Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Chart
Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Chart - Carbohydrate chains come in different lengths, and biologically. The simple sugars are galactose, fructose, glycogen,. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like elements present in carbohydrates, molecular building blocks of. What is an amino acid? • describe the chemical composition and general structure of carbohydrates. Having a phosphate group instead of the third fatty acid gives phospholipids a hydrophilic end. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids. Web this composition gives carbohydrates their name: Contain carbon covalently bonded to another carbon. Polymers of nucleotides) let’s take a closer look at the differences between the. Contain carbon covalently bonded to another carbon. Carbohydrate chains come in different lengths, and biologically. As we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: Each of them is discussed below. Protein is found in animal products and beans; Nucleic acids (dna and rna; Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monomer of carbohydrates:, elements of carbohydrates, glucose and more. Web have two fatty acids and one phosphate group bonded to the glycerol molecule. Web what is a monosaccharide? Carbohydrates are chemically defined as. Polymers of nucleotides) let’s take a closer look at the differences between the. Web protein carbohydrate lipid nucleic acid provides energy for body for insulation and protection Lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) 4. And fats or lipids are provided by oils,. Web this composition gives carbohydrates their name: And fats or lipids are provided by oils,. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. Web carbohydrates also have other important functions in humans, animals, and plants. Web the main substances found in every cell are a combination of lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids and proteins. 7) based on your answer to the two previous questions, what can you. This session will introduce the general structure and function of the biological macromolecules: Web there are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide. Web c, h, o, n, p. Web the four major classes of biological macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and. Web this composition gives carbohydrates their name: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monomer of carbohydrates:, elements of carbohydrates, glucose and more. Web what is a monosaccharide? Having a phosphate group instead of the third fatty acid gives phospholipids a hydrophilic end. This session will introduce the general structure and function of the biological macromolecules: Carbohydrates are chemically defined as. Each of these substances plays a different role in the body,. Carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (ch 2 o) n, where n is. 7) based on your answer to the two previous questions, what can you. Monomer found in nucleic acids. What is an unsaturated fatty acid? Lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) 4. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like elements present in carbohydrates, molecular building blocks of. Each of these substances plays a different role in the body,. Web the breakdown and synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids connect with the metabolic pathways of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle but enter the pathways. Web protein carbohydrate lipid nucleic acid provides energy for body for insulation and protection Each of them is discussed below. Having a phosphate group instead of the third fatty acid gives phospholipids. Web now that we’ve discussed the four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), let’s talk about macromolecules as. What is an unsaturated fatty acid? What is an amino acid? Web have two fatty acids and one phosphate group bonded to the glycerol molecule. Each of these substances plays a different role in the body,. Having a phosphate group instead of the third fatty acid gives phospholipids a hydrophilic end. Some will be both, in. Polymers of nucleotides) let’s take a closer look at the differences between the. Web c, h, o, n, p. Carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (ch 2 o) n, where n is. Each of them is discussed below. Protein is found in animal products and beans; Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids. Web carbohydrates also have other important functions in humans, animals, and plants. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like elements present in carbohydrates, molecular building blocks of. Web have two fatty acids and one phosphate group bonded to the glycerol molecule. This session will introduce the general structure and function of the biological macromolecules: Web now that we’ve discussed the four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), let’s talk about macromolecules as. Carbohydrates (polymers of sugars) 3. As we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: Web the breakdown and synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids connect with the pathways of glucose catabolism.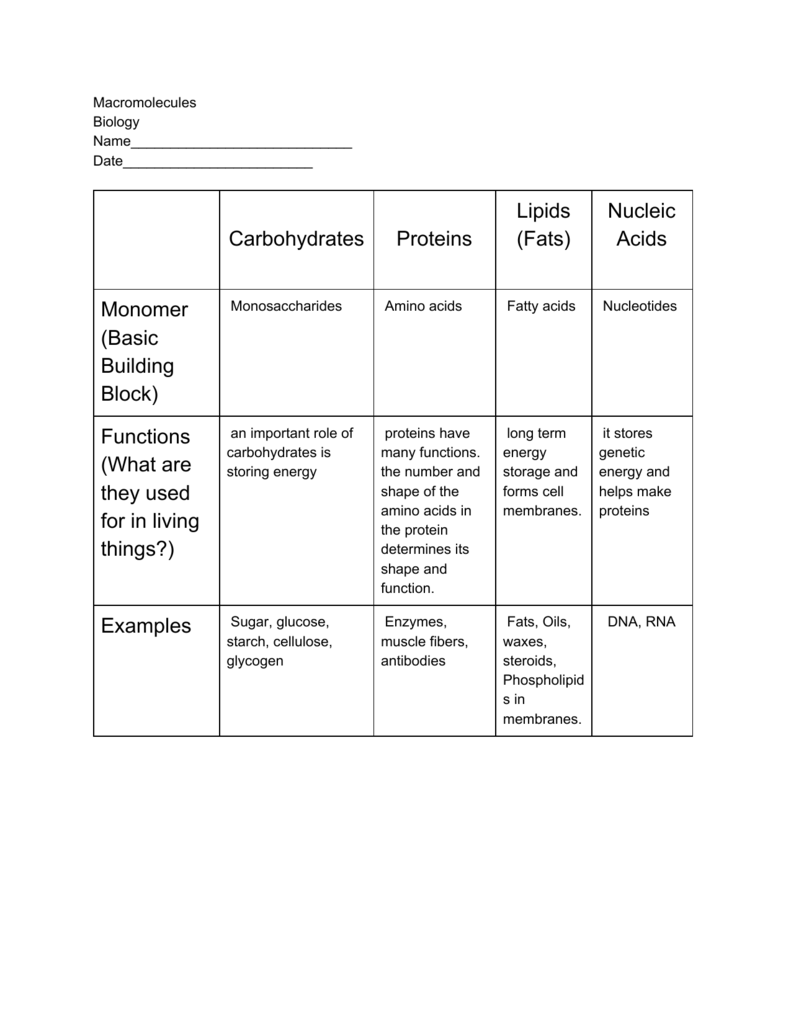
Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Chart
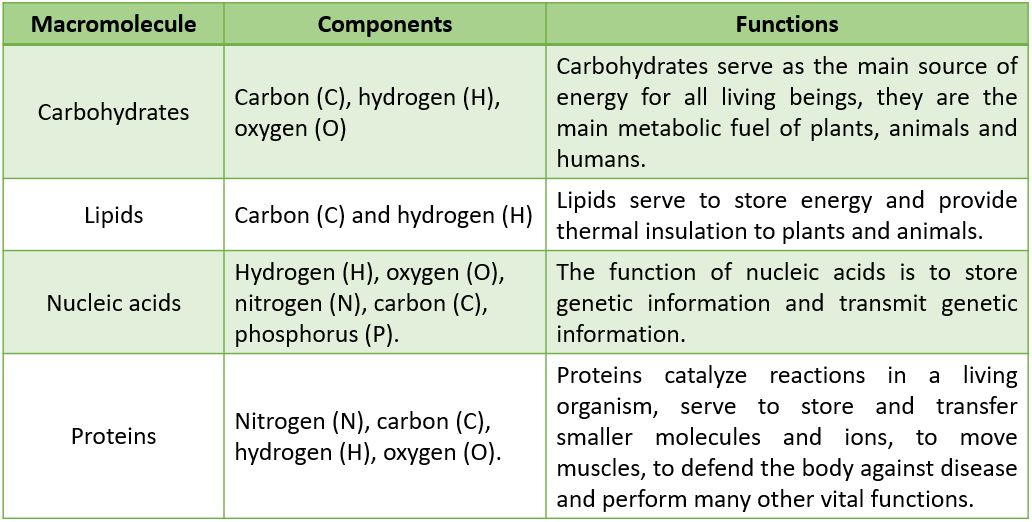
Compare The Structure And Function Of Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins

Table of Biomolecule, Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids Diagram

Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins And Nucleic Acids Chart
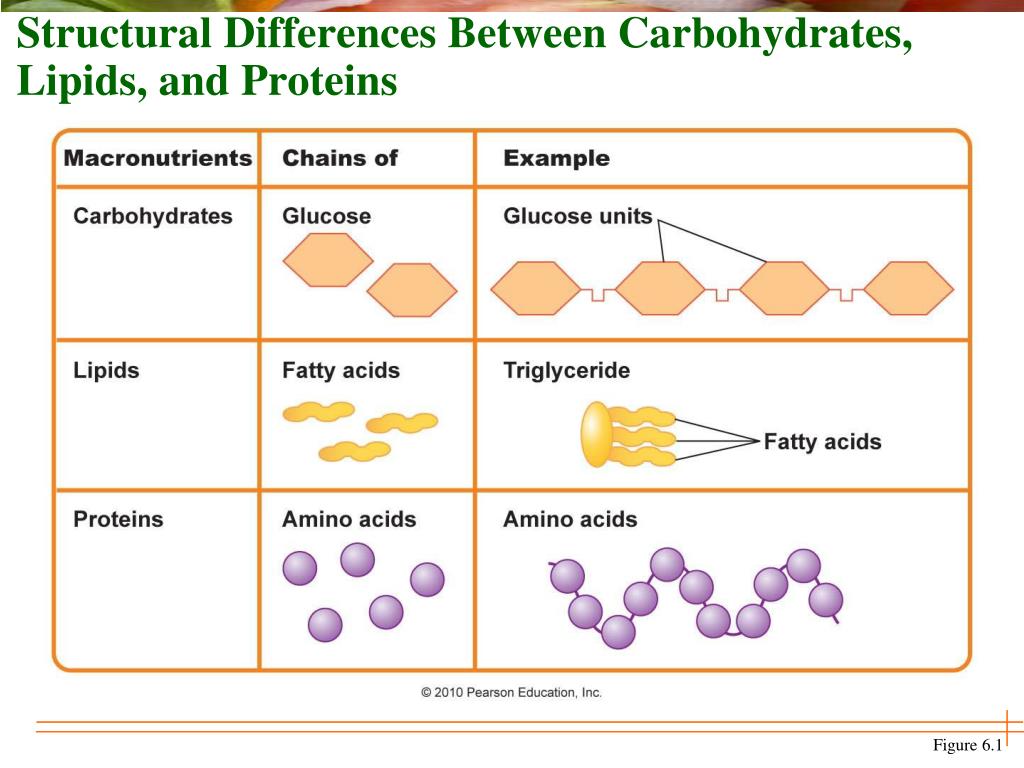
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins And Nucleic Acids Chart vrogue.co

Compare The Chemical Structure And Functions Of Carbohydrates Lipids

Protein, Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acid Elements of Biological

Compare The Chemical Structure And Functions Of Carbohydrates Lipids
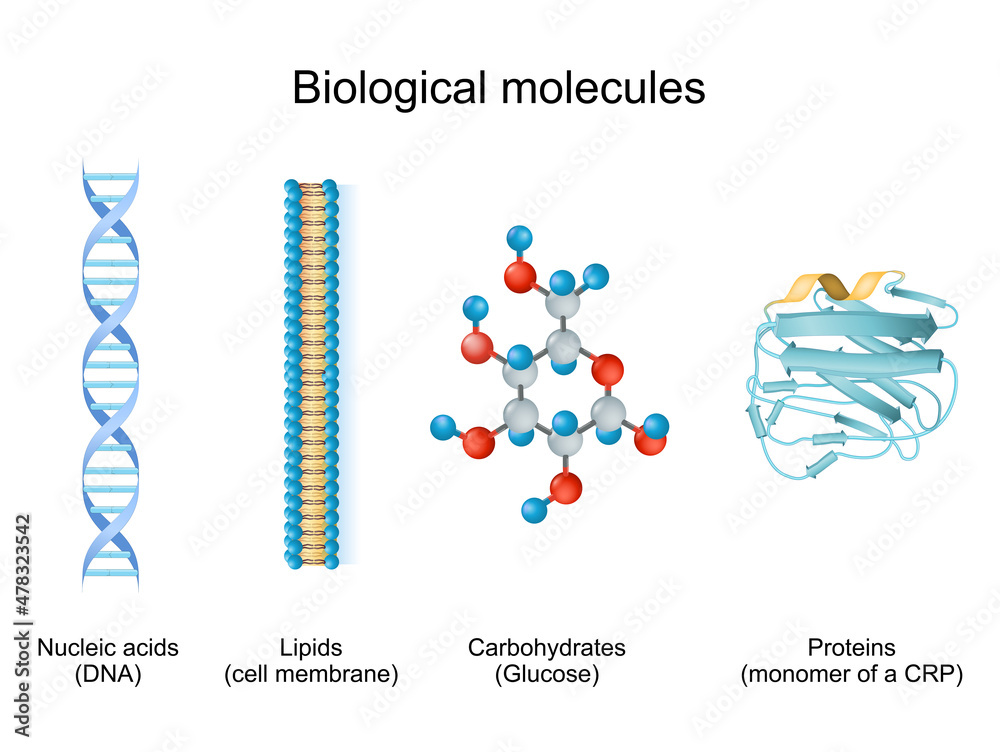
Types of biological molecule Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic acids and

Four Biomolecules Structure and Function Comparison Chart
Carbohydrate Chains Come In Different Lengths, And Biologically.
Lipids, Carbohydrates, And Nucleic Acids.
The Simple Sugars Are Galactose, Fructose, Glycogen,.
What Is An Amino Acid?
Related Post: