Draw The Free Body Diagram For The Following Problems
Draw The Free Body Diagram For The Following Problems - D) the beam in prob. D) the beam in prob. If the problem asks for it, use the net force to find mass or acceleration. B) the crane and boom in prob. Typically, a free body diagram consists of the following components: Subtract the forces in the negative direction from those in the positive direction. A) the beam in prob. In figure \(\pageindex{1a}\), a sled is pulled by force \(\vec{p}\) at an angle of 30°. Determine the reactions at the supports all problem solutions must include an fbd. This simplified diagram will allow us to more easily write out the equilibrium equations for statics or strengths of materials problems, or the equations of motion for dynamics problems. (a) identify all forces acting on the object. A) the cantilevered beam in prob. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. Determine the teactions at the supports at the fixed support a on the cantiliciered beam. B) the beam in prob. Web draw a free body diagram of the object. Web the first step in solving most mechanics problems will be to construct a free body diagram. Solution in this problem, the knowns are the magnitude and direction of force \(\vec{b}\) and moment \(\vec{c}\) and the dimensions of the beam. C) the beam in prob. Draw and label our long range. C) the rod in prob. C) the man and load in prob. Draw the object in isolation with the forces that act on it B) the rod in prob. Post any question and get expert help quickly. B) the rod in prob. A) the truss in prob. B) the beam in prob. Determine the components of the support reactions at the fixed support. However, it may help to indicate. (a) identify all forces acting on the object. Web the free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. D) the rod in prob. Commonly, air resistance and friction are neglected. (b) draw a suitable coordinate system. D) the beam in prob. At first, you may want to draw a circle around the object of interest to be sure you focus on labeling the forces acting on the object. It is a diagram including all forces acting on a given object without the other object in the system. D) the beam in prob. D) the beam in. You need to first understand all the forces acting on the object and then represent these force by arrows in the direction of the force to be. Draw the object under consideration; Web the first step in solving most mechanics problems will be to construct a free body diagram. Make sure the arrow lengths are relatively proportional to each other.. A) the cantilevered beam in prob. Draw the object in isolation with the forces that act on it D) the beam in prob. Hotell 6.25 m g2 6 m е g а b 2 m 11 m 1 m t1 mm prob. B) the beam in prob. D) the beam in prob. Web draw the contact forces on the dot with an arrow pointing away from the dot. Subtract the forces in the negative direction from those in the positive direction. C) the rod in prob. (b) draw a suitable coordinate system. A) the beam in prob. If the problem asks for it, use the net force to find mass or acceleration. Determine the forces that act on the object; Determine the teactions at the supports at the fixed support a on the cantiliciered beam. Make sure the arrow lengths are relatively proportional to each other. Hotell 6.25 m g2 6 m е g а b 2 m 11 m 1 m t1 mm prob. C) the rod in prob. A) the truss in prob. Web the first step in solving most mechanics problems will be to construct a free body diagram. That is, f net ≠ 0 f net ≠ 0 ). Determine the reactions at the supports all problem solutions must include an fbd. Solution in this problem, the knowns are the magnitude and direction of force \(\vec{b}\) and moment \(\vec{c}\) and the dimensions of the beam. B) the beam in prob. A) the beam in prob. Web the free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. Make sure the arrow lengths are relatively proportional to each other. B) the crane and boom in prob. D) the beam in prob. Deciding upon the relative size of opposing forces, 4. C) the beam in prob.[Solved] Draw freebody diagrams for each of the following objects in
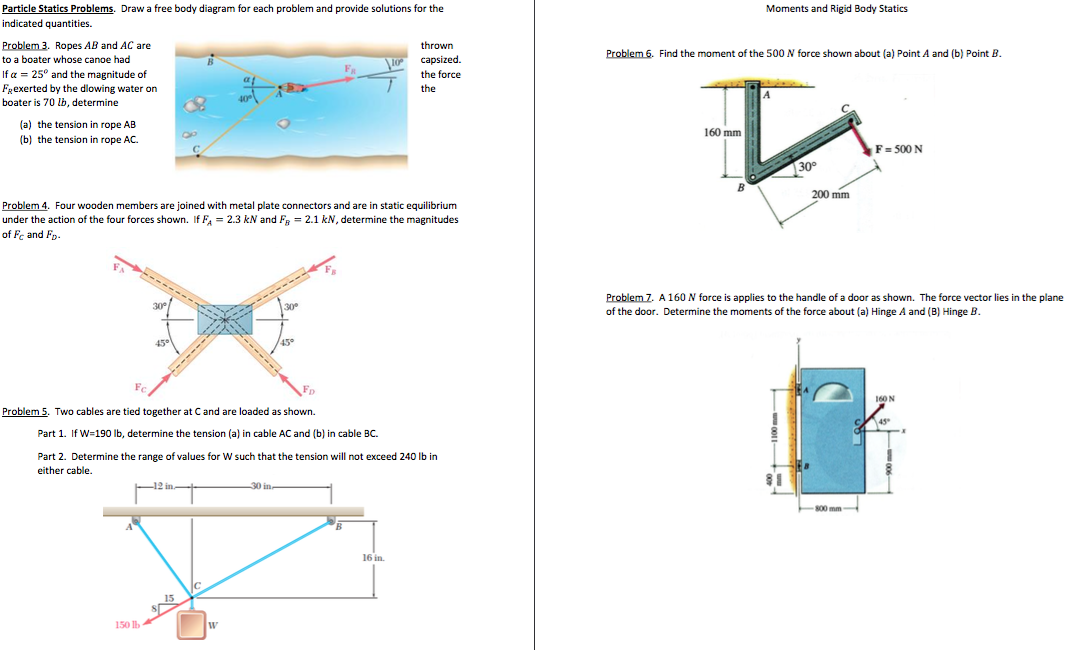
Solved Draw a free body diagram for each problem and provide

Solved Draw a Free Body Diagram and Utilize Newton's Second
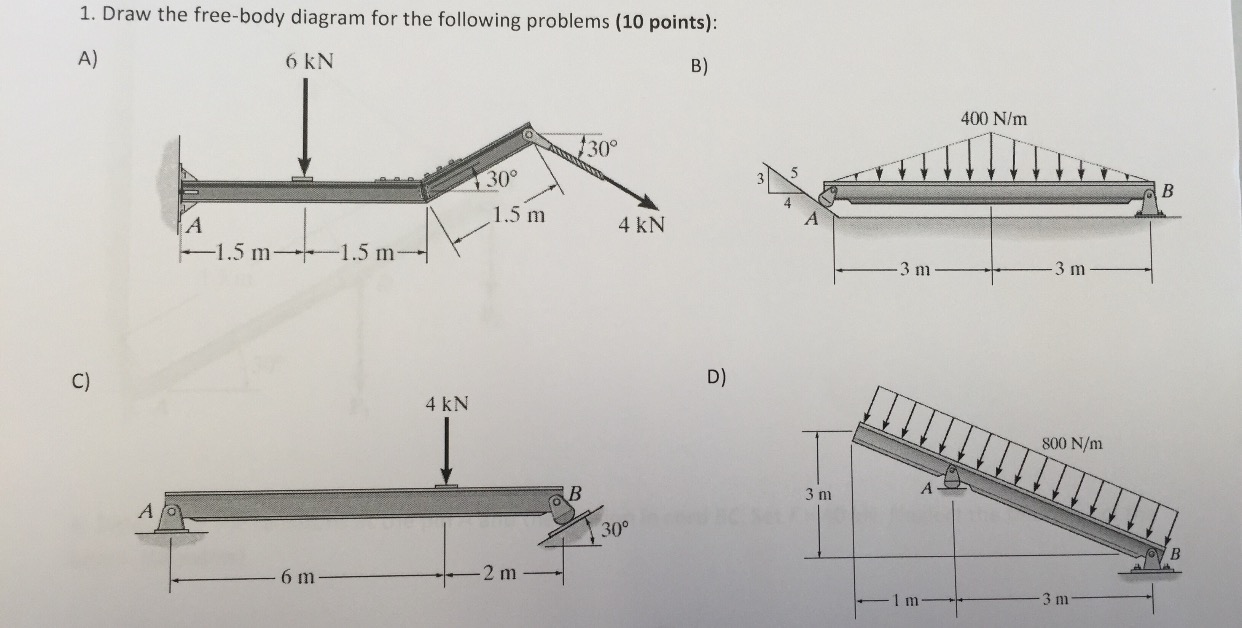
Solved Draw the freebody diagram for the following problems
Solved Draw free body diagram for the following situations
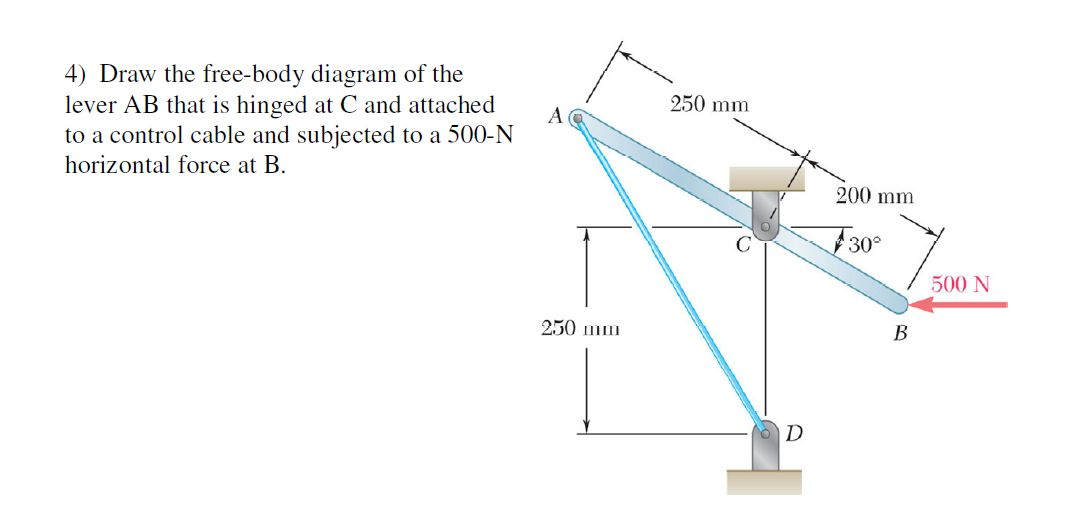
Solved Please draw free body diagrams for the following.
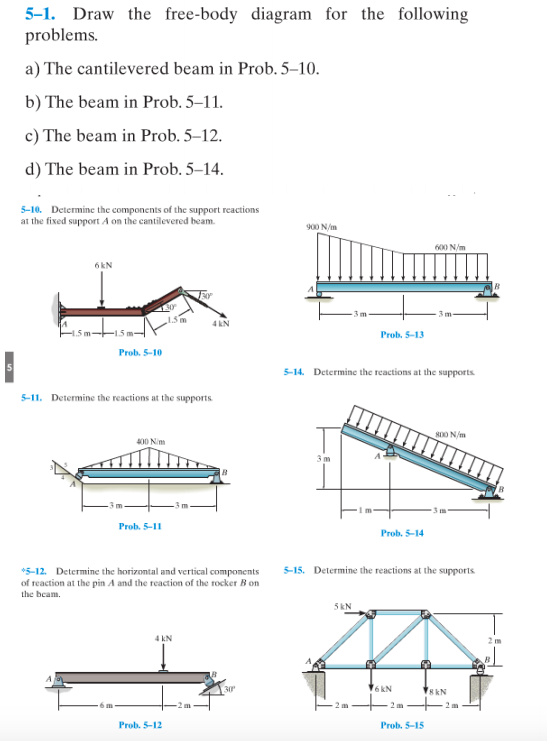
Solved 51. Draw the freebody diagram for the following

How to draw free body diagram??? Laws of Motion NEET JEE
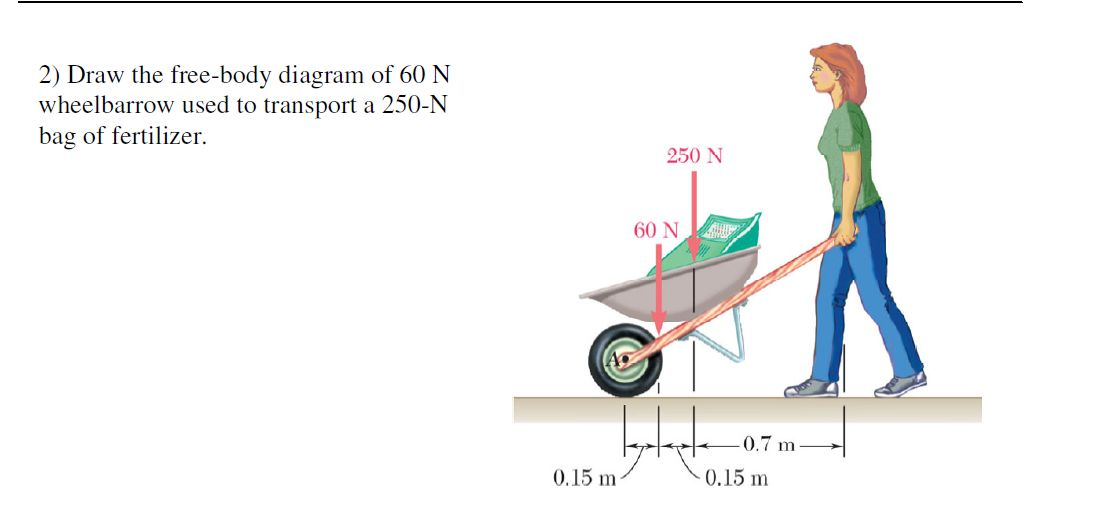
Solved Please draw free body diagrams for the following.
[Solved] Draw freebody diagrams for each of the following objects in
A) The Cantilevered Beam In Prob.
At First, You May Want To Draw A Circle Around The Object Of Interest To Be Sure You Focus On Labeling The Forces Acting On The Object.
Identifying The Types Of Forces Acting On The Object, 2.
B) The Beam In Prob.
Related Post:
