Chart Of Neurotransmitters And Their Functions
Chart Of Neurotransmitters And Their Functions - Neurotransmitters are chemicals that cross synapses to transmit impulses from a neuron to another neuron, glandular cell, or muscle cell. Web key neurotransmitters like glutamate, gaba, glycine, serotonin, dopamine, and acetylcholine are discussed, emphasizing their crucial roles in the nervous system. While neurotransmitters offer many necessary functions, they will align with these three classifications: A lot of nts are taken back into the vesicles for reuse. Web in this guide to neurotransmitters and what they do, you’ll learn about seven vital neurotransmitters and how they impact various functions in your brain, such as learning, memory, mood, and overall cognition. Web are you getting ready to take the ap® psychology exam? The human brain contains an estimated 86 billion neurons. We’ll also look at the receptor proteins that let the target cell “hear” the message. Those billions of brain cells communicate by passing chemical messages at the synapse, the small gap between cells, in a process called neurotransmission. Web a neurotransmitter influences a neuron in one of three ways: Web neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that your body can’t function without. Web there are more than 40 neurotransmitters in the human nervous system; Web written by kayt sukel. Neurotransmitter receptors support the propagation of signals in the human brain. Created by matthew barry jensen. Where does all the nt go? Updated on february 26, 2024. Are we making new vesicles all the time? An excitatory transmitter promotes the generation of an electrical signal called an action potential in the receiving neuron, while an inhibitory transmitter prevents it. Medically reviewed by nicholas r. Are we making new vesicles all the time? While the way that each neurotransmitter works is quite similar, the effects that each has are unique. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that carry, boost, and balance signals between neurons (also known as nerve cells) and target cells throughout the body. Medically reviewed by nicholas r. Web released from synaptic vesicles, neurotransmitters play. Web classification by function. It is also the primary mediator of nervous system plasticity. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers in the body. Web the major types of neurotransmitters include acetylcholine, biogenic amines, and amino acids. Web a neurotransmitter influences a neuron in one of three ways: Web there are a number of neurotransmitters used by the body for different functions, including acetylcholine, glutamate, gaba, glycine, dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Have no fear, because the ultimate ap® psych guide to neurotransmitters is here. Web neurotransmitters are chemical messengers in the nervous system. Synaptic vesicles are constantly emptied, recycled, and refilled. A neurotransmitter is a chemical messenger inside. A lot of nts are taken back into the vesicles for reuse. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that carry, boost, and balance signals between neurons (also known as nerve cells) and target cells throughout the body. The neurotransmitters can also be classified based on function (excitatory or inhibitory) and action (direct or neuromodulatory). Web key neurotransmitters like glutamate, gaba, glycine, serotonin,. Web the major types of neurotransmitters include acetylcholine, biogenic amines, and amino acids. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers in the body. Those billions of brain cells communicate by passing chemical messages at the synapse, the small gap between cells, in a process called neurotransmission. Researchers categorize neurotransmitters by their brain and bodily functions. Want to join the conversation? Are you nervous about keeping all those pesky neurotransmitters straight? Web how they work. It is also the primary mediator of nervous system plasticity. They relay information between individual neurons, and ultimately regulate a. Those billions of brain cells communicate by passing chemical messages at the synapse, the small gap between cells, in a process called neurotransmission. Created by matthew barry jensen. They regulate autonomic responses like breathing and heart rate and psychological functions such as learning, mood, fear, pleasure, and happiness. Are we making new vesicles all the time? Their job is to carry chemical signals (“messages”) from one neuron (nerve cell) to the next target cell. The neurotransmitters can also be classified based on function. Synaptic vesicles are constantly emptied, recycled, and refilled. Updated on march 06, 2019. Web neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that enable communication within the nervous system and between the nervous system and the rest of the body. It is also the primary mediator of nervous system plasticity. Web neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that your body can’t function without. Researchers categorize neurotransmitters by their brain and bodily functions. Those chemical messages are unique molecules called neurotransmitters. Web neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that your body can’t function without. Have no fear, because the ultimate ap® psych guide to neurotransmitters is here. Where does all the nt go? Web this document provides information on key neurotransmitters: Created by matthew barry jensen. Web the major types of neurotransmitters include acetylcholine, biogenic amines, and amino acids. An excitatory transmitter promotes the generation of an electrical signal called an action potential in the receiving neuron, while an inhibitory transmitter prevents it. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers in the body. Neurotransmitter receptors support the propagation of signals in the human brain. The human brain contains an estimated 86 billion neurons. Their job is to carry chemical signals (“messages”) from one neuron (nerve cell) to the next target cell. Web there are more than 40 neurotransmitters in the human nervous system; Want to join the conversation? A lot of nts are taken back into the vesicles for reuse.
Neurotransmitters And Their Functions Chart

Neurotransmitters And Their Functions Chart
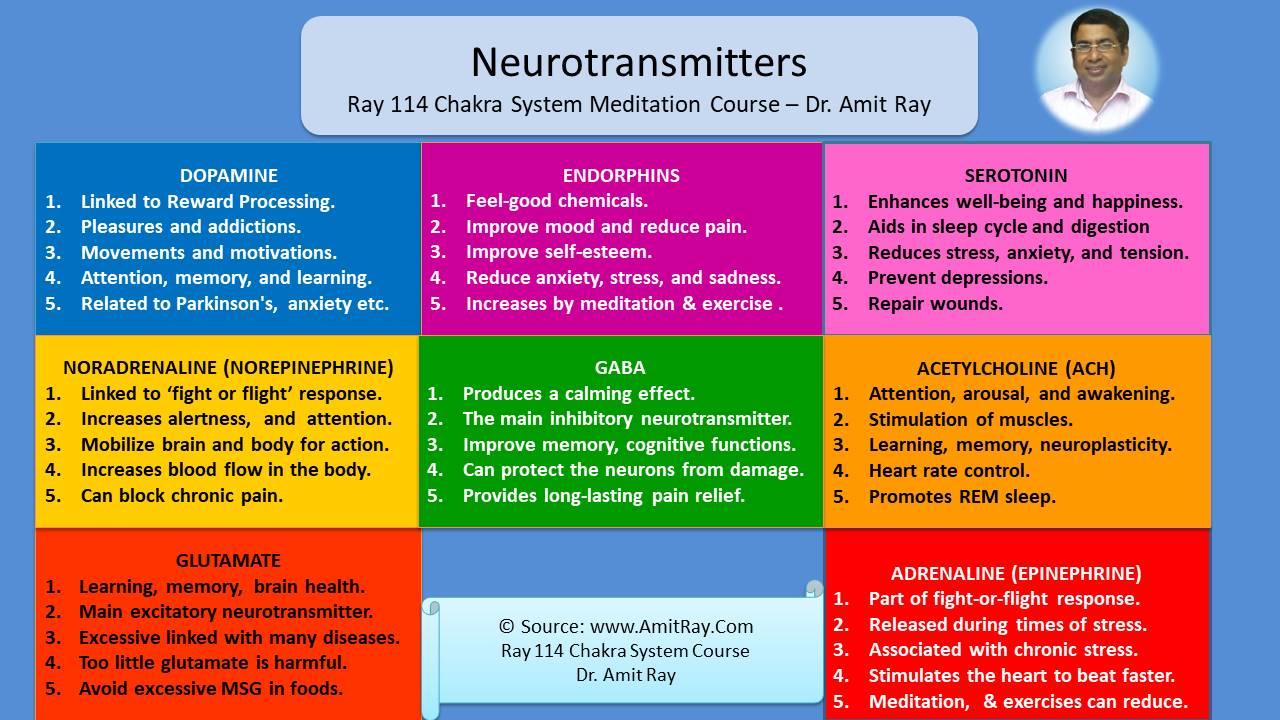
List of Important Neurotransmitters and their Functions Sri Amit Ray
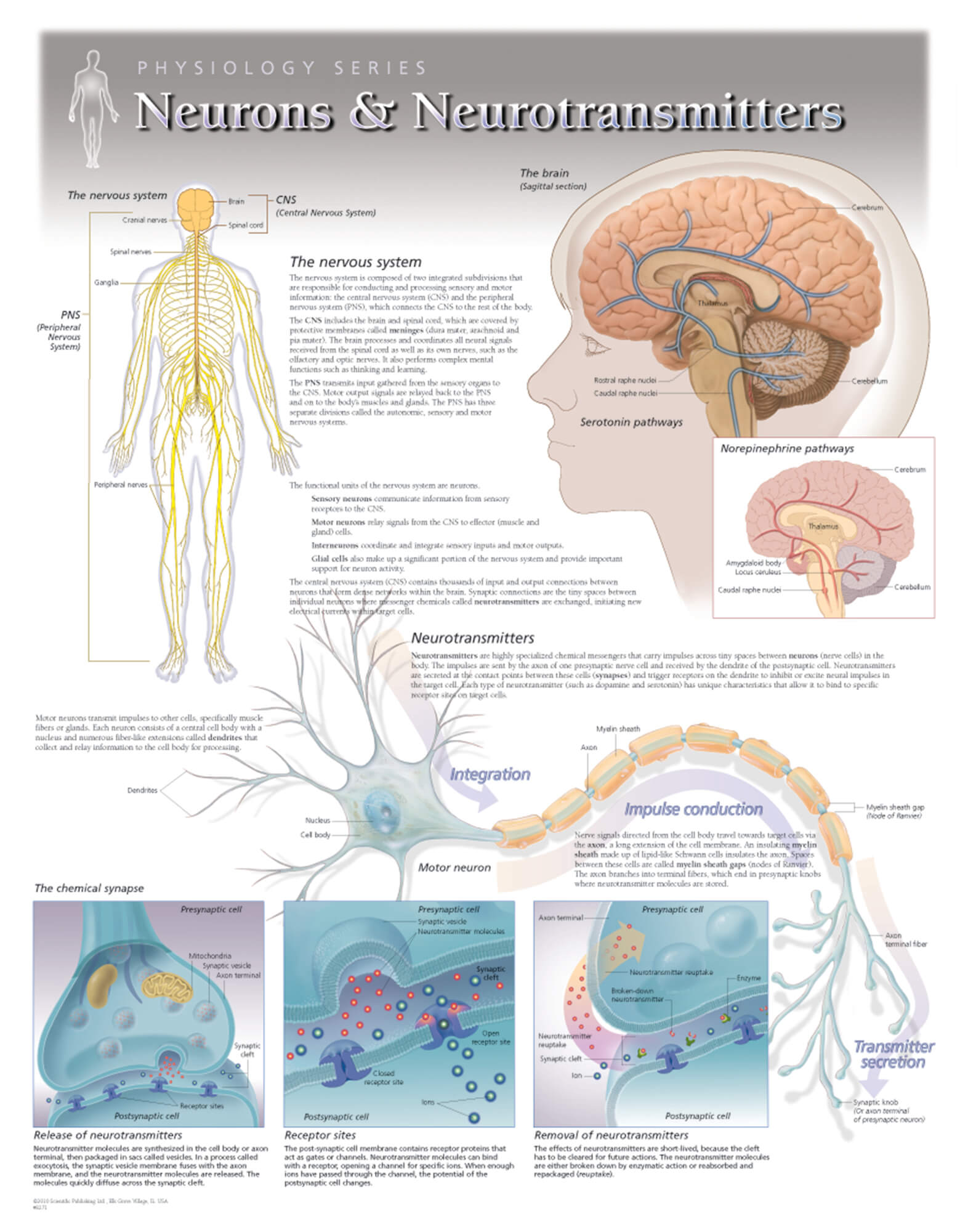
Neurotransmitters And Their Functions Chart

Neurotransmitters And Their Functions Chart

Neurotransmitters And Their Functions Chart
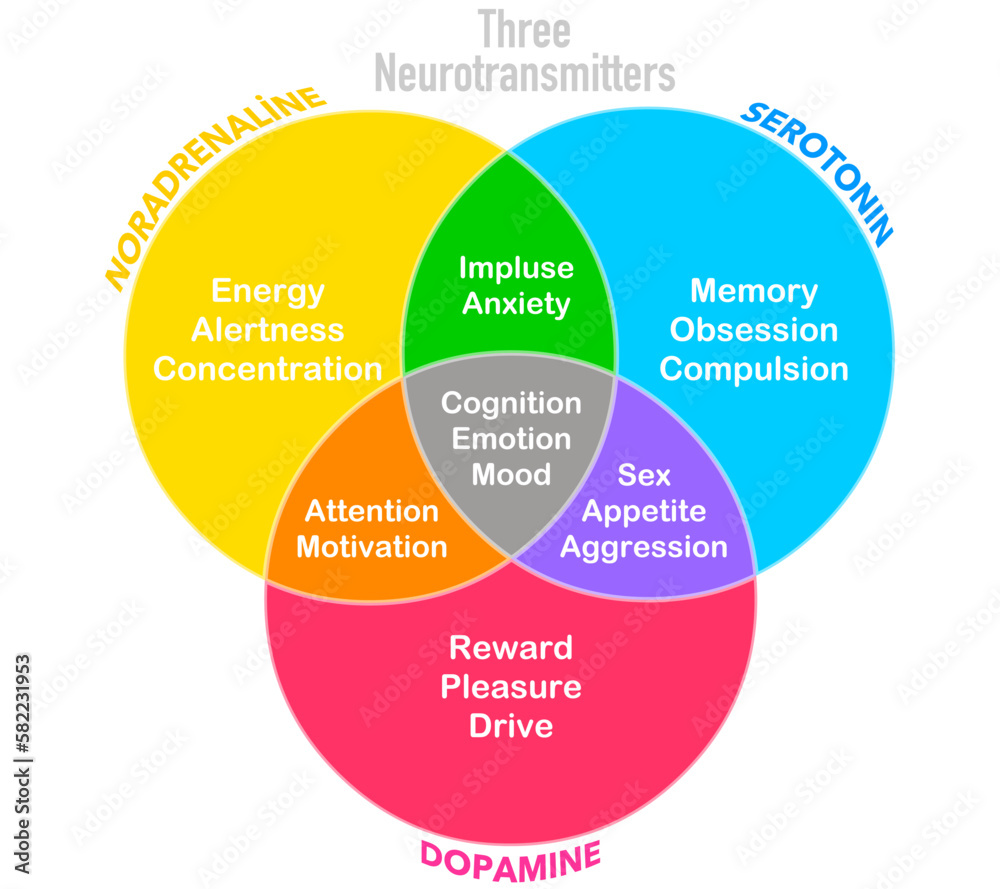
Neurotransmitters And Their Functions Chart
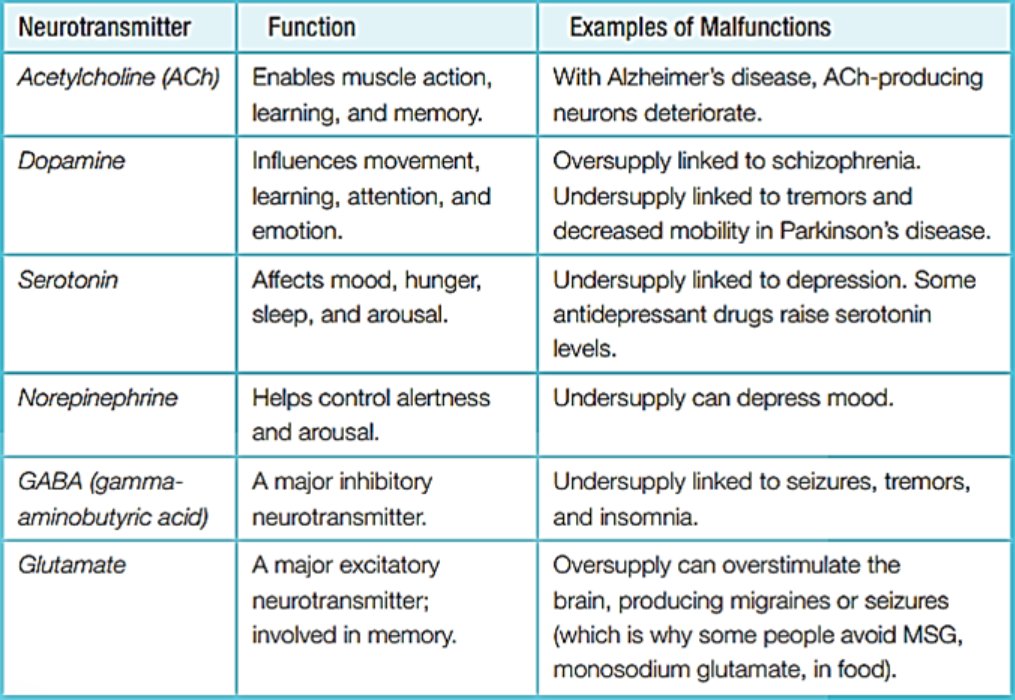
Neurotransmitters And Their Functions Chart

Axon Terminal The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Neurotransmitter Chart Do you know what chemicals are active in your
A Neurotransmitter Is A Chemical Messenger Inside The Body.
While The Way That Each Neurotransmitter Works Is Quite Similar, The Effects That Each Has Are Unique.
Web Key Neurotransmitters Like Glutamate, Gaba, Glycine, Serotonin, Dopamine, And Acetylcholine Are Discussed, Emphasizing Their Crucial Roles In The Nervous System.
In Other Words, Neurotransmitters Are Used To Send Signals From One Part Of The Body To Another.
Related Post: