Draw The Resonance Structure Of The Enolate Ion
Draw The Resonance Structure Of The Enolate Ion - Web chemistry chemistry questions and answers draw structural formulas for both resonance structures of the enolate ion obtained by treating the carbonyl compound below with. B) draw the two most important resonance contributors for the enolate ion. Web draw curved arrows to depict the formation of the keto form of an enolate ion via a strong base, represented by b. The c=c of an enol is very electron. Web as drawn, the two resonance structures on the bottom are identical; Web it requires either acid or base catalysis. This is because the negative change will be. Web of the two resonance structures of the enolate ion the one which places the negative charge on the oxygen is the most stable. Web a) circle these atoms that can also have a resonance structure with a negative charge. Web of the two resonance structures of the enolate ion the one which places the negative charge on the oxygen is the most stable. This is because the negative change will be better stabilized by the greater electronegativity of the oxygen. I believe the point was just to show that the electrons could move around. Organic chemistry (vollhardt and schore) 18: The c=c of an enol is very electron. As a result, protonation on o. As a result, protonation on o. Web 1.12 drawing chemical structures; The resonance forms stabilize the. Web as bases, lithium diisopropylamide (lda) or sodium hydride are needed. Web of the two resonance structures of the enolate ion the one which places the negative charge on the oxygen is the most stable. The c=c of an enol is very electron. But the enolate ion resonance structures also show that its negative charge is delocalized on the o of the c=o group. 22.6 reactivity of enolate ions; 22.7 alkylation of enolate ions; Organic chemistry (vollhardt and schore) 18: Complete the resonance structures of the enolate anion's keto. 22.7 alkylation of enolate ions; As a result, protonation on o. Web as drawn, the two resonance structures on the bottom are identical; B) draw the two most important resonance contributors for the enolate ion. Enols, enolates, and the aldol condensation: Web of the two resonance structures of the enolate ion the one which places the negative charge on the oxygen is the most stable. The acidity of the two potential hydrogen atoms is connected to the location of proton abstraction, which is. We consider first the mechanism of the acid catalyzed process: This is. As a result, protonation on o. Web a) circle these atoms that can also have a resonance structure with a negative charge. Web as bases, lithium diisopropylamide (lda) or sodium hydride are needed. This is because the negative change will be. Web of the two resonance structures of the enolate ion the one which places the negative charge on the. Web of the two resonance structures of the enolate ion the one which places the negative charge on the oxygen is the most stable. Complete the resonance structures of the enolate anion's keto. This is because the negative change will be. Web enolate conjugation can be represent by two major resonance forms represented by structures a and b which share. 70,000+ effective lessonsover 30 million usersengaging video tutorials Web the lower resonance form, which is called an enolate ion (or enolate), is the more stable of the two forms and, therefore, more prevalent. Complete the resonance structures of the enolate anion's keto. Web 1.12 drawing chemical structures; Web of the two resonance structures of the enolate ion the one which. Web as drawn, the two resonance structures on the bottom are identical; Web of the two resonance structures of the enolate ion the one which places the negative charge on the oxygen is the most stable. 70,000+ effective lessonsover 30 million usersengaging video tutorials Complete the resonance structures of the enolate anion's keto. This is because the negative change will. This is because the negative change will be better stabilized by the greater electronegativity of the oxygen. Web draw structural formulas for both resonance structures of the enolate ion obtained by treating the carbonyl compound below with base. But the enolate ion resonance structures also show that its negative charge is delocalized on the o of the c=o group. Web. I believe the point was just to show that the electrons could move around. Web of the two resonance structures of the enolate ion the one which places the negative charge on the oxygen is the most stable. You do not have to consider. Web 1.12 drawing chemical structures; B) draw the two most important resonance contributors for the enolate ion. 70,000+ effective lessonsover 30 million usersengaging video tutorials Web the anion formed in this case is an enolate anion which is highly resonance stabilized, as shown above. Web as drawn, the two resonance structures on the bottom are identical; Web of the two resonance structures of the enolate ion the one which places the negative charge on the oxygen is the most stable. Web and we could draw a resonance structure for this, so we could show these electrons in magenta moving in here to form a double bond, push these electrons off on. Enols, enolates, and the aldol condensation: The resonance forms stabilize the. 2.5 rules for resonance forms; 22.6 reactivity of enolate ions; The c=c of an enol is very electron. Web as bases, lithium diisopropylamide (lda) or sodium hydride are needed.
Enolate Ion Formation and Stability of Alpha Acidic Hydrogen YouTube
[Solved] Draw a major resonance contributor of this enolate anion

6. (4 pts.) Draw the two resonance structures of the enolate formed

SOLVED Draw the products for the following reactions H;o Draw two
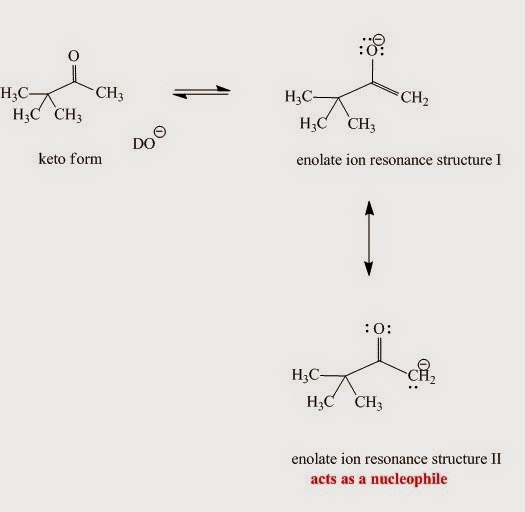
The chemistry of enolate ions Reactions with alkyl halides
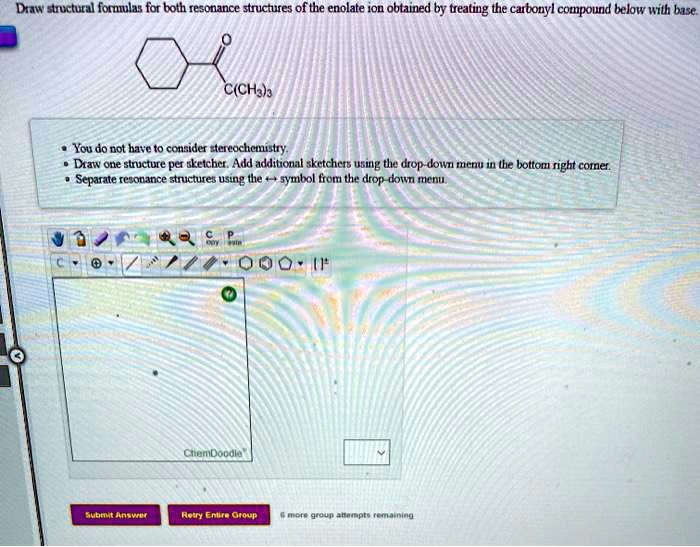
SOLVED Daw structural formulas for both resonance structures of the
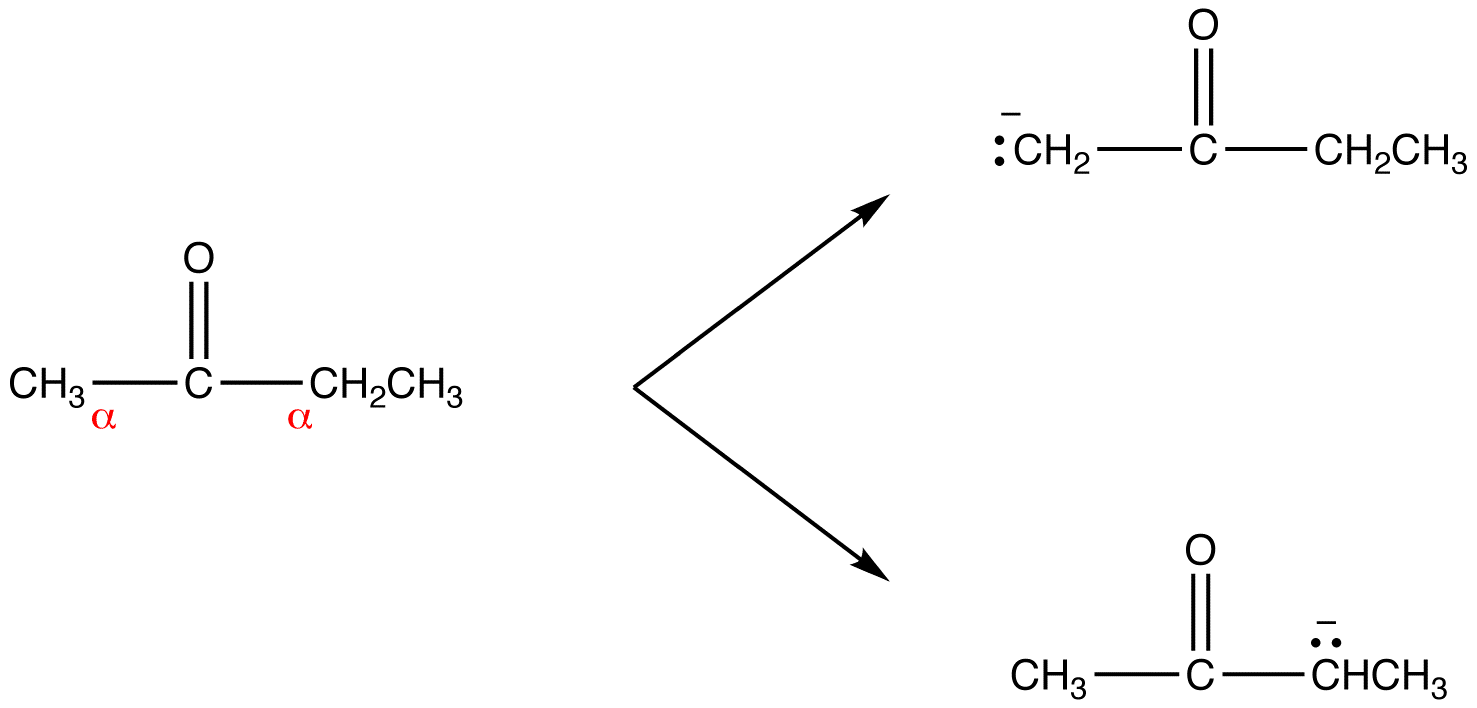
Enolate Ion Chemistry LibreTexts
[Solved] Write all of the resonance structures for the enolate ion that
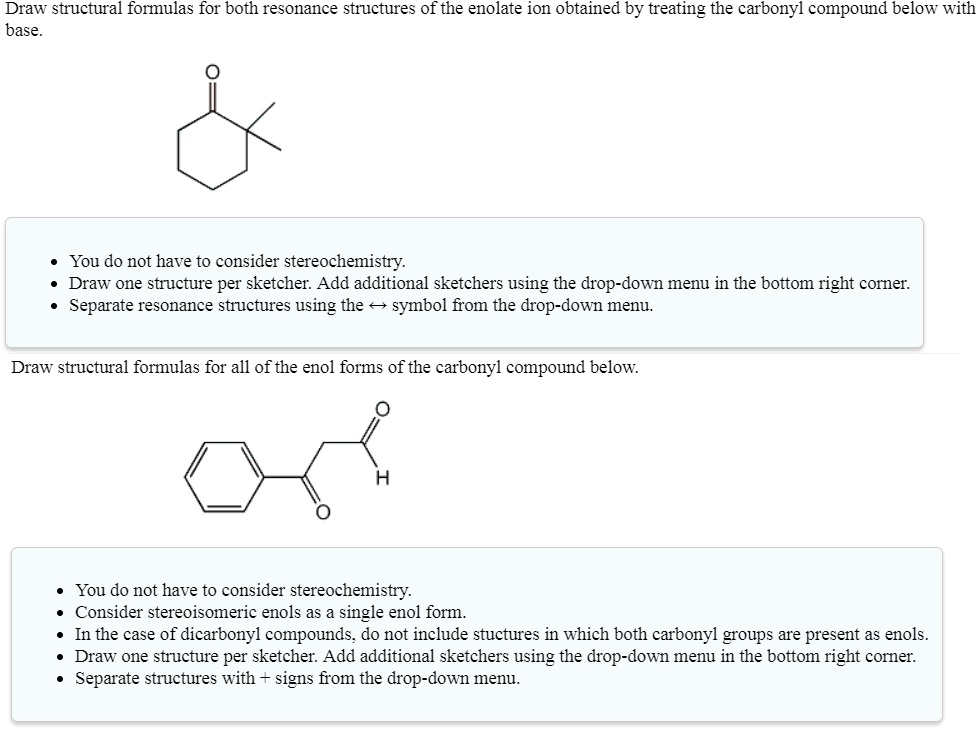
SOLVED Draw structural formulas for both resonance structures of the

SOLVED Draw structural formulas for both resonance structures of the
Web Enolate Conjugation Can Be Represent By Two Major Resonance Forms Represented By Structures A And B Which Share The Negative Charge (Shown Below).
Q Recall That The Rules Of Resonance Specify That Large Resonance.
Web Draw Structural Formulas For Both Resonance Structures Of The Enolate Ion Obtained By Treating The Carbonyl Compound Below With Base.
As A Result, Protonation On O.
Related Post: