Cranial Drawer Sign
Cranial Drawer Sign - Web the technique relies on a cranial advancement of the tibial tuberosity after an osteotomy of the tibial crest. Web the cranial drawer sign is definitive for diagnosing ccl rupture. The crest is stabilised with a cage and forked tension plate. This movement is known as a positive drawer sign. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with one hand and. Web a positive cranial drawer sign can be elicited, and radiographs show joint effusion and cranial dislocation of the tibia (fig. Web diagnosing cranial cruciate ligament pathology is easy when a supportive history, signalment, gait evaluation, and radiographic appearance are combined with positive results on tibial compression or cranial drawer tests. In general, radiographic images are used to visualize the instability of the stifle joint by tibial compression, to detect effusion and secondary osteoarthritic changes. Web however, if a partial tear is present, the cranial drawer sign may reveal only 2 mm to 3 mm of instability when the test is done with the stifle flexed and no instability with the stifle in extension [ 13 ]. Other signs of ccl rupture include “medial buttress” (thickening or scarring on the inside of the knee), and “tibial thrust” (another method to check for cranial displacement of the tibia). Manual cranial displacement of proximal tibia relative to distal femur ± cranial tibial thrust: However, some dogs with cranial cruciate ligament pathology do not have palpable stifle instability. Anesthesia may be necessary to move the limb to the extent needed because pain from a ruptured ccl can be severe, and muscle tension can restrict the motion of the joint. Many. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with one hand and. Web posted on april 21, 2008 (april 6, 2022) by mandie if it is suspected that your dog has a cranial cruciate ligament tear or rupture, your veterinarian will perform a physical exam to determine whether or not this type of injury can be ruled out. Web a. Most dogs with this injury cannot walk normally and they experience pain. Web the technique relies on a cranial advancement of the tibial tuberosity after an osteotomy of the tibial crest. The examiner positions himself by sitting on the examination table in front of the involved knee and grasping the tibia just below the joint line of. Web metrics the. Web procedure the patient should be supine with the hips flexed to 45 degrees, the knees flexed to 90 degrees and the feet flat on table. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with one hand and. Occurs rapidly after ligament rupture in most dogs provides ample indication for surgical joint exploration even in the absence of a. Web. Manual cranial displacement of proximal tibia relative to distal femur ± cranial tibial thrust: The crest is stabilised with a cage and forked tension plate. Other signs of ccl rupture include “medial buttress” (thickening or scarring on the inside of the knee), and “tibial thrust” (another method to check for cranial displacement of the tibia). Web in patients with a. Web the objective of traditional surgeries, based on the passive model, is the elimination of cranial drawer sign. Web is a reliable clinical sign of cruciate rupturepalpation of a medial buttress over the proximal tibia of the affected leg: Comparing the affected stifle with the normal stifle provides a ready frame of reference. Web metrics the cranial drawer sign is. Patella luxation, lumbosacral disease, hip dysplasia, iliopsoas strain, bone neoplasia, However, some dogs with cranial cruciate ligament pathology do not have palpable stifle instability. Comparing the affected stifle with the normal stifle provides a ready frame of reference. Web a positive cranial drawer sign can be elicited, and radiographs show joint effusion and cranial dislocation of the tibia (fig. Web. An examination performed while the patient is sedated is needed to confirm the findings. Patella luxation, lumbosacral disease, hip dysplasia, iliopsoas strain, bone neoplasia, A small bony fragment may be seen at the tibial insertion site of the cranial cruciate ligament in cases of ligament avulsion (22). How to perform the cranial drawer test. Web a positive cranial drawer sign. In general, radiographic images are used to visualize the instability of the stifle joint by tibial compression, to detect effusion and secondary osteoarthritic changes. Web the ability to move the tibia forward (cranially) with respect to a fixed femur is a positive cranial drawer sign indicative of a ccl rupture. Web in this video i give you some tips to. Cranial movement of tibial tuberosity as hock is manually flexed and gastrocnemius contracts ± meniscal click ddx: The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are. Web is a reliable clinical sign of cruciate rupturepalpation of a medial buttress over the proximal tibia of the affected leg: The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with one hand and. Most. Web ± cranial drawer sign: Often, with a chronic injury, the cranial drawer sign is less effective due some joint stabilization resulting from. In general, radiographic images are used to visualize the instability of the stifle joint by tibial compression, to detect effusion and secondary osteoarthritic changes. Cranial movement of tibial tuberosity as hock is manually flexed and gastrocnemius contracts ± meniscal click ddx: Web a positive cranial drawer sign can be elicited, and radiographs show joint effusion and cranial dislocation of the tibia (fig. Most dogs with this injury cannot walk normally and they experience pain. Web the loss of these normal findings indicates periarticular fibrosis, joint effusion or both. Many patients that do not seem to have a cranial drawer sign while awake have one once they are sedated and relaxed. Web the technique relies on a cranial advancement of the tibial tuberosity after an osteotomy of the tibial crest. The examiner positions himself by sitting on the examination table in front of the involved knee and grasping the tibia just below the joint line of. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are. Web sliding of the distal femur over the proximal tibia (positive drawer sign) indicates cranial cruciate ligament rupture. Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. Comparing the affected stifle with the normal stifle provides a ready frame of reference. Anesthesia may be necessary to move the limb to the extent needed because pain from a ruptured ccl can be severe, and muscle tension can restrict the motion of the joint. However, some dogs with cranial cruciate ligament pathology do not have palpable stifle instability.
Cruciate Disease The Cranial Drawer Test YouTube
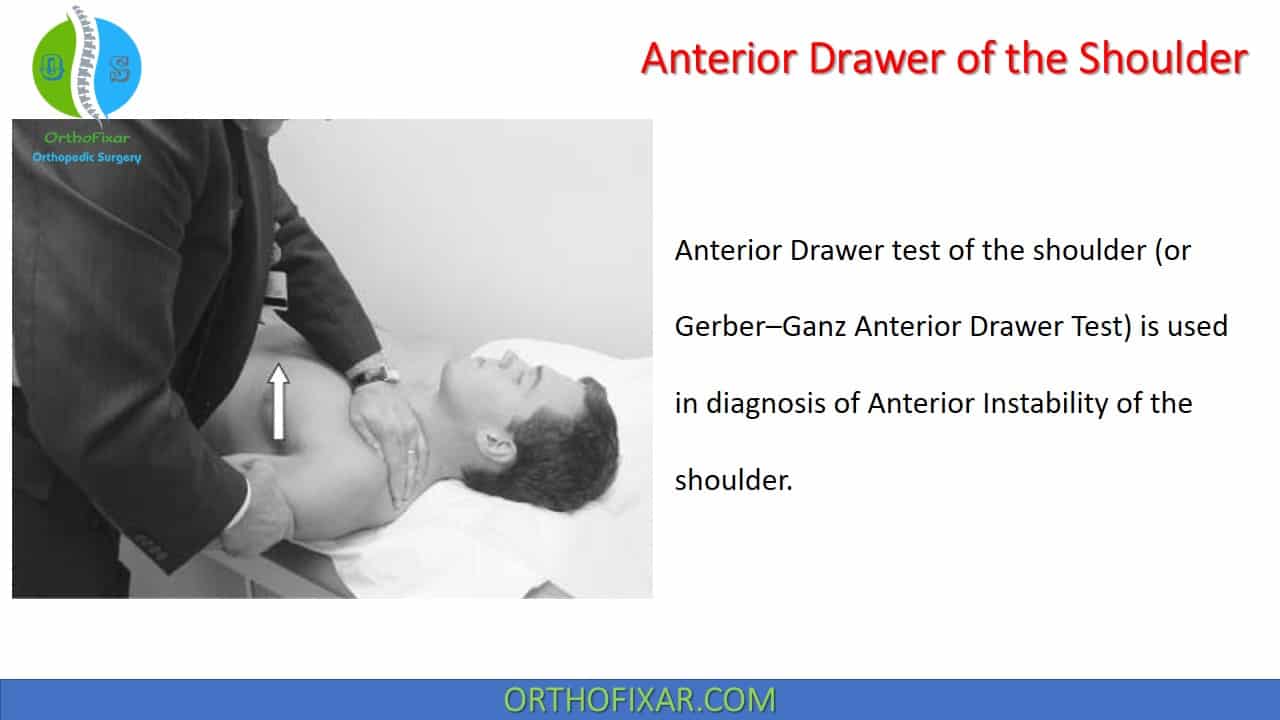
Anterior Drawer Test Shoulder

Drawer Test Bruin Blog
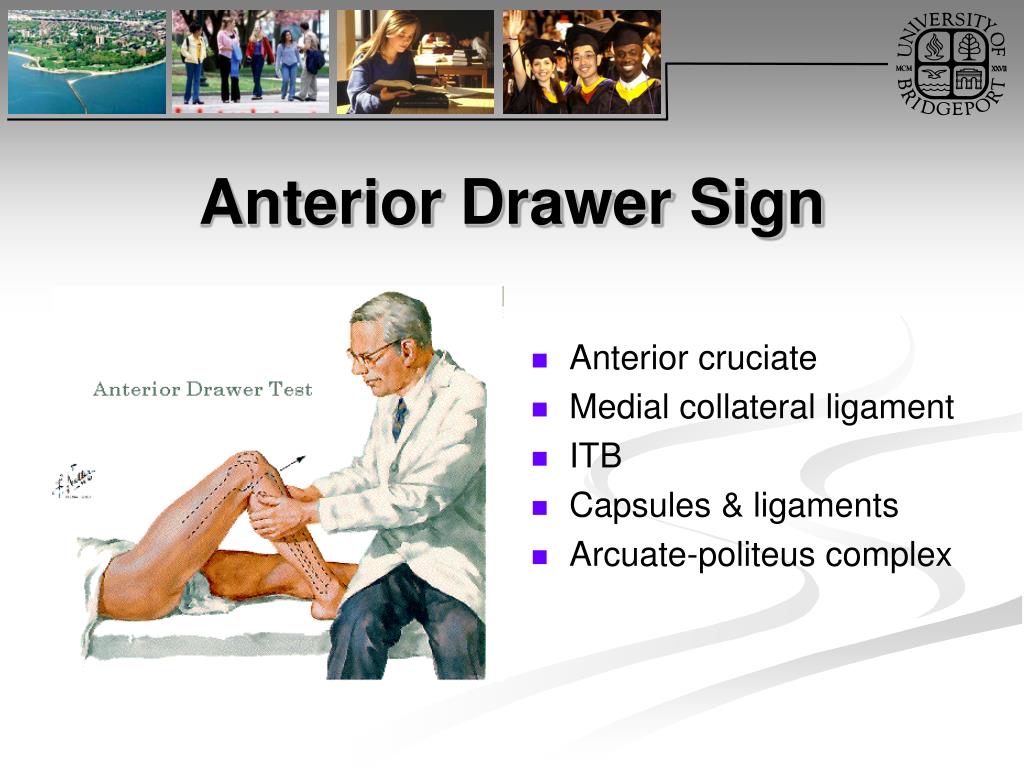
PPT Knee Orthopaedic Tests PowerPoint Presentation, free download

Positive cranial drawer sign in a dog with a cranial (anterior
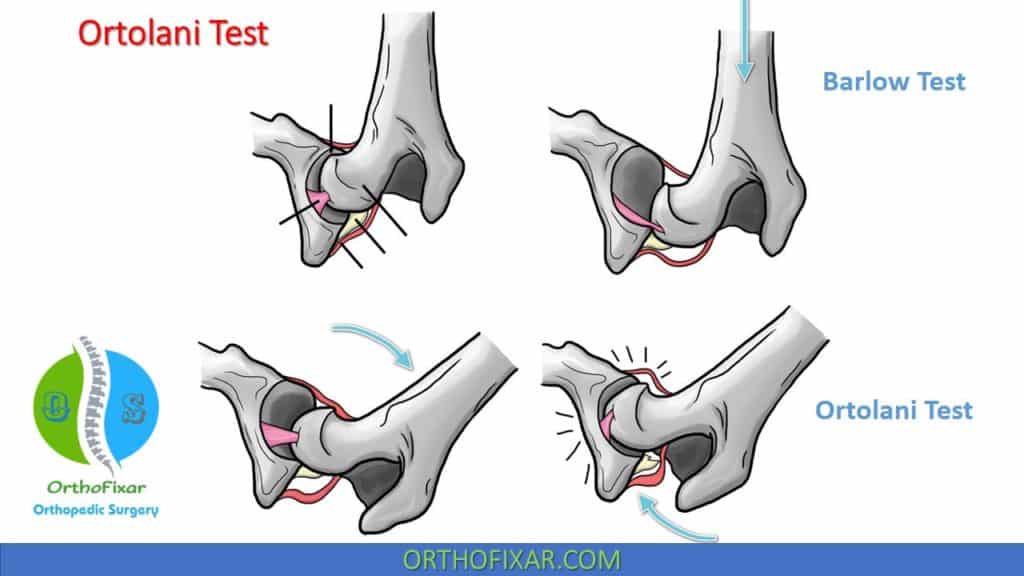
Ortolani Test OrthoFixar 2023
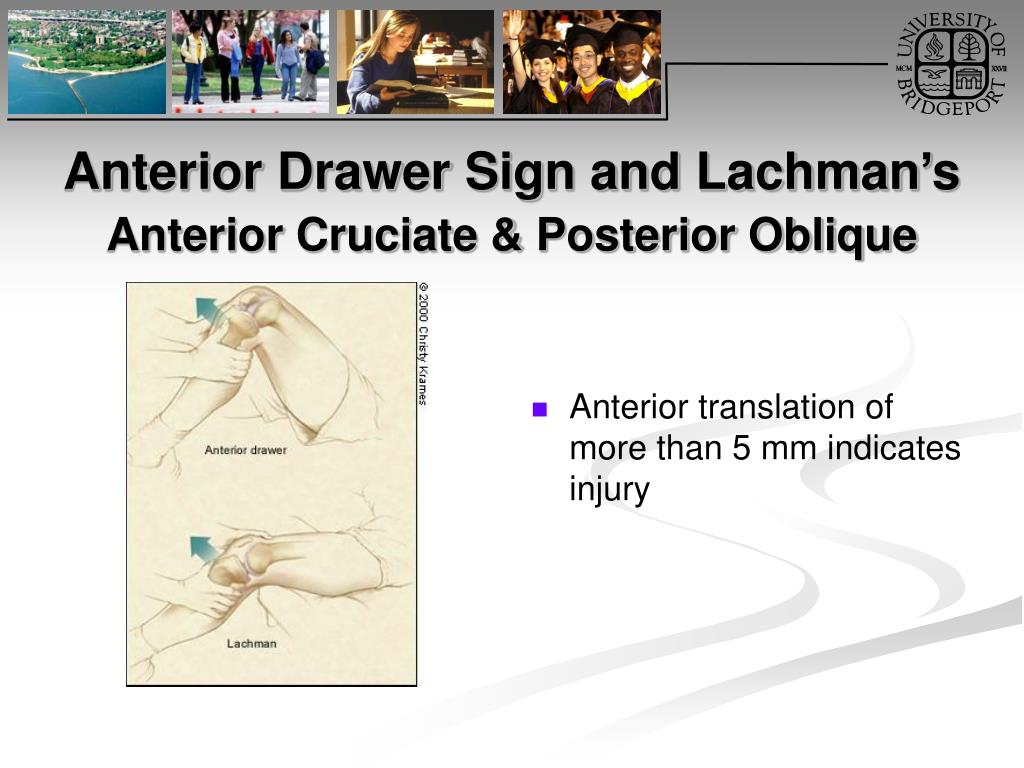
PPT Knee Orthopaedic Tests PowerPoint Presentation, free download

Drawer Test Bruin Blog
+drawer+test.jpg)
Anterior Drawer Sign Positive Drawer Gallery

Cranial Or Anterior Drawer Sign Drawer Gallery
The Objective Of The Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy Is Neutralization Of The Cranial Tibial Thrust And Not Complete Elimination Of The Drawer Sign.
Web Patients With Chronic Ruptures Associated With A Large Amount Of Scar Tissue And Arthritis May Not Exhibit Cranial Drawer.
Web The Objective Of Traditional Surgeries, Based On The Passive Model, Is The Elimination Of Cranial Drawer Sign.
This Movement Is Known As A Positive Drawer Sign.
Related Post: