Chart Of Macromolecules
Chart Of Macromolecules - Web a macromolecule is a very large molecule having a polymeric chain structure. Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. There are only a few known inorganic macromolecules. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); Web biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. The small molecular units that make up macromolecules are called monomers. Web proteins, polysaccharides, genes, ruber, and synthetic polymers consist of macromolecules. Web the four types of macromolecules are proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. For synthetic polymers, here are the abbreviations for some common polymers: They are joined together in a process known as. The image below depicts how the bacterial protein barnase undergoes modifications that involve changing its conformation, or shape. While they have different structures and functions, they are all composed of long complex chains of molecules (polymers) made up of simpler, smaller subunits (monomers). Web there are four classes of macromolecules that constitute all living matter: They can have very different. Web macromolecule, any very large molecule, usually with a diameter ranging from about 100 to 10,000 angstroms (10 −5 to 10 −3 mm). They are typically composed of thousands or more atoms. Molecular structure of glucose (opens a modal) dehydration. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s dry mass (recall that water makes up the majority of. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. The image below depicts how the bacterial protein barnase undergoes modifications that involve changing its conformation, or shape. Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. The four major classes of biological macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic. Synthetic fibers and experimental materials such as carbon nanotubes [2] [3] are also examples of macromolecules. Introduction to macromolecules (opens a modal) carbohydrates. Web energy from carbohydrates. This unit is part of the biology library. For synthetic polymers, here are the abbreviations for some common polymers: Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic. The small molecular units that make up macromolecules are called monomers. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); Web there are four classes of macromolecules that constitute all living matter: They can have very different shapes, although the most common structure involves a long chain. Web macromolecules are very large molecules. Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. There are only a few known inorganic macromolecules. Molecular structure of glucose (opens a modal) dehydration. Web biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. Web biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. Web macromolecules are very large molecules. The polymer is more than the sum of. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Web there are four major biological macromolecule classes (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,. Web biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. Web macromolecule, any very large molecule, usually with a diameter ranging from about 100 to 10,000 angstroms (10 −5 to 10. They are joined together in a process known as. They can have very different shapes, although the most common structure involves a long chain. Nucleic acids are made up of nitrogenous bases, sugars, and phosphate groups, and they carry genetic information. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Most macromolecules are. Molecular structure of glucose (opens a modal) dehydration. Macromolecules are large, complex molecules that are fundamental to both biological and chemical processes. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. They are typically composed of thousands or more atoms. Their molecular weights can range from the thousands to the millions. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Molecular structure of glucose (opens a modal) dehydration. Web biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. The molecule is the smallest unit of the substance that retains its characteristic properties. Web macromolecule, any very large molecule, usually with a diameter ranging from about 100 to 10,000 angstroms (10 −5 to 10 −3 mm). Nucleic acids are made up of nitrogenous bases, sugars, and phosphate groups, and they carry genetic information. Synthetic fibers and experimental materials such as carbon nanotubes [2] [3] are also examples of macromolecules. These macromolecules are the building blocks of cells and perform a wide range of functions in living organisms. Typically they are constructed from small, repeating units linked together to form this long chain. Solids formed mainly due to covalent bonds, organosilanes, siloxanes and organosiloxanes. Metabolism, or the conversion of food into energy, is the most common of these chemical processes. Web proteins, polysaccharides, genes, ruber, and synthetic polymers consist of macromolecules. In order to function in the cell, barnase has to be folded from a nonfunctional conformation into a functional conformation. They are joined together in a process known as. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s dry mass (recall that water makes up the majority of its complete mass). Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions.
Pre IB/GT Biology 1 Macromolecules Chart Diagram Quizlet
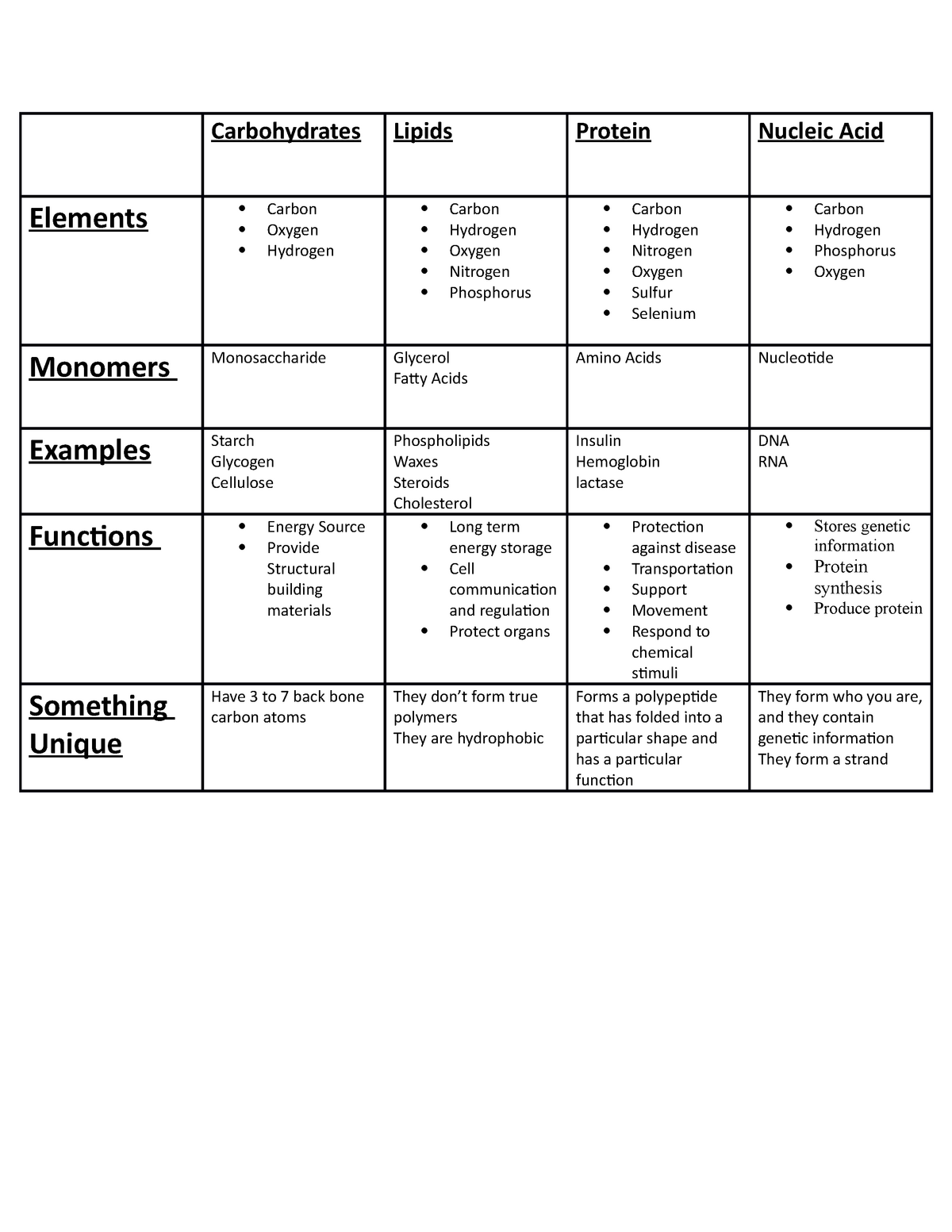
Macromolecules chart Lecture notes A Carbohydrates Elements Carbon
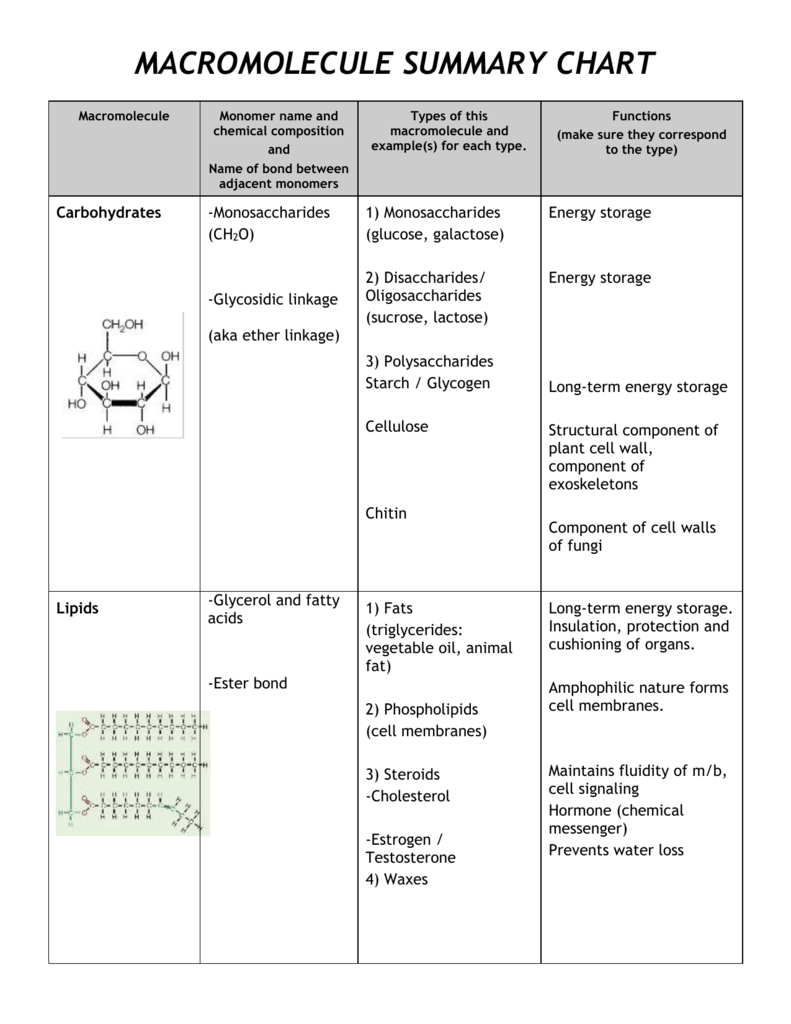
macromolecule summary chart
Macromolecules Chart Rae Rocks Teaching
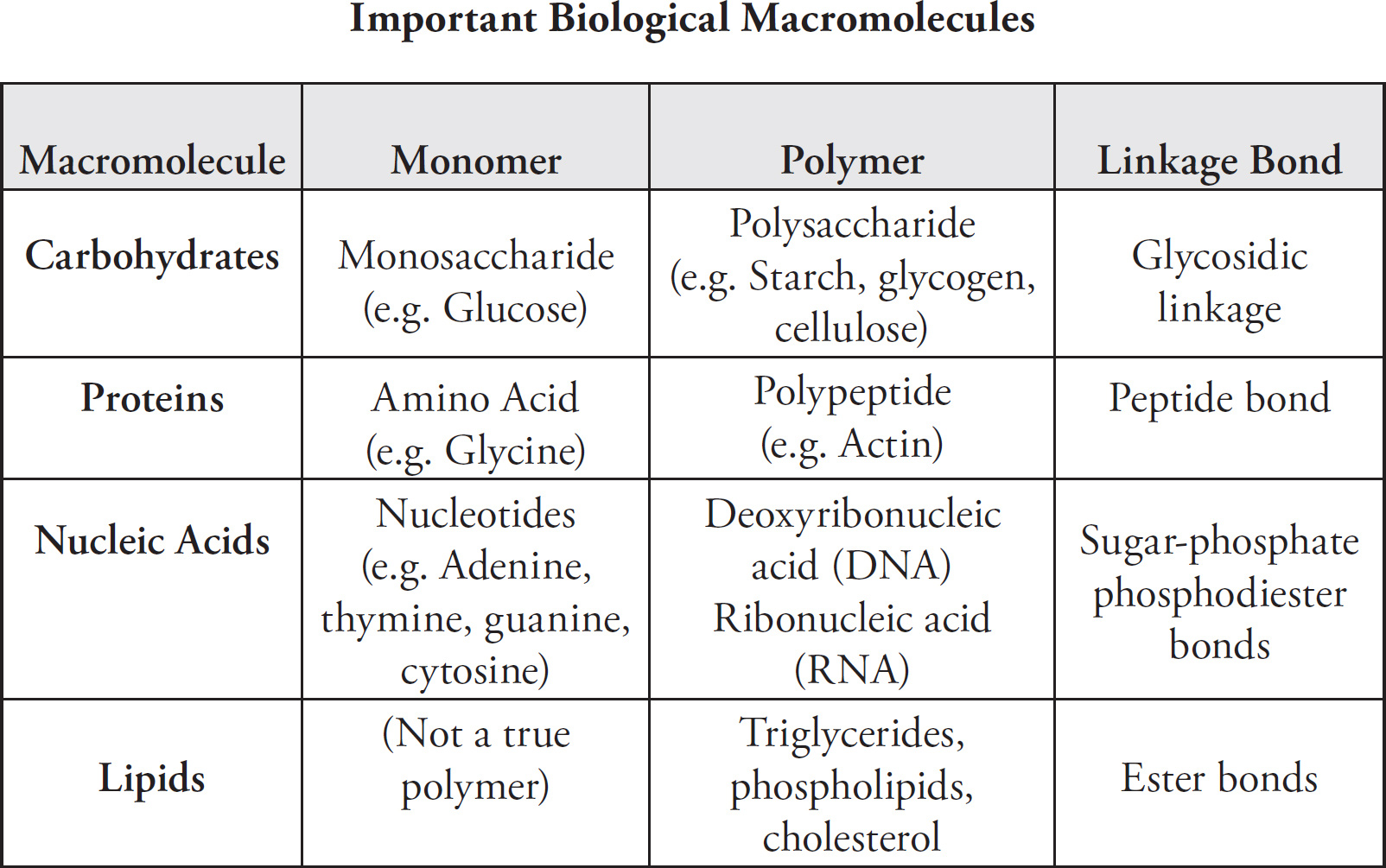
Biological macromolecules
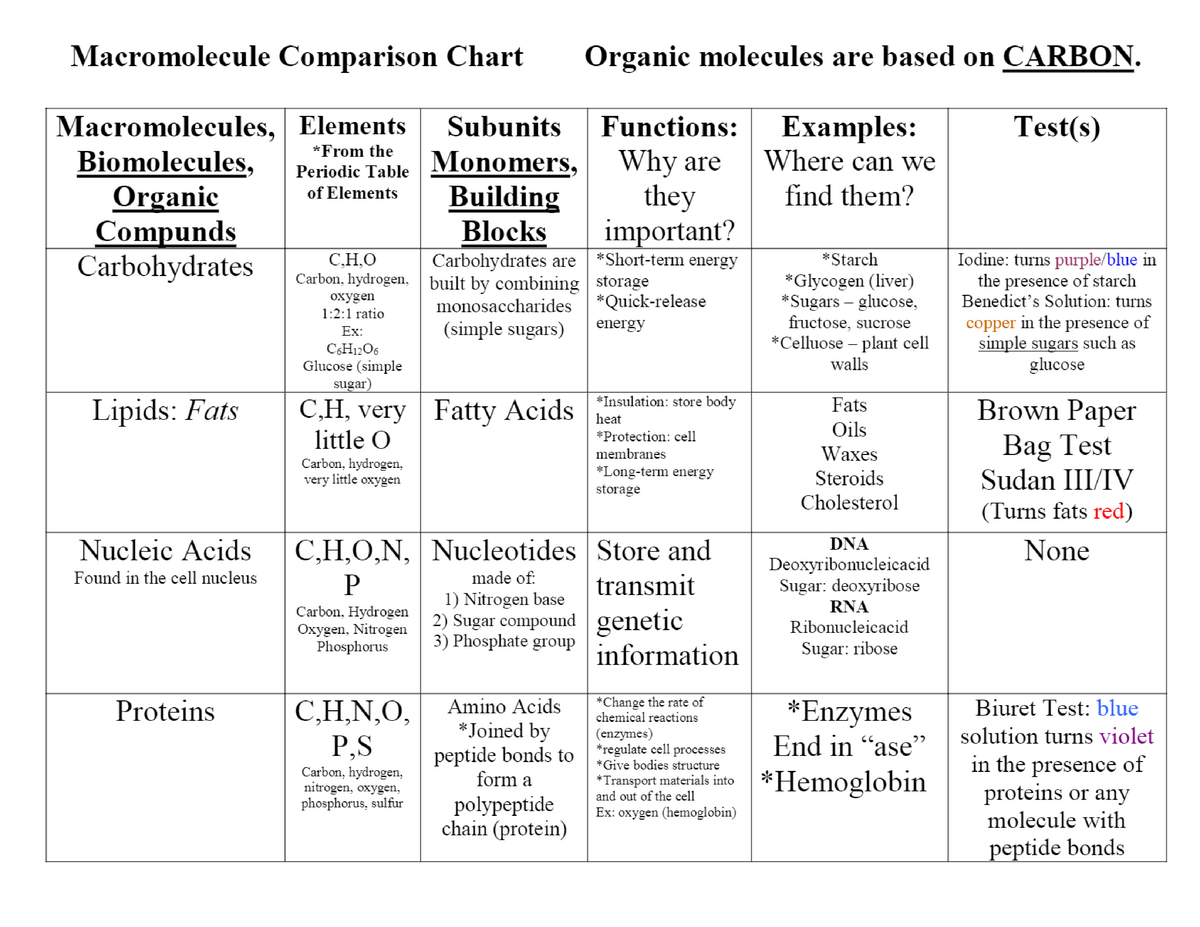
Macromolecule Comparison Chart Organic Bio201 Studocu
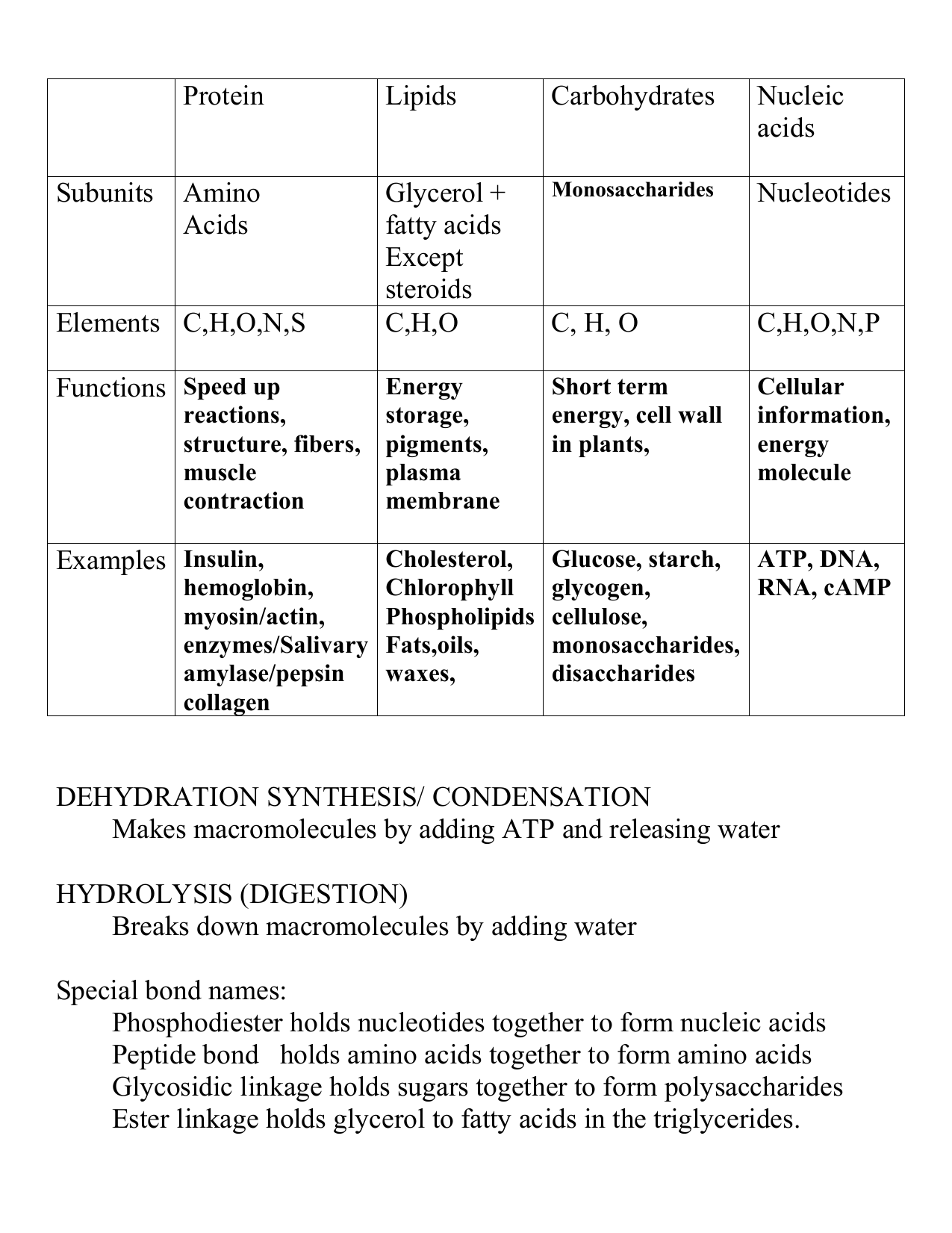
Biochemistry Macromolecules Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart

PDF Macromolecules Chart PDF document

2.3 Biologically Important Macromolecules Biology LibreTexts
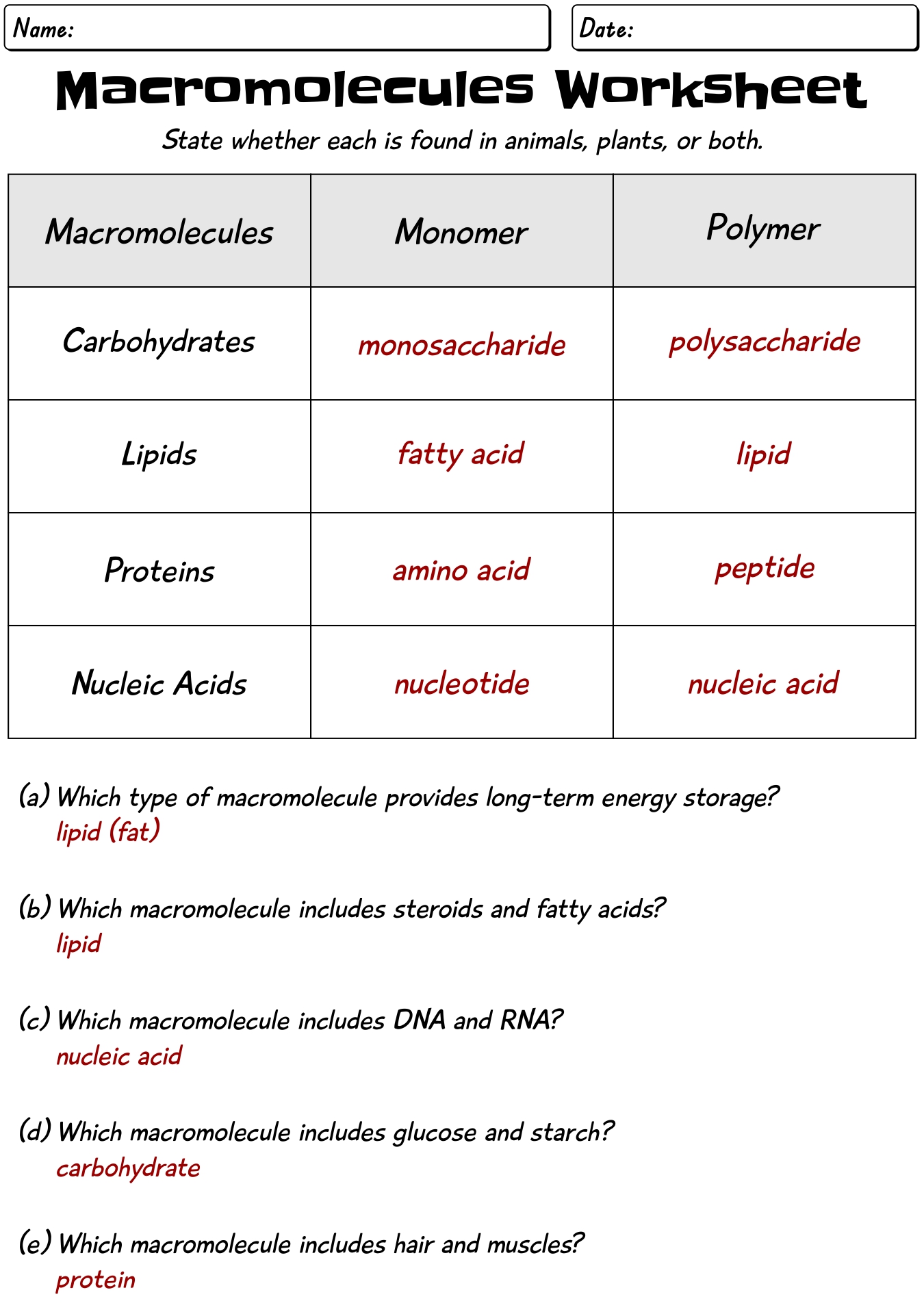
14 Biology Macromolecules Worksheets And Answers /
Browse Videos, Articles, And Exercises By Topic.
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, And Nucleic Acids.
Web There Are Four Main Types Of Macromolecules:
Web A Macromolecule Is A Very Large Molecule Having A Polymeric Chain Structure.
Related Post: