Draw Eukaryotic Cell
Draw Eukaryotic Cell - Although the eukaryotic nucleus breaks down during mitosis and meiosis as chromosomes form and cells divide, it spends most of its time in interphase, the time between cell divisions.this is where the status of genes (and therefore of the proteins. Web the division cycle of most eukaryotic cells is divided into four discrete phases: The nucleus separates the genetic blueprint, i.e., dna from the cell cytoplasm. Web 5 years ago 'pro' is a prefix which means primitive. For example, plant cells have chloroplasts, organelles that resemble mitochondria and are responsible for turning sunlight into useful energy for the cell (this is like. The features of eukaryotic cells are as follows: Web in this video showing how to draw a eukaryotic cell in easy steps. Web so far we’ve covered basic organelles found in a eukaryotic cell. It is made up of several types of organelles that. Web eukaryotic cells 2.3.1 draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell. That said, a prokaryotic living is a creature which has primitive/unidentified nucleus. Gene regulation is the process of controlling which genes in a cell's dna are expressed (used to make a functional product such as a protein). Eukaryotic cells are usually larger than prokaryotic cells, and they are found mainly in multicellular organisms. M, g 1, s, and g 2.. 2.3.2 annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the functions of each named structure. Web our natural world also utilizes the principle of form following function, especially in cell biology, and this will become clear as we explore eukaryotic cells (figure 4.3.1 4.3. Also identifying the difference between the plant and animal cell structure (both eukaryotic cells). Although the eukaryotic nucleus. It is made up of several types of organelles that. However, eukaryotic means a creature which has an identifiable nucleus. The cell grows (more.) the duration of these cell cycle phases varies considerably in different kinds of cells. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms. A typical eukaryotic cell is shown in figure below. It is made up of several types of organelles that. Overview of the cell and its contents. M, g 1, s, and g 2. Web characteristics of eukaryotic cells. Web in this video showing how to draw a eukaryotic cell in easy steps. M phase (mitosis) is usually followed by cytokinesis. Interphase and the mitotic (m) phase. Web unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: The cell is the smallest functional unit within a living organism, which can function independently. Interphase and the mitotic (m) phase. For example, plant cells have chloroplasts, organelles that resemble mitochondria and are responsible for turning sunlight into useful energy for the cell (this is like. The nucleus separates the genetic blueprint, i.e., dna from the cell cytoplasm. That said, a prokaryotic living is a creature which has primitive/unidentified nucleus. M, g 1, s, and. 2.3.2 annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the functions of each named structure. Overview of the cell and its contents. Web unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 'karyot' in the other hand means nucleus. M phase (mitosis) is usually followed by cytokinesis. Above all, eukaryotic cells are defined by the presence of a nucleus surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Although the eukaryotic nucleus breaks down during mitosis and meiosis as chromosomes form and cells divide, it. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Web drawing eukaryotic cells and annotating the functions of each of the organelles. Flagella and cilia are the locomotory organs in a eukaryotic cell. Different cells in a multicellular organism may express very different sets. Web unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: Above all, eukaryotic cells are defined by the presence of a nucleus surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Web so far we’ve covered basic organelles found in a eukaryotic cell. Web eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a nucleus. Web the division cycle of most eukaryotic cells is divided into four discrete phases: 'karyot' in the other hand means nucleus. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Web eukaryotic cells 2.3.1 draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell. Overview of the cell and its contents. The nucleus separates the genetic blueprint, i.e., dna from the cell cytoplasm. Web 5 years ago 'pro' is a prefix which means primitive. These organisms are grouped into the biological domain eukaryota. M, g 1, s, and g 2. M phase (mitosis) is usually followed by cytokinesis. Also identifying the difference between the plant and animal cell structure (both eukaryotic cells). Web eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a nucleus. Web unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: That said, a prokaryotic living is a creature which has primitive/unidentified nucleus. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: It is made up of several types of organelles that. Web how to draw eukaryotic cell/ step by step drawing for beginners eukaryotic cell, eukaryotic cell diagram, step by step drawing for beginners, biology diagram, diagrams, how to draw.
Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cellular Structures ALevel Biology

Eukaryotic cell diagram easy How to draw Eukaryotic cell diagram step
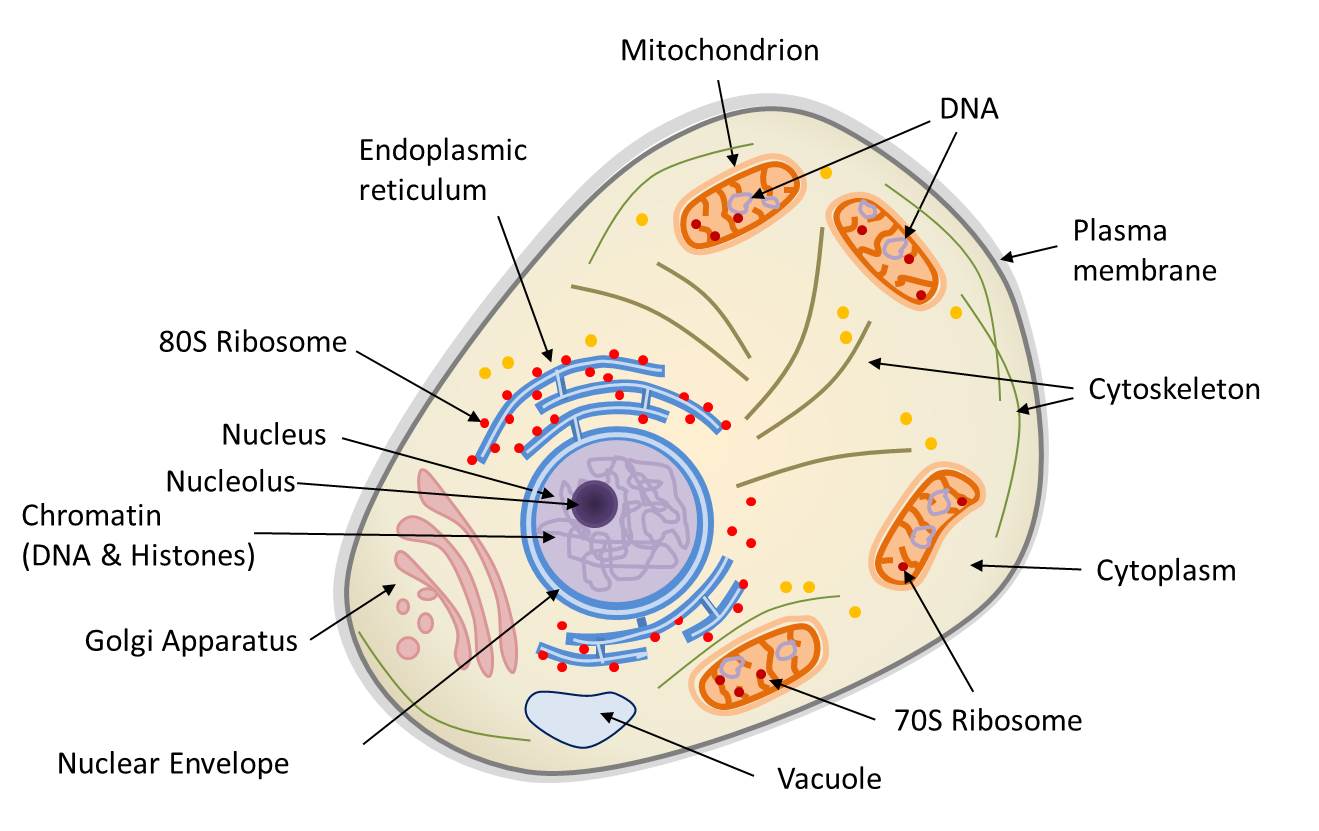
Symbiosis and evolution at the origin of the eukaryotic cell
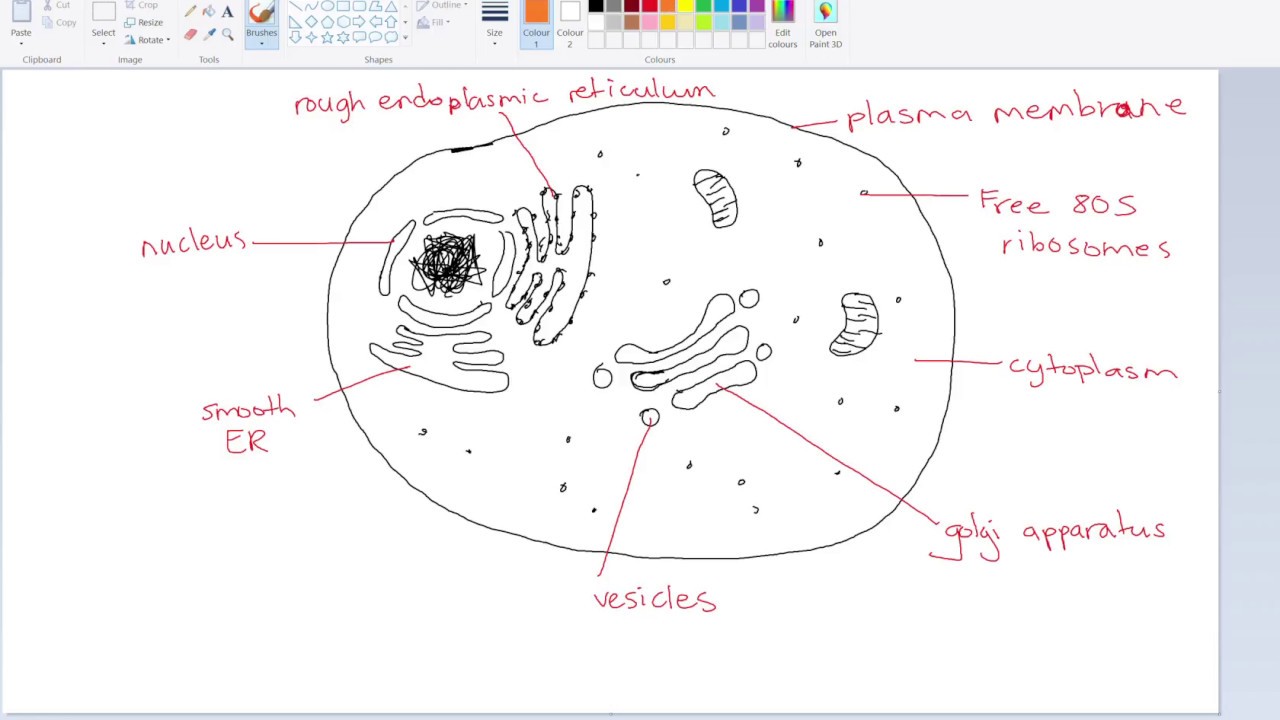
How to draw a Eukaryotic Cell IB Biology YouTube

Biology 101 Cells Owlcation
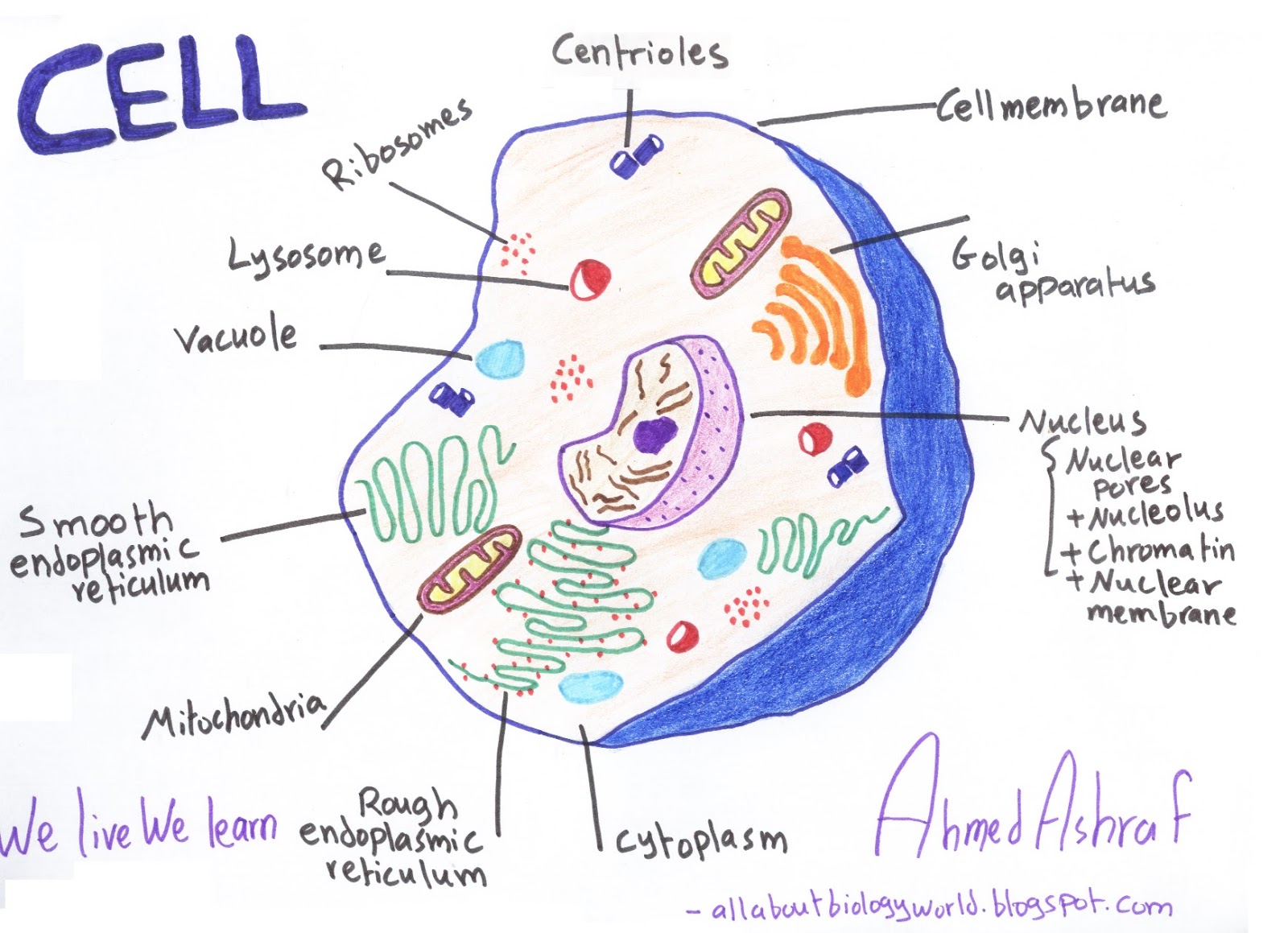
Biology Club Our cells 1 ( structure, function, division, disorder
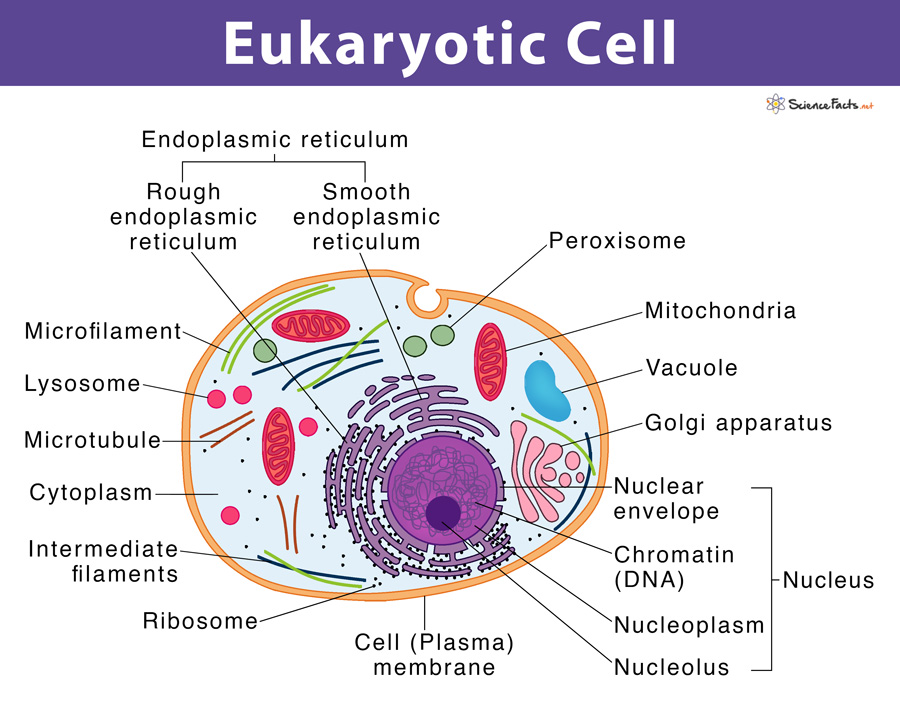
Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Structure, & Examples

Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Characteristics, Structure and Examples

Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell Drivenheisenberg
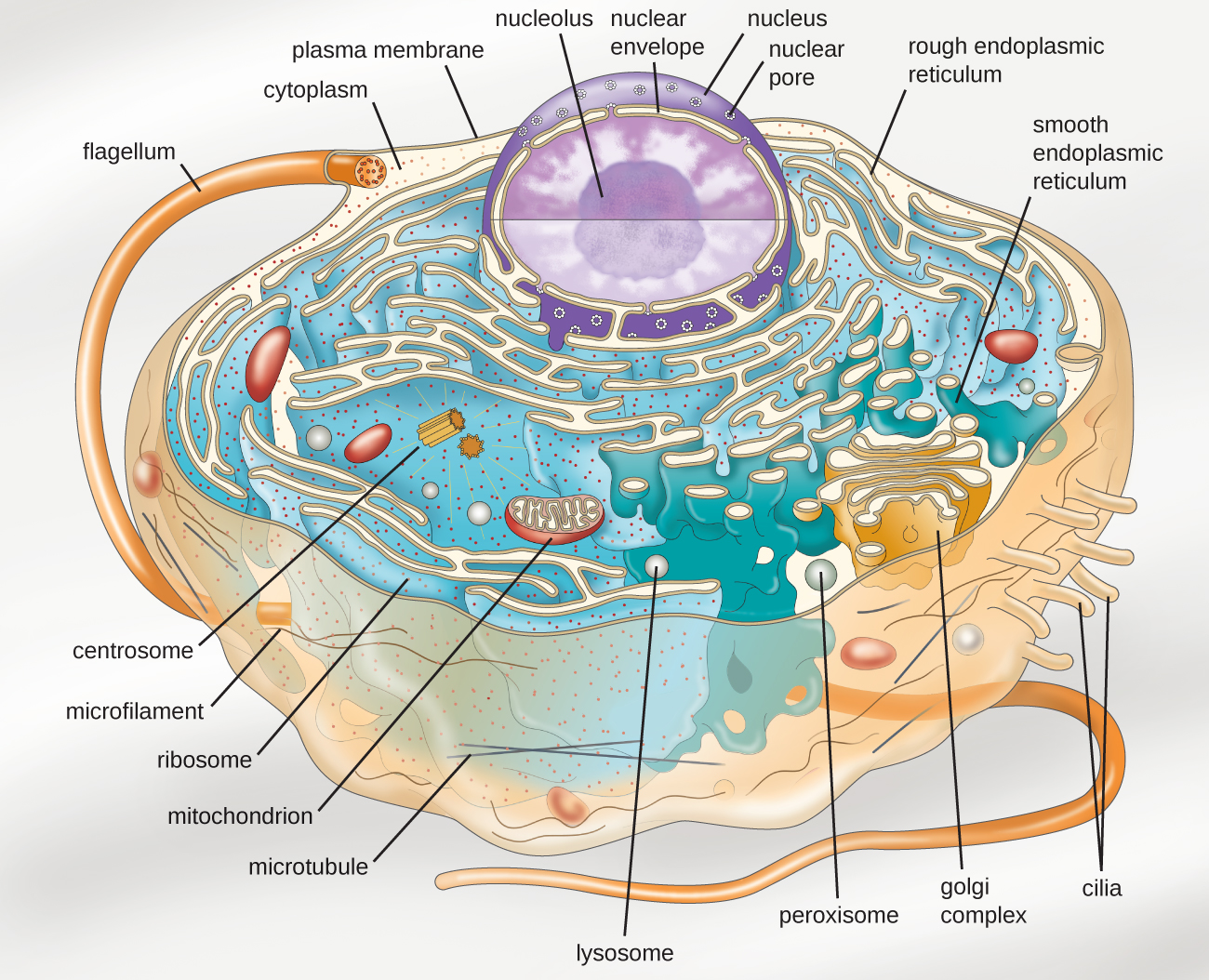
3.4 Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology 201
Web Our Natural World Also Utilizes The Principle Of Form Following Function, Especially In Cell Biology, And This Will Become Clear As We Explore Eukaryotic Cells (Figure 4.3.1 4.3.
Above All, Eukaryotic Cells Are Defined By The Presence Of A Nucleus Surrounded By A Complex Nuclear Membrane.
Web In This Video Showing How To Draw A Eukaryotic Cell In Easy Steps.
However, Not Every Cell Has Each Of These Organelles, And Some Cells Have Organelles We Haven’t Discussed.
Related Post: