Control Charts For Attributes
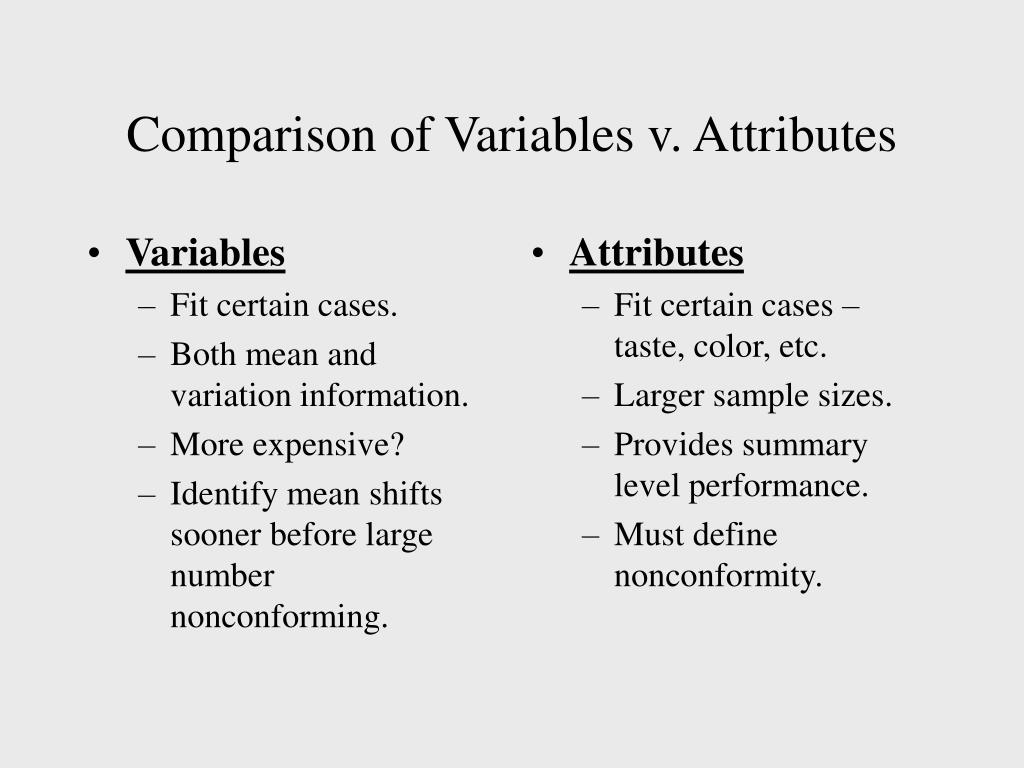
Control Charts For Attributes - Web control charts are simple, robust tools for understanding process variability. Web this chapter examines control charts for attributes and presents various types of control charts for attributes. The importance of measurement uncertainty analysis on statistical quality control. The shewhart control chart plots quality characteristics that can be measured and expressed numerically. 1) the ideal, 2) the threshold, 3) the brink of chaos and 4) the state of chaos (figure 1). Decide on which control charts for attributes to use in a given situation; These types of defects are binary in nature (yes/no), where a part has one or more defects, or it doesn’t. Processes fall into one of four states: Points on a chart that indicate only random or chance variation are the result of common causes and do not indicate the need for corrective action. Web the chapter explores four types of control charts for attributes: A control chart always has a central line for the average, an upper line for the upper control limit, and the lower line for the lower control limit. A control chart for attributes can provide overall quality information at a. Web control charts are used in the control phase of the dmaic (define, measure, analyze, improve, and control) process. To. Processes fall into one of four states: A control chart for attributes can provide overall quality information at a. The p control chart, np control chart, c control chart, and u control chart. Web 7 control charts for attributes. Web the chapter explores four types of control charts for attributes: 2 the p chart, fraction nonconforming or number nonconforming for a collection of items (more than one item), using binomial model. Web a control chart is a graphic presentation depicting whether a sample of data falls within the common or normal range of variation. A control chart for attributes can provide overall quality information at a. Similar content being viewed. Attribute charts monitor the process location and variation over time in a single chart. Web this month’s publication reviewed the four basic attribute control charts: Web this document provides an introduction to control charts for attributes. Similar content being viewed by others. Web this chapter analyzes control charts for variables and control charts for attributes. 1) the ideal, 2) the threshold, 3) the brink of chaos and 4) the state of chaos (figure 1). To help johnny figure out which one to make, let's look at all four. The chart doesn’t tell you why the defects happened, but it does give you the total or average counts per unit. Web control charts are simple, robust. Decide on which control charts for attributes to use in a given situation; Web to monitor the manufacturing process of laptops, a quality control engineer randomly selects a number of laptops from the production line, each day over. Points on a chart that indicate only random or chance variation are the result of common causes and do not indicate the. Points on a chart that indicate only random or chance variation are the result of common causes and do not indicate the need for corrective action. The chart doesn’t tell you why the defects happened, but it does give you the total or average counts per unit. The control limits are ±3σ from the centerline. Web the goal in reading. These limits let you know when unusual variability occurs. We measure weight, height, position, thickness, etc. Similar content being viewed by others. The equations for the average and control limits were given as well as the underlying assumptions for each type of control chart. The p control chart, np control chart, c control chart, and u control chart. The p control chart, np control chart, c control chart, and u control chart. Web this month’s publication reviewed the four basic attribute control charts: 1) the ideal, 2) the threshold, 3) the brink of chaos and 4) the state of chaos (figure 1). Processes fall into one of four states: The importance of measurement uncertainty analysis on statistical quality. The family of attribute charts include the: A process can be called stable or under statistical control if it has only one average and one standard. The charts help us track process statistics over time and help us understand the causes of the variation. Web the goal in reading a control chart for attributes is to define which points represent. Web this chapter examines control charts for attributes and presents various types of control charts for attributes. 1) the ideal, 2) the threshold, 3) the brink of chaos and 4) the state of chaos (figure 1). Attributes data arise when classifying or counting observations. Web a control chart displays process data by time, along with upper and lower control limits that delineate the expected range of variation for the process. The chart doesn’t tell you why the defects happened, but it does give you the total or average counts per unit. Total number of nonconformities per unit. To help johnny figure out which one to make, let's look at all four. The equations for the average and control limits were given as well as the underlying assumptions for each type of control chart. Attribute charts monitor the process location and variation over time in a single chart. 2 the p chart, fraction nonconforming or number nonconforming for a collection of items (more than one item), using binomial model. Similar content being viewed by others. Web the chapter explores four types of control charts for attributes: Web the control chart is a graph used to study how a process changes over time. Statistical formulas use historical records or sample data to calculate the control limits. Web control charts are used in the control phase of the dmaic (define, measure, analyze, improve, and control) process. We measure weight, height, position, thickness, etc.
Control charts for attributes

Types of Attribute Control Charts The P Chart VS C Chart

Control Chart for Attributes 1 Control Charts Continuous
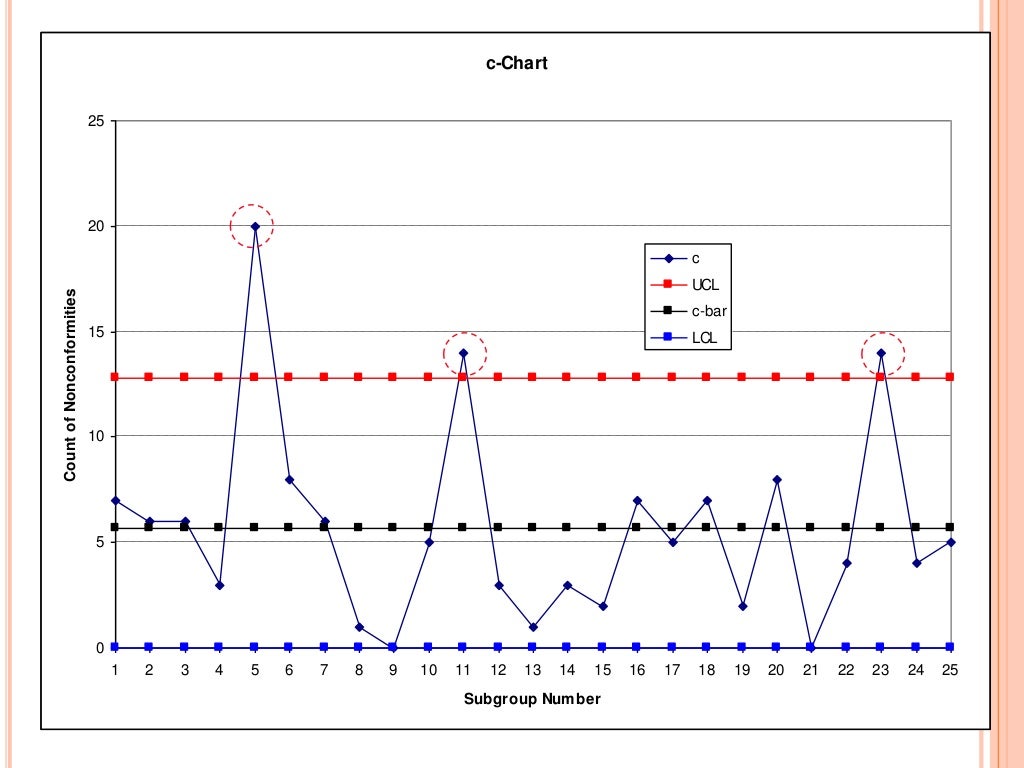
Control charts for attributes

Types Of Attribute Control Charts A Visual Reference of Charts Chart
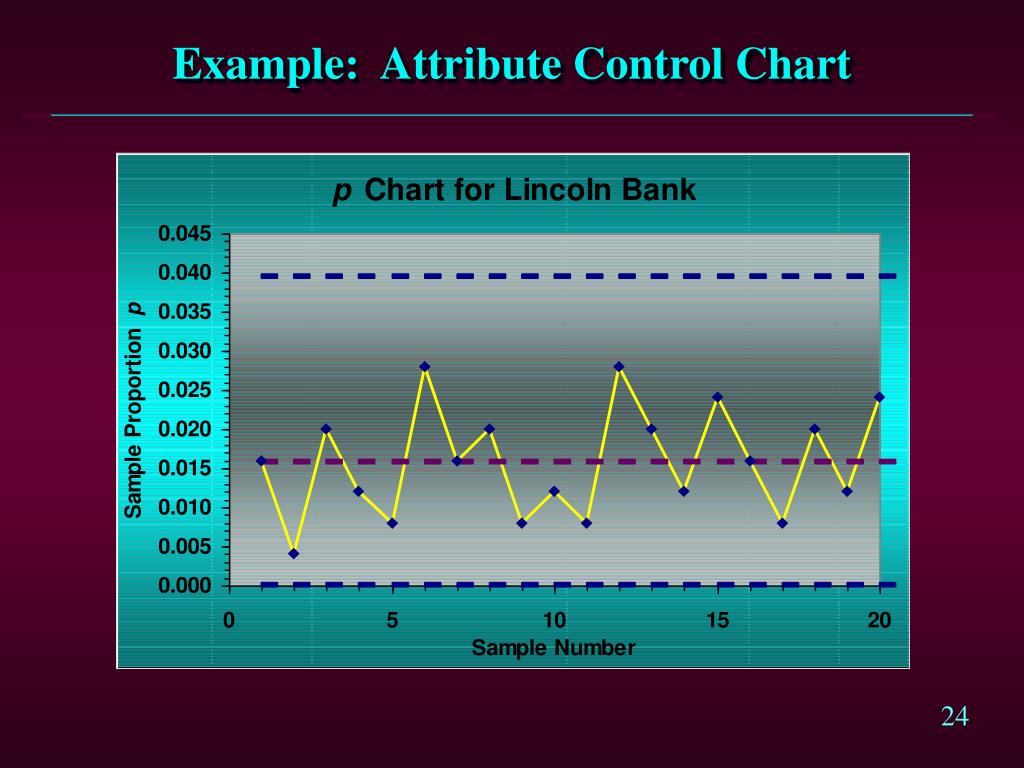
PPT Chapter 17 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3422491

Control Chart for Attributes 1 Control Charts Continuous
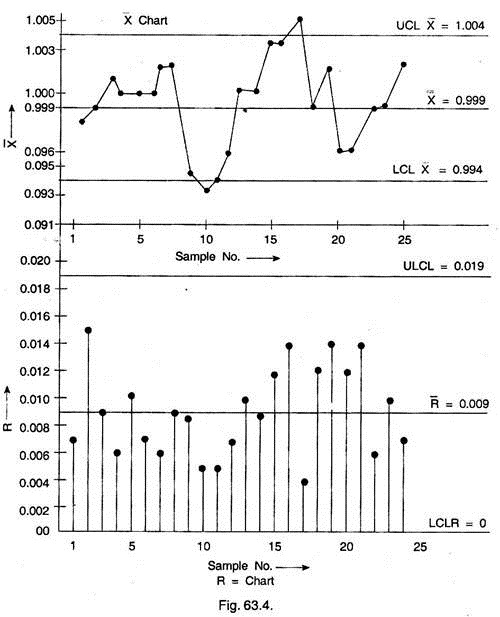
Control Charts for Variables and Attributes Quality Control
PPT Ch 12 Control Charts for Attributes PowerPoint Presentation

PPT SPC PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6115362
Examples Are The Proportion Of Broken Cookies In A Batch And The Proportion Of Cars Produced With A Misaligned Fender.
Web This Month’s Publication Reviewed The Four Basic Attribute Control Charts:
Points On A Chart That Indicate Only Random Or Chance Variation Are The Result Of Common Causes And Do Not Indicate The Need For Corrective Action.
Web This Document Provides An Introduction To Control Charts For Attributes.
Related Post: