Dogs Anatomy Chart
Dogs Anatomy Chart - The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. A dog’s skeleton is divided into the axial skeleton (skull, vertebrae, ribs, and sternum) and the appendicular skeleton (limbs, shoulder girdle, and pelvic girdle). Let’s review the anatomical terms used to describe the parts of the dogs, starting from head to tail. Some of the different canine joints are labeled. These are the smaller pads located beneath each toe, providing additional support and stability. Web this is why animalwised brings you this dog anatomy guide where we look at the general categories for muscles, bones and organs of dogs. Ecvdi, utrecht, netherland) were categorized topographically into seven chapters (head, vertebral column, thoracic limb, pelvic limb, larynx/pharynx,. A brief outline of diagnostic, Web your dog’s body explained (a simple guide to your dog’s anatomy) by k9 magazine. Cannes film festival (un certain regard) cast: Surely you're familiar with common features such as the legs, eyes, and tail… but how about the loin or the hock? Ecvdi, utrecht, netherland) were categorized topographically into seven chapters (head, vertebral column, thoracic limb, pelvic limb, larynx/pharynx,. Web here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine skeleton, containing the main joints of the dog and its structures from different. Web dog anatomy comprises the anatomical study of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog. Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. Web the following canine anatomy illustrations offer a look at various systems within the. Anyone who has ever run their hands over dogs of various breeds, ages and sizes will know that dogs are, despite being man's best friend, built entirely differently to humans. • the dorsal plane divides the dog into ventral and dorsal portions. Web anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: Web anatomy of a dog’s paw: Web dog anatomy comprises. The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are also illustrated. The images are transverse sections of the whole body and a. Web here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine muscles and skeleton from different anatomical standard views. In this article, you will learn the location of different organs from the different systems (like skeletal, digestive, respiratory, urinary, cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous, and special sense) of a dog with their important anatomical features. Ecvdi, utrecht, netherland) were categorized topographically into seven chapters (head, vertebral column, thoracic limb, pelvic limb, larynx/pharynx,. The following paragraphs explain all these aspects in brief,. Web anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: Some of the different canine joints are labeled. Web gain a comprehensive understanding of your dog's health with our veterinary guide to cat anatomy complete with diagrams, images and simple explanations. The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. Some. Also see professional content regarding management of dogs. In this article, you will learn the location of different organs from the different systems (like skeletal, digestive, respiratory, urinary, cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous, and special sense) of a dog with their important anatomical features. Web anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: The following paragraphs explain all these aspects in brief, along. • the sagittal plane divides the dog into right and left portions. If this plane were in the midline of the body, this is the median plane or median sagittal plane. Web the anatomy of a dog includes its skeletal structure, reproductive system, the internal organs, and its external appearance. Web your dog’s body explained (a simple guide to your. The following paragraphs explain all these aspects in brief, along with diagrams, which will help you understand them better. Surely you're familiar with common features such as the legs, eyes, and tail… but how about the loin or the hock? Dogs use their claws for gripping, digging, and defense. We discuss the internal and external anatomy of dogs so that. Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are also illustrated. If this plane were in the midline of the body, this is the median plane or median sagittal plane. Can you name all of the parts of a dog? Web here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine skeleton, containing the main joints of the dog and its. In this article, you will learn the location of different organs from the different systems (like skeletal, digestive, respiratory, urinary, cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous, and special sense) of a dog with their important anatomical features. Web here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine muscles and skeleton from different anatomical standard views (lateral, medial, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral / palmar.). Also see professional content regarding management of dogs. Web posterior view of the skeleton with lateral view of the skull. Web anatomical terms you should know. Cannes film festival (un certain regard) cast: Anyone who has ever run their hands over dogs of various breeds, ages and sizes will know that dogs are, despite being man's best friend, built entirely differently to humans. These are the smaller pads located beneath each toe, providing additional support and stability. The images are transverse sections of the whole body and a. Muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). Some of the different canine joints are labeled. Although dogs look very different from people, they share many of our body’s characteristics. Ecvdi, utrecht, netherland) were categorized topographically into seven chapters (head, vertebral column, thoracic limb, pelvic limb, larynx/pharynx,. Web your dog’s body explained (a simple guide to your dog’s anatomy) by k9 magazine. Although these pictures are fairly basic, they still provide insight that can help the average dog owner gain a working idea of what's beneath all that fur. Web dog anatomy comprises the anatomical study of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog.
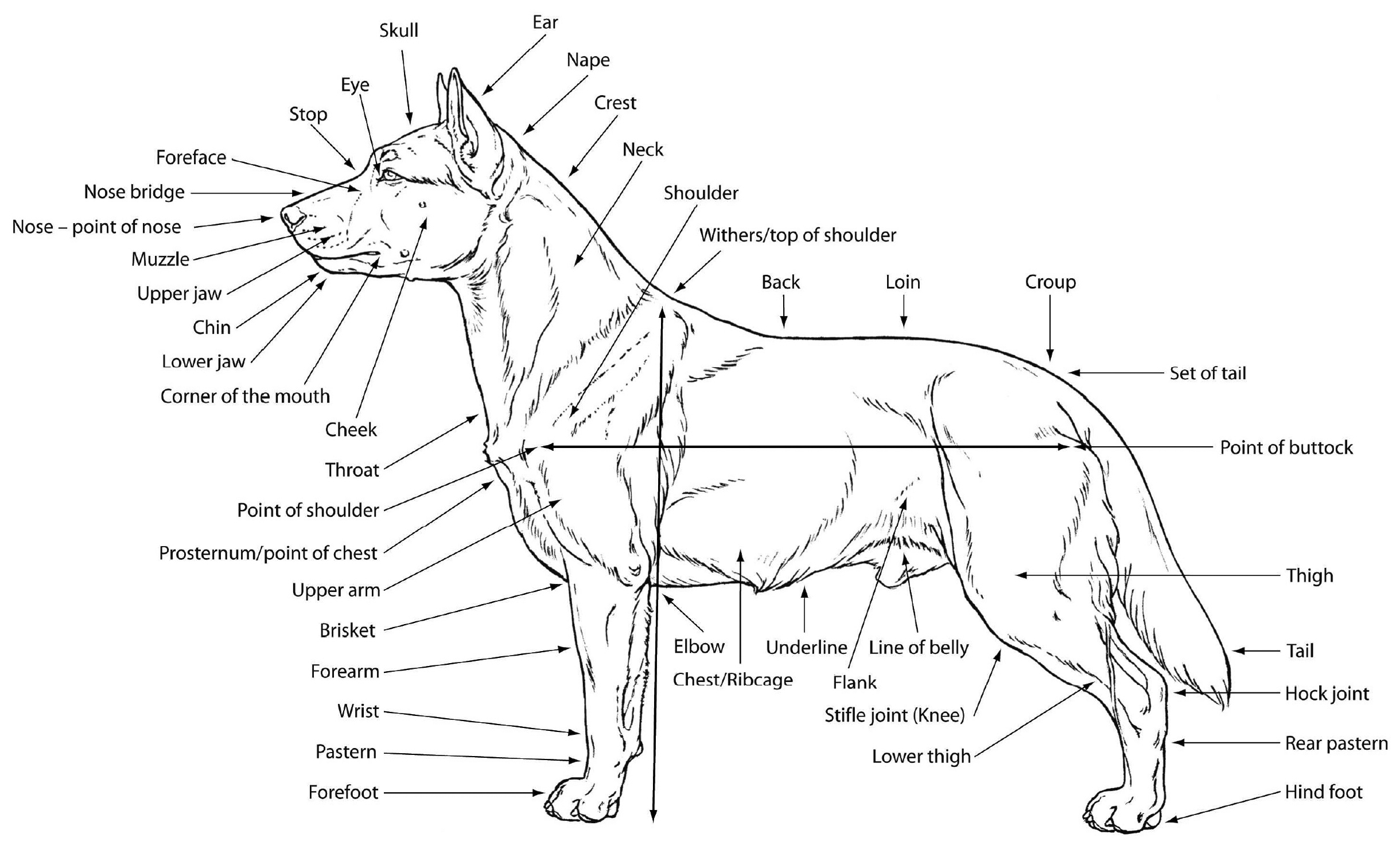
Dog Anatomy Head Anatomical Charts & Posters

Anatomy of dog skeleton with labeled inner bone scheme vector
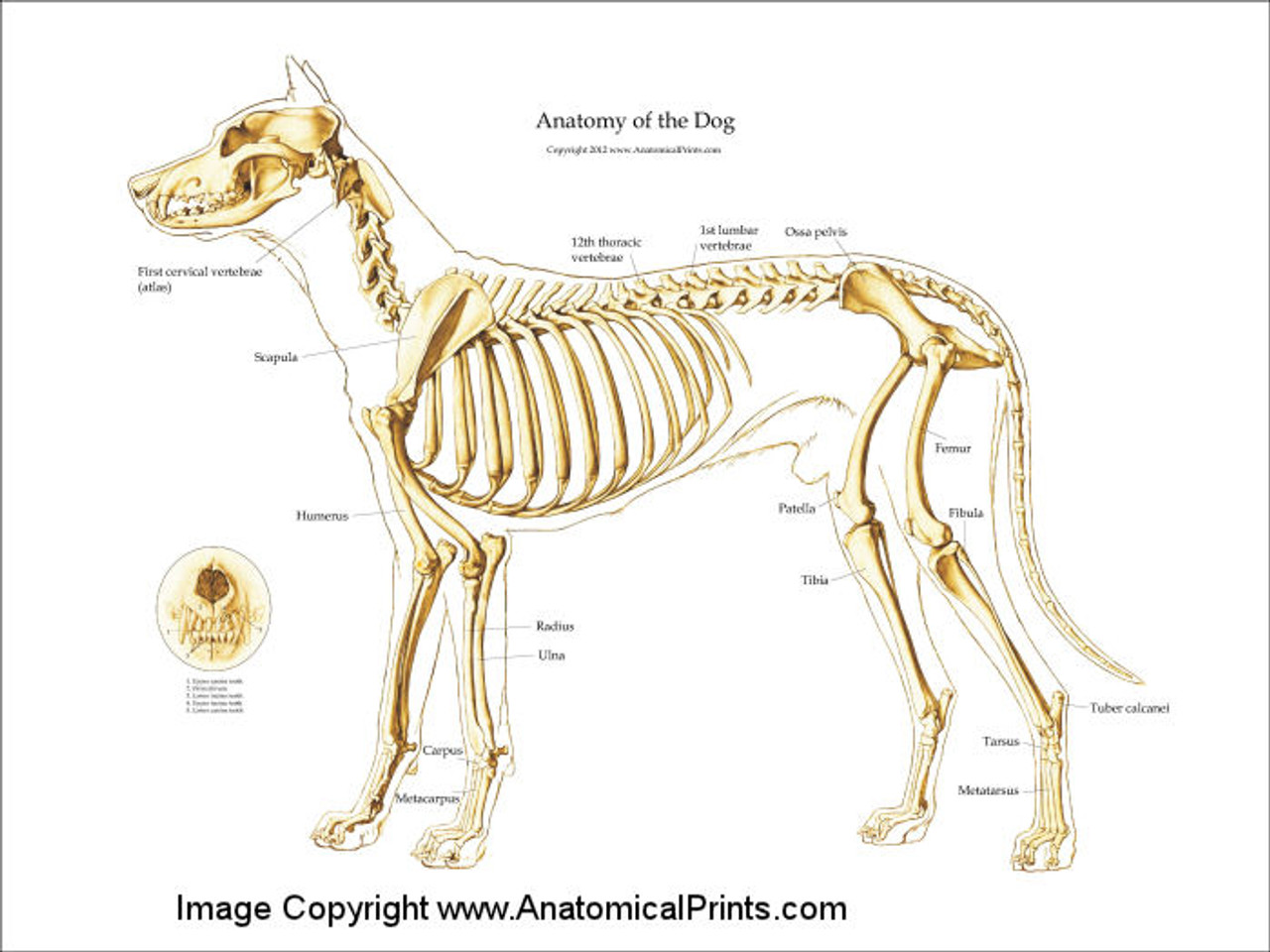
Canine Skeleton Poster Clinical Charts and Supplies
M. Douglas Wray Dog Anatomy
Dog Anatomy Laminated Poster Clinical Charts and Supplies
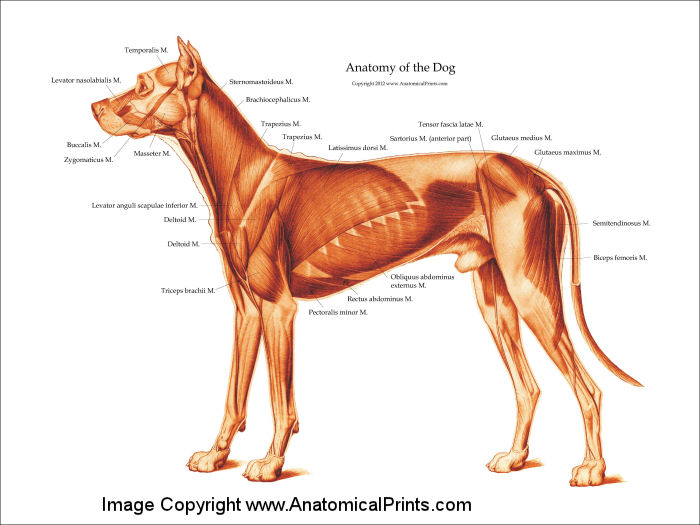
Dog Anatomical Chart Muscles

dog anatomy Dog Care Training Grooming
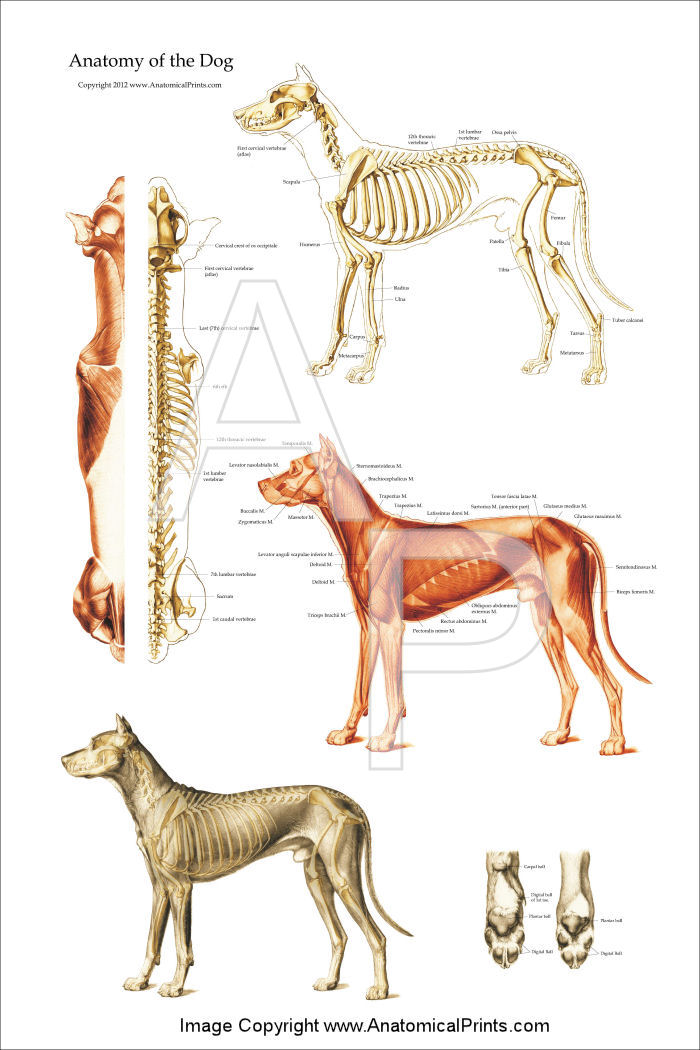
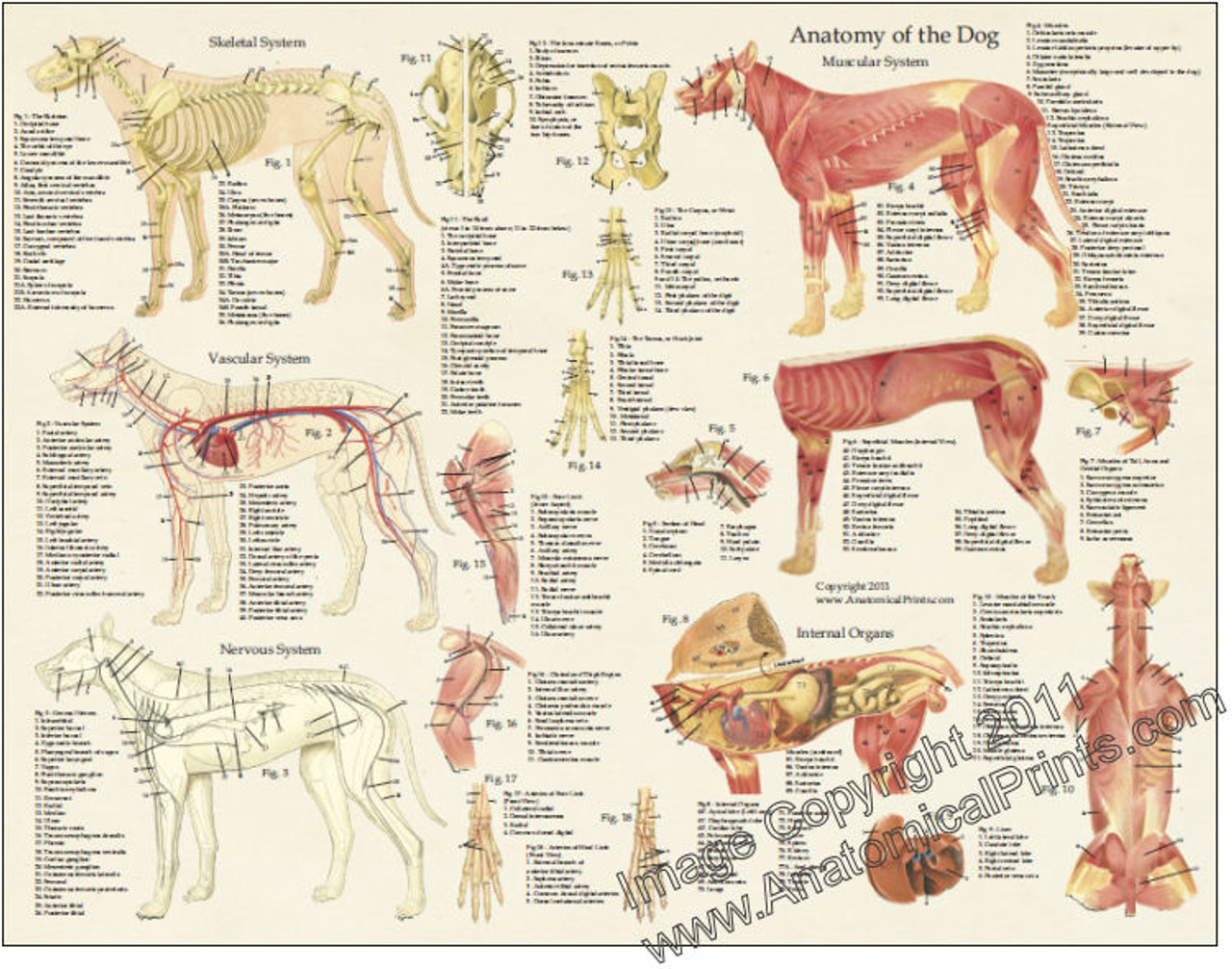
Dog Anatomical Chart Bones and Muscles
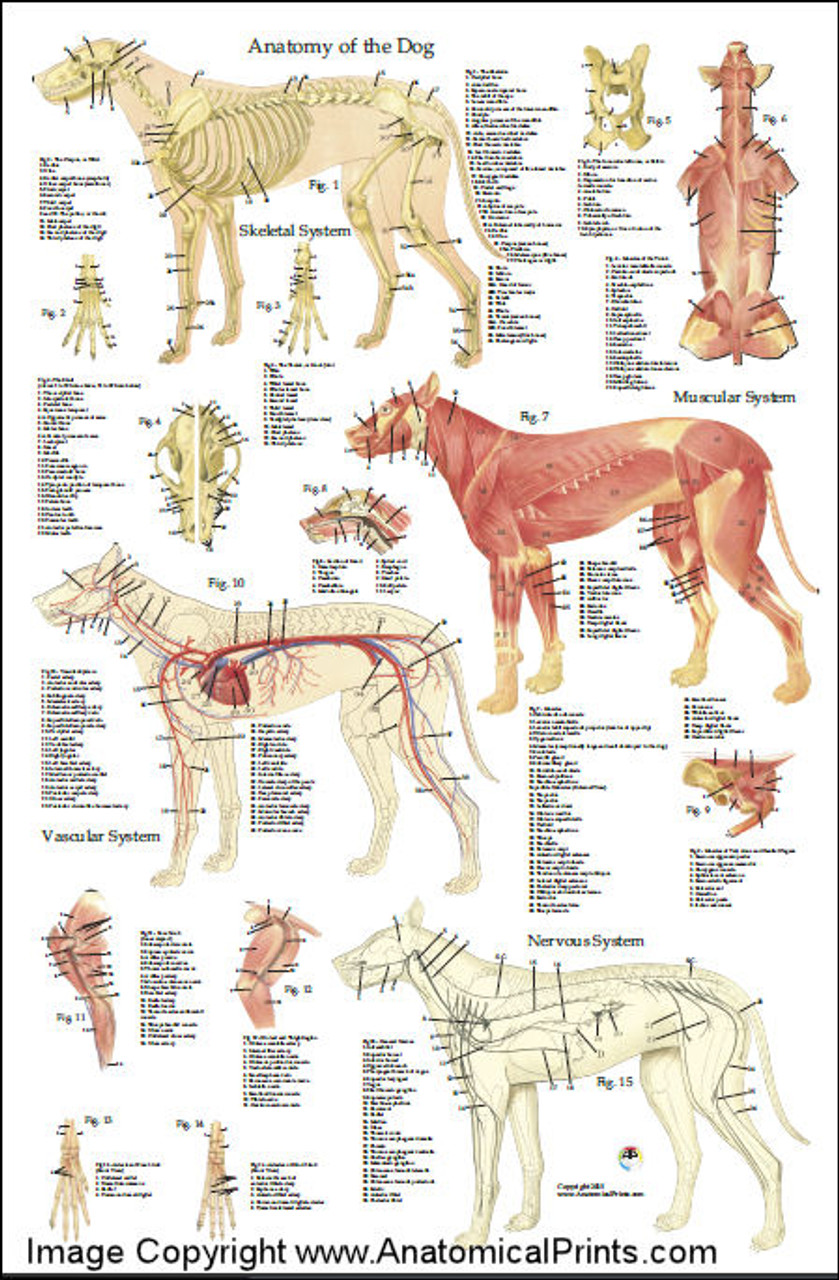
Dog Anatomy Chart The Y Guide
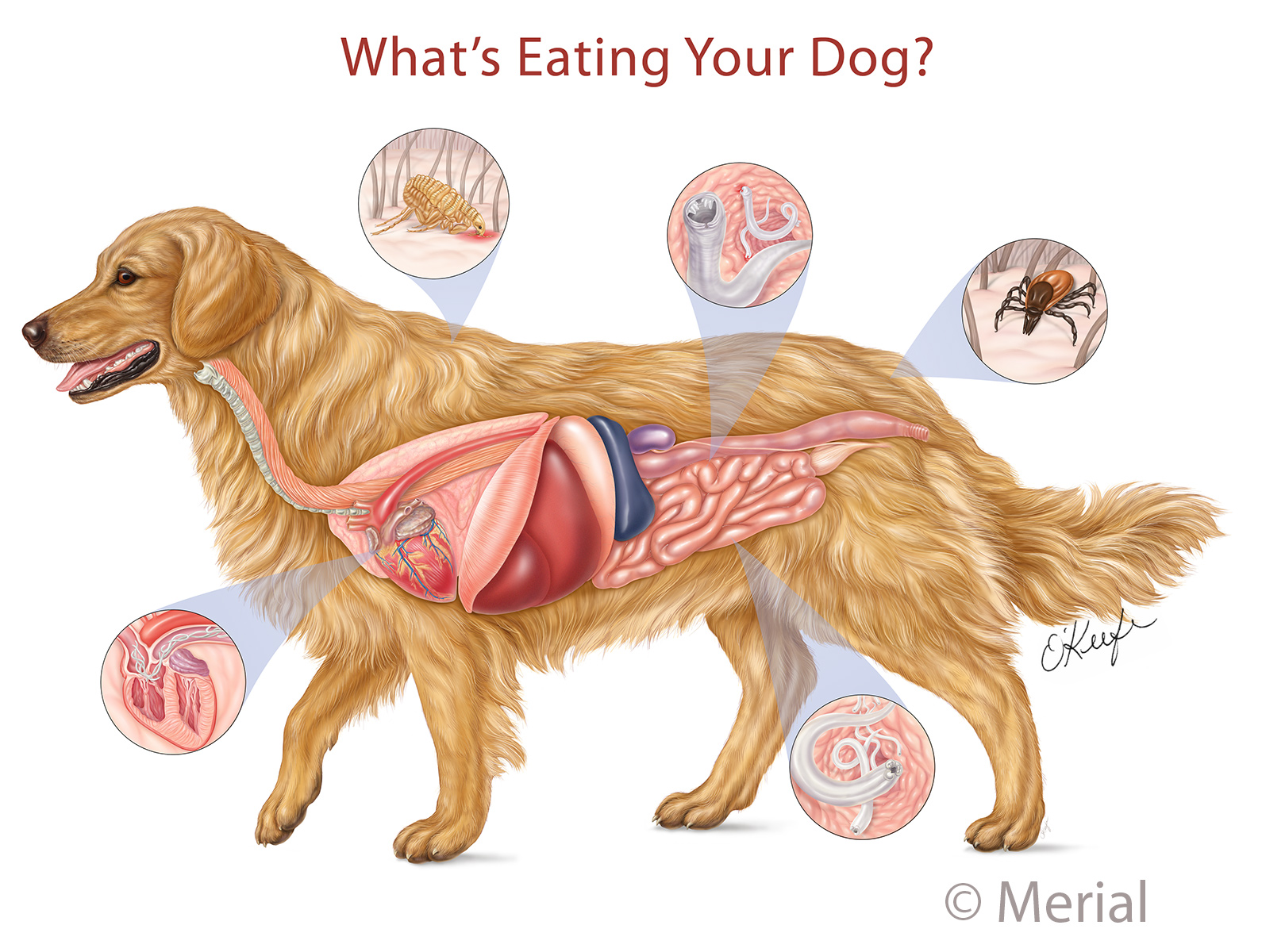
Dog Internal Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
Web Here Are Presented Scientific Illustrations Of The Canine Skeleton, With The Main Dog's Bones And Its Structures Displayed From Different Anatomical Standard Views (Cranial, Caudal, Lateral, Medial, Dorsal, Palmar.).
Digestive And Urinary Tracts |.
Web The Anatomy Of A Dog Includes Its Skeletal Structure, Reproductive System, The Internal Organs, And Its External Appearance.
• The Sagittal Plane Divides The Dog Into Right And Left Portions.
Related Post: