Corn Hail Damage Chart
Corn Hail Damage Chart - Look for color other than a healthy cream or light yellow. The first step after hail damages corn or soybeans is to determine how much yield potential you have left. Web corn harvested as silage must be appraised as grain prior to harvest. Estimate yields accordingly, or use the chart below. Distribution of the plant stand. Yield potential of the existing crop. Nebraska extension experts offer tips and tricks in assessing hail damage. (3) unless allowed in the. Web corn crop damage and replant options. Seed availability of earlier maturing hybrids. Web for direct damage occurring through the tasseled growth stage, plants must be applied to the applicable corn stand reduction chart if they are cut off below the growing point, dead or damaged to the extent where they will not compete appreciably for nutrients, light and water. Web corn crop damage and replant options. The seven factors for evaluating whether. Web for direct damage occurring through the tasseled growth stage, plants must be applied to the applicable corn stand reduction chart if they are cut off below the growing point, dead or damaged to the extent where they will not compete appreciably for nutrients, light and water. At emergence, the plant's growing point. The first step after hail damages corn. 80% stand = 80% potential) and are in addition to losses shown in the defoliation chart. Web production loss estimates in corn from hail damage is a critical first step for determining the need to replant or to make adjustments on future inputs. Hail reduced this cornfield to stumps. The first step in assessing yield loss due to defoliation is. Estimate yields accordingly, or use the chart below. Web complete defoliation of v4 corn caused yield loss of 1.1% to 25.9% and were primary attributed to reduced ear size as a result of reduce leaf area and, to a lesser extent, a small change in plant population (johnson 1978). The seven factors for evaluating whether to replant: To assess whether. Web for direct damage occurring through the tasseled growth stage, plants must be applied to the applicable corn stand reduction chart if they are cut off below the growing point, dead or damaged to the extent where they will not compete appreciably for nutrients, light and water. Web hail affects corn yields in three ways: According to hail industry tables,. The seven factors for evaluating whether to replant: Web hail and wind damage to minnesota corn: Nebraska extension experts offer tips and tricks in assessing hail damage. Review guidelines to help assess losses. At emergence, the plant's growing point. Hail reduced this cornfield to stumps. Nebraska extension experts offer tips and tricks in assessing hail damage. Web yield loss in corn due to hail damage results primarily from 1) stand reduction caused by plant death and 2) leaf area reduction caused by hail damage to the leaves. Web making decisions on what to do with a damaged corn crop. Nebraska extension experts offer tips and tricks in assessing hail damage. Failure to give notice so the aip can appraise the acreage before harvesting the acreage for silage will result in a declaration that such acreage is destroyed without The first step in assessing yield loss due to defoliation is to establish the stage of plant growth at the time. According to hail industry tables, complete leaf loss at r2 results in 73 percent yield loss (see table). Seed availability of earlier maturing hybrids. Assessing the yield consequences of hail damage in corn therefore requires that the severity of each of these factors be estimated. 80% stand = 80% potential) and are in addition to losses shown in the defoliation. Distribution of the plant stand. Learn how to protect your corn plants from hail damage and how it will impact your yields. At emergence, the plant's growing point. Yield potential of the existing crop. Any crop damage will reduce the plant’s ability to compete with weeds, but the greatest losses are caused by defoliation, especially during the pollination growth stage. Web 4 min read. Web in this publication, we will examine how hail damages the corn plant, how the degree of damage can be determined and how the extent of yield loss is estimated. Web yield loss in corn due to hail damage results primarily from 1) stand reduction caused by plant death and 2) leaf area reduction caused by hail damage to the leaves. 80% stand = 80% potential) and are in addition to losses shown in the defoliation chart. Distribution of the plant stand. Web hail and wind damage to minnesota corn: Failure to give notice so the aip can appraise the acreage before harvesting the acreage for silage will result in a declaration that such acreage is destroyed without (3) unless allowed in the. Hail reduced this cornfield to stumps. Assessing damage, estimating yield loss, replanting considerations and caring for damaged fields. Assessing the yield consequences of hail damage in corn therefore requires that the severity of each of these factors be estimated. The first step after hail damages corn or soybeans is to determine how much yield potential you have left. Nebraska extension experts offer tips and tricks in assessing hail damage. Web most corn in the affected area was in the blister stage (r2). Review guidelines to help assess losses. Look for color other than a healthy cream or light yellow.
Hail Damage Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master

Hail Damaged Corn PlantDOC

MidSeason Hail Damage Assessments in Corn and Soybeans CropWatch

Hail Damage to Corn PlantDOC
Corn Hail Decision Guide Pioneer® Seeds

How to Spot Hail Damage Middle Creek Roofing Roofing Blog

Corn Hail Damage Chart
Hail Corn Agronomy Sunflower District

Hail Damage Threshold Assessment McAllen Valley Roofing Co.

Corn Hail Decision Guide Pioneer® Seeds
Learn How To Protect Your Corn Plants From Hail Damage And How It Will Impact Your Yields.
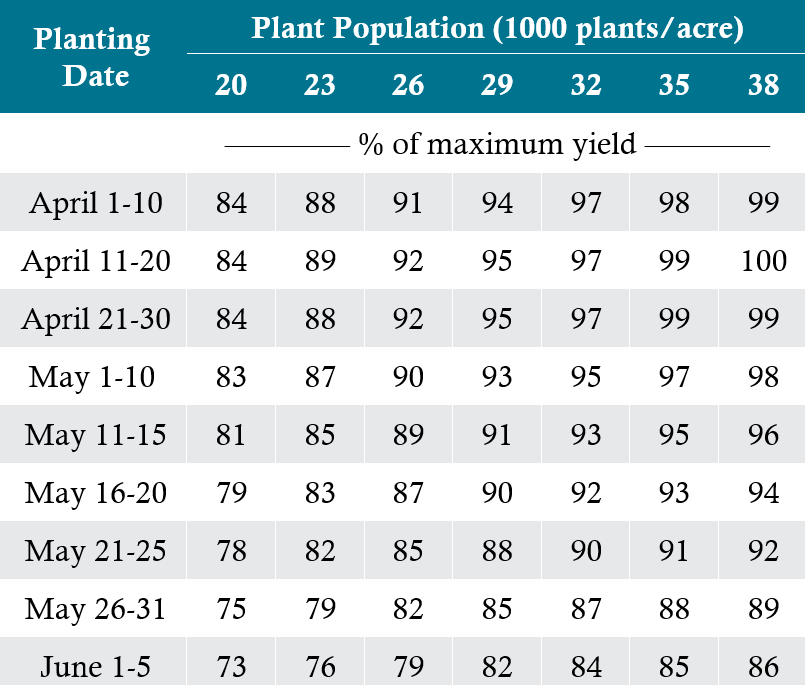
Estimate Yields Accordingly, Or Use The Chart Below.
Web Hail Affects Corn Yields In Three Ways:
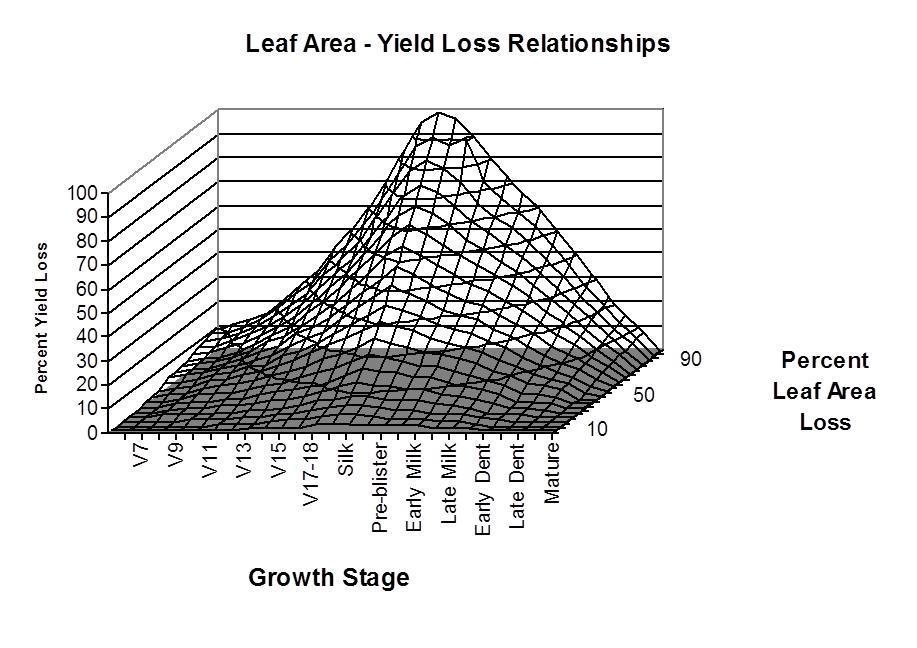
Web Complete Defoliation Of V4 Corn Caused Yield Loss Of 1.1% To 25.9% And Were Primary Attributed To Reduced Ear Size As A Result Of Reduce Leaf Area And, To A Lesser Extent, A Small Change In Plant Population (Johnson 1978).
Related Post: