Calculus Sign Chart
Calculus Sign Chart - Web we create a first derivative sign chart to summarize the sign of \(f'\) on the relevant intervals, along with the corresponding behavior of \(f\text{.}\) figure \(\pageindex{4}\). In the derivatives and the shape of a graph section, we will analyze graphs of functions using calculus. To establish a sign chart (number lines) for f ' , first set f ' equal to zero and then solve for x. Resourcefunction [ signchart] [ expr, x] The f'(𝑥) sign diagram displays intervals for which the function is increasing or decreasing. Web a sign diagram provides key information about a function such as: F (x) = −x5+ 5 2 x4 + 40 3 x3+5 f ( x) = − x 5 + 5 2 x 4 + 40 3 x 3 + 5. Note that these can be written as. (ax +b)(gx + h)(px + q)(sx + t) > 0. For example, of the type. Web here are the basics of how to create a sign chart and how to use it to solve inequalities. Resourcefunction [ signchart] [ expr, x] Web signchart | wolfram function repository. For example, of the type. Web derivativesigncharts | wolfram function repository. Resourcefunction [ derivativesigncharts] [ f, x] creates a grid of sign charts for f(x), f' (x) and f'' (x). Web to construct a sign chart of a function $f$ in a interval $i = (a,b)$ or $[a,b]$, you need the requirement that $f$ is continuous in $i$. In this example we used the fact that the only place that a. Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which can be factorized into linear binomials. Get a grid of sign charts for a function and its first and second derivatives. Web today i stumbled upon a question involving sign charts. In this example we used the fact that the only place that a derivative can change sign. Which one is f, which is the first derivative, and which is the second? Web a sign diagram provides key information about a function such as: Web today i stumbled upon a question involving sign charts. Web to construct a sign chart of a function $f$ in a interval $i = (a,b)$ or $[a,b]$, you need the requirement that $f$. It explains how to graph polynomial functions using the signs of the first derivative and the second. Determine the sign chart of the function given by: Web signs and sign charts the other method is to use a sign chart with the signs of the factors. The f(𝑥) sign diagram displays where the function outputs are positive or negative. Which. 2 signs \multiply and \divide as follows: (ax +b)(gx + h)(px + q)(sx + t) > 0. 1 a linear factor, ax + b, will be zero at one point (x = b a) and will be positive on one side of the zero and negative on the other. Get a grid of sign charts for a function and its. Determine the sign chart of the function given by: It could also be less than or less than or equal or greater than or equal, but the process is not much effected. Web today i stumbled upon a question involving sign charts. Resourcefunction [ signchart] [ expr, x] Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which. 2 signs \multiply and \divide as follows: Resourcefunction [ signchart] [ expr, x] Web today i stumbled upon a question involving sign charts. In the derivatives and the shape of a graph section, we will analyze graphs of functions using calculus. Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which can be factorized into linear binomials. Which one is f, which is the first derivative, and which is the second? Web use a sign chart to determine where a function is positive or negative. The f'(𝑥) sign diagram displays intervals for which the function is increasing or decreasing. 4.5.3 use concavity and inflection points to explain how the sign of the second derivative affects the shape. In the derivatives and the shape of a graph section, we will analyze graphs of functions using calculus. In this example we used the fact that the only place that a derivative can change sign is at the critical points. Get a number line diagram with information about where a function is positive, negative, zero or discontinuous. Web 4.5.1 explain. For example, of the type. Web signchart | wolfram function repository. The question goes something like this: F (x) = −x5+ 5 2 x4 + 40 3 x3+5 f ( x) = − x 5 + 5 2 x 4 + 40 3 x 3 + 5. Web how to create a sign chart to determine where a function is positive and negative. The f'(𝑥) sign diagram displays intervals for which the function is increasing or decreasing. Web example 1 determine all intervals where the following function is increasing or decreasing. Resourcefunction [ derivativesigncharts] [ f, x] creates a grid of sign charts for f(x), f' (x) and f'' (x). Web how to make a sign diagram with a step by step example. (ax +b)(gx + h)(px + q)(sx + t) > 0. Web here are the basics of how to create a sign chart and how to use it to solve inequalities. Since sign chart is based on bolzano's theorem. A sign diagram tells you where your function has positive or negative values. For example, of the type (ax+b) (gx+h) (px+q) (sx+t)>0 it could also be less than or less than or equal or greater than or. Web to construct a sign chart of a function $f$ in a interval $i = (a,b)$ or $[a,b]$, you need the requirement that $f$ is continuous in $i$. In the derivatives and the shape of a graph section, we will analyze graphs of functions using calculus.
How to Understand Sign Diagrams

Basic calculus symbols Trosaw

"Calculus Symbols" Canvas Print by coolmathposters Redbubble

Calculus Symbols Calculus, Physics and mathematics, Math methods

Sign Chart Calculus

Sign chart calculus qustmama
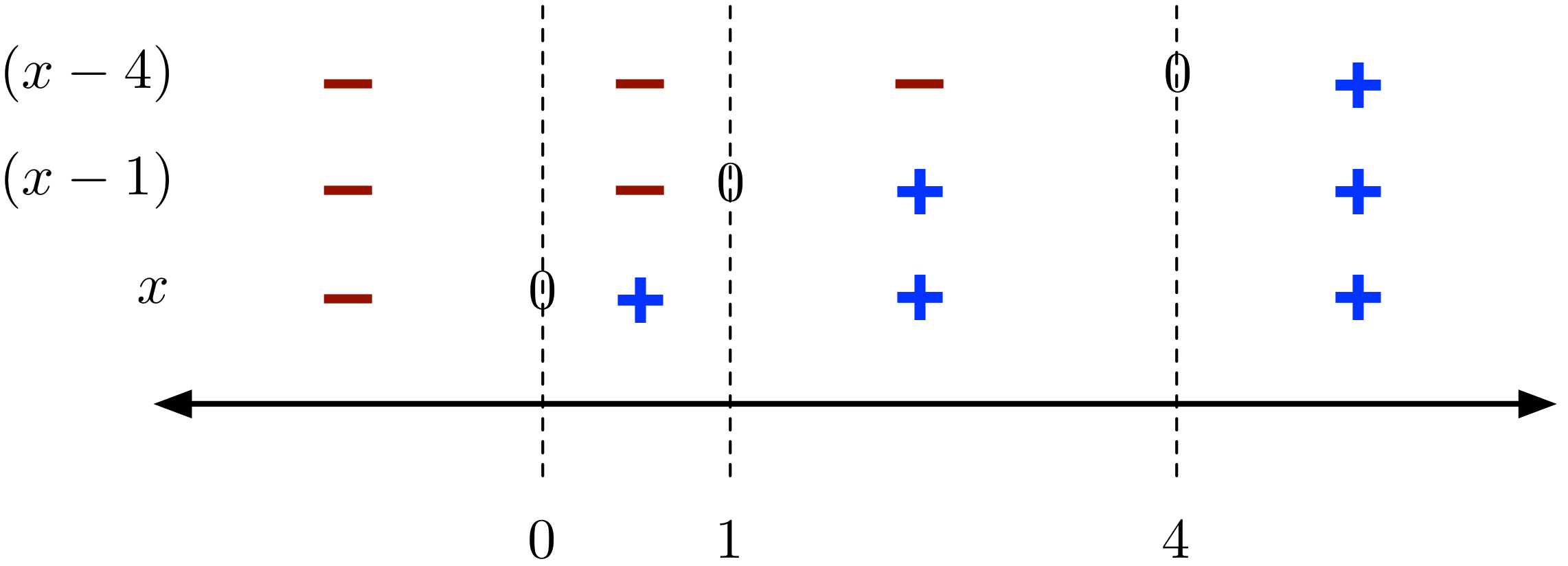
Inequalities Worked Examples

How to Understand Sign Diagrams

Basic Calculus Symbols

Sign Chart Math A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
All The Signs Should Be Positive, Since The Square Of A Nonzero Real Number Is Positive.
Web Sign Chart Is Used To Solve Inequalities Relating To Polynomials, Which Can Be Factorized Into Linear Binomials.
Then Determine The Sign Of The Derivative On Either Side Of Each Of The Critical Points.
For Readability Purpose, These Symbols Are Categorized By Topic And Function Into Tables.
Related Post: