Chart Of Nitrogen Cycle
Chart Of Nitrogen Cycle - Web the nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical cycle that converts nitrogen into various forms throughout the ecosystem. Web in general, the nitrogen cycle has five steps: By environmental health program december 16, 2011. 2, the nitrogen that enters living systems by nitrogen fixation is eventually converted from organic nitrogen back into nitrogen gas by bacteria. Web there is a long sequence of periodic characteristics of reservoir water storage and discharge in large hydropower stations. What is the nitrogen cycle? The steps of the nitrogen cycle are described below. Nitrogen is an essential element for life that organisms use in the synthesis of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web the nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. It is also essential to life: There’s lots of nitrogen in the atmosphere. Web in addition to n 2 and nh 3, nitrogen exists in many different forms, including both inorganic (e.g., ammonia, nitrate) and organic (e.g., amino and nucleic acids) forms. What is the nitrogen cycle? When organisms die, decomposition will. Nitrogen is an essential element for life that organisms use in the synthesis of. 2, the nitrogen that enters living systems by nitrogen fixation is eventually converted from organic nitrogen back into nitrogen gas by bacteria. This process occurs in three steps in terrestrial systems: Web the nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical cycle that converts nitrogen into various forms throughout the ecosystem. Nitrification is the process by which microorganisms convert ammonium to nitrate to. Web the nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical cycle that converts nitrogen into various forms throughout the ecosystem. Materials such as carbon, nitrogen and water are recycled in the ecosystem. Web from an ecological perspective, the nitrogen cycle consists of the following stages: Web the nitrogen cycle has traditionally been divided into three processes — n 2 fixation, nitrification, and denitrification. Materials such as carbon, nitrogen and water are recycled in the ecosystem. Web the nitrogen cycle has traditionally been divided into three processes — n 2 fixation, nitrification, and denitrification ( figure 2) — and microbes have historically been labeled by their identified participation in one of these processes, that is, ‘nitrogen fixers’, ‘nitrifiers’ and ‘denitrifiers’. Nitrogen, a component of. (ii) nitrification, (iii) nitrogen uptake by plants, advertisements: The nitrogen cycle explains how nitrogen flows between animals, bacteria, plants, the atmosphere, and the soil on earth. This animation of the biogeochemical nitrogen cycle illustrates the main steps of the cycle in air, water, and soils. Web in addition to n 2 and nh 3, nitrogen exists in many different forms,. Nitrogen is an essential element for life that organisms use in the synthesis of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web the nitrogen cycle has traditionally been divided into three processes — n 2 fixation, nitrification, and denitrification ( figure 2) — and microbes have historically been labeled by their identified participation in one of these processes, that is, ‘nitrogen. Plants and animals need nitrogen to make proteins but they cannot take it in from the air. Web there is a long sequence of periodic characteristics of reservoir water storage and discharge in large hydropower stations. Web in addition to n 2 and nh 3, nitrogen exists in many different forms, including both inorganic (e.g., ammonia, nitrate) and organic (e.g.,. This animation of the biogeochemical nitrogen cycle illustrates the main steps of the cycle in air, water, and soils. Web the nitrogen cycle is the cyclic movement of nitrogen in different chemical forms between living organisms and the environment. Web the nitrogen cycle has traditionally been divided into three processes — n 2 fixation, nitrification, and denitrification ( figure 2). (iv) fixation of nitrogen, and. Web the nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The unloaded rock mass formed by blasting and excavation in the reservoir slope of the reservoir fluctuation zone is not only subjected to the penetration erosion caused by the. The unloaded rock mass formed by blasting and excavation in the reservoir slope of the reservoir fluctuation zone is not only subjected to the penetration erosion caused by the change of the water level of the reservoir slope,. Web as shown in figure 20.4.2 20.4. Web the nitrogen cycle has traditionally been divided into three processes — n 2 fixation,. Web the nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical cycle that converts nitrogen into various forms throughout the ecosystem. Nitrogen is an essential element for life that organisms use in the synthesis of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids. When organisms die, decomposition will. A key building block of dna, which determines our genetics, is essential to plant growth, and therefore necessary for the food we grow. Web microbial nitrogen guilds play crucial roles in the oceanic nitrogen cycle, but their composition and importance across specific depths and conditions remain unclear. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Web from an ecological perspective, the nitrogen cycle consists of the following stages: Web the nitrogen cycle is the cyclic movement of nitrogen in different chemical forms between living organisms and the environment. Web in addition to n 2 and nh 3, nitrogen exists in many different forms, including both inorganic (e.g., ammonia, nitrate) and organic (e.g., amino and nucleic acids) forms. Web the nitrogen cycle has traditionally been divided into three processes — n 2 fixation, nitrification, and denitrification ( figure 2) — and microbes have historically been labeled by their identified participation in one of these processes, that is, ‘nitrogen fixers’, ‘nitrifiers’ and ‘denitrifiers’. It involves several processes such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, decay and putrefaction. Web in general, the nitrogen cycle has five steps: Nitrogen, the most abundant element in our atmosphere, is crucial to life. Nitrogen, a component of proteins and nucleic acids , is essential to life on earth. Web nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere. In fact, nitrogen makes up about 78% of the air.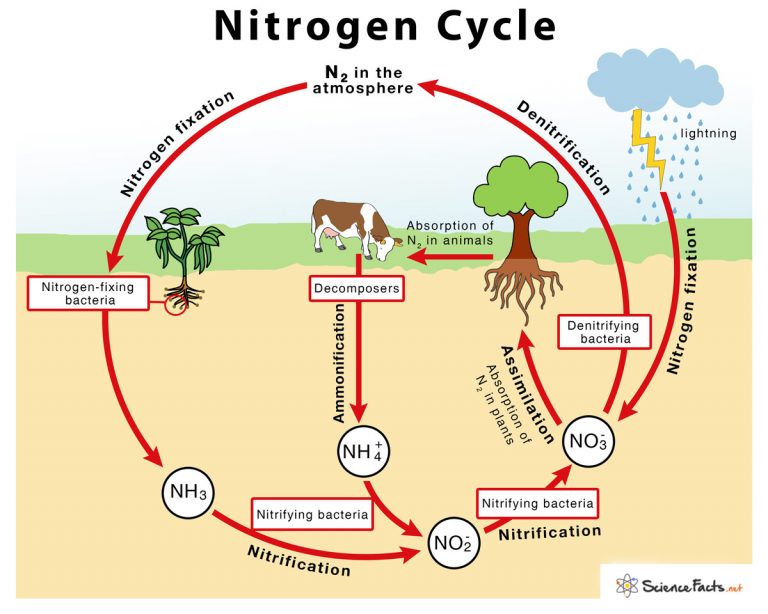
Nitrogen Cycle Definition, Steps, Importance with Diagram
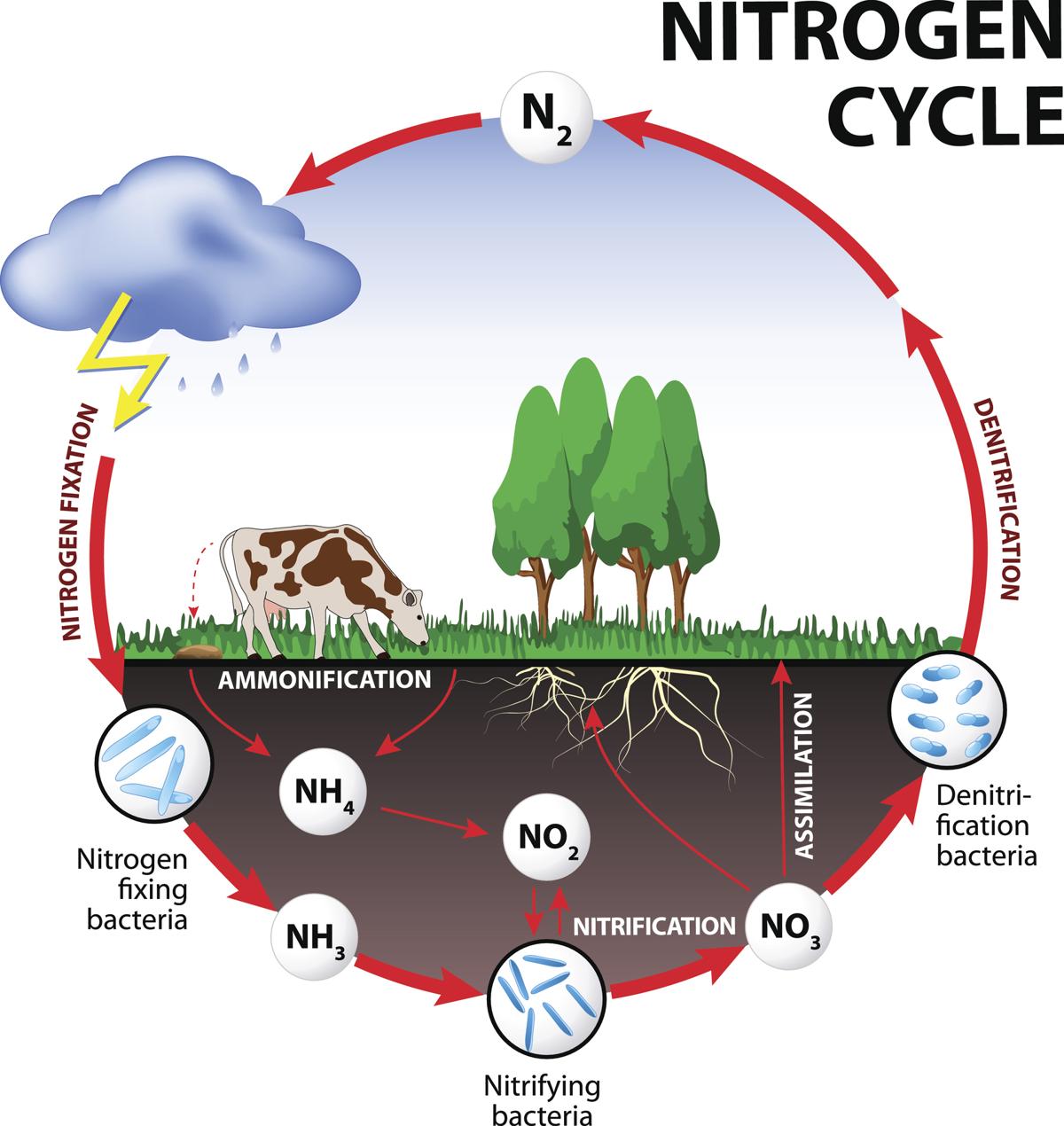
Nitrogen cycle Steps of Nitrogen cycle Online Biology Notes

Diagram of the Nitrogen Cycle U.S. Geological Survey
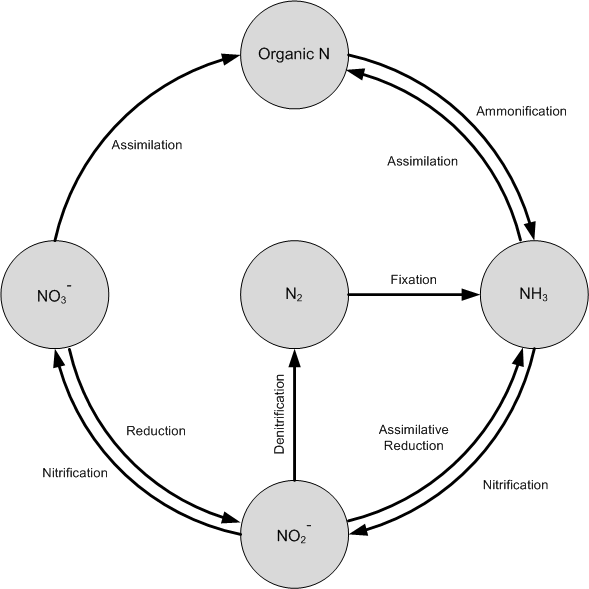
Nitrogen Cycle...

Nitrogen Cycle Diagram with Steps Explained Teachoo Concepts

Understanding the Nitrogen Cycle Beginners Education AlgaeBarn

What is the Nitrogen Cycle? Science for Kids

Nitrogen Cycle Process Steps With Diagrams Explained
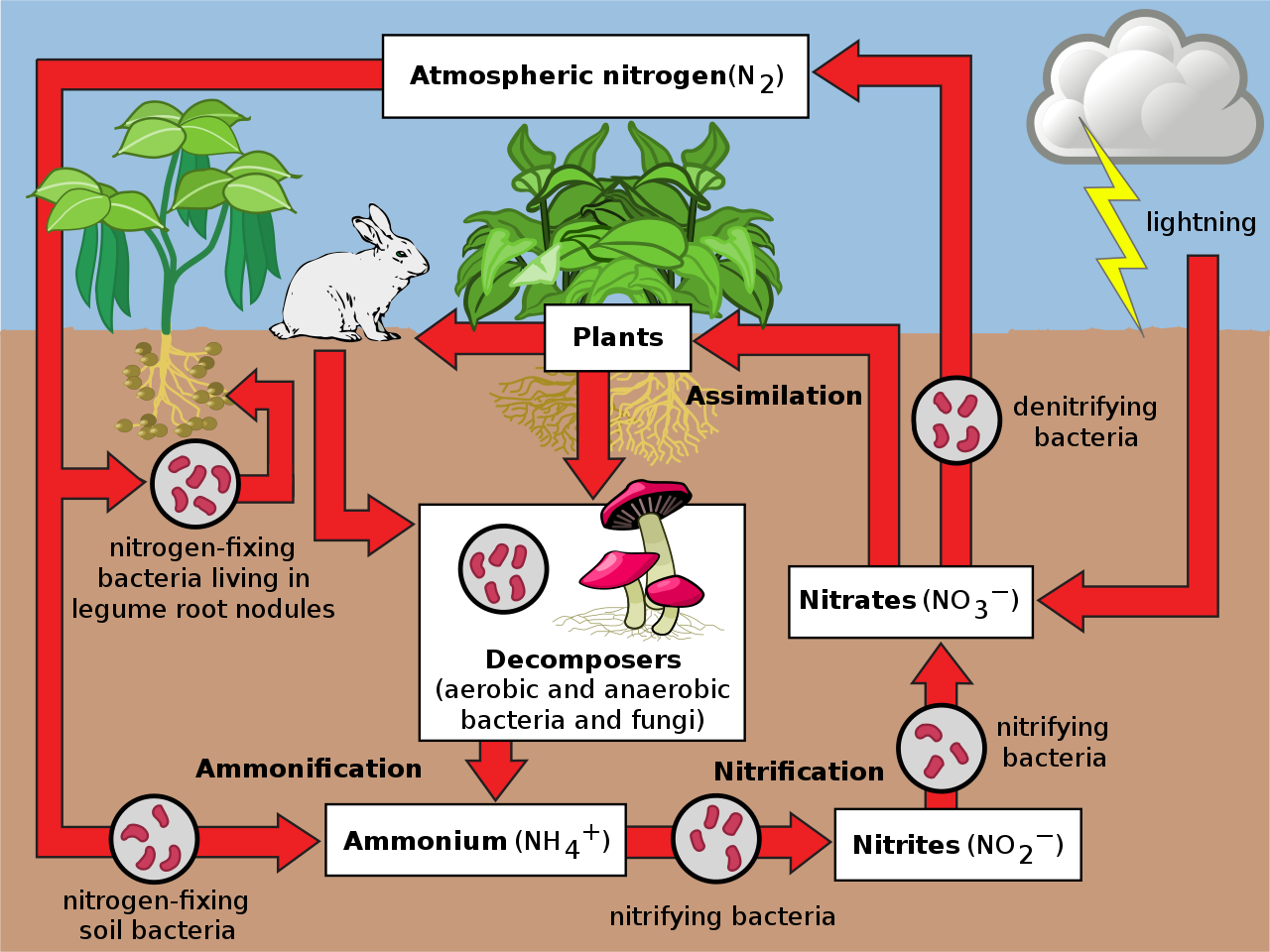
What is Nitrogen Cycle? Diagram, Stages, Importance Tutoroot
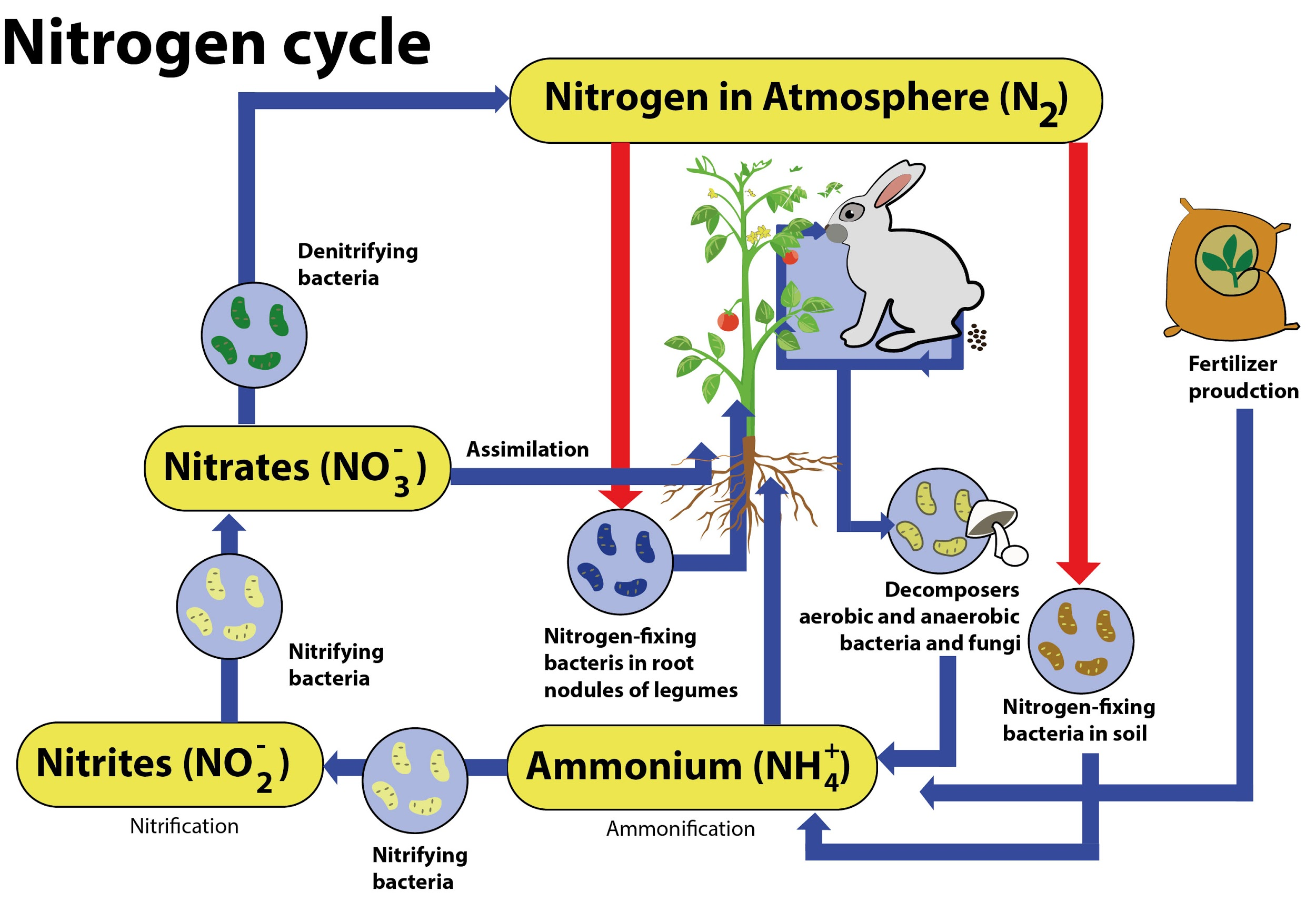
Describe the nitrogen cycle with the help of a diagram.
Through The Cycle, Atmospheric Nitrogen Is Converted To A Form Which Plants Can Incorporate Into New Proteins.
Web This Interactive Activity Adapted From The University Of Alberta Illustrates How, Through A Process Called Fixation, Nitrogen Flows From The Atmosphere, Into The Soil, Through Various Organisms, And Back To The Atmosphere In A Continuous Cycle.
Bacteria Involved In The Nitrogen.
Explain The Nitrogen Cycle With The Help Of A Diagram.
Related Post: