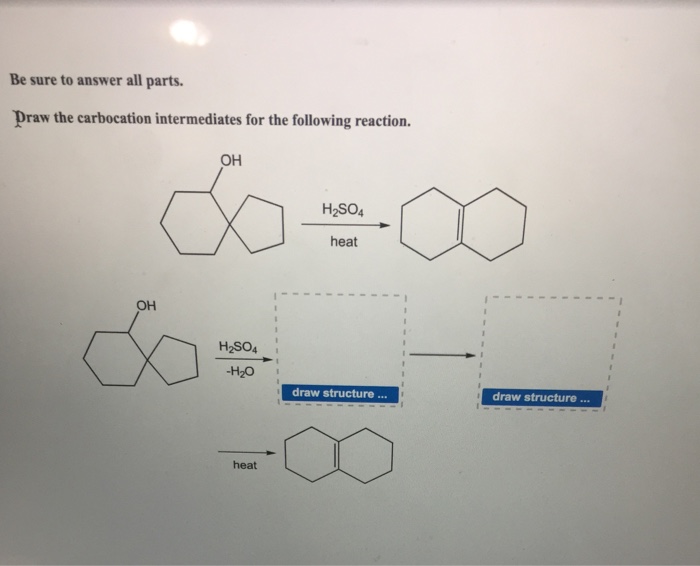
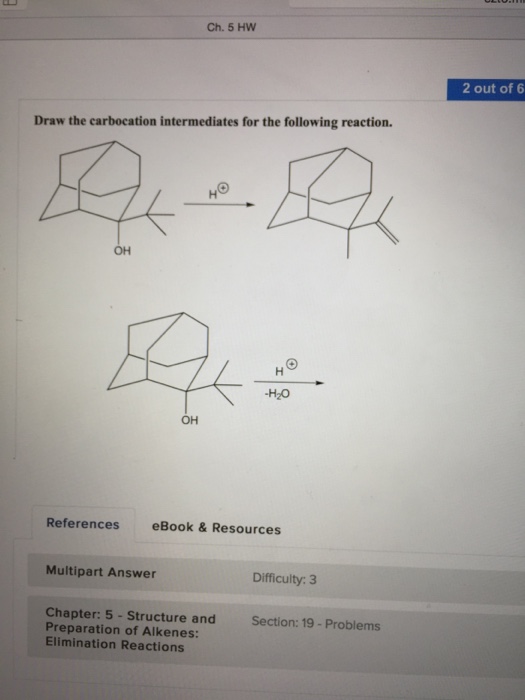
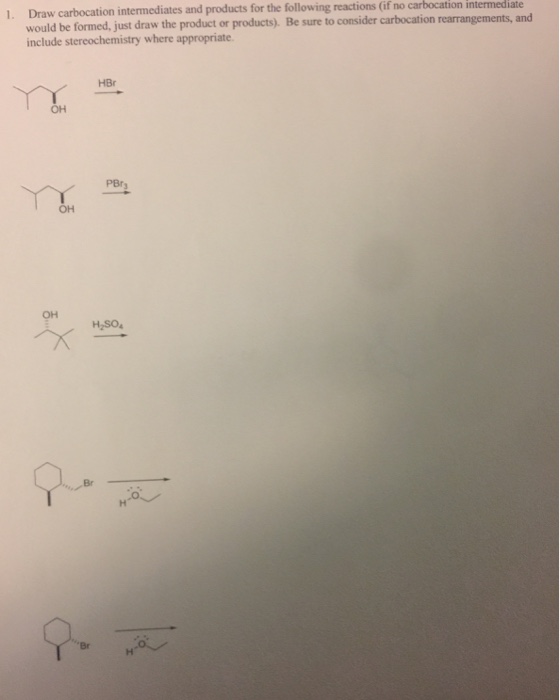Draw The Carbocation Intermediates For The Following Reaction
Draw The Carbocation Intermediates For The Following Reaction - Show 2 possible products for the reaction and what will favor elimination. Draw a mechanism for the following reaction with the cationic intermediate and explain the presence of both products2. First intermediate second intermediate heat this problem has been solved! Draw the product of the attached reaction, including stereochemistry. Identify the reaction and the starting material. Web 100% (8 ratings) top expert. Draw the carbocation intermediates for the following reaction. Web the following molecular model is that of a carbocation. In the first step the hydroxyl group is get protonated and then water molecule is removed which leads to the formation of the first intermediate with the secondary carbocation which is less stable as compared to the tertiary carbocation and therefore it undergoes the rearrangement where the methyl group is shifted to secondary. Comparing the relative stability of reaction intermediates. Since the charged carbon atom does not satisfy the octet rule, it is unstable and therefore highly reactive. Comparing the relative stability of reaction intermediates. Identify the intermediate carbocation as being primary, secondary, or tertiary. Be sure to answer all parts. Identify the reaction and the starting material. Web draw the carbocation intermediates for the following reaction this problem has been solved! Web organic chemistry with a biological emphasis by tim soderberg (university of minnesota, morris) a carbocation is a cation in which carbon has an empty p orbital and bears a positive charge creating a highly reactive intermediate. Draw the carbocation intermediates for the following reaction. A. Web it is important to know the hierarchy of reaction intermediates such as radicals, carbocations, carbanions. Draw a mechanism for the following reaction with the cationic intermediate and explain the presence of both products2. In the vinyl carbocation, the positive charge is on the carbon atom with the double bond therefore it is sp hybridized. Web science chemistry chemistry questions. Identify the allylic carbocation intermediates. It is not accurate to say, however, that carbocations with higher substitution are always more. If the substrate is one that does not undergo an el reaction, explain why. Draw the structures of both. Web organic chemistry with a biological emphasis by tim soderberg (university of minnesota, morris) a carbocation is a cation in which. Here we present a quick guide to reaction intermediate hierarchies. Oh khso4 170°c oh khso4 rearrangement h20 finish structure finish structure. • products resulting from more stable (rearranged) carbocation intermediates will be more abundant • products resulting from less stable (unrearranged) carbocation intermediates will be less abundant. For example, one of the key steps in the biosynthesis of cholesterol is. Web the empirical formula for vinyl cation is c2h3+. Show 2 possible products for the reaction and what will favor elimination. Draw two resonance structures for the carbocation, indicating the positions of the double bonds. Draw the carbocation intermediates for the following reaction. While, carbanions are the opposite: Comparing the relative stability of reaction intermediates. The following structure represents the carbocation intermediate formed in the addition reaction of hbr to two different alkenes. A carbocation is an organic molecule, an intermediate, that has a carbon atom bearing a positive charge and three bonds instead of four. 2 concept hydride shift 3m 7. This problem has been solved! Show 2 possible products for the reaction and what will favor elimination. Methyl carbocations are even less stable. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Draw two resonance structures for the carbocation, indicating the positions of the double bonds. Draw a mechanism for the following reaction with the cationic intermediate and. If it has carbocation intermediate draw it’s structure. The following structure represents the carbocation intermediate formed in the addition reaction of hbr to two different alkenes. This problem has been solved! Web 100% (8 ratings) top expert. The reaction given is not clear, but the starting material is aehehci. Identify the allylic carbocation intermediates. Web that said, in reactions with rearrangeable carbocation intermediates, you will typically get a mixture of products: Draw the structures of both. A carbocation is an organic molecule, an intermediate, that has a carbon atom bearing a positive charge and three bonds instead of four. While, carbanions are the opposite: As soon as the intermediate is formed in the first step by reaction of ethylene with h + , it reacts further with br − in a second step to give the final product, bromoethane. Web draw the carbocation intermediates for the following reaction this problem has been solved! Draw two resonance structures for the carbocation, indicating the positions of the double bonds. Web it is important to know the hierarchy of reaction intermediates such as radicals, carbocations, carbanions. Web organic chemistry with a biological emphasis by tim soderberg (university of minnesota, morris) a carbocation is a cation in which carbon has an empty p orbital and bears a positive charge creating a highly reactive intermediate. Web draw the carbocation intermediates for the following reaction. Web the following molecular model is that of a carbocation. 2 concept hydride shift 3m 7. In the vinyl carbocation, the positive charge is on the carbon atom with the double bond therefore it is sp hybridized. Identify the intermediate carbocation as being primary, secondary, or tertiary. In the first step the hydroxyl group is get protonated and then water molecule is removed which leads to the formation of the first intermediate with the secondary carbocation which is less stable as compared to the tertiary carbocation and therefore it undergoes the rearrangement where the methyl group is shifted to secondary. Oh khso4 170°c oh khso4 rearrangement h20 finish structure finish structure. Web chemistry questions and answers. Methyl carbocations are even less stable. Web 100% (8 ratings) top expert. Show 2 possible products for the reaction and what will favor elimination.Solved Draw the carbocation intermediates for the following
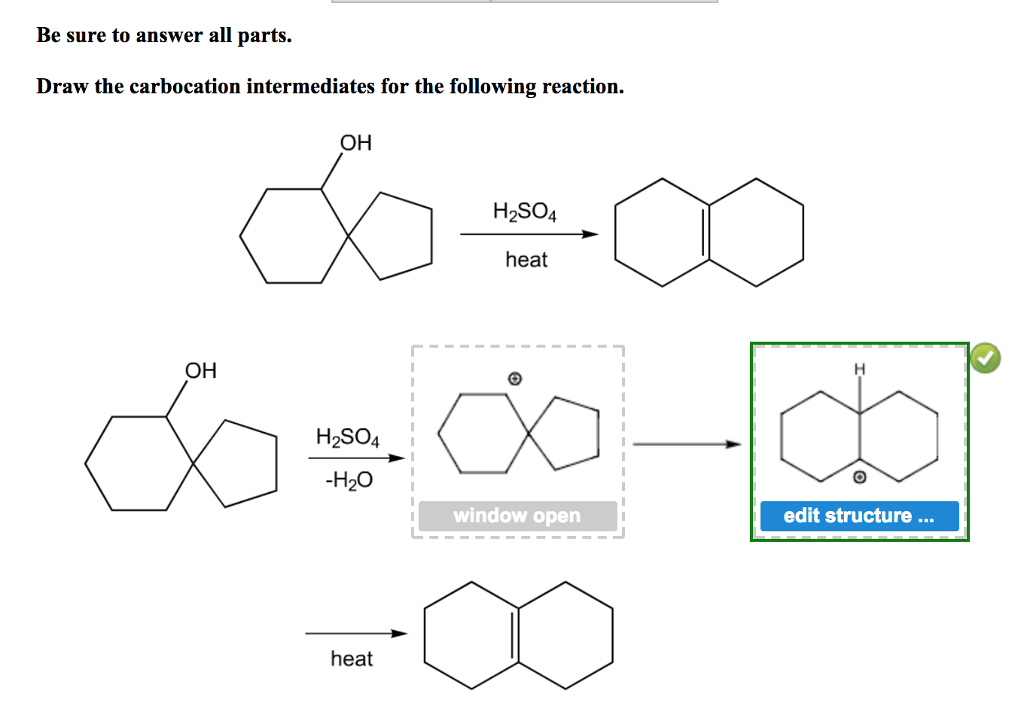
Solved Be sure to answer all parts. Draw the carbocation
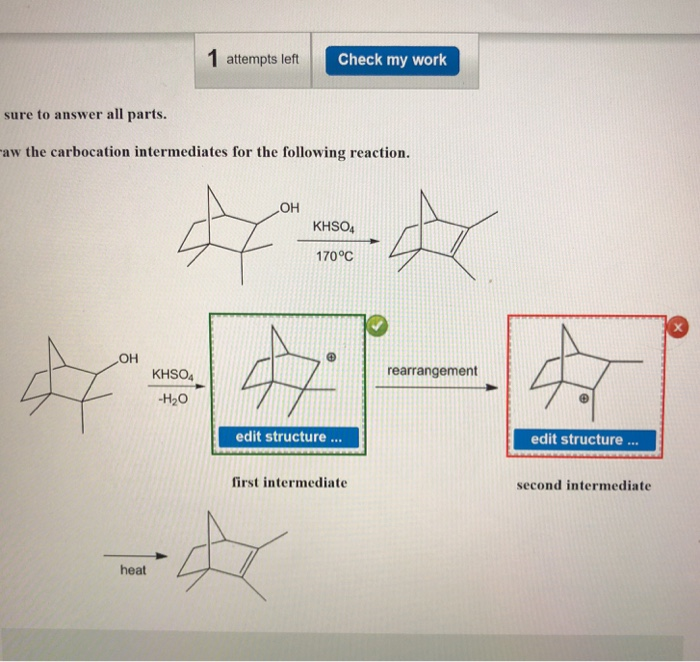
Solved Draw the carbocation intermediates for the following
Solved Draw the carbocation intermediates for the following
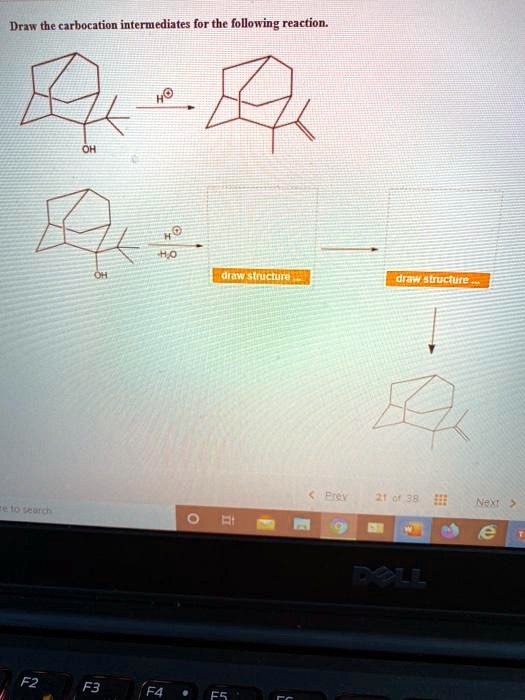
SOLVED Draw the carbocation intermediates for the following reaction
Solved Draw carbocation intermediates and products for the
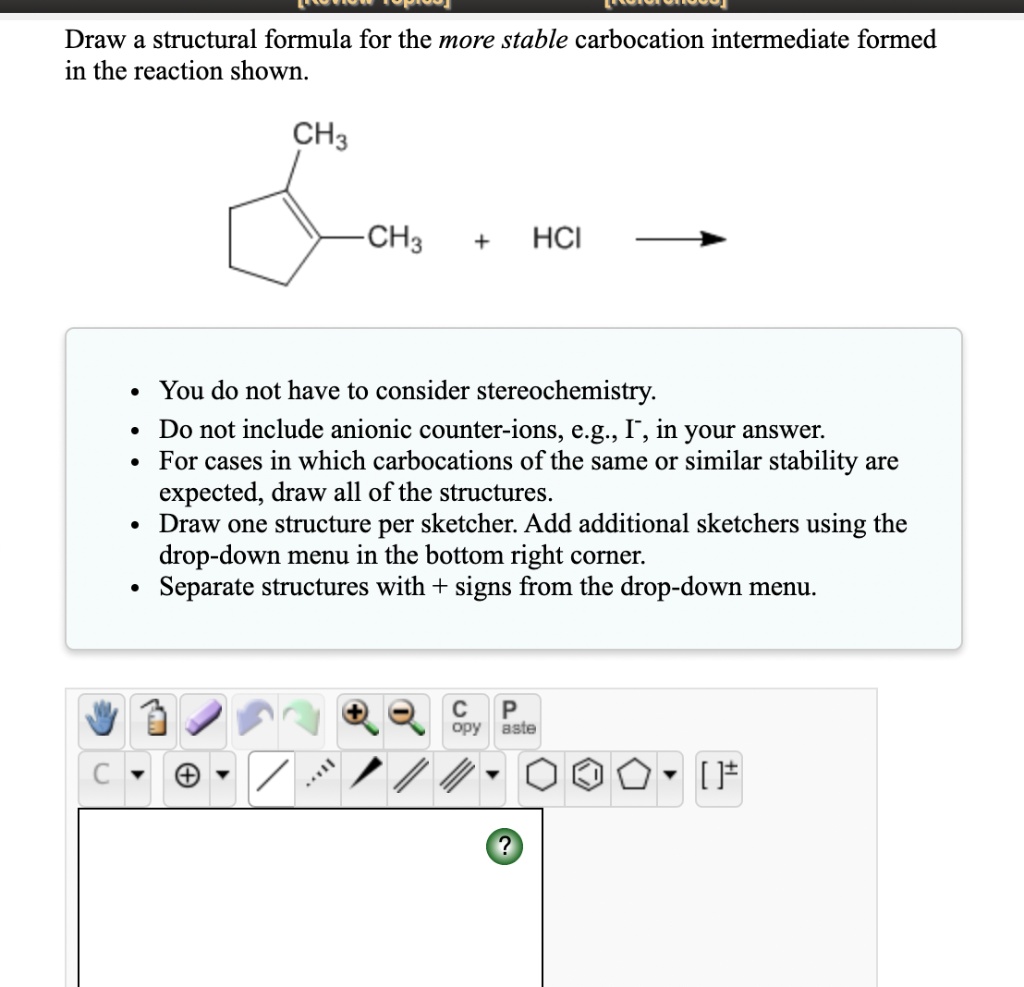
SOLVED Draw a structural formula for the more stable carbocation
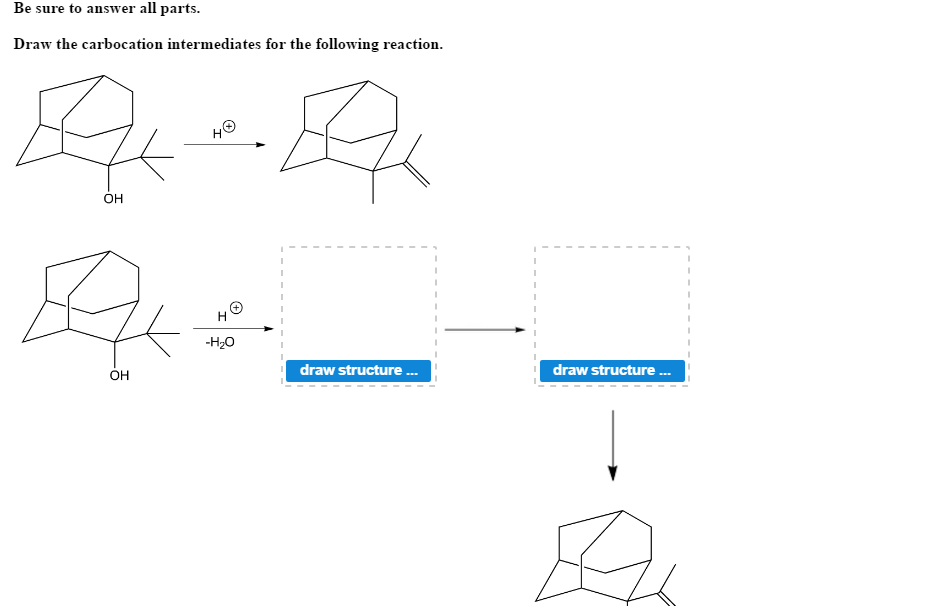
Solved Draw the carbocation intermediates for the following
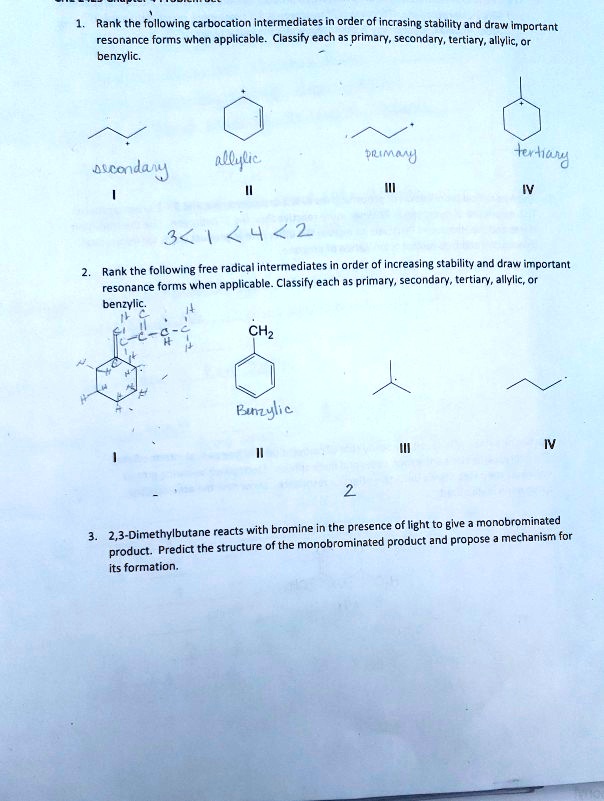
SOLVEDRank the following carbocation intermediates in order of
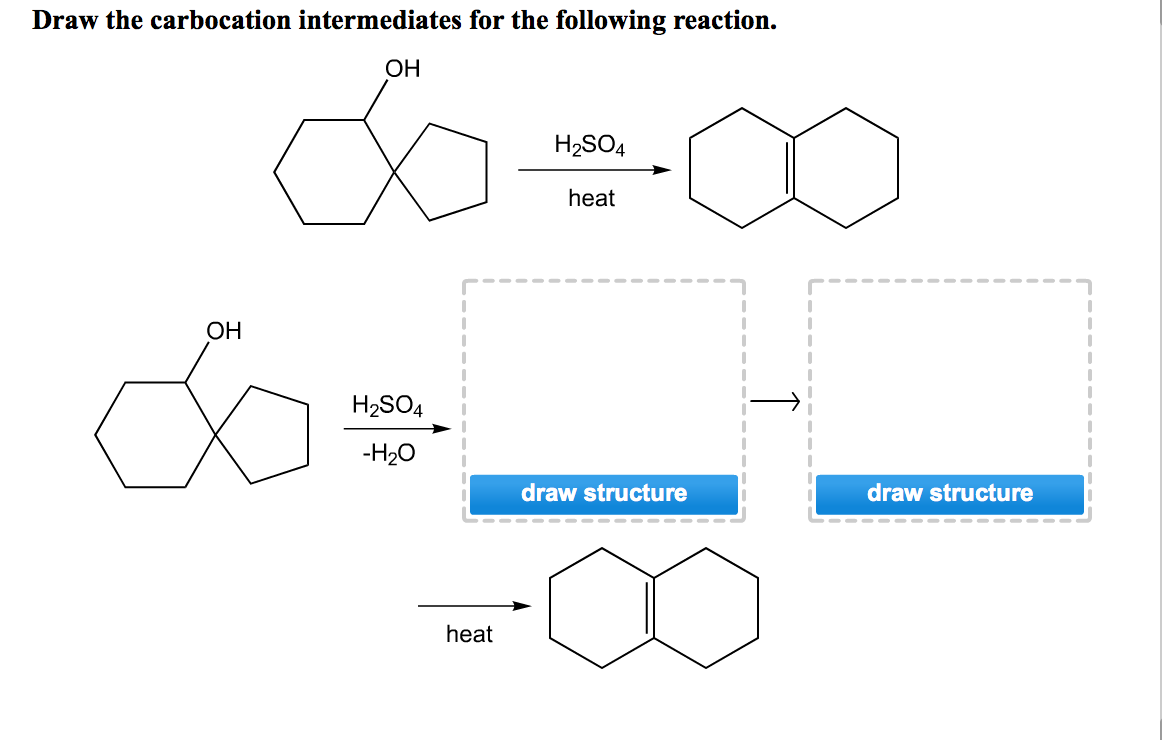
Solved Draw the carbocation intermediates for the following
Web The Empirical Formula For Vinyl Cation Is C2H3+.
Web Primary Carbocations Are Highly Unstable And Not Often Observed As Reaction Intermediates;
Draw The Structures Of The Alkenes And Rank Them According To The Amount That Would Be Formed.
The Reaction Given Is Not Clear, But The Starting Material Is Aehehci.
Related Post: