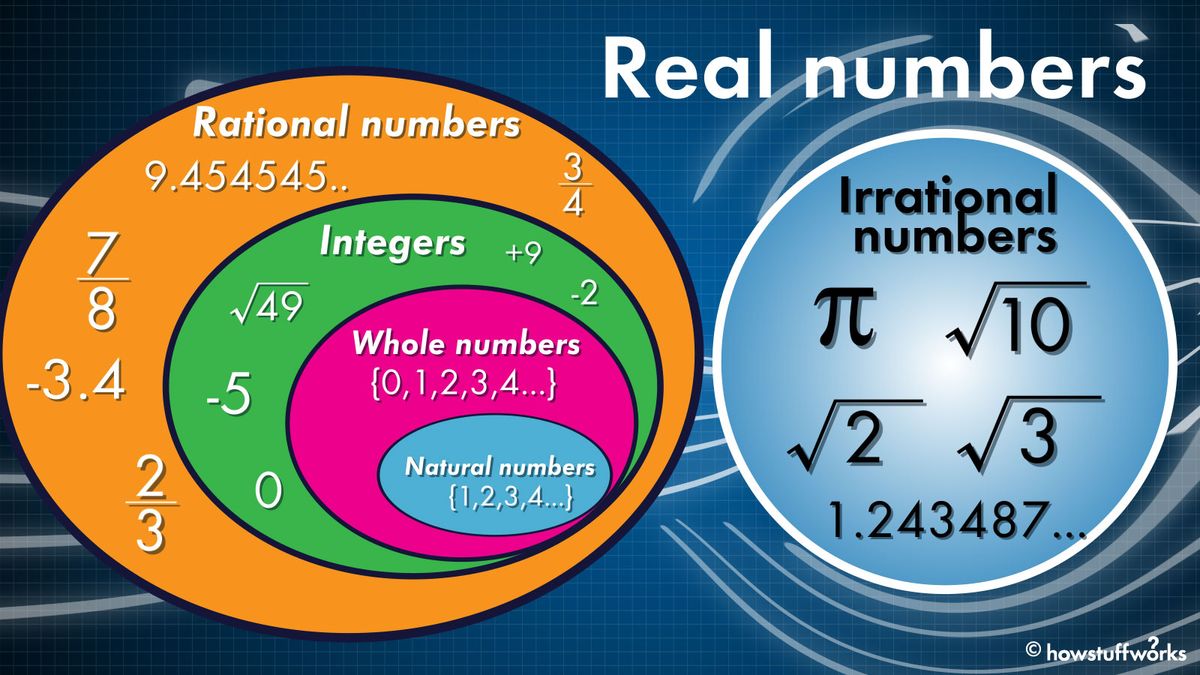
Chart Of Rational And Irrational Numbers
Chart Of Rational And Irrational Numbers - Rational numbers can be written as fractions and ratios. Sums and products of irrational numbers. A rational number, in mathematics, can be defined as any number which can be represented in the form of p/q where q ≠ 0. The real numbers include natural numbers or counting numbers , whole numbers, integers, rational numbers (fractions and repeating or terminating decimals), and irrational numbers. Explain how the sets of numbers (counting, whole, integer, rational, irrationals, reals) are related to each other. Web the key difference between rational and irrational numbers is, the rational number is expressed in the form of p/q whereas it is not possible for irrational number (though both are real numbers ). Irrational numbers are numbers with decimal representations that do not terminate or contain a repeating block of digits. We cannot write irrational numbers, such as the square root of 8 and pi, in this way. A few examples of irrational numbers are π , 2 ,. Learn other forms, such as decimals, in which these types of numbers can appear. Sum of rational & irrational is irrational. In this article, we are going to discuss the differences between rational and irrational numbers. Web in your own words, explain the difference between a rational number and an irrational number. Level up on the above skills and collect up to 720 mastery points. Web so, what are rational and irrational numbers? Web many people are surprised to know that a repeating decimal is a rational number. For every rational number, we can write them in the form of p/q, where p and q are integer values. A few examples of irrational numbers are π , 2 ,. Irrational numbers are numbers with decimal representations that do not terminate or contain a. Web rational numbers are the numbers which are integers and fractions. Did you know that there's always an irrational number between any two rational numbers? Definition of rational and irrational numbers. If the decimal form of a number. Irrational numbers are numbers with decimal representations that do not terminate or contain a repeating block of digits. Does not stop and does not repeat, the number is irrational. A rational number is a number that can be expressed as a ratio that takes the form: We cannot write irrational numbers, such as the square root of 8 and pi, in this way. The set of rational numbers is denoted by \(\mathbb{q}\). Identifying rational and irrational numbers math. Rational numbers can be written as fractions and ratios. For every rational number, we can write them in the form of p/q, where p and q are integer values. The most common rational numbers are positive and negative integers. Product of rational & irrational is irrational. Intro to rational & irrational numbers. If a rational number is still in the form p/q it can be a little difficult to use, so i have a special page on how to: Web let's summarize a method we can use to determine whether a number is rational or irrational. A rational number is a number that can be expressed as a ratio that takes the. A few examples of irrational numbers are π , 2 ,. Where q is not zero. If a rational number is still in the form p/q it can be a little difficult to use, so i have a special page on how to: Irrational numbers cannot be written as a ratio. Web difference from irrational numbers. Web many people are surprised to know that a repeating decimal is a rational number. Sum of rational & irrational is irrational. The venn diagram below shows examples of all the different types of rational, irrational numbers including integers, whole numbers, repeating decimals and more. For every rational number, we can write them in the form of p/q, where p. Web let's summarize a method we can use to determine whether a number is rational or irrational. A few examples of irrational numbers are π , 2 ,. Product of rational & irrational is irrational. Does not stop and does not repeat, the number is irrational. Web determine if the number is rational (r) or irrational (i). The most common irrational number used in math is pi. Rational numbers can be written as fractions and ratios. We can write any rational number as the ratio of two integers. Sum of rational & irrational is irrational. We cannot write irrational numbers, such as the square root of 8 and pi, in this way. Irrational numbers cannot be written as a ratio. Otherwise it is called an irrational number. In this article, we are going to discuss the differences between rational and irrational numbers. Definition of rational and irrational numbers. The most common rational numbers are positive and negative integers. Intro to rational & irrational numbers. The real numbers include natural numbers or counting numbers , whole numbers, integers, rational numbers (fractions and repeating or terminating decimals), and irrational numbers. A rational number, in mathematics, can be defined as any number which can be represented in the form of p/q where q ≠ 0. We can write any rational number as the ratio of two integers. Does not stop and does not repeat, the number is irrational. Web learn the difference between rational and irrational numbers, learn how to identify them, and discover why some of the most famous numbers in mathematics, like pi and e, are actually irrational. Irrational numbers are numbers with decimal representations that do not terminate or contain a repeating block of digits. A few examples of irrational numbers are π , 2 ,. On the other end, irrational numbers are the numbers whose expression as a fraction is not possible. Did you know that there's always an irrational number between any two rational numbers? The set of rational numbers is denoted by \(\mathbb{q}\).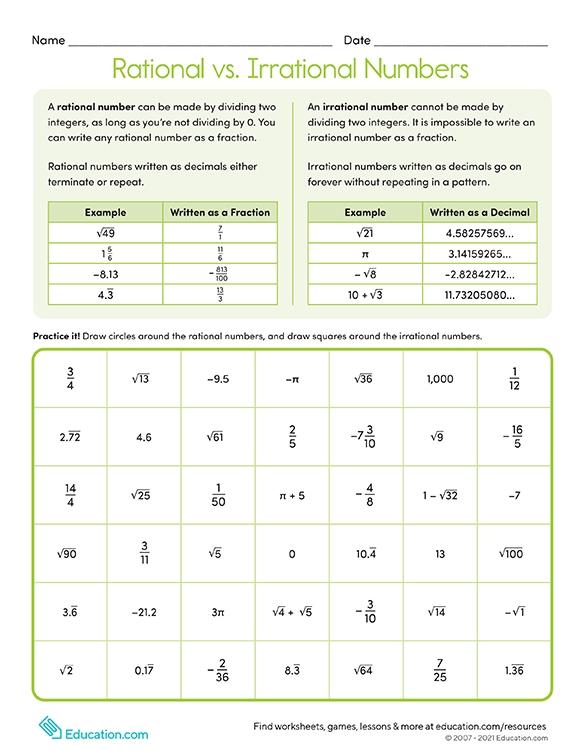
Printables Rational vs. Irrational Numbers HP® United Kingdom
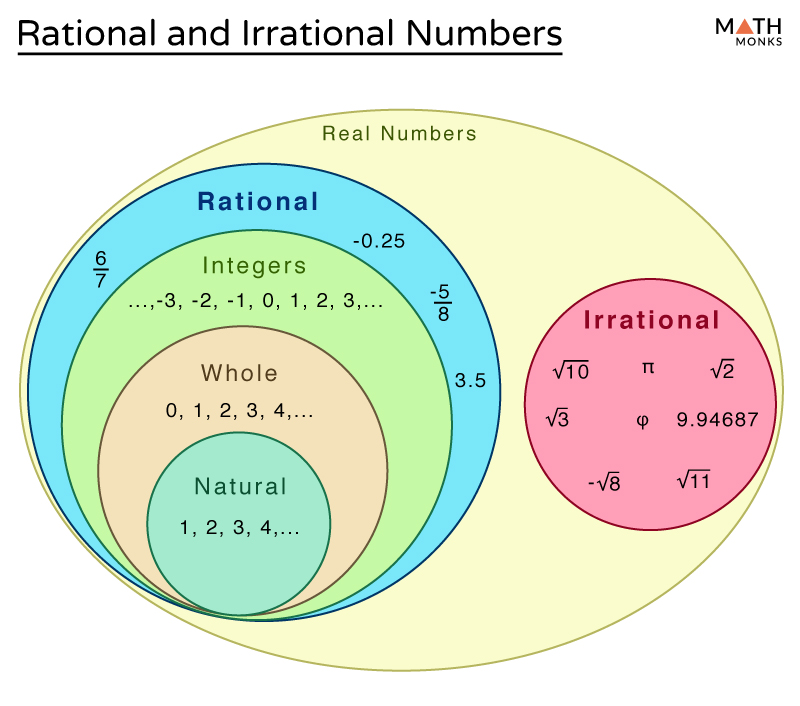
Rational and Irrational Numbers Differences & Examples

Rational vs. Irrational Numbers 4 Key Differences, Definition

Rational Irrational Numbers Chart
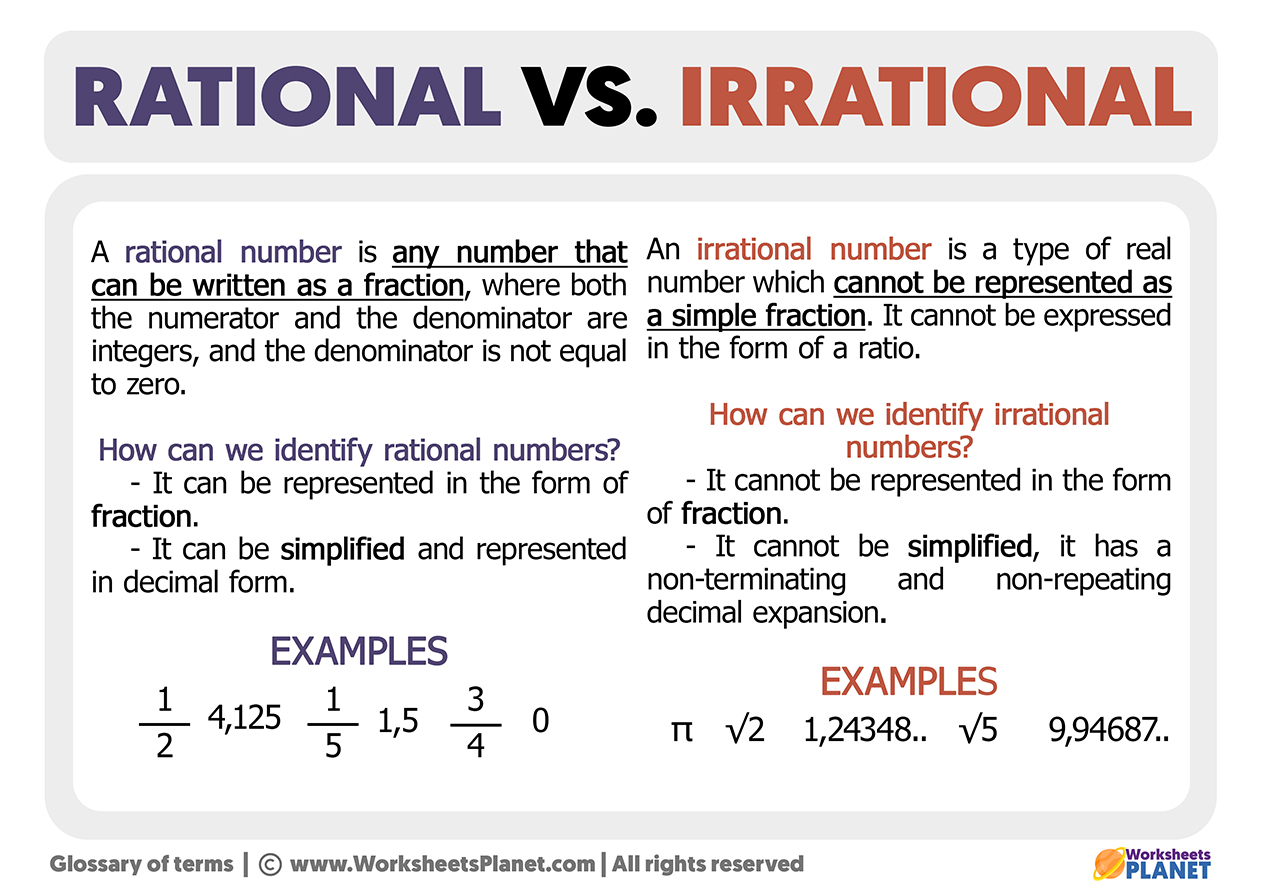
Rational And Irrational Numbers
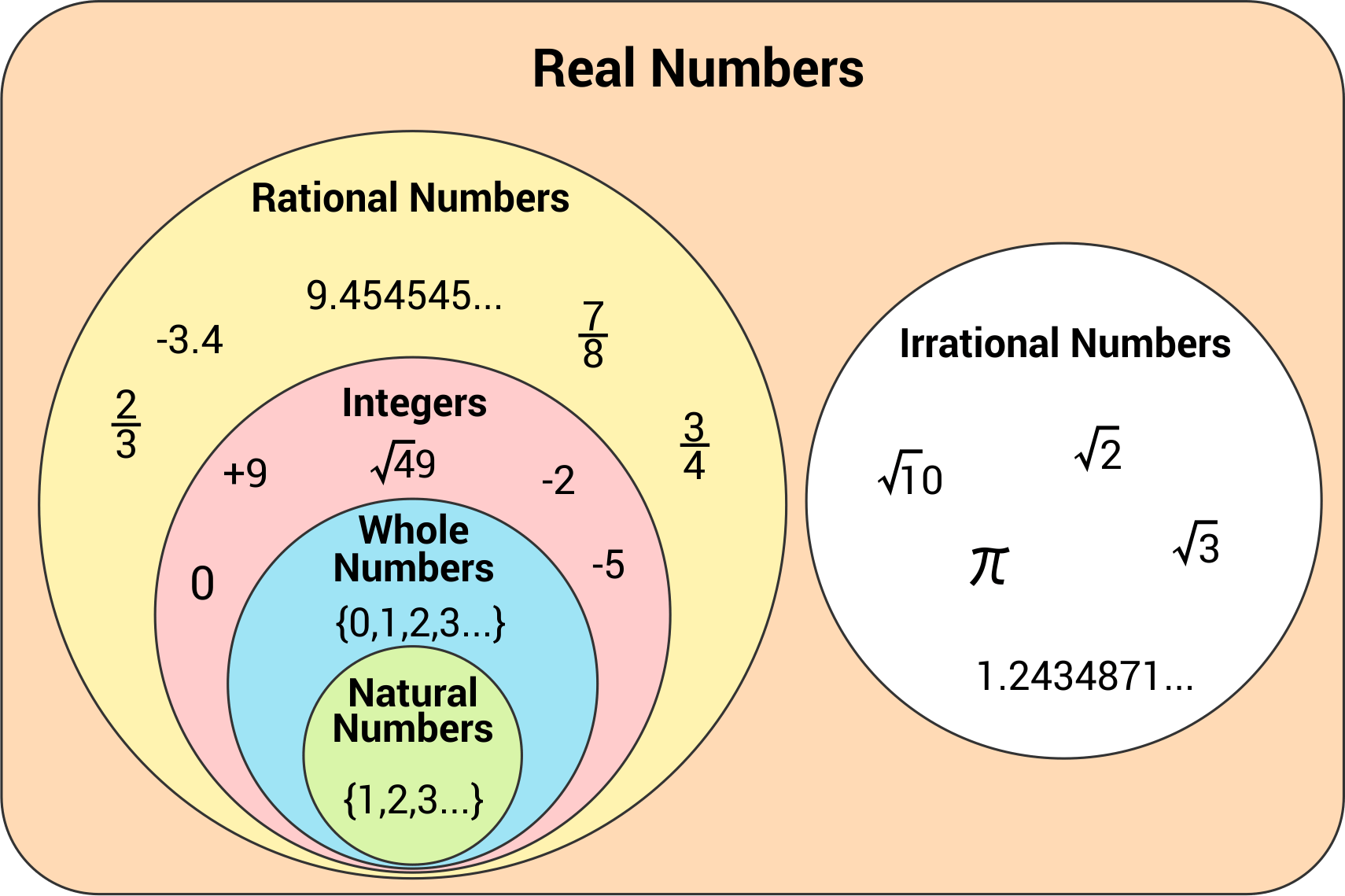
Rational And Irrational Numbers Examples
What's the Difference Between Rational and Irrational Numbers? Flipboard
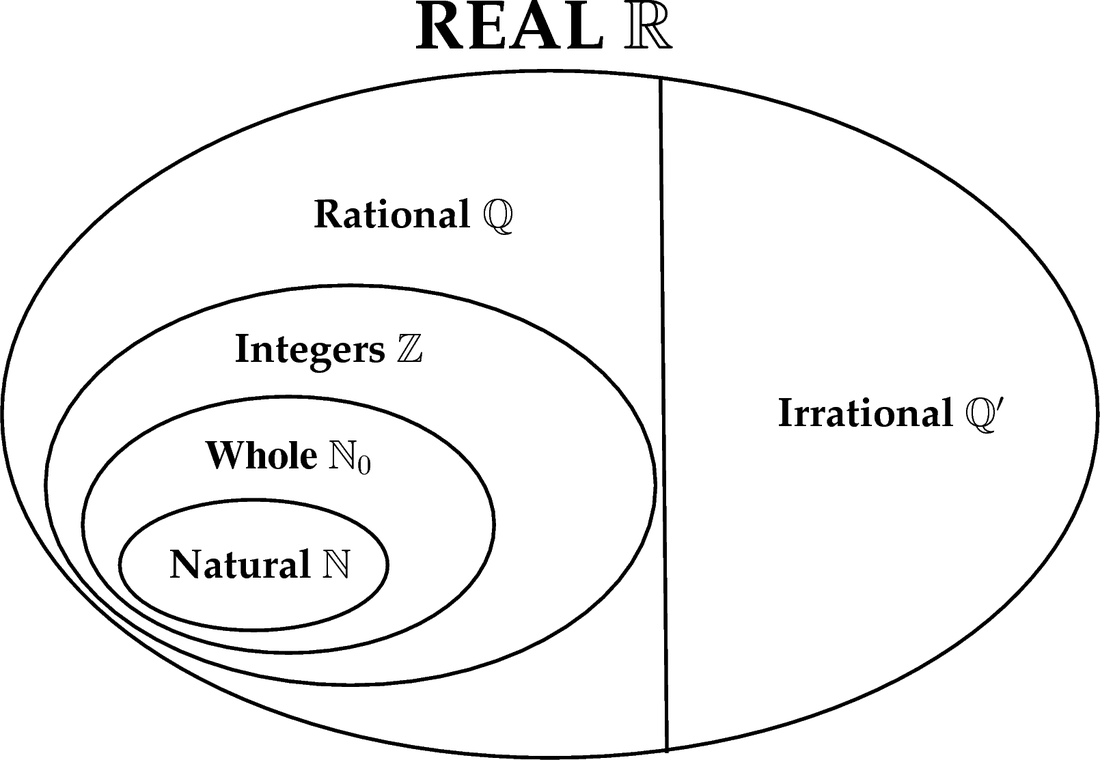
Rational Numbers Lefere Math

Real Numbers System Card Sort (Rational, Irrational, Integers, Whole
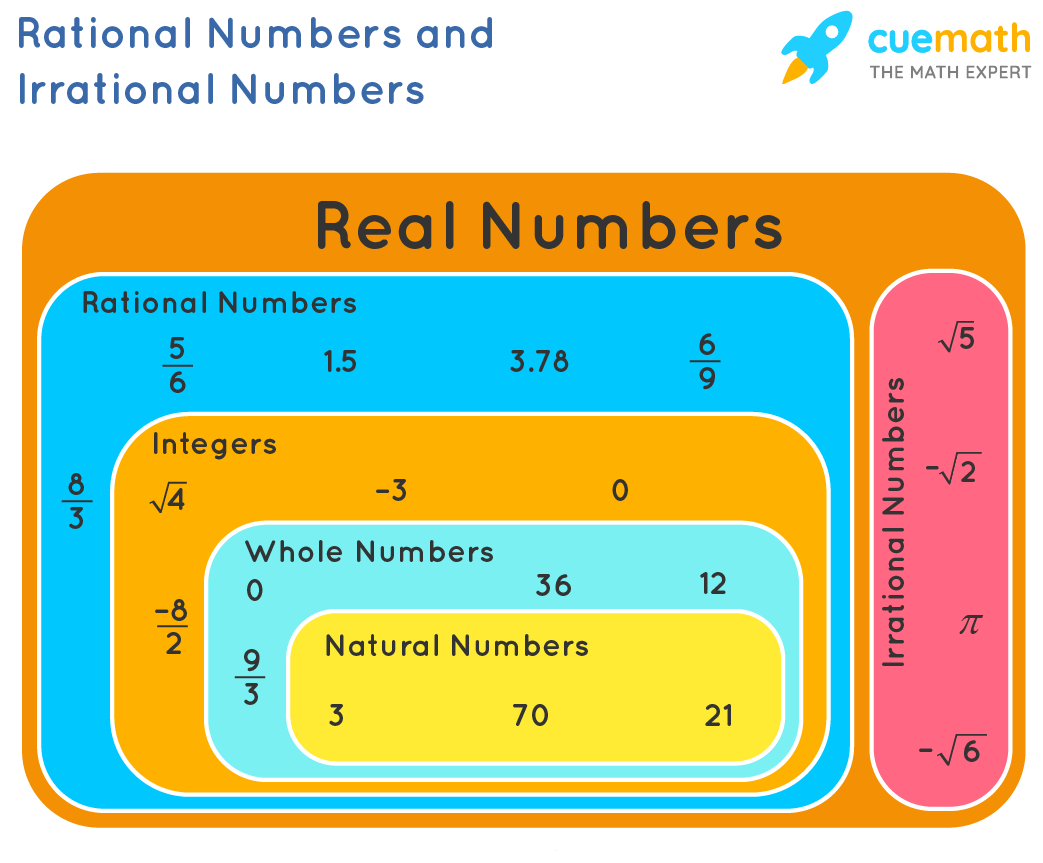
Is 3 8 a Rational Number
Learn The Definitions, More Differences And Examples Based On Them.
Sum Of Rational & Irrational Is Irrational.
Where Q Is Not Zero.
Learn For Free About Math, Art, Computer Programming, Economics, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Medicine, Finance, History, And More.
Related Post: