Fetal Heart Rate Categories Chart
Fetal Heart Rate Categories Chart - Physicians can purchase the emodule, access it at the link below, and receive cme credit once they achieve 80% or higher on the posttest. Web fetal heart rate monitoring consists of an electrode attached directly to the fetal head or a maternal abdominal ultrasound to detect the fetal heart rate plus an external tocodynamometer to identify contractions (8). How your baby's heart rate changes. Very early in pregnancy, it is typically around 110 bpm. It is measurable sonographically from around 6 weeks and the normal range varies during gestation, increasing to around 170 bpm at 10 weeks and decreasing from then to around 130 bpm at term. Web most researchers and doctors define normal fetal heart rate as between 110 to 160 beats per minute (bpm), with some experts using narrower parameters, such as 110 to 150 bpm or 120 to 160 bpm. Check out a suggested systematic approach from the aafp below! This system has been widely adopted in the united states and elsewhere, and is the basis for this topic. This content is only available to members and subscribers. Intrapartum fetal heart rate monitoring: The relationship between these two variables is widely accepted to. Web at some point during labor, category i patterns were observed in over 99 percent of tracings, category ii patterns were observed in 84 percent of tracings, and category iii patterns were observed in 0.1 percent of tracings. Web the system divides all fetal heart rate tracings into one of. Web as such, clinicians are faced daily with the management of fetal heart rate (fhr) tracings. The interpretation of the fetal heart rate tracing should follow a systematic approach with a full qualitative and quantitative description. Web the system divides all fetal heart rate tracings into one of five categories: This lets your healthcare provider see how your baby is. Web a systematic approach to fhr interpretation. Green (no acidemia, no intervention required), blue, yellow, orange or red (evidence of actual or impending fetal asphyxia, rapid delivery recommended). Web the purpose of this document is to review nomenclature for fetal heart rate assessment, review the data on the efficacy of efm, delineate the strengths and shortcomings of efm, and describe. Fetal heart rate may speed up to 140 to 170 bpm around the ninth week and slow to. Web a normal fetal heart rate (fhr) usually ranges from 120 to 160 beats per minute (bpm) in the in utero period. Web category classification, including images and multimedia. Web the following tables are reproduced from cg190. Web as such, clinicians are. How your baby's heart rate changes. Check out a suggested systematic approach from the aafp below! This system has been widely adopted in the united states and elsewhere, and is the basis for this topic. Web at some point during labor, category i patterns were observed in over 99 percent of tracings, category ii patterns were observed in 84 percent. Web a normal heart rate for a fetus can range from 110 to 160 beats per minute (bpm). Web the following tables are reproduced from cg190. How your baby's heart rate changes. Web the system divides all fetal heart rate tracings into one of five categories: Diagnostic criteria — a category i pattern ( waveform 1) is defined by: Intrapartum fetal heart rate monitoring: Nomenclature, interpretation, and general management principles. Fetal heart rate may speed up to 140 to 170 bpm around the ninth week and slow to. Web the purpose of this document is to review nomenclature for fetal heart rate assessment, review the data on the efficacy of efm, delineate the strengths and shortcomings of efm, and. The interpretation of the fetal heart rate tracing should follow a systematic approach with a full qualitative and quantitative description. Very early in pregnancy, it is typically around 110 bpm. Fetal heart rate may speed up to 140 to 170 bpm around the ninth week and slow to. Intrapartum fetal heart rate monitoring: Web category classification, including images and multimedia. Web a normal fetal heart rate (fhr) usually ranges from 120 to 160 beats per minute (bpm) in the in utero period. Web the system divides all fetal heart rate tracings into one of five categories: Fetal heart rate may speed up to 140 to 170 bpm around the ninth week and slow to. Web category classification, including images and. Web as such, clinicians are faced daily with the management of fetal heart rate (fhr) tracings. Web the procedure for intrapartum fhr monitoring, physiology behind fhr accelerations and decelerations, classification of fhr tracings, and use of ancillary tests to evaluate the fetus will be discussed here. How your baby's heart rate changes. Your healthcare provider may do fetal heart monitoring. Web at some point during labor, category i patterns were observed in over 99 percent of tracings, category ii patterns were observed in 84 percent of tracings, and category iii patterns were observed in 0.1 percent of tracings. Web health library / diagnostics & testing / fetal heart rate monitoring. Web the following tables are reproduced from cg190. How your baby's heart rate changes. Web the purpose of this document is to review nomenclature for fetal heart rate assessment, review the data on the efficacy of efm, delineate the strengths and shortcomings of efm, and describe a system for efm classification. Web the system divides all fetal heart rate tracings into one of five categories: Providers use fetal heart rate monitoring to check the health of your baby. Web as such, clinicians are faced daily with the management of fetal heart rate (fhr) tracings. Web acog practice bulletin no. Web fetal heart rate monitoring consists of an electrode attached directly to the fetal head or a maternal abdominal ultrasound to detect the fetal heart rate plus an external tocodynamometer to identify contractions (8). Baseline rate of 110 to 160 beats per. Web category i pattern: The relationship between these two variables is widely accepted to. Diagnostic criteria — a category i pattern ( waveform 1) is defined by: Your healthcare provider may do fetal heart monitoring during late pregnancy and labor. Web these traditional classification systems for fetal heart rate interpretation during labor are based on grouping certain features of fetal heart rate (ie, baseline fetal heart rate, baseline variability, accelerations, and decelerations) into different categories (eg, category i, ii, and iii tracings, “normal, suspicious, and pathologic” or “norm.
Standardization of fetal heart rate pattern management Is
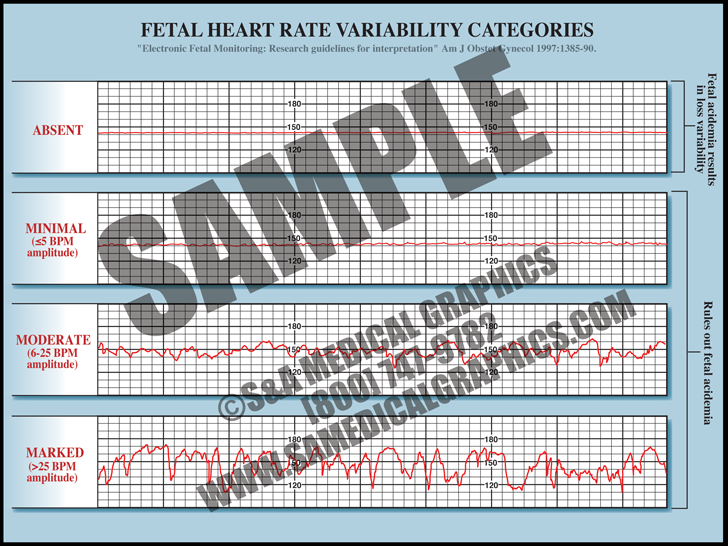
FHR Variability Categories S&A Medical Graphics
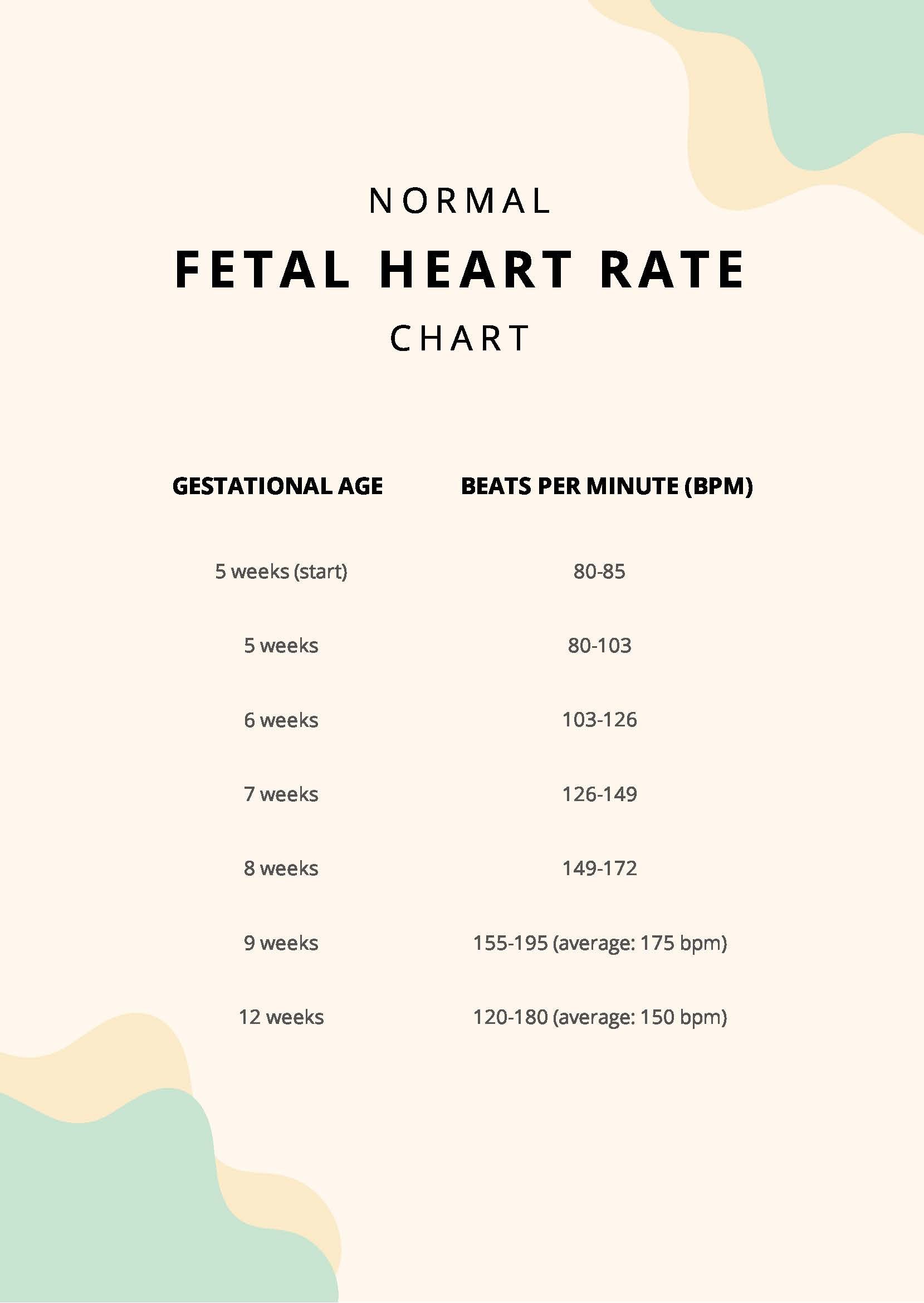
Free Heart Rate Chart By Age And Gender PDF

Fetal Heart Tones Heart tone, Fetal heart rate, Midwife assistant
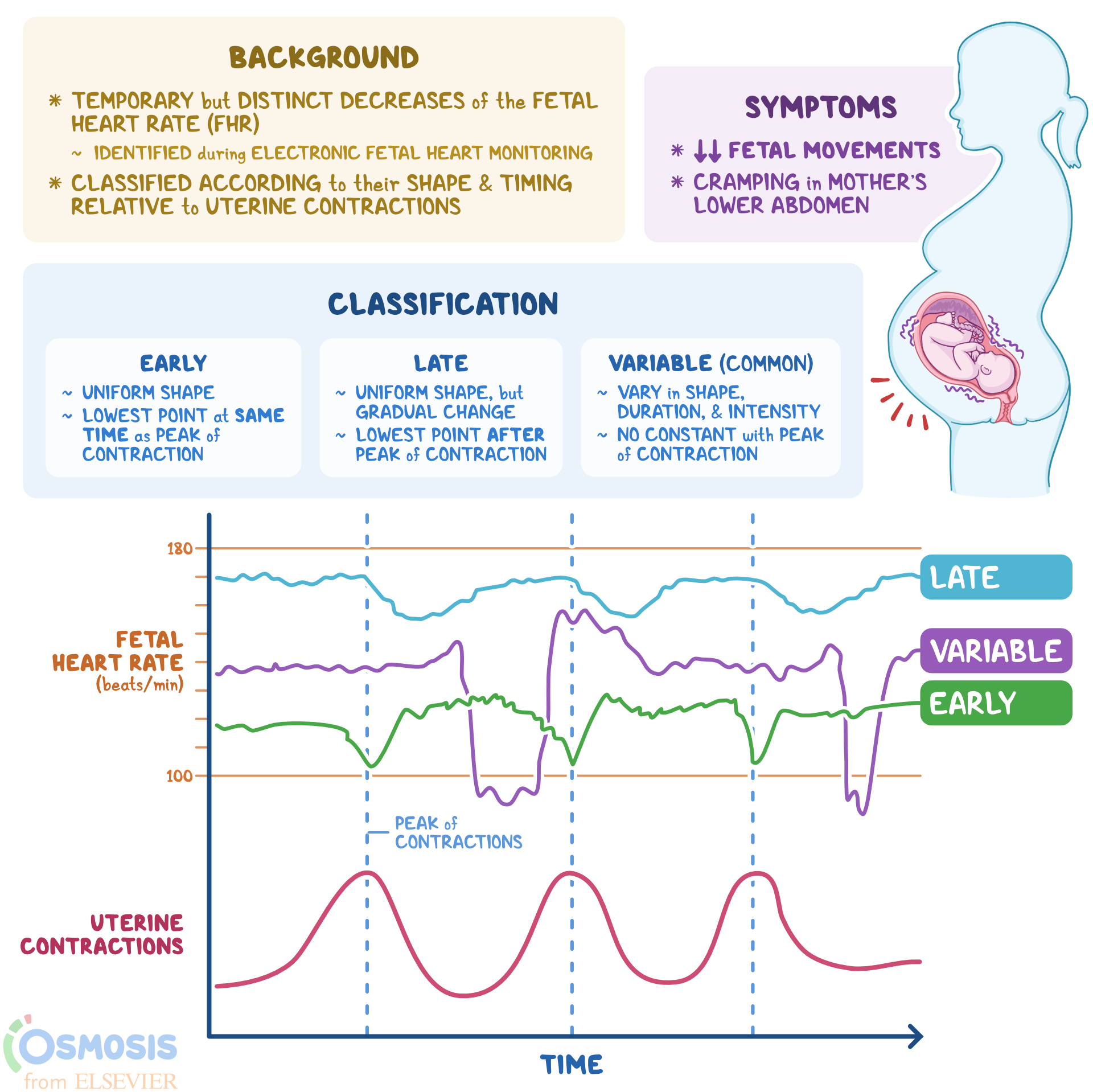
How To Read Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring Strips BEST GAMES WALKTHROUGH
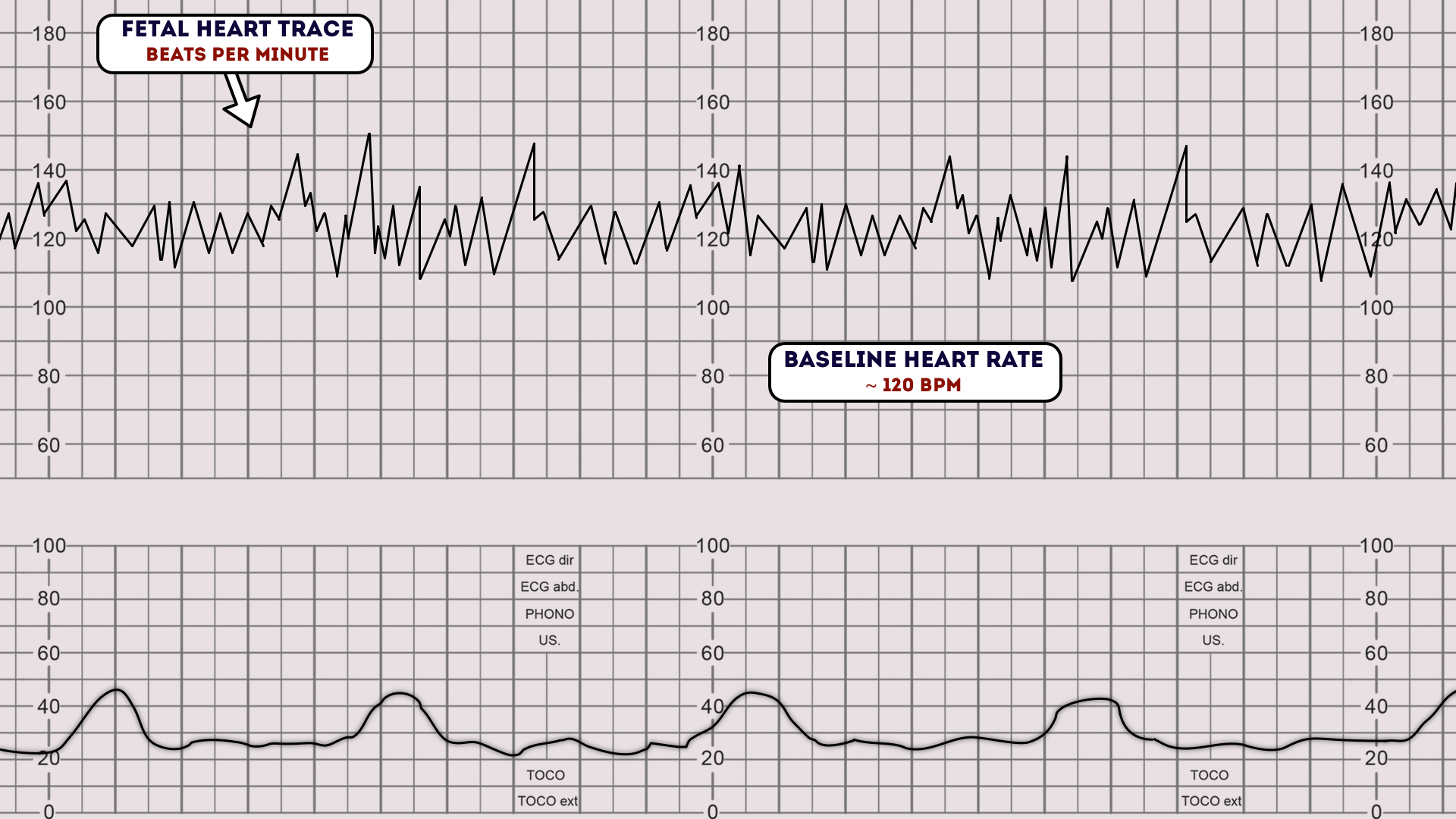
How to Read a CTG CTG Interpretation Geeky Medics

fetal heart rate monitor Google Search Nursing school tips
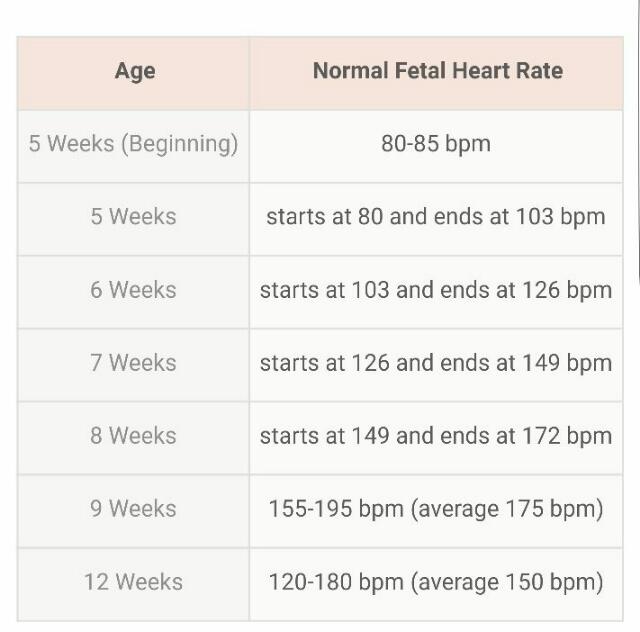
21 Awesome Fetal Heart Rate By Week Chart

Standardization of fetal heart rate pattern management Is
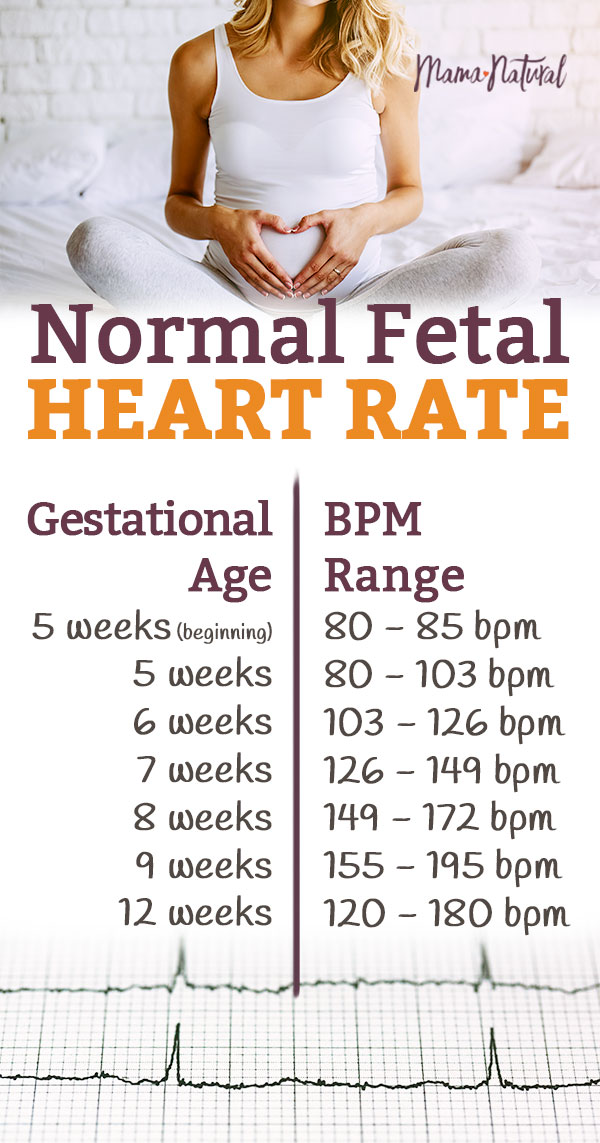
Normal Fetal Heart Rate Is Your Baby on Track? Mama Natural
The Fetal Heart Rate Tracing Shows All Of The Following:
This System Has Been Widely Adopted In The United States And Elsewhere, And Is The Basis For This Topic.
Web A Normal Fetal Heart Rate (Fhr) Usually Ranges From 120 To 160 Beats Per Minute (Bpm) In The In Utero Period.
Web The Procedure For Intrapartum Fhr Monitoring, Physiology Behind Fhr Accelerations And Decelerations, Classification Of Fhr Tracings, And Use Of Ancillary Tests To Evaluate The Fetus Will Be Discussed Here.
Related Post: