Draw And Label A Phospholipid
Draw And Label A Phospholipid - Phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phospholipid molecules. Web this short clip from the lesson lipids: The phosphorylated component contains ethanolamine here. Web start studying phospholipid structure labeling. Step 2/3 next, we can draw two straight lines extending from the head to represent the fatty acid chains. Web in this video, we're going to actually explore in detail the structure of phospholipids in our cell membrane. Web (a) an electron micrograph of unfixed, unstained phospholipid vesicles—liposomes—in water rapidly frozen to liquid nitrogen temperature. The two tails are made up of fatty acids (chains of carbon atoms) that aren’t compatible with, or repel, water ( hydrophobic ). Each phospholipid is made up of two fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a glycerol molecule. The head is a phosphate molecule that is attracted to water ( hydrophilic ). Web draw the general structure of a phospholipid. Step 2/3 next, we can draw two straight lines extending from the head to represent the fatty acid chains. Web the phospholipid bilayer consists of two adjacent sheets of phospholipids, arranged tail to tail. Phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phospholipid molecules. Web 1) phospholipids there are. A phospholipid is a lipid that contains a phosphate group and is a major component of cell membranes. A phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule which means it has both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic component. Phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phospholipid molecules. Web to draw a simple phospholipid, we can start by drawing a. The hydrophobic tails associate with one another, forming the interior of the membrane. This phospholipid contains hexahydric alcohol called inositol in its phosphorylated component. Lipids are molecules that include fats, waxes, and some vitamins, among others. Web start studying label the phospholipid bilayer. This imparts the amphiphilic nature to phospholipids. We will explore its components, structure, functions, examples & all about it. And all of this is held together by glycerol backbone. Web start studying phospholipid structure labeling. This phospholipid contains hexahydric alcohol called inositol in its phosphorylated component. Gardening biology basics branches of biology importance of biology domain archaea domain eukarya biological organization biological species concept biological. Each phospholipid is made up of two fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a glycerol molecule. Web start studying phospholipid structure labeling. Web (a) an electron micrograph of unfixed, unstained phospholipid vesicles—liposomes—in water rapidly frozen to liquid nitrogen temperature. This phospholipid has nitrogen containing choline in its phosphorylated component. Web to draw a simple phospholipid, we can start by drawing. This phospholipid has nitrogen containing choline in its phosphorylated component. The bilayer structure of the liposomes is readily apparent. Web (a) an electron micrograph of unfixed, unstained phospholipid vesicles—liposomes—in water rapidly frozen to liquid nitrogen temperature. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Describe the occurrence and importance of phosphoglycerides in plant and animal tissues. Step 2/3 next, we can draw two straight lines extending from the head to represent the fatty acid chains. The head is a phosphate molecule that is attracted to water ( hydrophilic ). Inside the circle, we can draw a phosphate group (po4) and a glycerol molecule (c3h8o3). This phospholipid has nitrogen containing choline in its phosphorylated component. Web phospholipids. Biological membranes usually involve two layers of phospholipids with their tails pointing inward, an arrangement called a phospholipid bilayer. Lipids are molecules that include fats, waxes, and some vitamins, among others. A phospholipid is a type of lipid molecule that is the main component of the cell membrane. The head is a phosphate molecule that is attracted to water (. And all of this is held together by glycerol backbone. Web start studying phospholipid structure labeling. (a) on the diagram (right) label the hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends of the phospholipid. Drawing of the fluid mosaic model. This imparts the amphiphilic nature to phospholipids. Web the chemical formulas for each part of the phospholipid structure can be seen below: The hydrophilic (polar) head group and hydrophobic tails (fatty acid chains) are depicted in. Just to briefly remind us, our phospholipid is often drawn like this. Biological membranes usually involve two layers of phospholipids with their tails pointing inward, an arrangement called a phospholipid bilayer.. Biological membranes usually involve two layers of phospholipids with their tails pointing inward, an arrangement called a phospholipid bilayer. Web draw the general structure of a phosphoglyceride. Web to draw a simple phospholipid, we can start by drawing a circle to represent the head. Describe the occurrence and importance of phosphoglycerides in plant and animal tissues. Web this short clip from the lesson lipids: The phosphorylated component contains ethanolamine here. A phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule which means it has both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic component. The hydrophilic (polar) head group and hydrophobic tails (fatty acid chains) are depicted in. Just to briefly remind us, our phospholipid is often drawn like this. Web the chemical formulas for each part of the phospholipid structure can be seen below: The head and the two tails. (b) a drawing of a small spherical liposome The polar heads contact the fluid inside and outside of the cell. The two tails are made up of fatty acids (chains of carbon atoms) that aren’t compatible with, or repel, water ( hydrophobic ). Step 2/3 next, we can draw two straight lines extending from the head to represent the fatty acid chains. The hydrophobic tails, each containing either a saturated or an unsaturated fatty acid, are long hydrocarbon chains.
Phospholipid Structure Labeling Diagram Quizlet
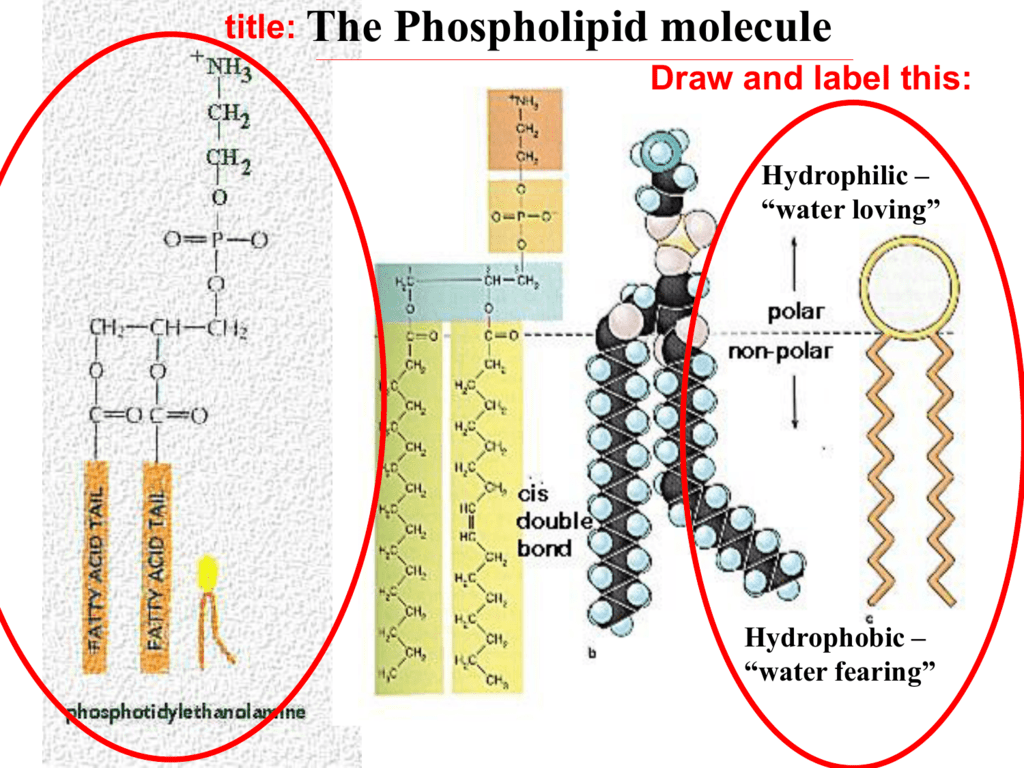
On the back of it draw and label the phospholipid

Lipids · Microbiology
14.3 Phospholipids in Cell Membranes Chemistry LibreTexts
/phospholipid_molecule-58adc6f95f9b58a3c9d1143f.jpg)
How Phospholipids Help Hold a Cell Together
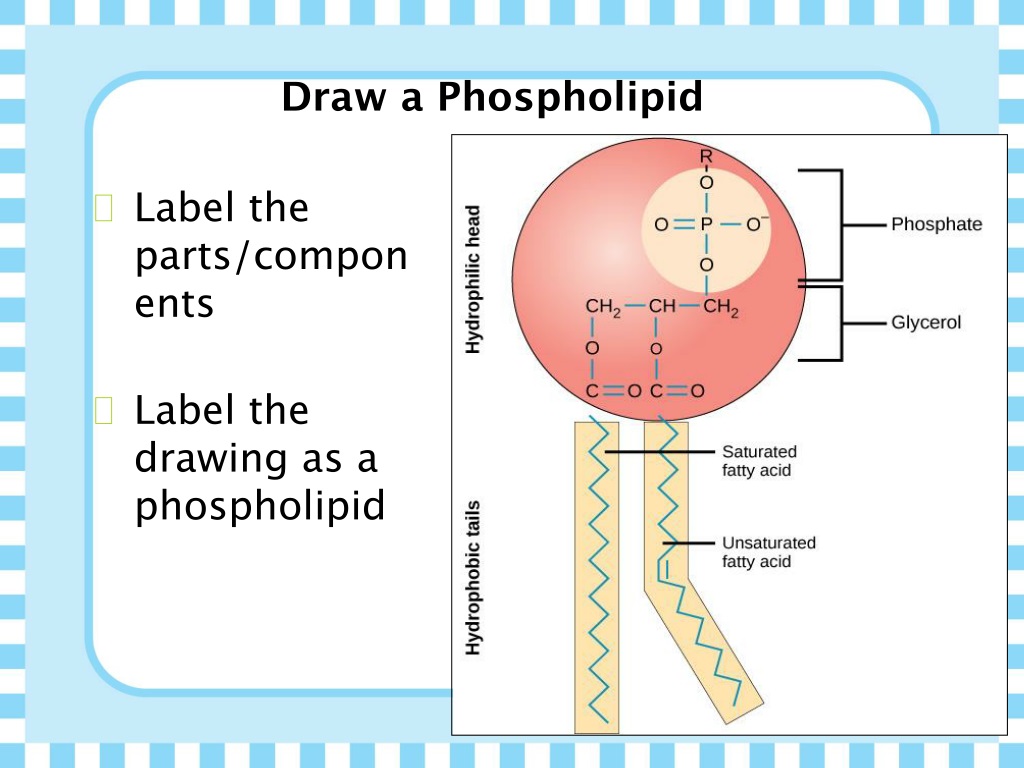
label the different components of a phospholipid. Membrane plasma
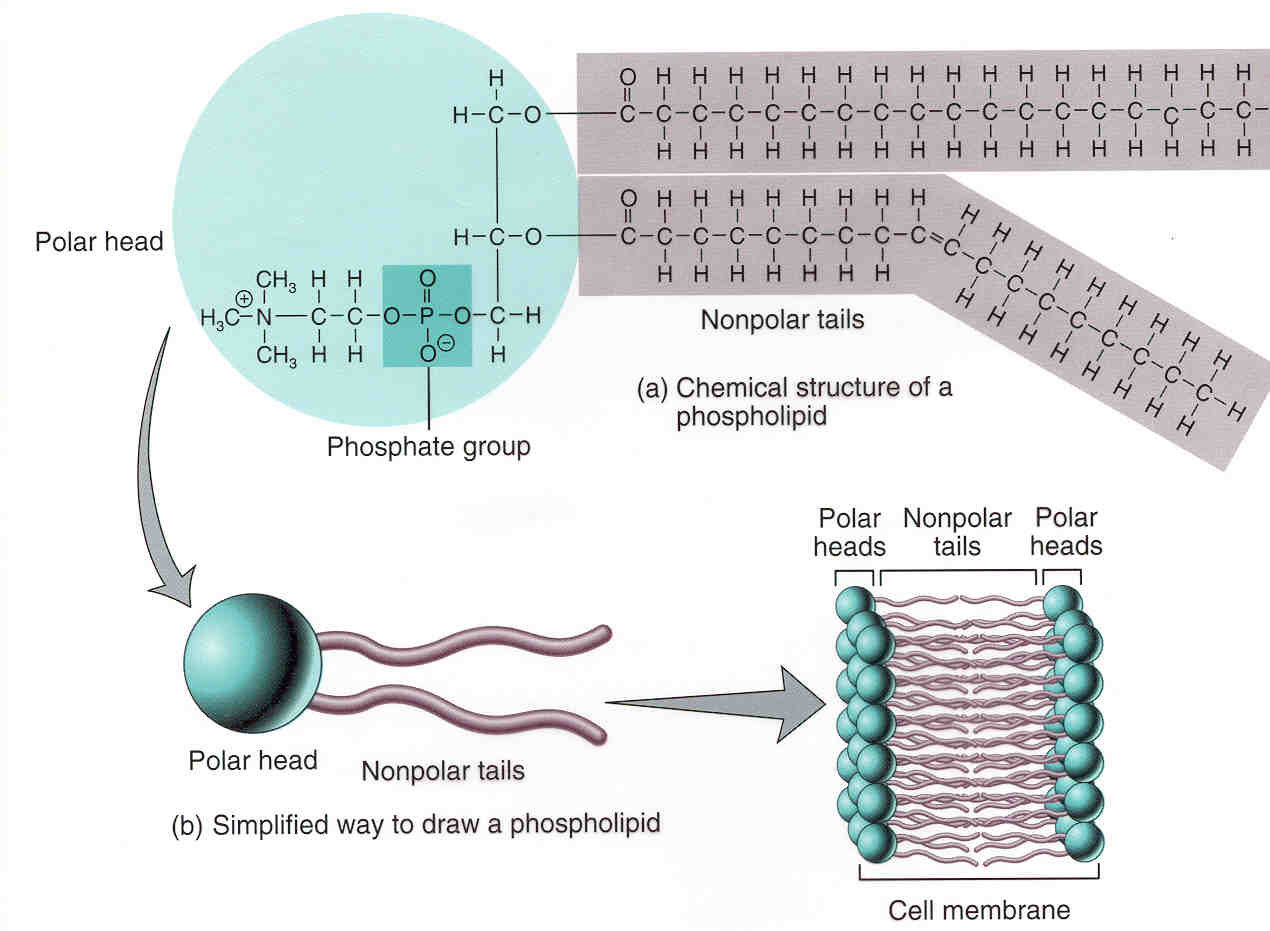
Phospholipid Bilayer Introduction, Structure and Functions

33 Label The Different Components Of A Phospholipid Label Design

How to Draw a Phospholipid Bilayer YouTube

3.5C Phospholipids Biology LibreTexts
The Bilayer Structure Of The Liposomes Is Readily Apparent.
We Will Explore Its Components, Structure, Functions, Examples & All About It.
The Hydrophobic Tails Associate With One Another, Forming The Interior Of The Membrane.
This Phospholipid Has Nitrogen Containing Choline In Its Phosphorylated Component.
Related Post:
