Draw The Basic Structure Of A Nucleotide
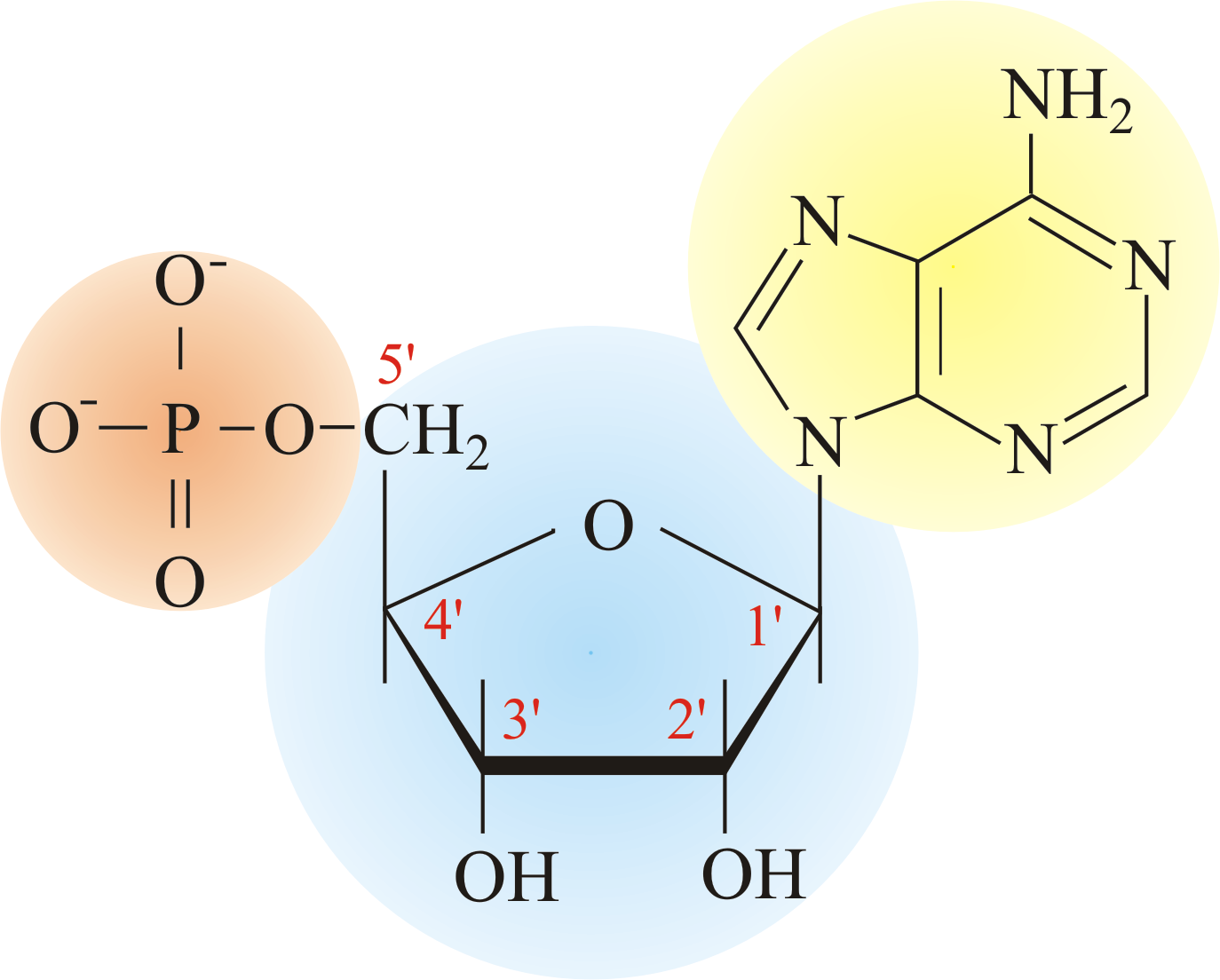
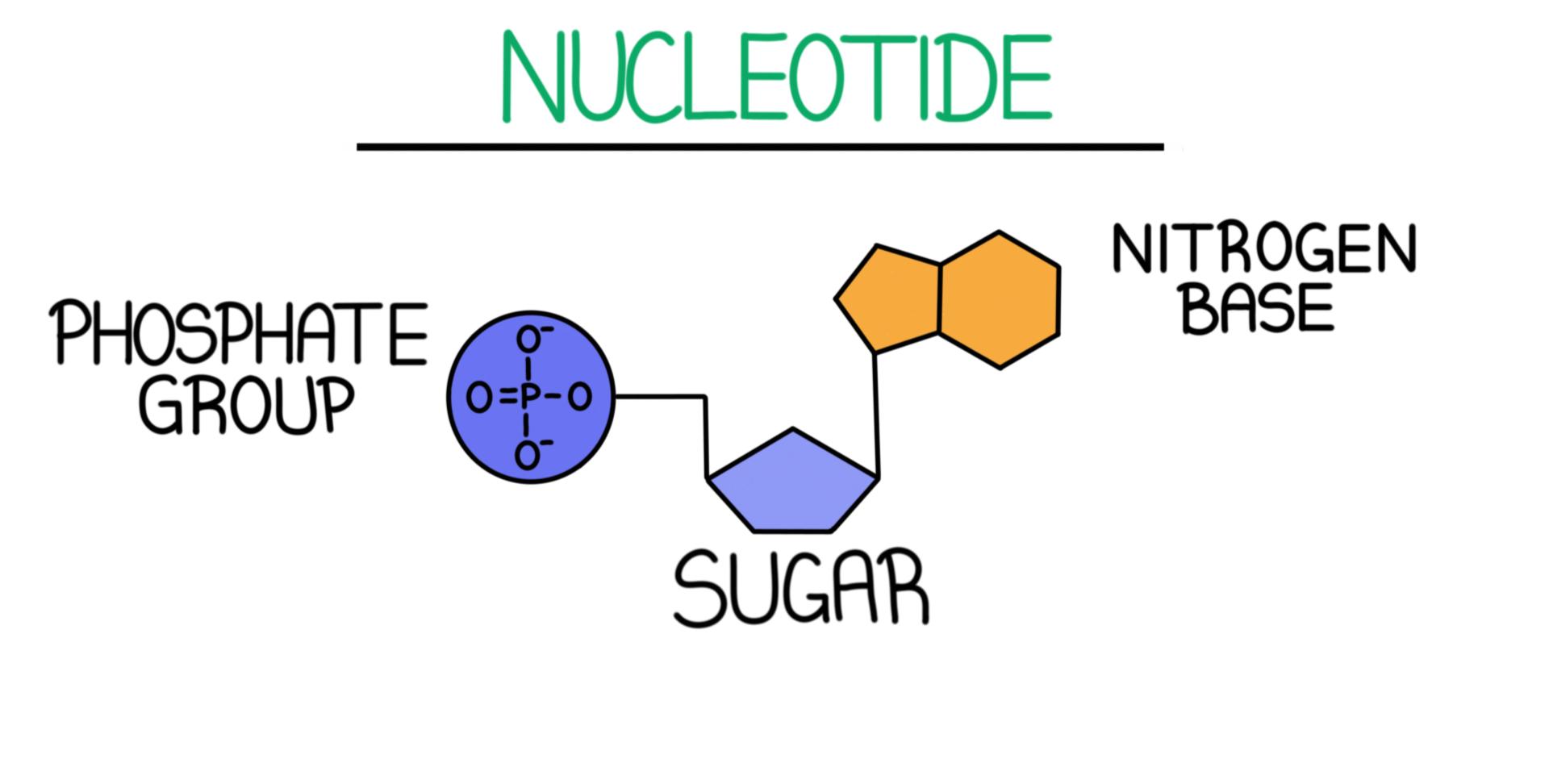
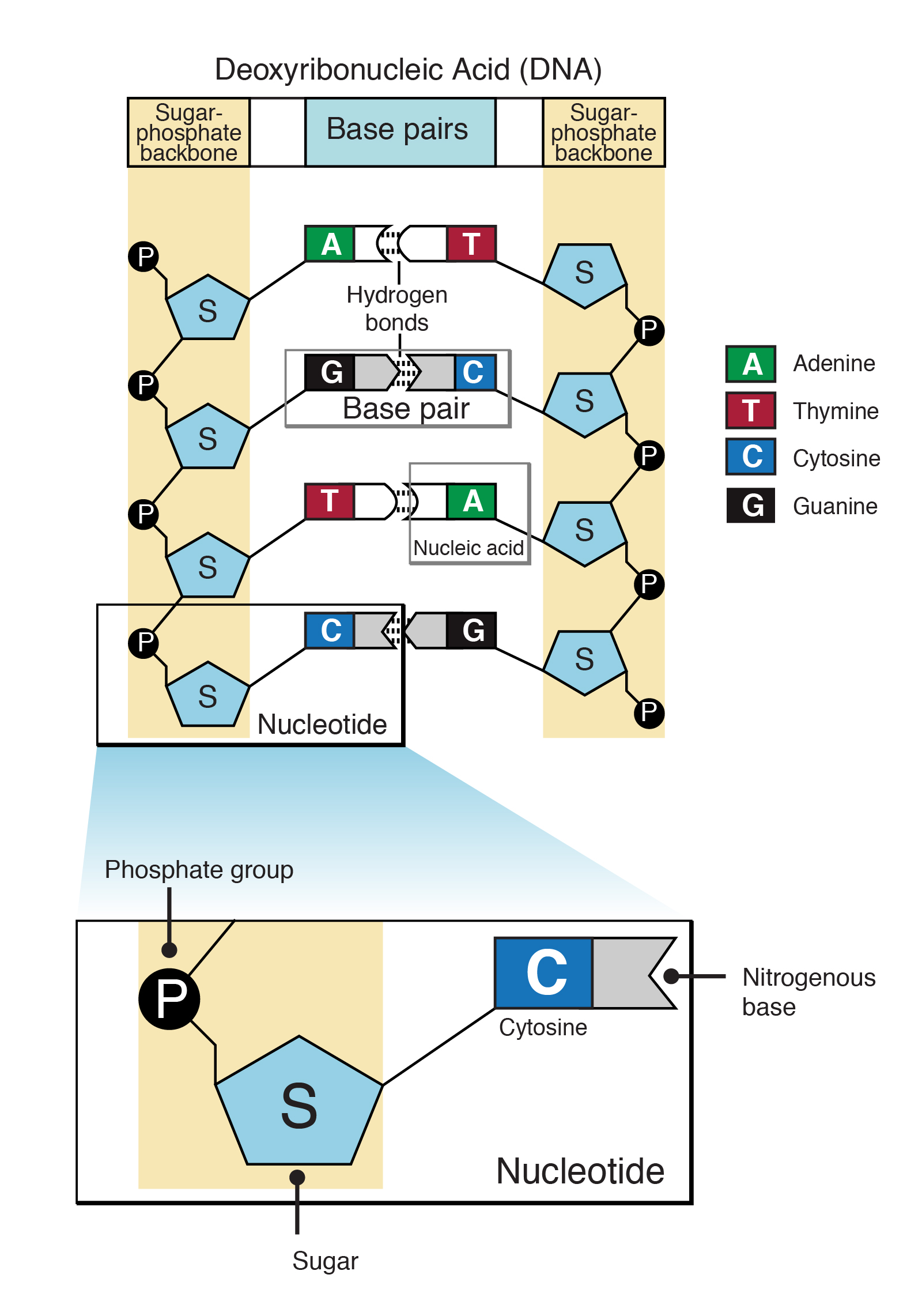
Draw The Basic Structure Of A Nucleotide - Nucleotides are an essential part of dna, rna, and cell function, and they can serve many purposes depending on their structure and chemical compounds. The four nucleobases in dna are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; The nitrogenous base can be a purine, such as adenine (a) and guanine (g), or a pyrimidine, such as. Draw a simple diagram of the structure of dna, identify and label the 5’ and 3’ ends on a dna or rna diagram Web a nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (rna and dna). The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. Hence, nucleotides are known as the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. Hydrogen bonds hold the structure together in the middle. A nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. Carbon residues in the pentose are numbered 1′ through 5′ (the prime distinguishes these residues from those in the base, which are numbered without using a prime notation). Nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. Web dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. The nitrogenous base can be a purine, such as adenine (a) and guanine (g), or a pyrimidine, such as. Indicate the nitrogen atom by which a given purine or pyrimidine base attaches to the sugar. Web the core structure of a nucleic acid monomer is the nucleoside, which consists of a sugar residue + a nitrogenous base that is attached to the sugar residue at the 1′ position as shown in figure \(\pageindex{2}\). Dna contains adenine (a), guanine (g), cytosine (c) and. Each of these chains is known as a dna chain, or a dna. A nucleotide comprises a pentose sugar. Hence, nucleotides are known as the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. Pay attention to bond angles and represent them as complete as possible. Web key concepts and summary. Web a dna molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotide subunits. The bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, pair up through hydrogen bonds, creating the rungs of the dna ladder. Sketch a section of nucleic acid to show. Web the building blocks of dna are nucleotides. Web nucleotides are a class of organic compounds that make up nucleic acid, the substance that defines hereditary traits of all living organisms. Web a. These substances play a role in various processes such as cell signalling, enzyme reactions. The sugar utilized for rna monomers is ribose, whereas dna monomers utilize deoxyribose that has lost the hydroxyl functional. Web draw the general structure of a nucleotide and a nucleoside. Nitrogenous base purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Web a dna molecule. Nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. Show all the atoms, bonds, and lone pairs. Pay attention to bond angles and represent them as complete as possible. The sugar molecule has a central position in the nucleotide, with the base attached to one of its carbons and the phosphate group (or groups) attached to another. Deoxyribonucleotides. Web [1] nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: The bases used in dna are adenine (a), cytosine (c), guanine (g) and thymine (t). The sugar molecule has a central position in the nucleotide, with the base attached to one of its carbons and the phosphate group (or groups) attached to another. The second portion of the nucleotide is the. Only the a phosphate is included in the polymer. Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. Sketch a section of nucleic acid to show. The four nucleobases in dna are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; A nucleotide comprises a pentose sugar. Pay attention to bond angles and represent them as complete as possible. These substances play a role in various processes such as cell signalling, enzyme reactions. Regardless of the nucleotide, the sugar is always the same. Web a nucleotide is made up of three components: In rna, uracil is used in place of thymine. Web draw the general structure of a nucleotide and a nucleoside. Web [1] nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: Web key concepts and summary. Web draw the basic structure of a single nucleotide (using circle, pentagon and rectangle). There are four nitrogenous bases in dna, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). Nitrogenous base purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. A nucleotide comprises a pentose sugar. Adenine and guanine are purines. Indicate the nitrogen atom by which a given purine or pyrimidine base attaches to the sugar component in nucleotides and nucleosides. Carbon residues in the pentose are numbered 1′ through 5′ (the prime distinguishes these residues from those in the base, which are numbered without using a prime notation). Dna and rna are simply long polymers of nucleotides called polynucleotides. Web both deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: Web the core structure of a nucleic acid monomer is the nucleoside, which consists of a sugar residue + a nitrogenous base that is attached to the sugar residue at the 1′ position as shown in figure \(\pageindex{2}\). This molecule is made up of two strands that wrap around each other. Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides, each of which contains a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains deoxyribose sugar and rna. There are four nitrogenous bases in dna, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). Pay attention to bond angles and represent them as complete as possible. Hence, nucleotides are known as the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. The nitrogenous base is the central information carrying part of the nucleotide structure. Each of these chains is known as a dna chain, or a dna strand.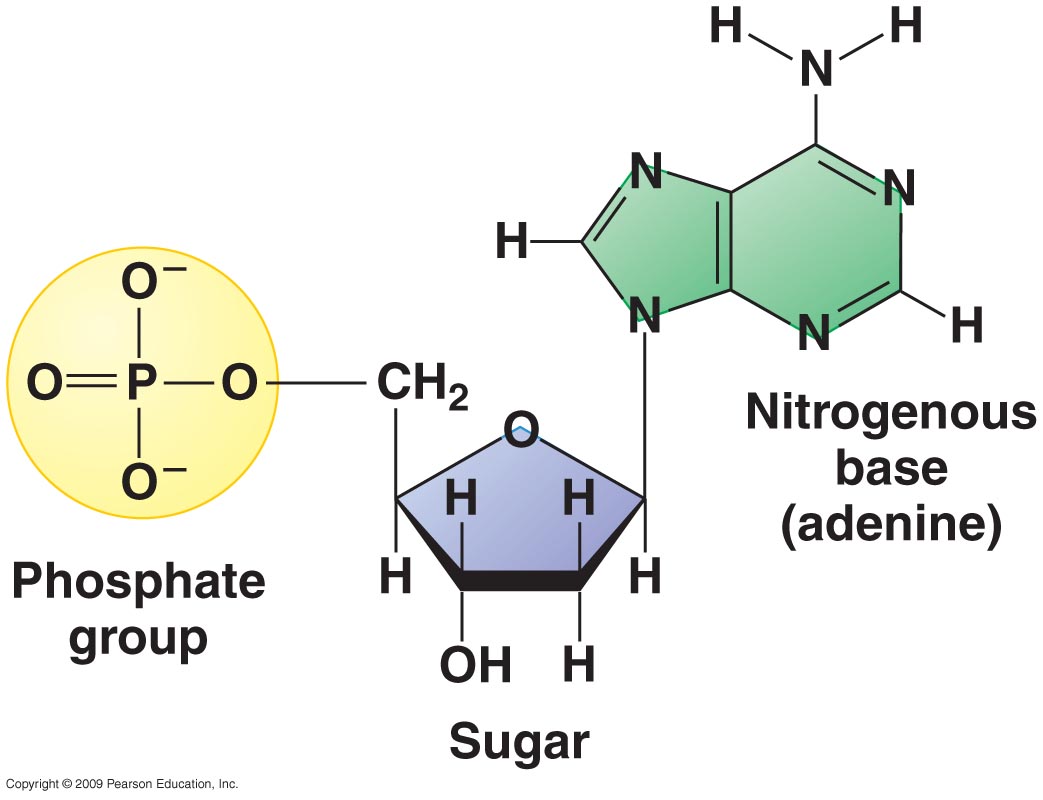
Nucleotides Castell Alun High School Biology
Nucleotide Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary
DNA Structure — Overview & Diagrams Expii
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotide_base-5b6335bdc9e77c002570743e.jpg)
Draw And Label The Three Parts Of A Nucleotide Pensandpieces
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected

What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?

Structure of a Nucleotide Tutorial Sophia Learning

Nucleotide Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function

What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
Nucleotide
Web Each Nucleotide Is Made Up Of Three Parts:
Dna Contains Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C) And.
In Rna, The Base Uracil (U) Takes.
Figure 9.3 (B) Cytosine And Thymine Are Pyrimidines.
Related Post: