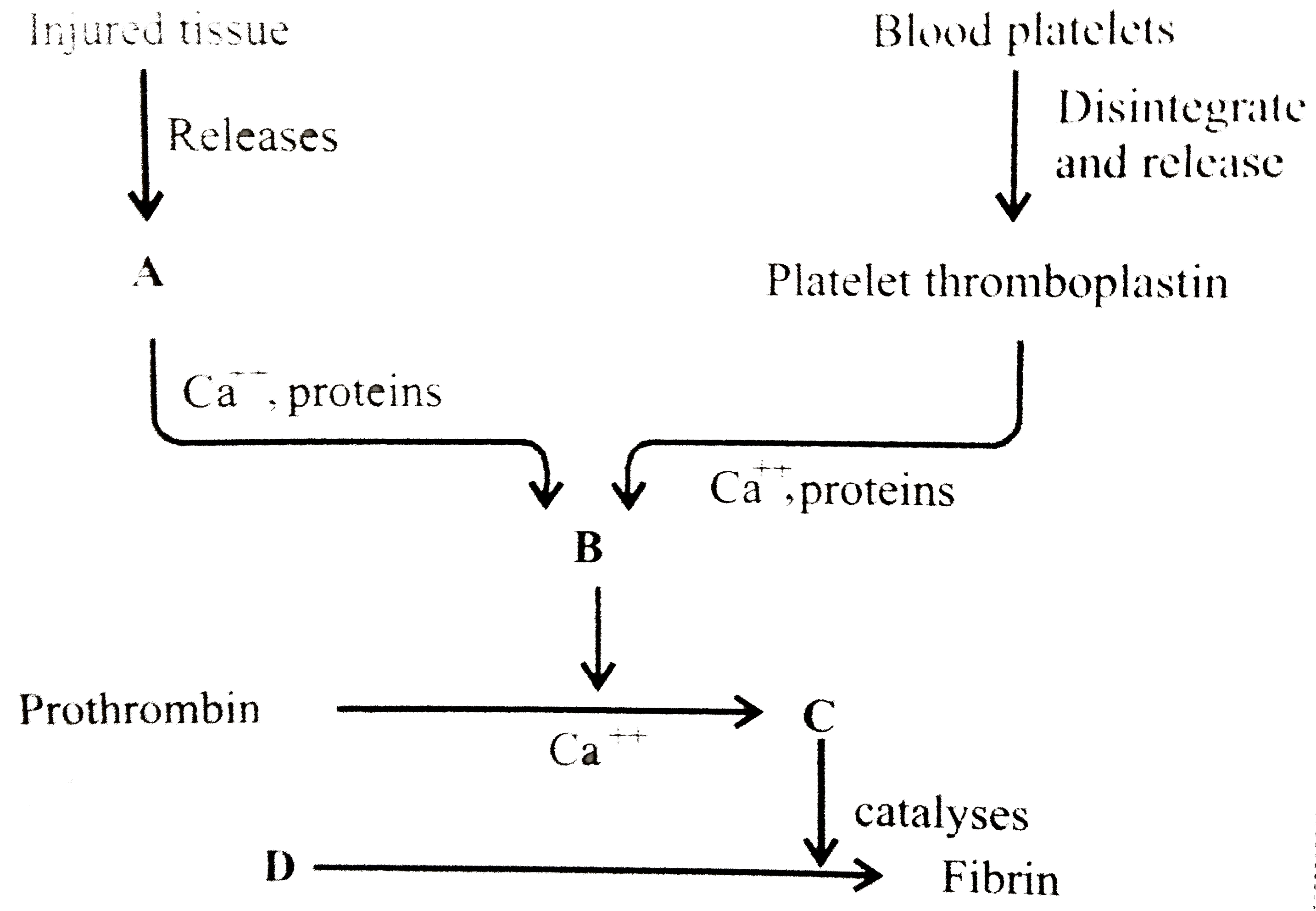
Describe the process of blood clotting.

Hemostasis · Anatomy and Physiology

Flow Chart Blood Clotting Process Diagram
If A Dvt Is Not Treated, It Can Move Or Break Off And Travel To The Lungs, Which Can Cause A Pe.
This Blood Clotting Is A Complex Process Involving Many Clotting Factors (Incl.
According To The Flowchart, The Missing Word In Statement 2 Is The Name Of A Tissue Factor That Is Produced By Damaged Blood Vessels, After A Blood Vessel Is Damaged.
This Capability Is Essential To Keep You Alive, Particularly With Significant Injuries.
Related Post: