Draw A Successive Ionization Energy Diagram For Aluminum
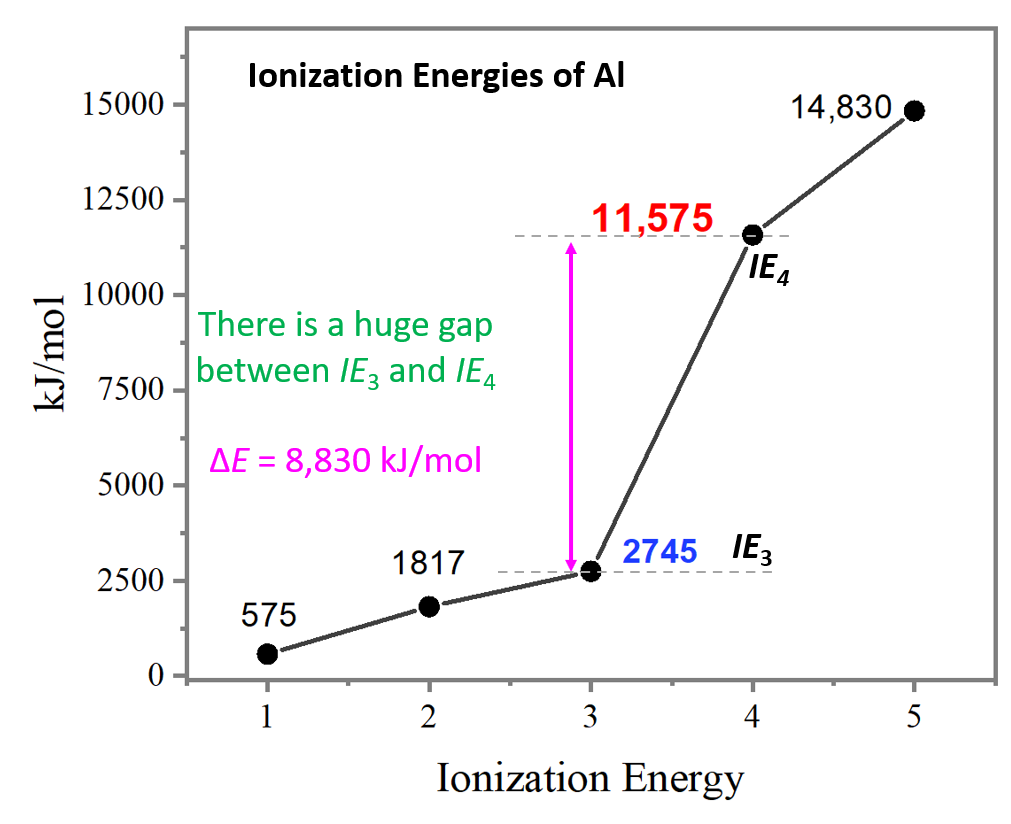
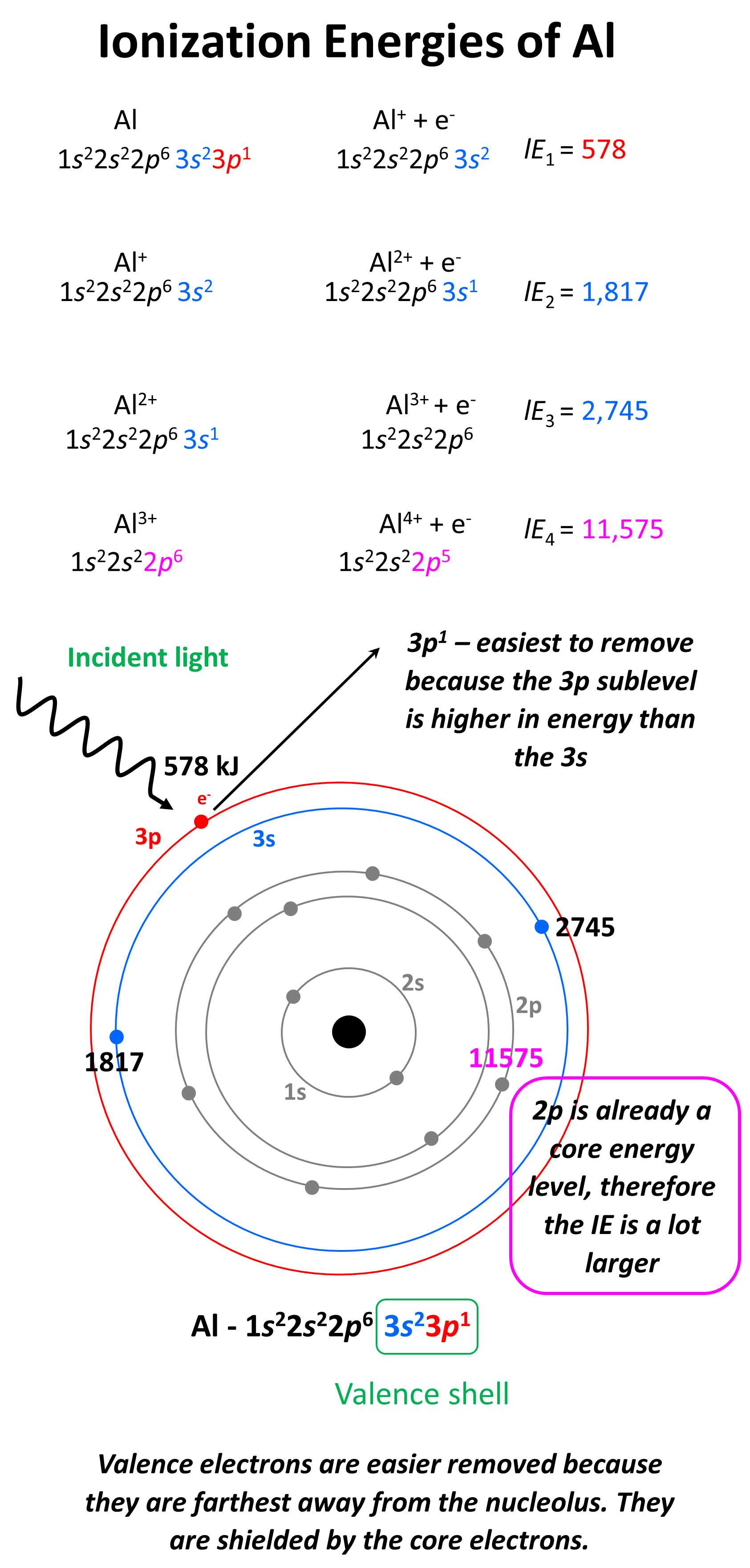
Draw A Successive Ionization Energy Diagram For Aluminum - Web to draw a successive ionization energy diagram for aluminum, we will use the ionization energy data given on page 60. The second ionization energy of aluminum is larger than the first, and the third ionization energy is even larger. I 3 i_3 i 3 = 2,745 kj/mol. 2nd ionization energy, 1816 kj ⋅ mol−1; Although it takes a considerable amount of energy to remove three electrons from an aluminum atom to form an al 3+ ion, the energy needed to break into the filled. Web label each peak in the spectrum to show which subshell it represents (i.e., 1s, 2s, etc.) on diagram above. The values mentioned in the chart are given in electron volts (ev). I 1 i_1 i 1 = 578 kj/mol. The first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost (valence). Web so without actually providing the ionization energies for all the group 13 elements, they could say that the element has the second highest first ionization energy in its group, which would be aluminum. Web the first ionization energy of aluminum is smaller than magnesium. For instance, the ionization energy of sodium (alkali metal) is 496kj/mol (1) whereas chlorine's first ionization energy is 1251.1 kj/mol (2). In this article, i have discussed in detail how to easily write the complete electron configuration of aluminum. From the picture, we can see that the fourth ionization. 4th ionization energy, 11600 kj ⋅ mol−1. 1st ionization energy, 577 kj ⋅ mol−1; The second ionization energy of aluminum is larger than the first, and the third ionization energy is even larger. But even that wouldn’t work well since gallium (the element beneath aluminum) has about the same first ionization energy as aluminum. Web each successive ionization energy would. Web chemists define the ionization energy ( i i) of an element as the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from the gaseous atom e e in its ground state. But even that wouldn’t work well since gallium (the element beneath aluminum) has about the same first ionization energy as aluminum. I i is therefore the energy required. Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. The second ionization energy of aluminum is larger than the first, and the third ionization energy is even larger. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period. Now, what about trends up and down the periodic table? I 4. Thus, many students find it confusing that, for example, the 5p orbitals fill immediately after the 4d, and immediately before the 6s.the filling order is based on observed experimental results, and has been confirmed by theoretical calculations. I 1 i_1 i 1 = 578 kj/mol. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements. Web the first four ionisation energies of aluminium, for example, are given by. As you go from left to right, you go from low ionization energy to high ionization energy. Now, what about trends up and down the periodic table? Web x 2+ → x 3+ + e − ionization energy for different elements there is an ionization energy for. I 3 i_3 i 3 = 2,745 kj/mol. As you go from left to right, you go from low ionization energy to high ionization energy. It would start off with the lowest ionization energy. In this article, i have discussed in detail how to easily write the complete electron configuration of aluminum. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well. The ionization energy is measured in joules (j) or electron volts (ev). Web al,z = 13:1s22s22p63s23p1. E(g) → e+(g) +e− energy required=i (2.9.1) (2.9.1) e ( g) → e ( g) + + e − energy required=i. Web ionization energy increases here. 1st ionization energy, 577 kj ⋅ mol−1; I 2 i_2 i 2 = 1,817 kj/mol. And then beryllium and magnesium are on the other side of the periodic table in terms of group two way. Now, what about trends up and down the periodic table? An element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of. Web electron configuration for aluminum (al, al3+ ion) aluminum is the 13th element in the periodic table and its symbol is ‘al’. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. Thus, many students find it confusing that, for example, the 5p orbitals fill immediately after the 4d, and. Web label each peak in the spectrum to show which subshell it represents (i.e., 1s, 2s, etc.) on diagram above. Web x 2+ → x 3+ + e − ionization energy for different elements there is an ionization energy for each successive electron removed. It would start off with the lowest ionization energy. Some of these electrons are more tightly bound in the atom than others. Web each successive ionization energy would be larger in magnitude than the previous one. This jump corresponds to removal of the core electrons, which are harder to remove than the valence electrons. I 4 i_4 i 4 = 11,577 kj/mol Web ionization energy increases here. In this article, i have discussed in detail how to easily write the complete electron configuration of aluminum. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2: On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period. Web to draw a successive ionization energy diagram for aluminum, we will use the ionization energy data given on page 60. Periodic properties of the elements Thus, many students find it confusing that, for example, the 5p orbitals fill immediately after the 4d, and immediately before the 6s.the filling order is based on observed experimental results, and has been confirmed by theoretical calculations. The ionization energy is measured in joules (j) or electron volts (ev). But even that wouldn’t work well since gallium (the element beneath aluminum) has about the same first ionization energy as aluminum.Ionisation Energy AS Level Teaching Resources

Question Video Correlation between Ionization Energy and Electron

12.1 Successive ionisation energies (HL) YouTube

Atomic structure
Ionization energy Chemistry Steps

Explaining Successive Ionisation Energies YouTube
Electron arrangements

Atomic structure

Successive Ionisation Energy vigglegiggle
Ionization energy Chemistry Steps
Web The Successive Ionization Energy Diagram Is Shown In The Picture Below.
Web Ionization Energy Chart Of All The Elements Is Given Below.
2Nd Ionization Energy, 1816 Kj ⋅ Mol−1;
And Then Beryllium And Magnesium Are On The Other Side Of The Periodic Table In Terms Of Group Two Way.
Related Post:
