Flow Of Lymph Chart
Flow Of Lymph Chart - Functioning almost like a sponge, the lymphatic system absorbs excess lymph fluid from the body’s organs and returns it to the blood stream. Web lymph flows from the lymphatic capillaries, through lymphatic vessels, and then is dumped into the circulatory system via the lymphatic ducts located at the junction of the jugular and subclavian veins in the neck. Web the lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. Web lymph flows from the lymphatic capillaries, through lymphatic vessels, and then is dumped into the circulatory system via the lymphatic ducts located at the junction of the jugular and subclavian veins in the neck. 3d models help you explore the anatomy and physiology. Web the lymphatic vessels transport lymph fluid around the body. Web the lymphatic system controls lymph flow and the ability to fight infection. The deep lymphatic vessels of the head and neck arise from the deep cervical lymph nodes. Along the way, the lymph travels through the lymph nodes, which are commonly found near the groin, armpits, neck, chest, and abdomen. Web protecting your body against invaders. It produces and releases lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and other immune cells. Lymphatic vessels drain fluid called lymph from tissues throughout the body and return the fluid to the venous system through 2 collecting ducts. The superficial vessels drain lymph from the scalp, face and neck into the superficial ring of lymph nodes at the junction of. Lymph is composed of white blood cells, triglycerides, bacteria, cell debris, water, and protein. They can be classified as either primary lymphoid organs (bone marrow and thymus) where de novo synthesis and maturation of lymphocytes occur; It has a composition comparable to blood plasma. 3d models help you explore the anatomy and physiology. First is the maintenance of fluid balance,. Your lymphatic system is part of your immune system. Lymph is composed of white blood cells, triglycerides, bacteria, cell debris, water, and protein. The journey of lymph begins with the extravasation of fluid and cells from the blood capillaries into the interstitium. Lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc. Web this video illustrates normal lymphatic anatomy and flow. Lymphoid tissues are collections of lymphocytes strategically located at potential sites of infection. The superficial vessels drain lymph from the scalp, face and neck into the superficial ring of lymph nodes at the junction of the neck and head. Or secondary lymphoid organs where activation of. We retrospectively investigated alterations in the ploidy status, proliferative cell. Without it neither the. The immune and lymphatic systems. The lymphatic system cleverly returns fluid to the circulatory system without a pump. Web the lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. Web lymph flows from the lymphatic capillaries, through lymphatic vessels, and then is dumped into the. The lymphatic system is an elaborate network of vessels that act harmoniously to pump fluid and cells, collectively called lymph, from the interstitial space into the blood circulation. Web 1 anatomy and physiology. Lymphoid tissues are collections of lymphocytes strategically located at potential sites of infection. Without it neither the circulatory system nor the immune system would function. The lymph. Lymphoid organs include the spleen, thymus and tonsils; The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in immune function and in the delivery of vital nutrients to the body. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lymphatic tissue and lymph. Lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc. The lymph flows from the afferent vessels. Without it neither the circulatory system nor the immune system would function. Web lymph flows from the lymphatic capillaries, through lymphatic vessels, and then is dumped into the circulatory system via the lymphatic ducts located at the junction of the jugular and subclavian veins in the neck. The superficial vessels drain lymph from the scalp, face and neck into the. Web this video illustrates normal lymphatic anatomy and flow. Web the lymphocytes are transported through lymph fluid and leave the node through the efferent vessels to travel to other parts of the body to perform adaptive immune response functions. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lymphatic tissue and lymph. Web the lymphatic system. The lymph flows from the afferent vessels into the sinuses of the lymph node, and then out of the node through the efferent vessels. It produces and releases lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and other immune cells. Web the lymphatic system partly functions to convey lymphatic fluid, or lymph, through a network of lymphatic channels, filter lymphatic fluid. Web protecting your body against invaders. Web this video illustrates normal lymphatic anatomy and flow. Web lymph flows from the lymphatic capillaries, through lymphatic vessels, and then is dumped into the circulatory system via the lymphatic ducts located at the junction of the jugular and subclavian veins in the neck. Learn all about the vessels, nodes, nodules, and ducts of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system cleverly returns fluid to the circulatory system without a pump. Web 1 anatomy and physiology. The lymphatic system as a functional whole includes several organs whose association as a system is not readily apparent. The deep lymphatic vessels of the head and neck arise from the deep cervical lymph nodes. The lymph flows from the afferent vessels into the sinuses of the lymph node, and then out of the node through the efferent vessels. Without it neither the circulatory system nor the immune system would function. Lymphatic vessels, ducts and tracts; Here, let us discuss the circulation of. Network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body’s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens. We retrospectively investigated alterations in the ploidy status, proliferative cell. Web the lymphatic system is a network of vessels and organs that regulates the amount of fluid in the human body and defends it against infections. The superficial vessels drain lymph from the scalp, face and neck into the superficial ring of lymph nodes at the junction of the neck and head.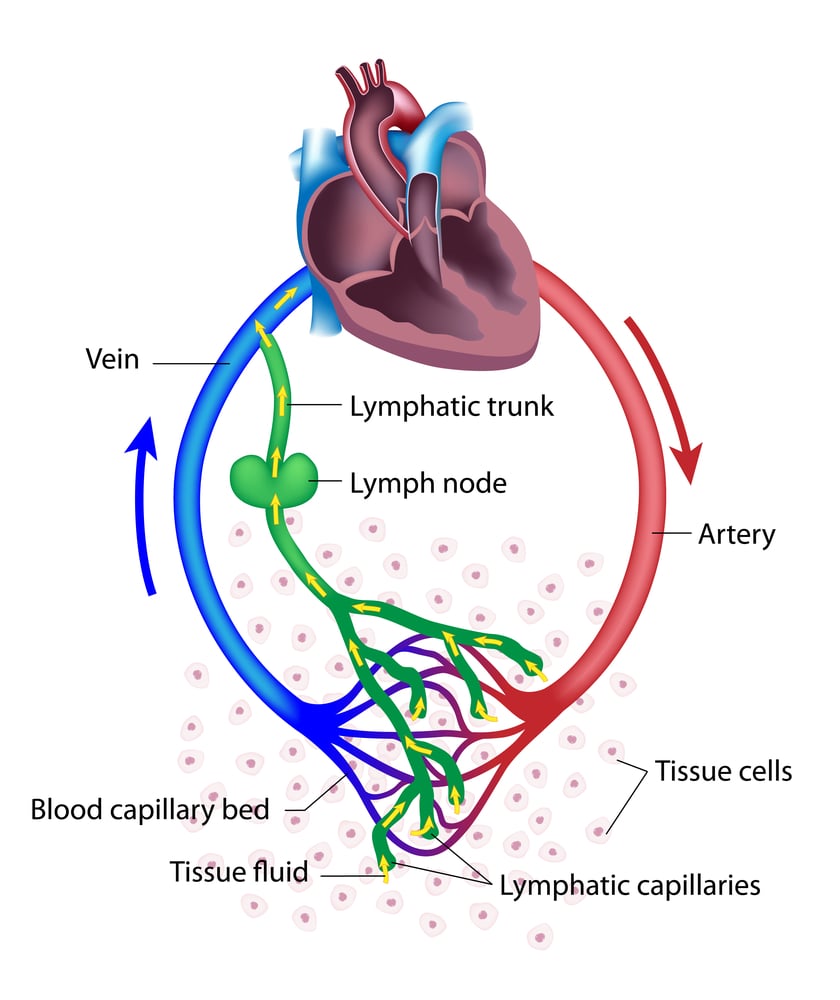
Circulation Of Lymph Flow Chart
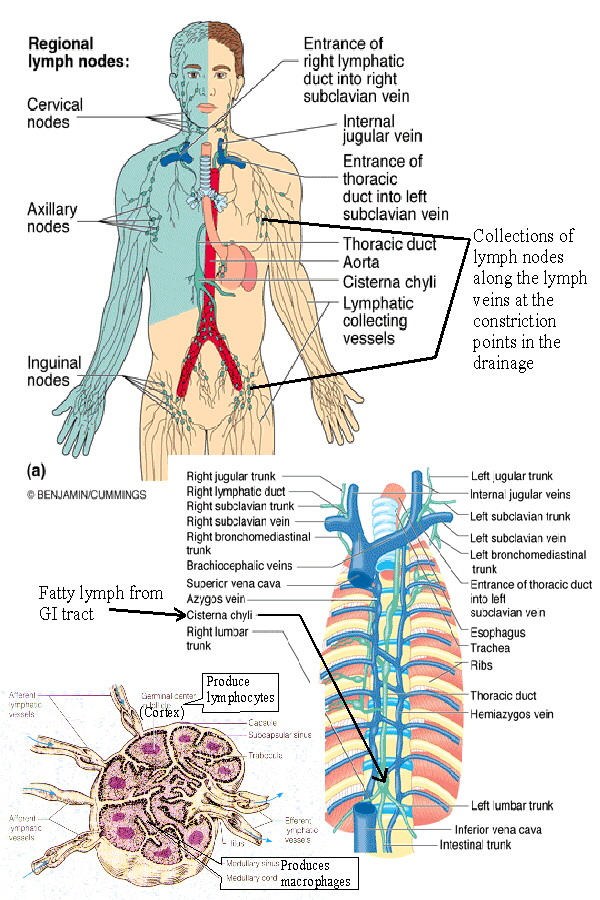
Understanding the Lymphatic System

Lymphatic System Flow Chart
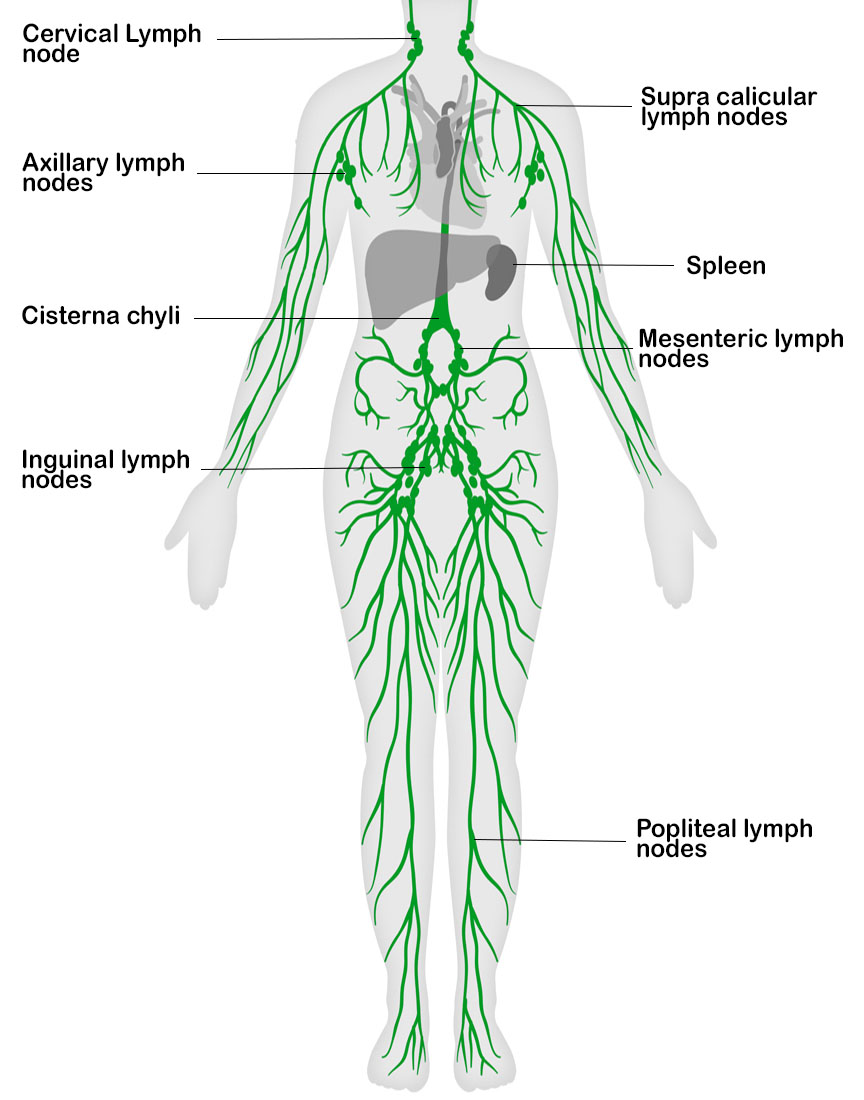
Lymphatic System Flow Chart
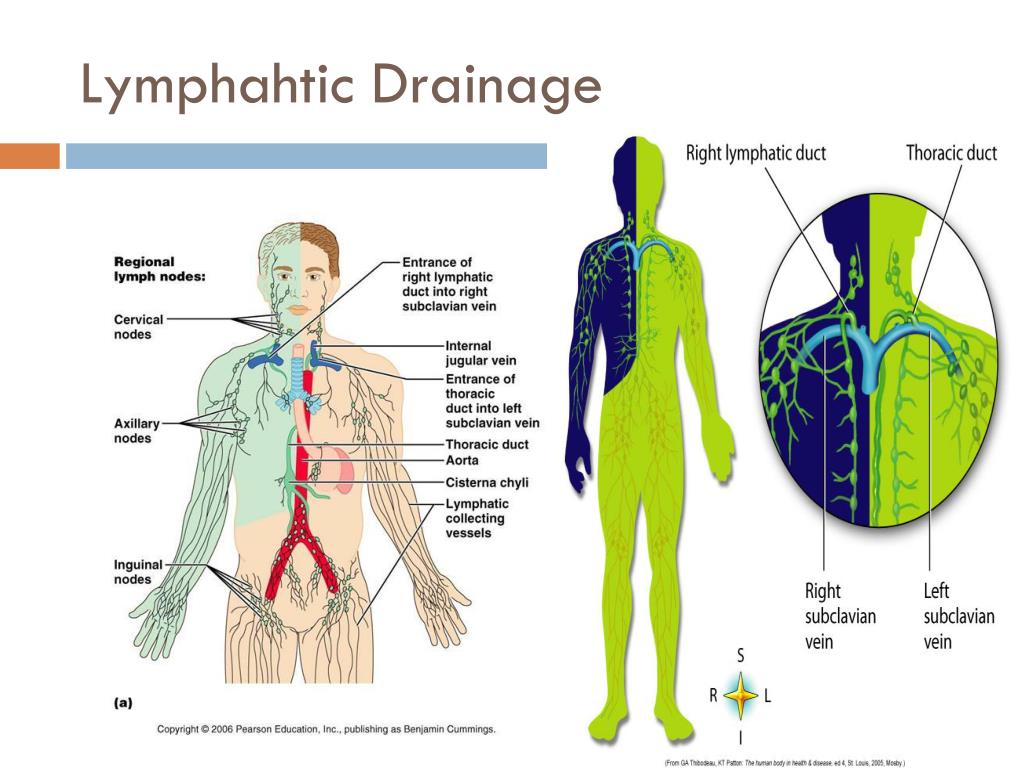
Lymphatic System Drainage Chart
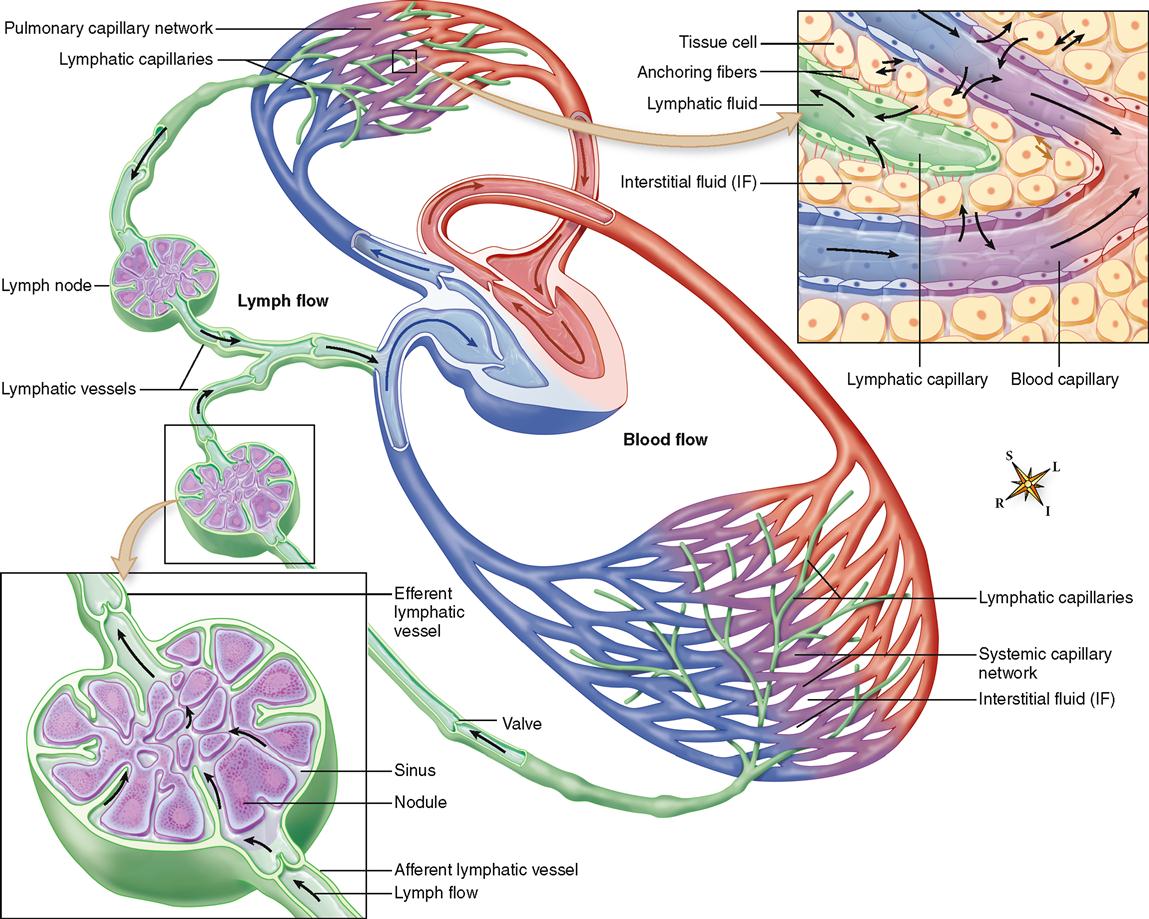
Lymphatic System Basicmedical Key
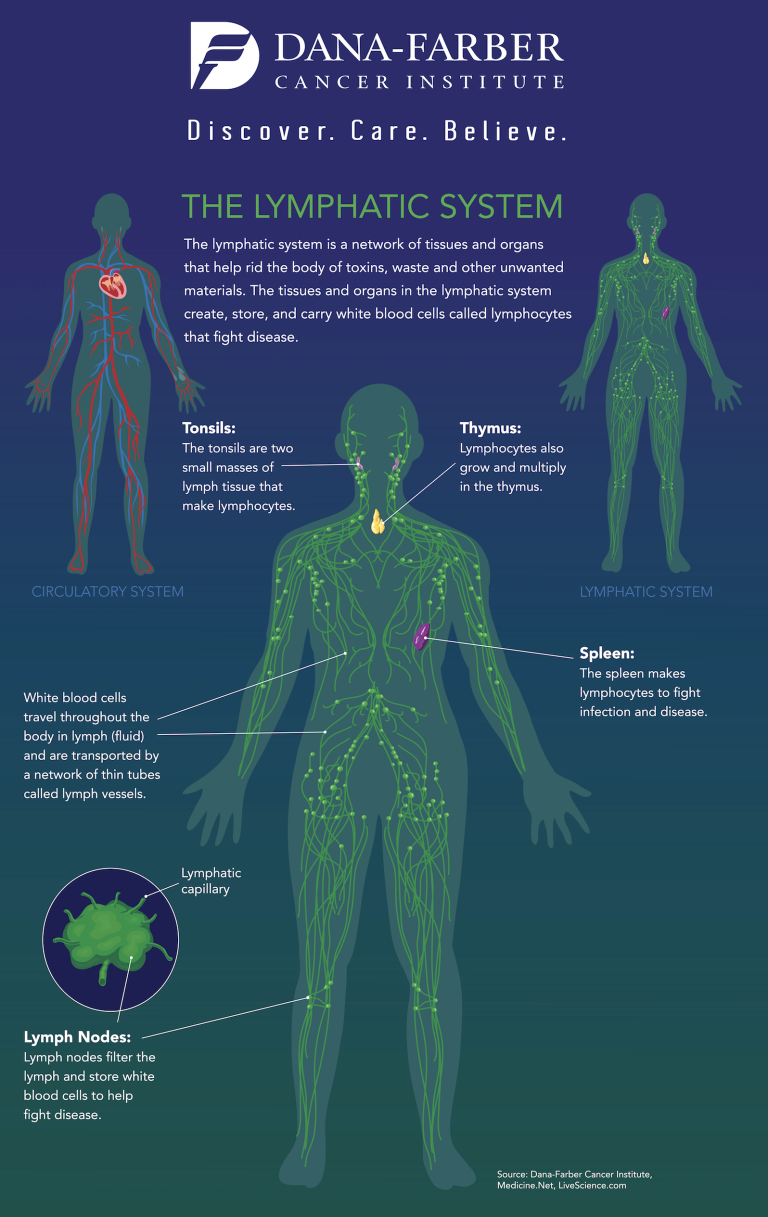
lymph nodes diagram
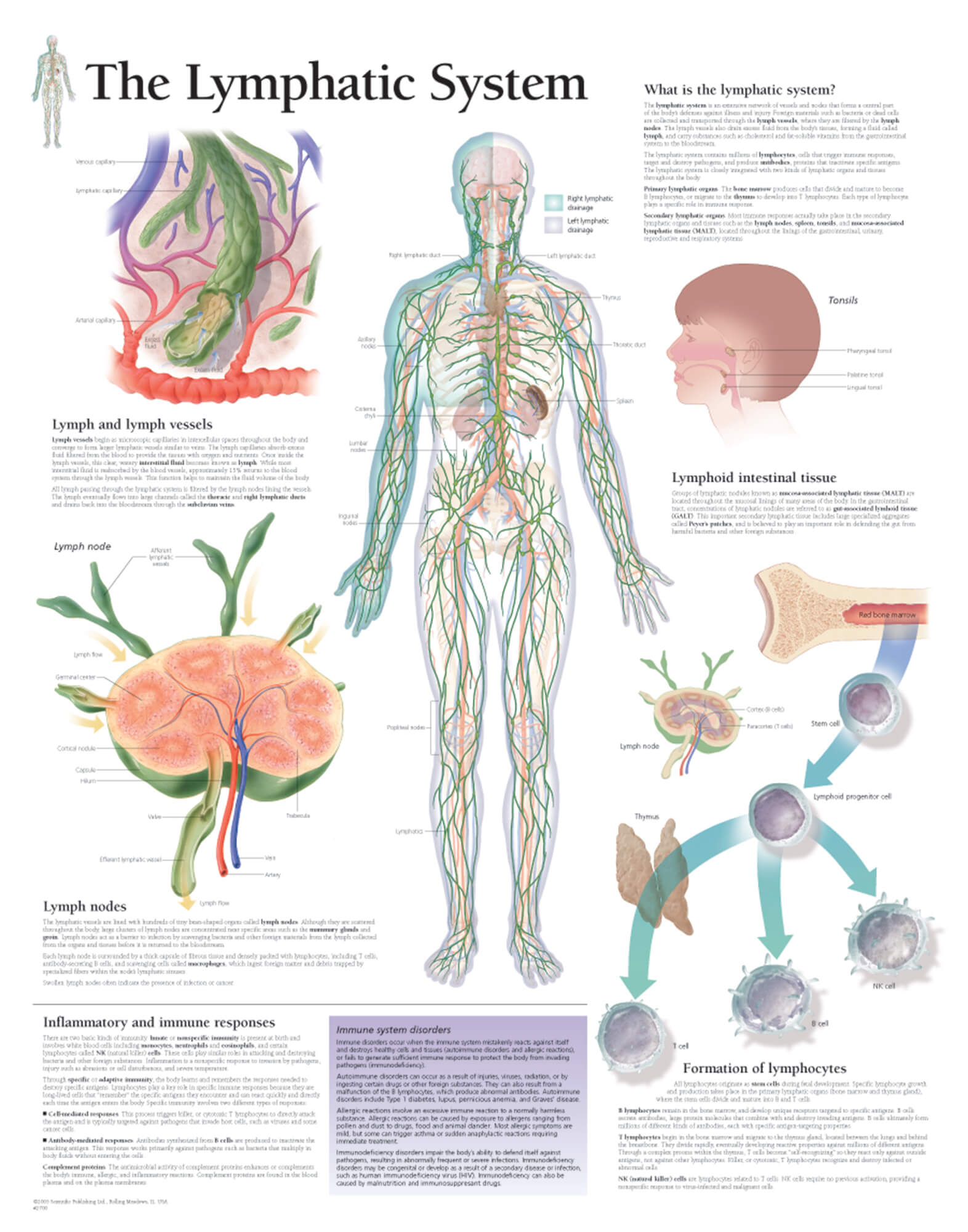
The Lymphatic System Scientific Publishing
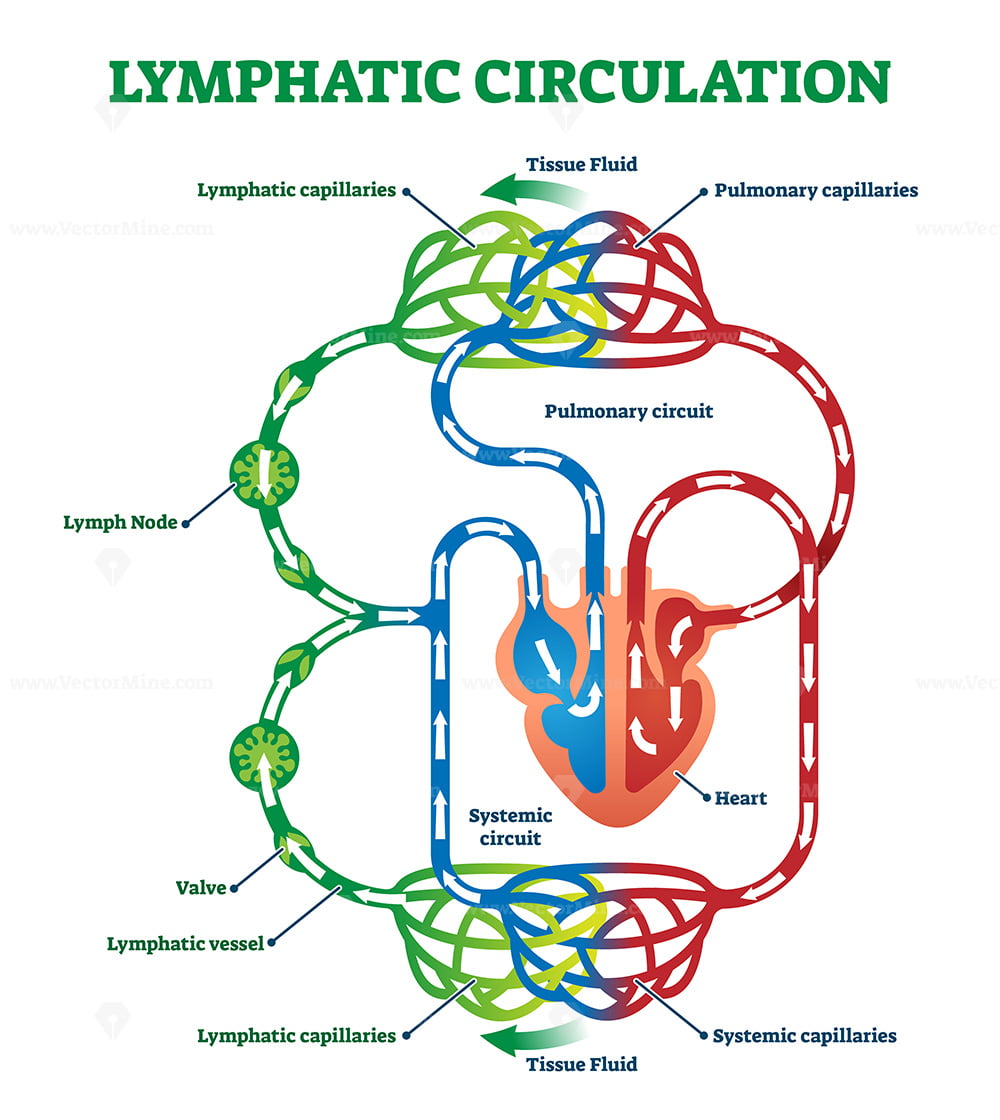
Lymphatic circulation system with lymph transportation vector
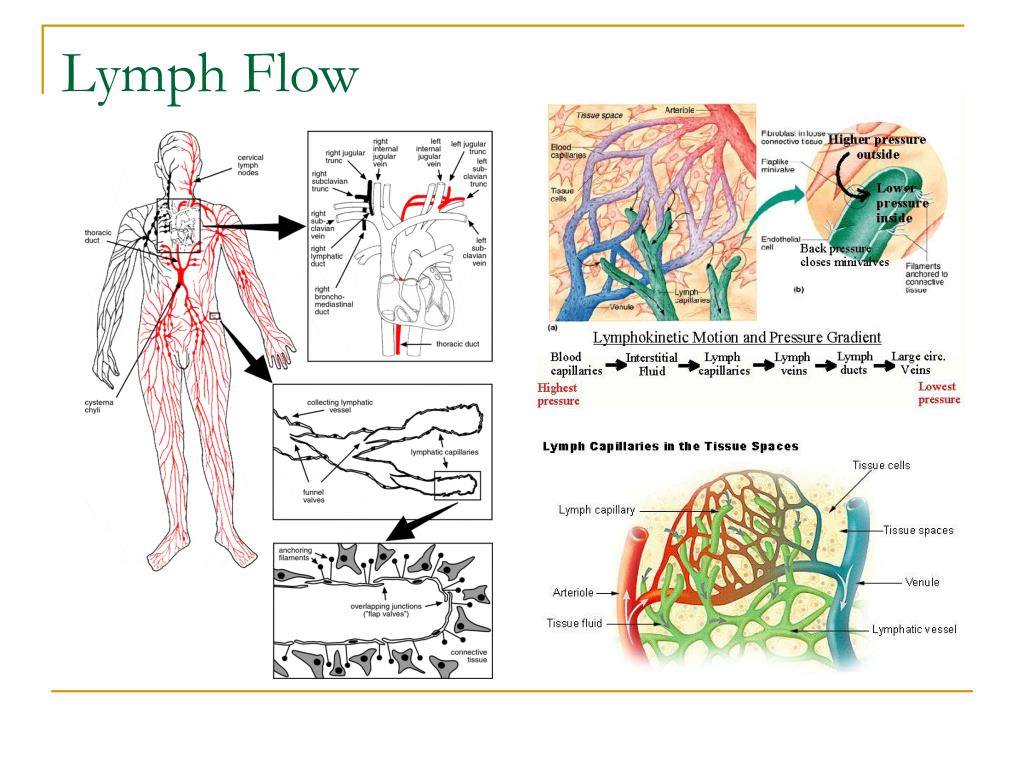
Lymphatic System Flow Direction Chart
Your Lymphatic System Is Part Of Your Immune System.
The Lymphatic System Is An Elaborate Network Of Vessels That Act Harmoniously To Pump Fluid And Cells, Collectively Called Lymph, From The Interstitial Space Into The Blood Circulation.
Web Lymph Flows From The Lymphatic Capillaries, Through Lymphatic Vessels, And Then Is Dumped Into The Circulatory System Via The Lymphatic Ducts Located At The Junction Of The Jugular And Subclavian Veins In The Neck.
The Lymph Typically Moves From Lymphatic Vessels To Lymphatic Trunks, Collecting Ducts, And Ultimately Into The Subclavian Veins.
Related Post: