Corn Nitrogen Use Chart
Corn Nitrogen Use Chart - You can see which parts of the corn are using the bulk of the nitrogen during. Web spring and summer weather volatility plus poor n use efficiency emphasize the importance of improving corn (zea mays l.) n management strategies. For example, here is a. Therefore, a 200 bu/acre corn crop would require approximately 200 lb of n/acre. Web this increase in corn yields (by over 2 bu/acre per year since 1980), while n rates remained constant, indicates that nitrogen use efficiency (nue, bu/lb n) has increased significantly. Web between v1 and v3, plant need for n is minimal; Of n per acre per day. Web the chlorophyll meter test estimates the nitrogen status of the growing corn crop based on the color of the corn leaves. Web every bushel of corn grain requires about one pound of n; Web the authors explained that nitrogen fertilizer recommendations were traditionally linked to expected yield level. Determining the optimal nitrogen (n) application rate is crucial for maximizing crop yield. Finding the maximum return to n and most profitable n rate. Very high = more than 196 bu/a; Of n per acre per day. Nue increases are the result of improvements in both hybrid genetics and. Of n per acre per day. Web every bushel of corn grain requires about one pound of n; Starting around v6, n uptake increases sharply to about 4. You can see which parts of the corn are using the bulk of the nitrogen during. Web corn plants use large quantities of nitrogen (n) to grow and yield. During the first 35 days after planting, a corn crop needs a little less than 2 lb. Web by rhonda brooks september 1, 2022. Web spring and summer weather volatility plus poor n use efficiency emphasize the importance of improving corn (zea mays l.) n management strategies. Finding the maximum return to n and most profitable n rate. Midwest sparks. Web the authors explained that nitrogen fertilizer recommendations were traditionally linked to expected yield level. Of n per acre per day. For example, here is a. During the first 35 days after planting, a corn crop needs a little less than 2 lb. Finding the maximum return to n and most profitable n rate. Determining the optimal nitrogen (n) application rate is crucial for maximizing crop yield. Guidelines for use of nitrogen fertilizer for corn grown following corn or soybean when supplemental irrigation is not used During the first 35 days after planting, a corn crop needs a little less than 2 lb. Finding the maximum return to n and most profitable n rate.. The above graph shows results over 2 years (6 total sites in oklahoma) where corn forage n uptake can be predicted from growth stages ranging from v8 to v10. A regional (corn belt) approach to nitrogen rate guidelines. Average yield = < 135 bu/a; Web during the growing season, corn plants must extract approximately 336 lbs of nitrogen, 153 lbs. Average yield = 136 to 165 bu/a; Therefore, a 200 bu/acre corn crop would require approximately 200 lb of n/acre. Finding the maximum return to n and most profitable n rate. Average yield = 166 to 195 bu/a; For example, here is a. Web the chlorophyll meter test estimates the nitrogen status of the growing corn crop based on the color of the corn leaves. A regional (corn belt) approach to nitrogen rate guidelines. Web total corn n, p, k, mg, s, zn uptake and partitioning across four plant stover fractions for corn averaging 230 bushels/acre. Web spring and summer weather volatility plus. Average yield = 136 to 165 bu/a; Web the chlorophyll meter test estimates the nitrogen status of the growing corn crop based on the color of the corn leaves. Web by rhonda brooks september 1, 2022. Very high = more than 196 bu/a; During the first 35 days after planting, a corn crop needs a little less than 2 lb. You can see which parts of the corn are using the bulk of the nitrogen during. Web spring and summer weather volatility plus poor n use efficiency emphasize the importance of improving corn (zea mays l.) n management strategies. Determining the optimal nitrogen (n) application rate is crucial for maximizing crop yield. Nue increases are the result of improvements in. Midwest sparks controversy, but the solution may be easier. “for corn following either corn or wheat, the recommendation was. Web this increase in corn yields (by over 2 bu/acre per year since 1980), while n rates remained constant, indicates that nitrogen use efficiency (nue, bu/lb n) has increased significantly. Web spring and summer weather volatility plus poor n use efficiency emphasize the importance of improving corn (zea mays l.) n management strategies. Of n per acre per day. A regional (corn belt) approach to nitrogen rate guidelines. Average yield = 166 to 195 bu/a; Guidelines for use of nitrogen fertilizer for corn grown following corn or soybean when supplemental irrigation is not used Web by rhonda brooks september 1, 2022. During the first 35 days after planting, a corn crop needs a little less than 2 lb. Web the chart below offers a look at nitrogen uptake throughout the growing season. Therefore, a 200 bu/acre corn crop would require approximately 200 lb of n/acre. The above graph shows results over 2 years (6 total sites in oklahoma) where corn forage n uptake can be predicted from growth stages ranging from v8 to v10. Web the chlorophyll meter test estimates the nitrogen status of the growing corn crop based on the color of the corn leaves. Average yield = < 135 bu/a; Web the authors explained that nitrogen fertilizer recommendations were traditionally linked to expected yield level.
Corn Nitrogen Management
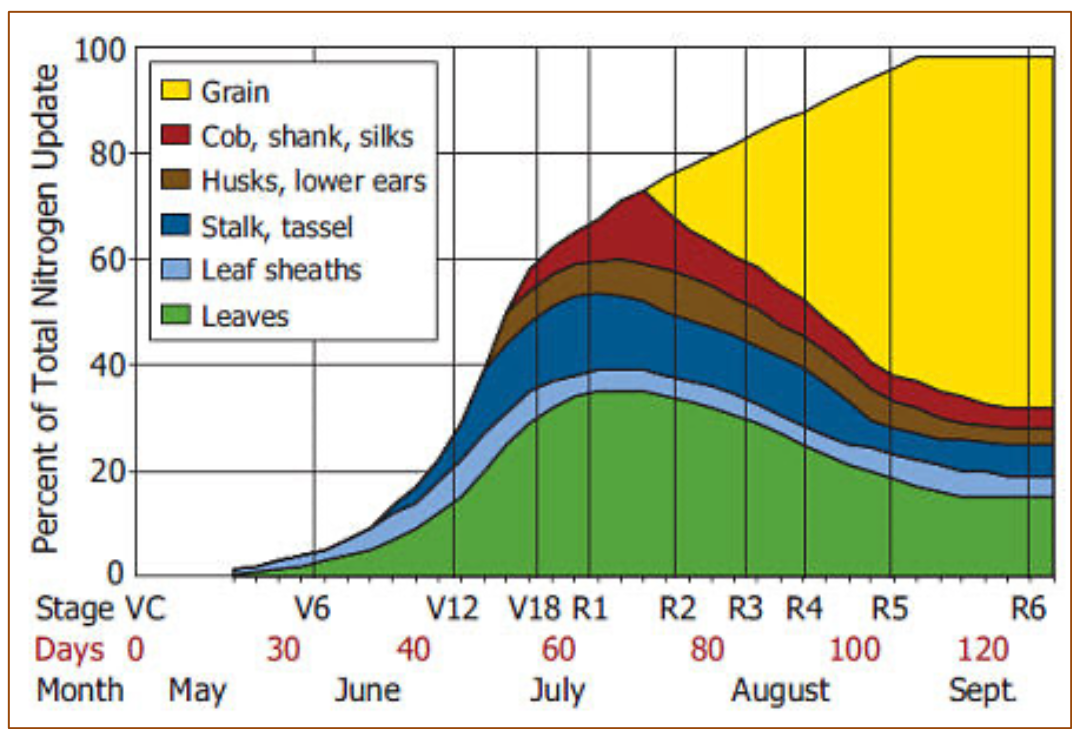
Assessing and managing nitrogen losses in corn Michigan Farm News

Corn wholeplant nitrogen uptake (WPNU) at various fertilizer and
Legend Seeds InSeason Nitrogen Management Tips for Corn

Minnesota Corn Nitrogen Updated AgFax
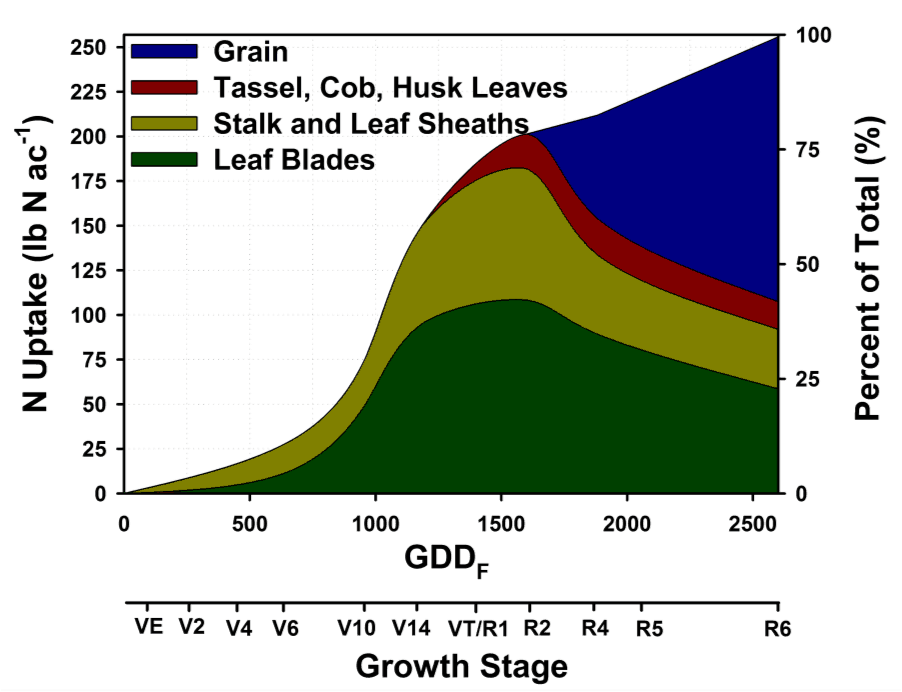
Nitrogen stabilizers The Andersons
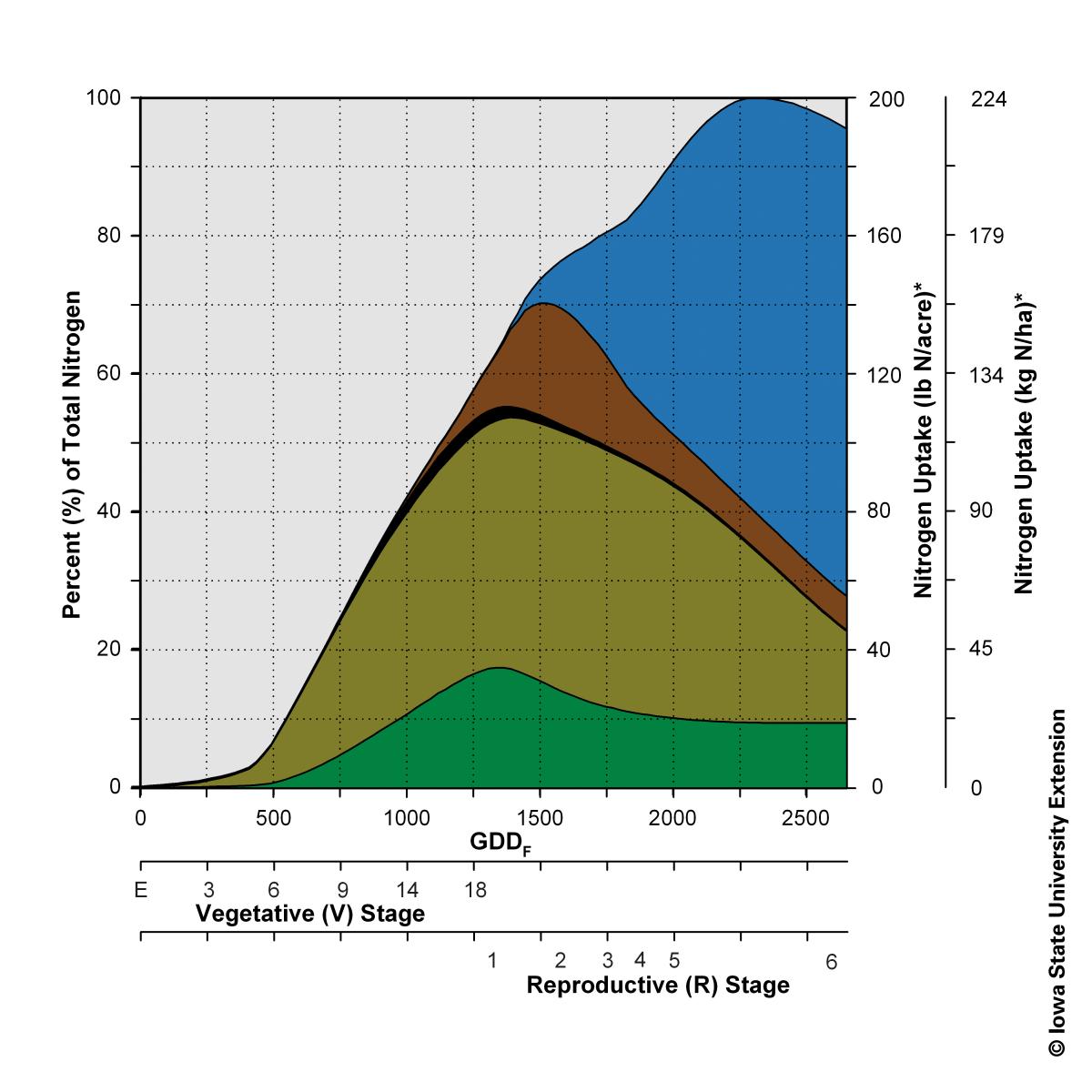
Managing and Preparing for Nitrogen Loss CropWatch University of
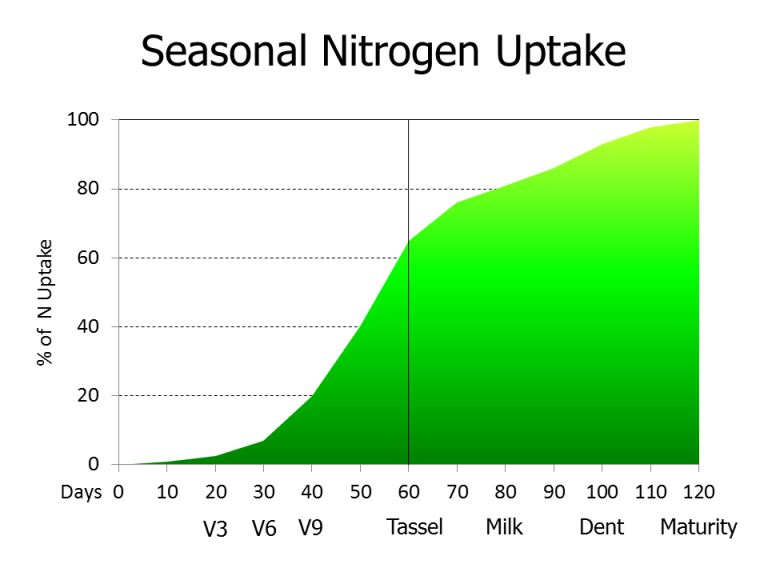
Practices which Can Increase Nitrogen Use Efficiency for MidSouth Corn
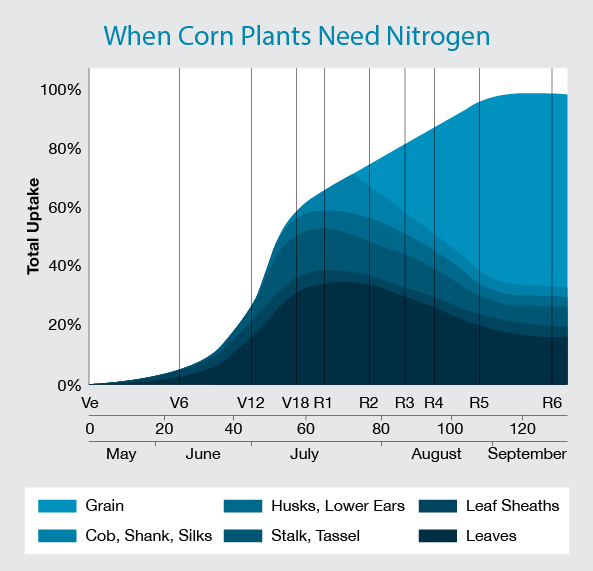
How to Manage Nitrogen AgWeb
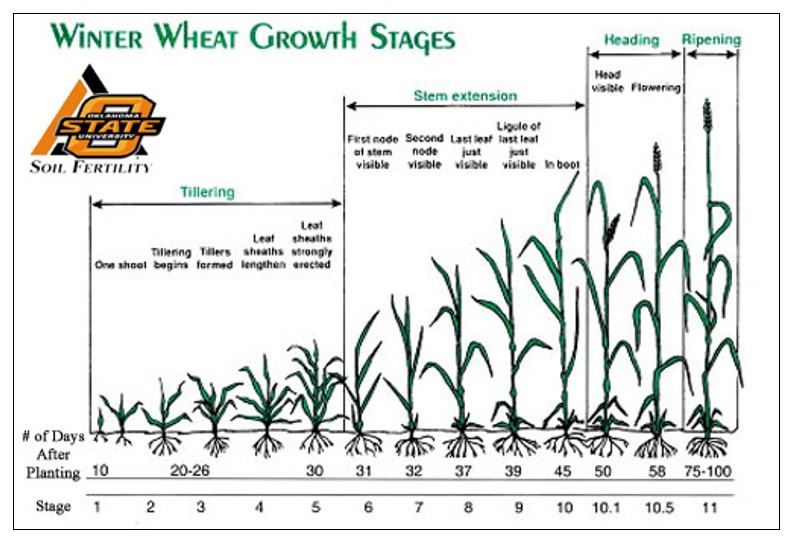
Nitrogen Uptake in Corn and Wheat, nitrogen use efficiency
Web Between V1 And V3, Plant Need For N Is Minimal;
Web Corn Plants Use Large Quantities Of Nitrogen (N) To Grow And Yield.
Very High = More Than 196 Bu/A;
Nue Increases Are The Result Of Improvements In Both Hybrid Genetics And.
Related Post: