Drawing Of Commensalism
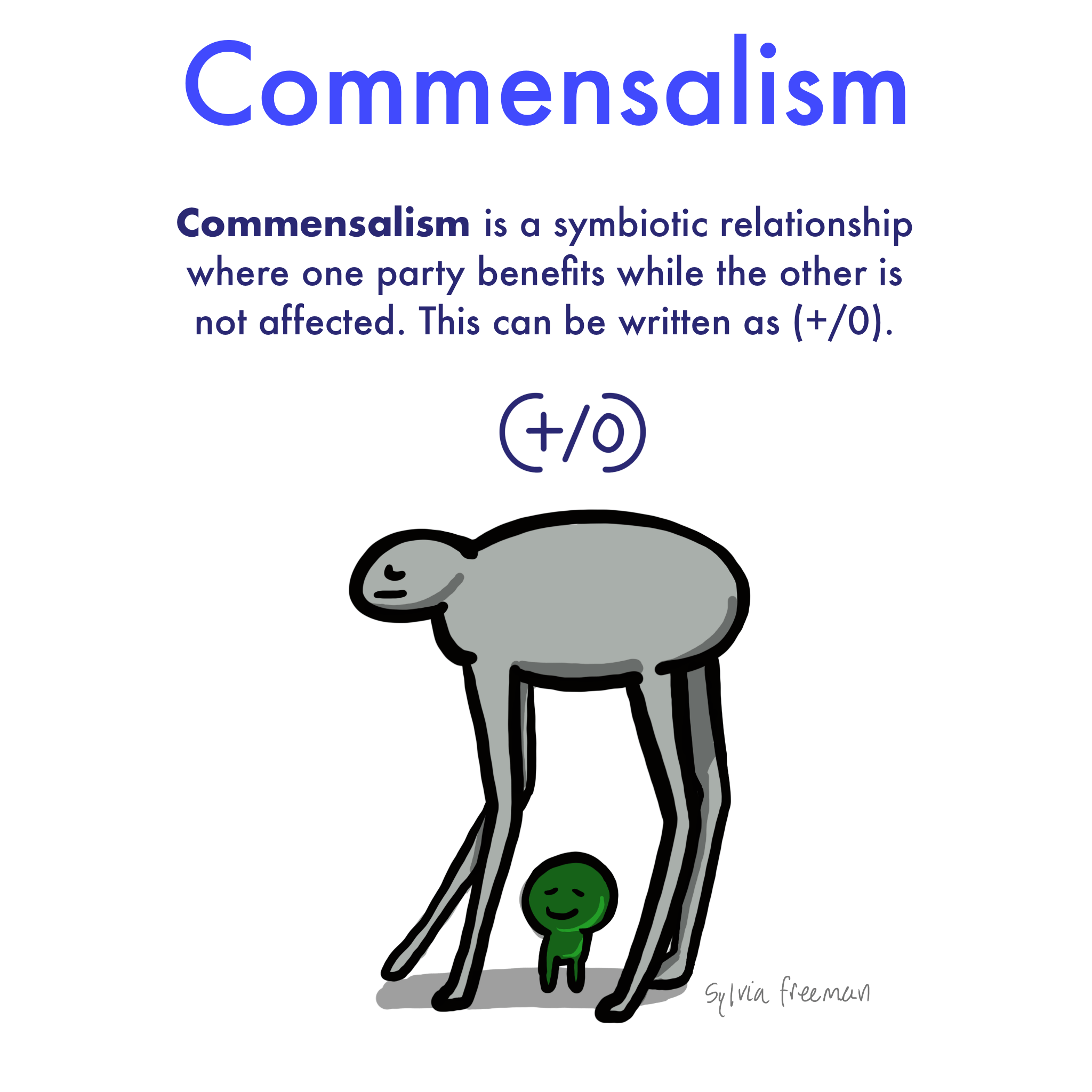
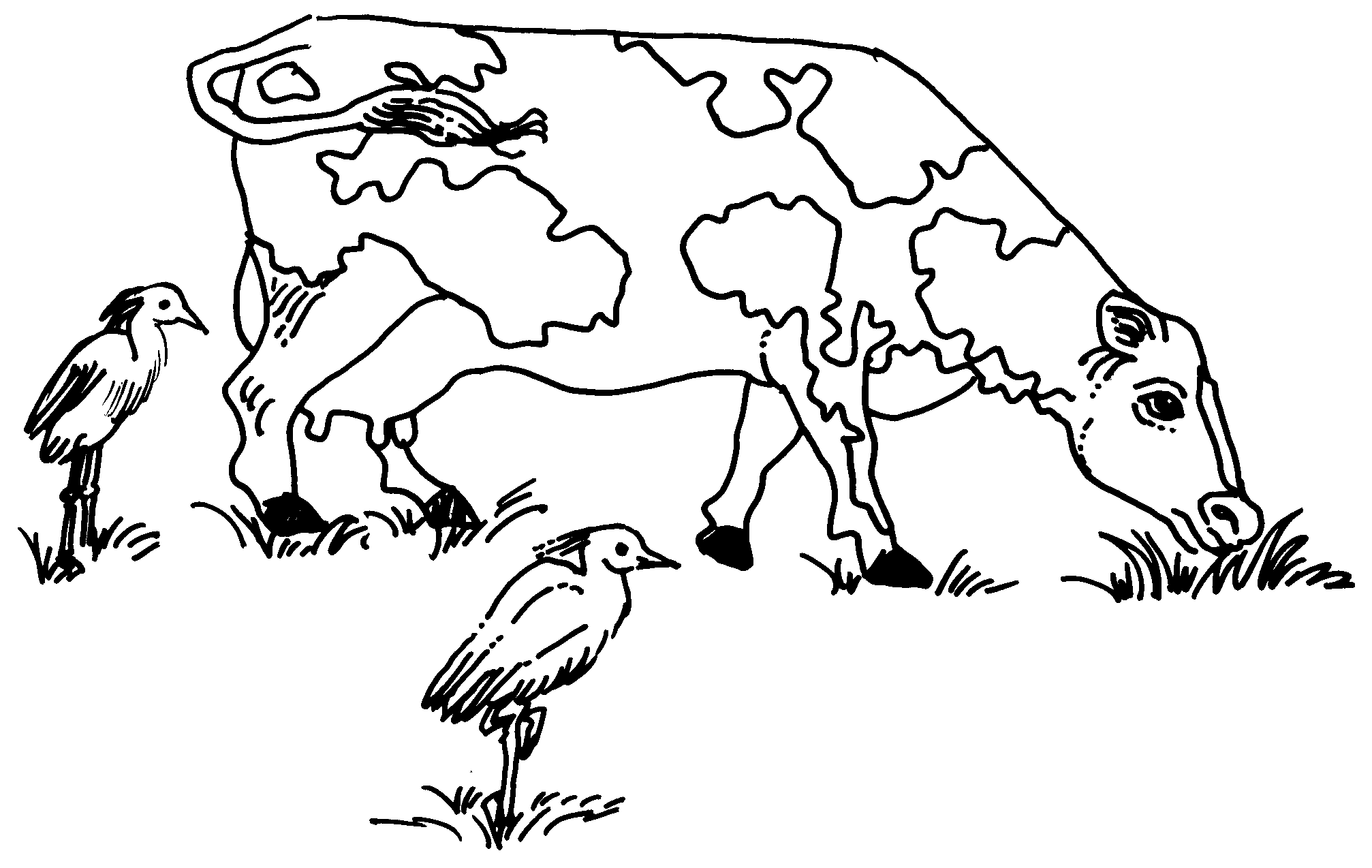
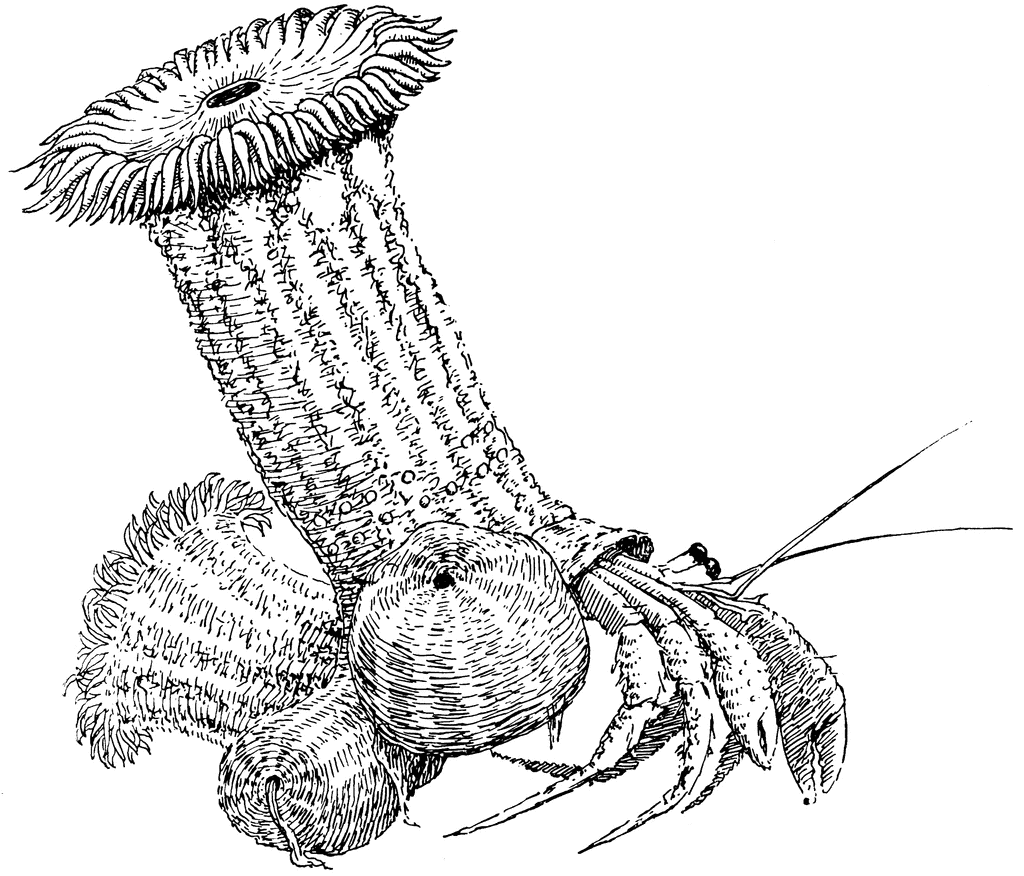
Drawing Of Commensalism - Commensalisms, interactions between two species in which one species benefits and the other experiences no net effect, are frequently mentioned in the ecological literature but are surprisingly little studied. Web commensalism is a type of facilitation that occurs when one species benefits from an interaction, while the other neither benefits or is harmed. Web what is the meaning of commensalism in biology? A symbiotic relationship between two species in which one benefits and the other is unaffected. Many potential commensal relationships are difficult to identify because it is difficult to demonstrate that one partner is unaffected by the presence of the other. The commensal—the species that benefits from the association—may obtain nutrients, shelter, support, or locomotion from the host species, which is. Usually, the host species offers shelter, support, food, or locomotion. An organism uses another for housing, such as a bird nesting in a tree's hollow. It is a biological interaction that organisms form, in. Commensalism in a commensal relationship, one species benefits and there is a neutral effect on the other—it neither benefits nor is harmed. This can be contrasted with other types of symbiosis, such as mutualism and parasitism. Commensalism in a commensal relationship, one species benefits and there is a neutral effect on the other—it neither benefits nor is harmed. Most of the interactions occurring in the natural world affect both organisms in some way. Here we review and synthesize our limited understanding of. Web commensalism is a symbiotic relationship between two species, where one species benefits while the other is neither helped nor significantly harmed. There are four main symbiotic relationships: Web commensalism (+/0) is defined as a unilateral relationship between two species that benefits one species without consequence to the other. A commensal species benefits from another species by obtaining locomotion, shelter,. Web commensalism is a symbiotic relationship between two species, where one species benefits while the other is neither helped nor significantly harmed. An organism uses another for housing, such as a bird nesting in a tree's hollow. Web what is the meaning of commensalism in biology? Web commensalism exemplifies nature’s remarkable ability to create mutually beneficial relationships where one organism. An organism uses another for housing, such as a bird nesting in a tree's hollow. A symbiotic relationship between two species in which both partners benefit. How to draw adamsia showing commensalism step by step2. The three main types of commensalism are inquilinism, metabiosis, and phoresy. Commensalisms, interactions between two species in which one species benefits and the other experiences. Web because different species often inhabit the same spaces and share—or compete for—the same resources, they interact in a variety of ways, known collectively as symbiosis. Web commensalism is a relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits, and one is unaffected. How to draw adamsia showing commensalism step by step2. Commensalisms, interactions between two species in which one. How to draw adamsia showing commensalism step by step2. Web commensalism (+/0) is defined as a unilateral relationship between two species that benefits one species without consequence to the other. Commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship or biological interaction where one species benefits from the other without causing any harm or benefit to the other. How could commensalism turn. This can be contrasted with other types of symbiosis, such as mutualism and parasitism. Web commensalism exemplifies nature’s remarkable ability to create mutually beneficial relationships where one organism benefits without harming another. Web commensalism is of different types depending on the strength and duration of the interaction and the purposes. The best example of commensalism is sea barnacles attached to. How could commensalism turn into a mutualistic relationship? Web commensalism, mutualism, and parasitism are the three main categories of symbiosis found in nature. A symbiotic relationship between two species in which one benefits and the other is unaffected. Web commensalism is of different types depending on the strength and duration of the interaction and the purposes. A commensal species benefits. Web commensalism (+/0) is defined as a unilateral relationship between two species that benefits one species without consequence to the other. An organism uses another for housing, such as a bird nesting in a tree's hollow. Web commensalism exemplifies nature’s remarkable ability to create mutually beneficial relationships where one organism benefits without harming another. How to draw adamsia commensalism easily3.. Web a major distinction is that, while in the former the species mostly resemble forms of commensalism, the latter includes species currently confirmed as social parasites, thus, being closely related to parasitism. The species that benefits is known as the commensal species. A symbiotic relationship between two species in which one benefits and the other is unaffected. The three main. Web a major distinction is that, while in the former the species mostly resemble forms of commensalism, the latter includes species currently confirmed as social parasites, thus, being closely related to parasitism. Web commensalism, in biology, a relationship between individuals of two species in which one species obtains food or other benefits from the other without either harming or benefiting the latter. See all creative images trending image searches christmas background Web commensalism is a type of relationship between two living organisms in which one organism benefits from the other without harming it. The examples discussed here illustrate just a fraction of the vast array of symbiotic connections found throughout ecological systems. Web commensalism is a type of symbiosis in which one organism benefits from a relationship with a different species of organism while that species is neither harmed nor benefits from the relationship. A commensal species benefits from another species by obtaining locomotion, shelter, food, or support from the host species, which (for the most part) neither benefits nor is harmed. Labeled living together explanation educational scheme. Here we review and synthesize our limited understanding of commensalism. The species that benefits is known as the commensal species. Web what is the meaning of commensalism in biology? The simplest commensalism definition is that it’s a type of symbiosis where one organism benefits and the other neither benefits nor is harmed. There are four recognized forms of commensalism: Many potential commensal relationships are difficult to identify because it is difficult to demonstrate that one partner is unaffected by the presence of the other. Photos curated content curated sets signature collection essentials collection diversity and inclusion sets The commensal—the species that benefits from the association—may obtain nutrients, shelter, support, or locomotion from the host species, which is.
Commensalism Definition and Examples
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/commensalism-definition-and-examples-4114713-v2-706cadecce404b008d6620bb061841cc.png)
Commensalism Definition, Examples, and Relationships
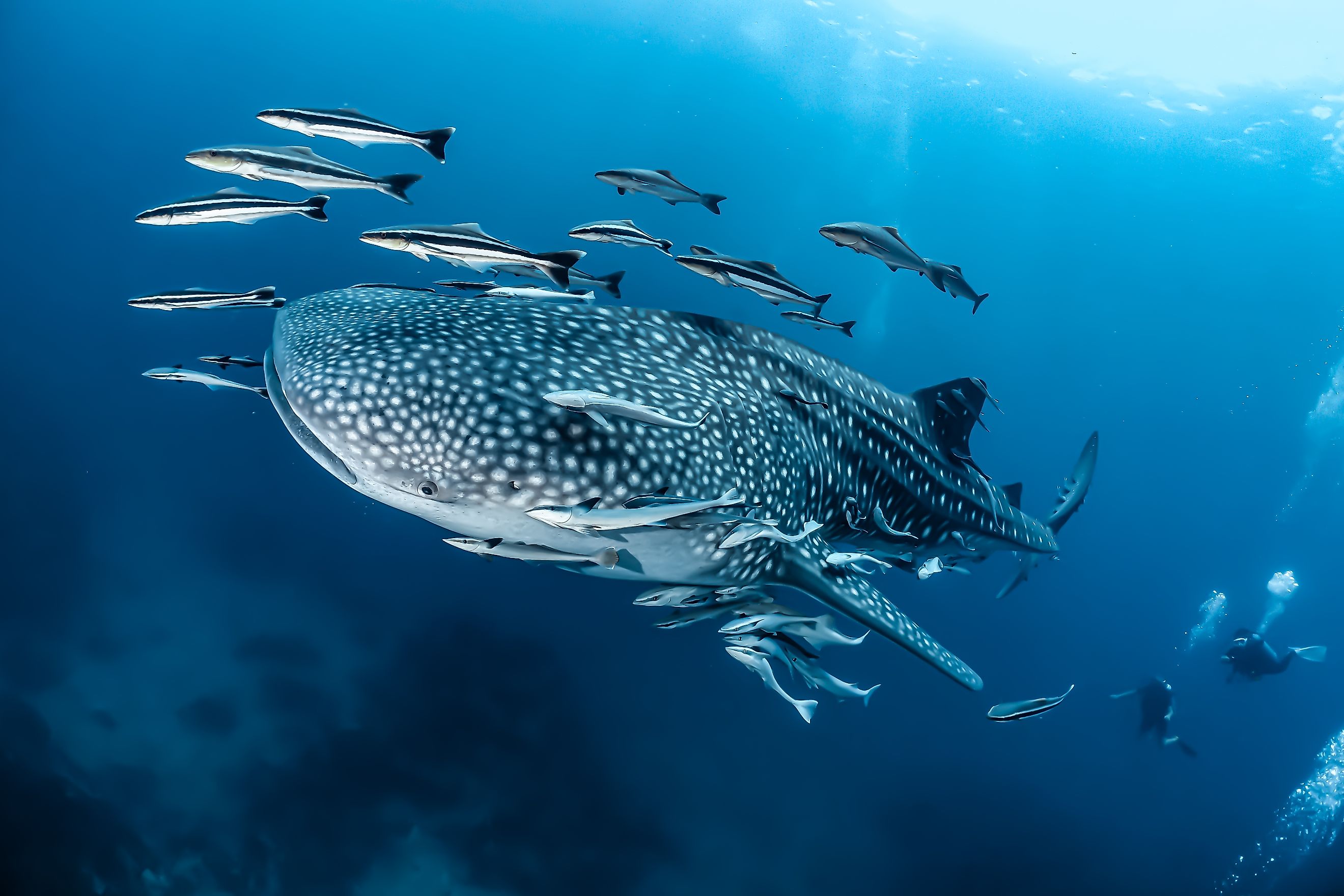

Commensalism Barnacles And Whales Drawing

Commensalism Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary

Commensalism Science, Biology, Ecosystem Problems ShowMe
Commensalism — Definition & Examples Expii
Example Of A Commensalism Relationship drawing free image download
Commensalism ClipArt ETC

Examples Of Commensalism In Nature WorldAtlas
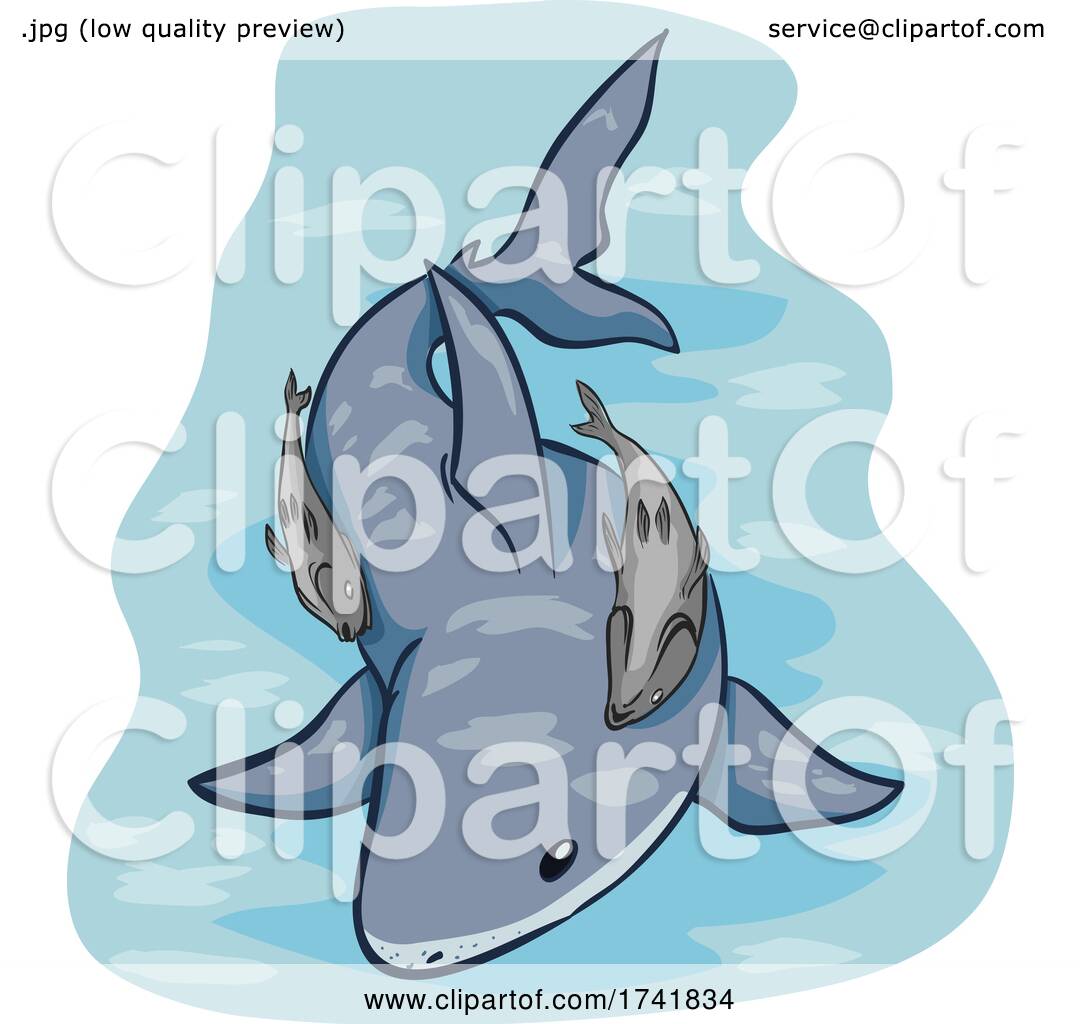

Commensalism Remora Illustration by BNP Design Studio 1741834
Web Commensalism Exemplifies Nature’s Remarkable Ability To Create Mutually Beneficial Relationships Where One Organism Benefits Without Harming Another.
Inquilinism Is A Type Of Commensalism Where One Of The Species Uses The Body Or A Cavity With The Body Of The Other Organisms As A Living.
Commensalism Is A Symbiotic Relationship Between Two Organisms Where One Organism Is Benefited From The Other, Whereas The Other Is Neither Harmed Nor Benefited.
How Could Commensalism Turn Into A Mutualistic Relationship?
Related Post: