Cell Cycle Flow Chart
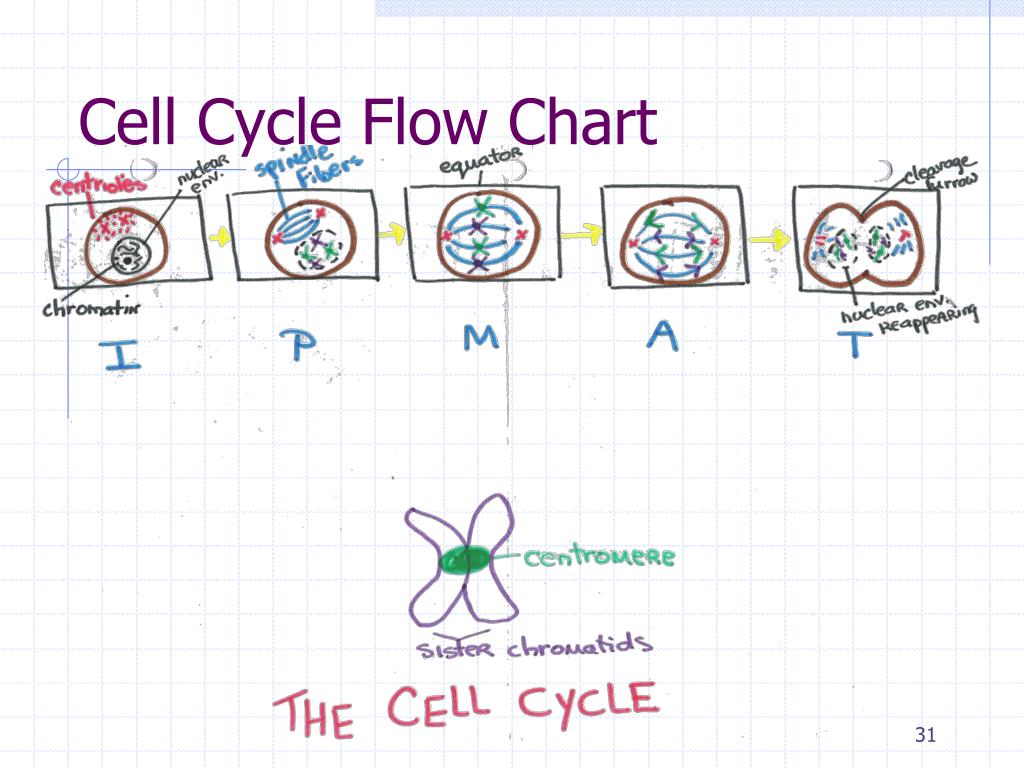
Cell Cycle Flow Chart - The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components:. This is the “gap” between the. Web cell cycle analysis by quantitation of dna content was one of the earliest applications of flow cytometry. Web by showing growth during the cell cycle as a chart, we can see where different types of growth occur. It is important to define the. Web the cell cycle is a repeating series of events that cells go through. Web understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms both internal and external to the cell. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. The cell cycle consists of: Web cell cycles consist of two main phases: Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period (interphase) followed by. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components:. Web what you’ll learn to do: Web cell cycles consist of two main phases: In this article, we will look at the different stages of this. Web understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms both internal and external to the cell. The outer ring identifies when a cell is in interphase (i) and when it is in mitosis (m). The dna of mammalian, yeast, plant or bacterial cells can be stained by.. Explain how the three internal control checkpoints occur at the end of g 1, at. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. In eukaryotic cells, there are two growth phases, and cell. It includes growth, dna synthesis, and cell division. G 1 (gap or growth 1) phase: Web the graphic below shows a visual representation of the cell cycle. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a. Explain how the three internal control checkpoints occur at the end of g 1, at. In interphase, a newly formed cell and its nucleus enquiring a series of. The dna of mammalian, yeast, plant or bacterial cells can. It is important to define the. The outer ring identifies when a cell is in interphase (i) and when it is in mitosis (m). Web cell cycles consist of two main phases: The most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of dna in the chromosomes and then segregate the copies. Web typical examples. Web the cell cycle is a repeating series of events that cells go through. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components:. Web the cell cycle describes an orderly sequence of events that are highly regulated. Web identify the stages of the cell cycle, by picture and by description of major milestones.. The most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of dna in the chromosomes and then segregate the copies. G 1 = growth and preparation of the chromosomes for replication, s = synthesis of dna and duplication of the centrosome, g. In this article, we will look at the different stages of this. The. Web flow cytometry can be used for cell cycle analysis to estimate the percentages of a cell population in the different phases of the cell cycle, or it can be used with other reagents. It is important to define the. Web the different phases of a cell cycle include: Web the cell cycle describes an orderly sequence of events that. Cell cycle has different stages called g1, s, g2, and m. Web what you’ll learn to do: Web the different phases of a cell cycle include: The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that. Web the cell cycle is a repeating series of events that cells go through. This is the “gap” between the. Web the graphic below shows a visual representation of the cell cycle. Web understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms both internal and external to the cell. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period (interphase) followed by. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. In interphase, a newly formed cell and its nucleus enquiring a series of. Web typical examples are the total length of the cell cycle, the length and variability of distinct cell cycle phases, the presence of quiescent or senescent cells, or the presence of. G 1 = growth and preparation of the chromosomes for replication, s = synthesis of dna and duplication of the centrosome, g. The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that. Identify the stages of the cell cycle, by picture and by description of major milestones. Web the cell cycle describes an orderly sequence of events that are highly regulated. This is the “gap” between the. Web identify the stages of the cell cycle, by picture and by description of major milestones. The dna of mammalian, yeast, plant or bacterial cells can be stained by. The outer ring identifies when a cell is in interphase (i) and when it is in mitosis (m). It is important to define the. In this article, we will look at the different stages of this. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. Rna and protein concentration * s increase throughout the g1, s, and g2. Web the cell cycle is the process a cell undertakes to replicate all of its genetic material and divide into two identical cells. Web the graphic below shows a visual representation of the cell cycle.
the cell cycle Biology notes, Cell cycle, Cell biology notes

26. Cell cycle greek.doctor

Stages of Mitosis Mitosis, Nuclear membrane, Flow chart

Make a flow chart to show the cell cycle and explain cell division

Cellular Differentiation Anatomy and Physiology I

Stages of the Cell Cycle Mitosis (Interphase and Prophase) Owlcation

Schematic presentation of PLK functions and localizations during the
PPT Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division PowerPoint Presentation

The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology

Section 3 Cell Cycle Nitty Gritty Science THE CELL CYCLE WORKSHEET
Web Cell Cycles Consist Of Two Main Phases:
It Includes Growth, Dna Synthesis, And Cell Division.
Web By Showing Growth During The Cell Cycle As A Chart, We Can See Where Different Types Of Growth Occur.
Web Figure 7.2.1 Cell Cycle:
Related Post: