Chart Of Hydrocarbons
Chart Of Hydrocarbons - Describe the reactions characteristic of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Web hydrohalogenation and hydration follow markovnikov’s rule which states that the hydrogen is added to the carbon with the most hydrogen atoms originally bonded to it. Web estimated at 511 billion barrels, the area would rank as the second largest crude oil reserve by region in the world, behind only that of the middle east, whose proven reserves stood at over 871. Web the diagram below summarises the main fractions from crude oil and their uses and the trends in properties. Identify structural and geometric isomers of hydrocarbons Describe the reactions characteristic of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons; Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and arenes. Name saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, and molecules derived from them; Select one of three hydrocarbons: The hydrocarbons ethane, ethene, and ethyne provide an example of how each type of bond can affect the geometry of a molecule: Typically, hydrocarbons are colourless gases that have very weak odours. Aromatic compounds derive their names from the fact that many of these compounds in the early days of discovery were grouped because they were oils with fragrant odors. The hydrocarbons ethane, ethene, and ethyne provide an example of how each type of bond can affect the geometry of a molecule:. Web the predominant use of hydrocarbons is as a combustible fuel source. Because alkane molecules are nonpolar, they are insoluble in water, which is a polar solvent, but are soluble in nonpolar and slightly polar solvents. Web main groups of hydrocarbons: Aromatic compounds derive their names. Web let’s consider their physical properties first. Aromatic compounds derive their names from the fact that many of these compounds in the early days of discovery were grouped because they were oils with fragrant odors. Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and arenes. Explain the importance of hydrocarbons and the reason for their diversity. To make four covalent bonds, the c atom bonds to four h atoms, making the molecular. Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and arenes. Select one of three hydrocarbons: Identify primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary c ′ s and h ′ s. It also offers a specialty products segment for lubricants. Name saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, and molecules derived from them. Web main groups of hydrocarbons: Web hydrocarbons are organic compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. As we considered organic structures in the earlier portions of this book, alkanes were presented as examples because they are in many ways the simplest of organic molecules. They are broadly classified into two groups: Hydrocarbons are a class of organic compounds formed solely. Name saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, and molecules derived from them; Web estimated at 511 billion barrels, the area would rank as the second largest crude oil reserve by region in the world, behind only that of the middle east, whose proven reserves stood at over 871. Identify structural and geometric isomers of hydrocarbons Image modified from carbon: Aromatic compounds derive. The diagram for methane is misleading, however; Methane is the predominant component of natural gas. Web the diagram below summarises the main fractions from crude oil and their uses and the trends in properties. The hydrocarbons ethane, ethene, and ethyne provide an example of how each type of bond can affect the geometry of a molecule: Learn about the types,. Select all / deselect all. An acyclic saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula c n h 2n+2. Web that is because aramco is the linchpin of the strategy of muhammad bin salman, saudi arabia’s crown prince and de facto ruler, to end his country’s reliance on oil, diversify its economy and. Describe the reactions characteristic of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons;. The classifications for hydrocarbons are summarized below. Web estimated at 511 billion barrels, the area would rank as the second largest crude oil reserve by region in the world, behind only that of the middle east, whose proven reserves stood at over 871. Methane is the predominant component of natural gas. Methane, for example, has the shape of a regular. Identify primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary c ′ s and h ′ s. The classifications for hydrocarbons are summarized below. As we considered organic structures in the earlier portions of this book, alkanes were presented as examples because they are in many ways the simplest of organic molecules. Methane is the predominant component of natural gas. Web molweight, melting and. The four general classes of hydrocarbons are: Web estimated at 511 billion barrels, the area would rank as the second largest crude oil reserve by region in the world, behind only that of the middle east, whose proven reserves stood at over 871. Web hydrocarbons are the principal constituents of petroleum and natural gas and serve as fuels, lubricants, and raw materials for various products. An acyclic saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula c n h 2n+2. Note that the gases leave at the top of the column, the liquids condense in the middle. Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and arenes. Methane, for example, has the shape of a regular tetrahedron with carbon at the centre and a hydrogen atom at each corner. Image modified from carbon: Aromatic compounds derive their names. Describe the reactions characteristic of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Web explain the importance of hydrocarbons and the reason for their diversity; Web understand some physical properties like melting points, boiling points, and solubilities of hydrocarbons. The diagram for methane is misleading, however; Figure 2 , by openstax college, biology ( cc by 3.0 ). They are broadly classified into two groups: Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and arenes.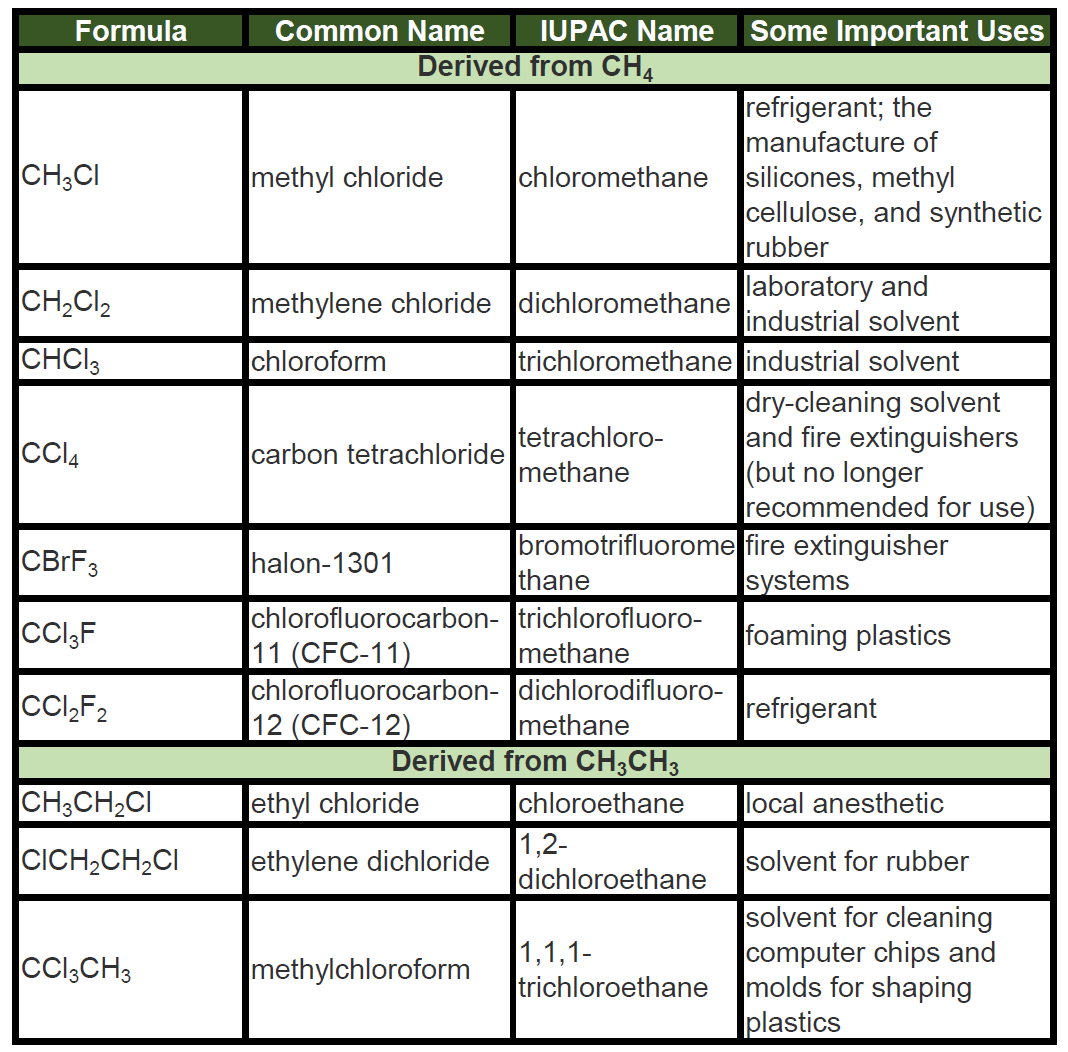
Chemical properties of hydrocarbons. Properties of Hydrocarbons. 20221024

1. Classification of Hydrocarbons YouTube
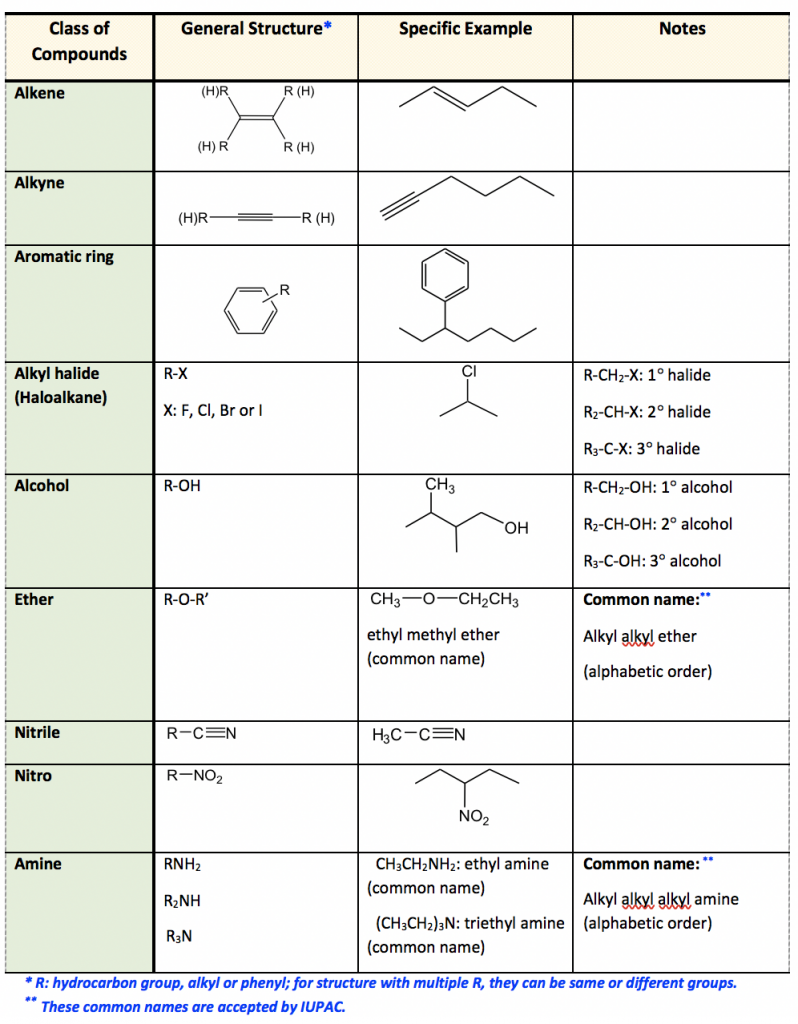
Naming Hydrocarbons Chart

3.2. Nomenclature of unsaturated hydrocarbons Organic Chemistry 1 An

Chemical Structures of Various Categories of Hydrocarbons Download

Schematic of Hydrocarbon Categories Download Scientific Diagram
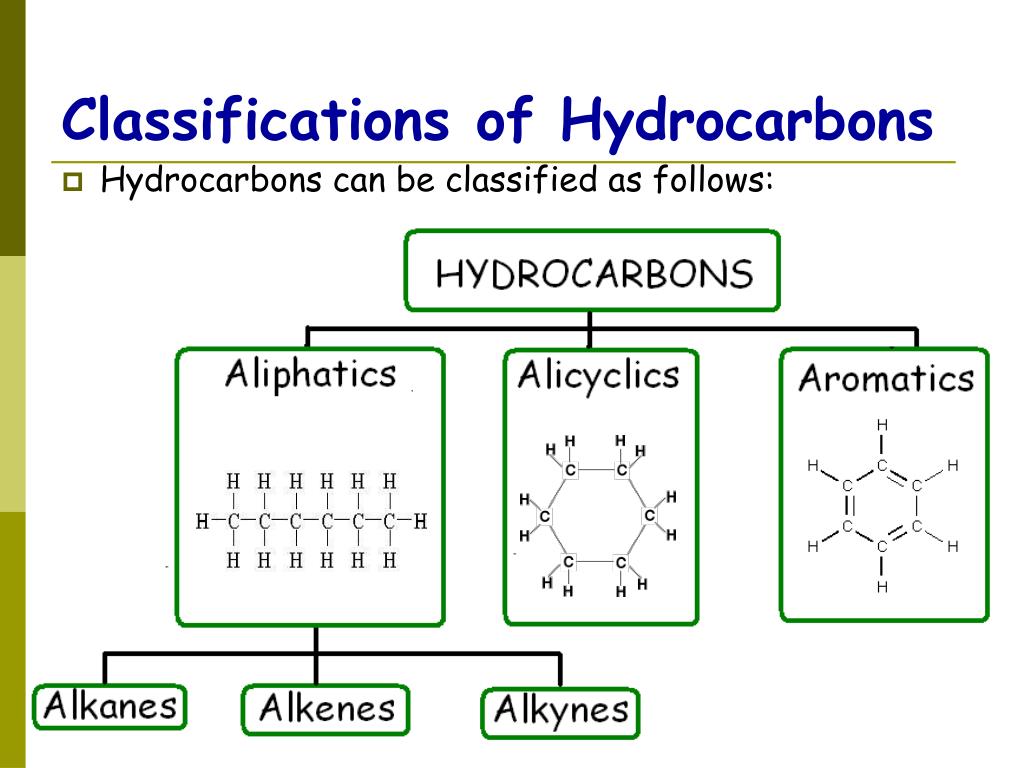
Classification Of Hydrocarbons My XXX Hot Girl

Chemistry GCSE Revision Organic Chemistry

Naming Hydrocarbons Chart
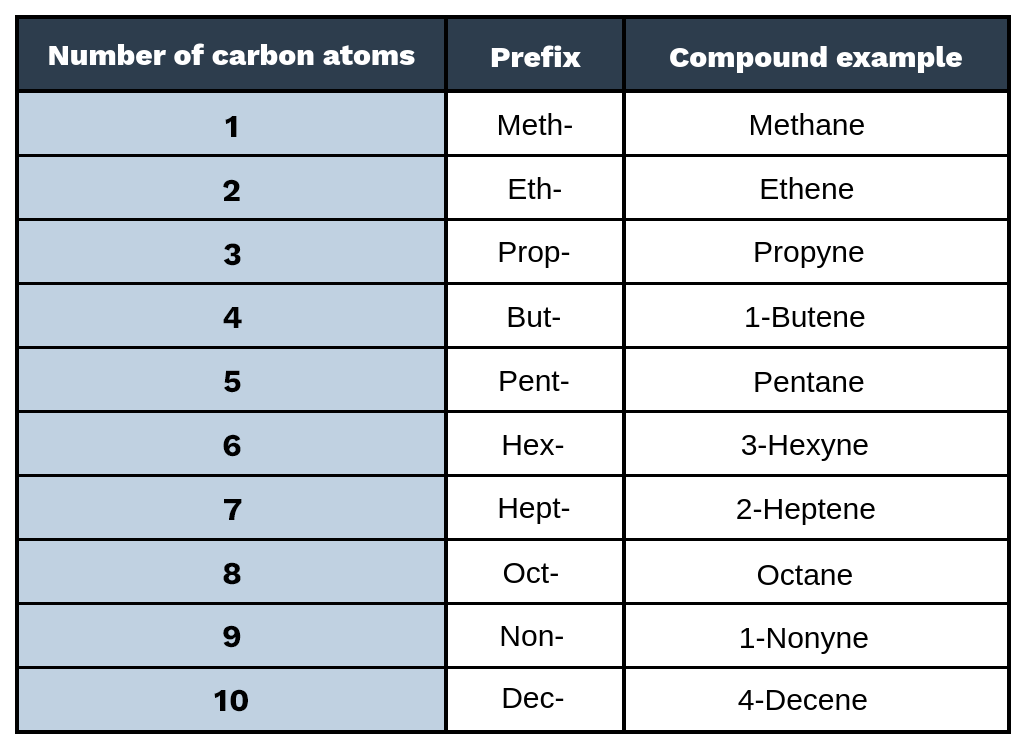
Naming Hydrocarbons Chart
The Hydrocarbons Ethane, Ethene, And Ethyne Provide An Example Of How Each Type Of Bond Can Affect The Geometry Of A Molecule:
Identify Structural And Geometric Isomers Of Hydrocarbons
As We Considered Organic Structures In The Earlier Portions Of This Book, Alkanes Were Presented As Examples Because They Are In Many Ways The Simplest Of Organic Molecules.
Select One Of Three Hydrocarbons:
Related Post: