Glycol Water Mixture Chart
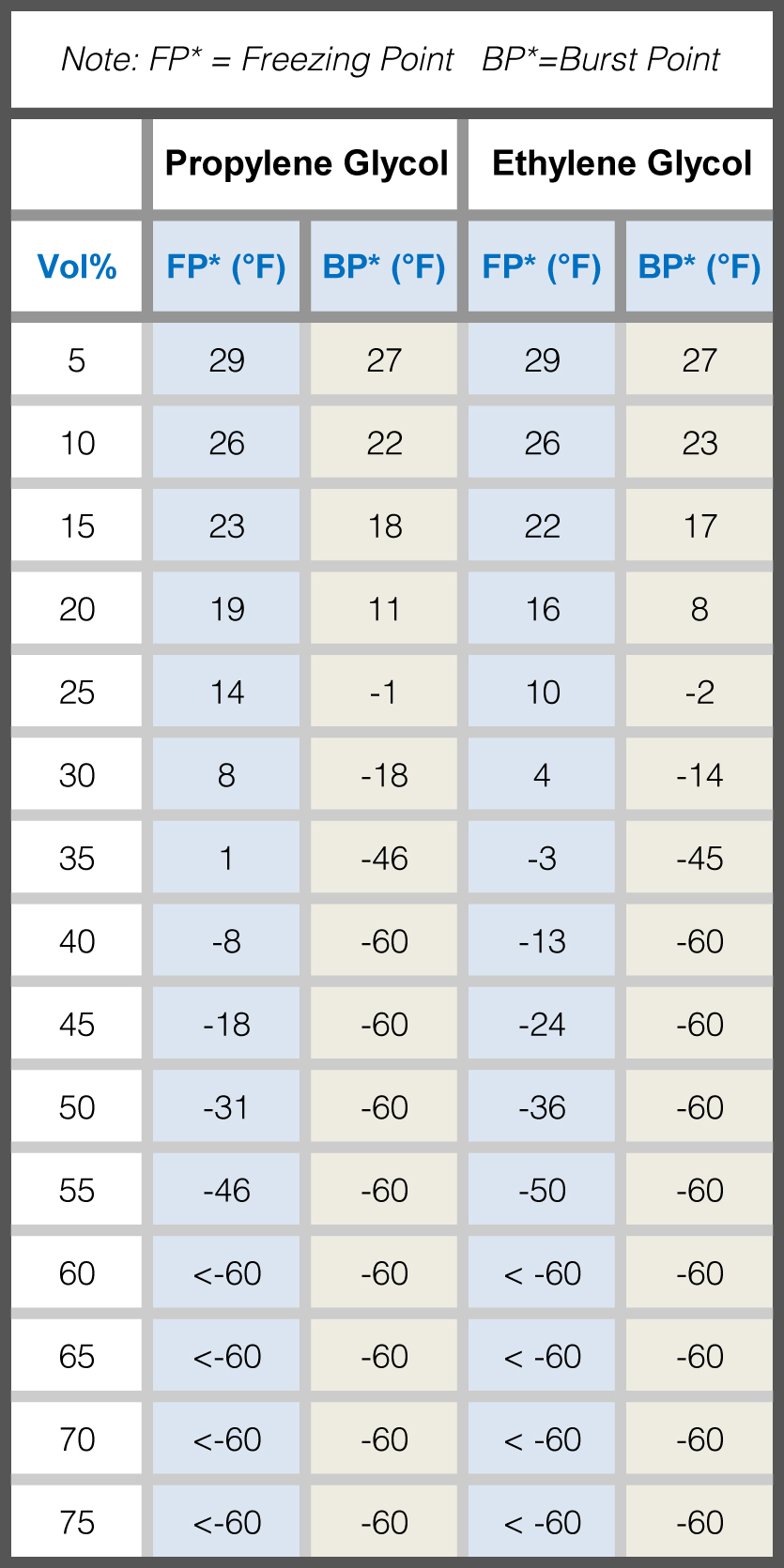
Glycol Water Mixture Chart - Calculate concentration for glycol freezing point or burst point protection. The required concentration of inhibited glycol needed in your system depends on the kind of cold weather protection that is needed. Web freezing point of aqueous solutions. Web see the charts below for help determining what percentage of glycol your system needs. ¤ ethylene glycol ¤ inhibitor package & water ¤ color ¤ ph of solution @ 33% glycol ¤ specific gravity @ 60/60 f ¤ reserve alkalinity (min) 95% 5% fluorescent yellow. Web glycol / water specific gravity chart. Entering the following values in the ac6/ac7’s “specific gravity” menu option will adjust the displayed readings for various water/glycol mixtures. Web specific heat, viscosity and specific weight of a water and ethylene glycol solution vary significantly with the percent of ethylene glycol and the temperature of the fluid. In both cases the fit was chosen to match data from gregory (table 3 and 7) m3: Web reference this chart in deciding how much glycol is necessary for your product. The main job of glycol is to prevent freezing of the process fluid and ensure consistent flow at the operating temperature. The highest yields of ethylene glycol occur at acidic or neutral ph with a large excess of water. The end uses for ethylene glycol are numerous (see table 1). The charts are based on different concentrations at various temperatures.. Mixing the two lowers the freezing point of water, allowing it to run through a chiller system at. Specific gravity is referenced to water at 15.6 °c. Entering the following values in the ac6/ac7’s “specific gravity” menu option will adjust the displayed readings for various water/glycol mixtures. Calculate concentration for glycol freezing point or burst point protection. The charts are. This reaction can be catalyzed by either acids or bases, or can occur at neutral ph under elevated temperatures. Fill in all white input fields and click ‘calculate’. The highest yields of ethylene glycol occur at acidic or neutral ph with a large excess of water. The charts are based on different concentrations at various temperatures. Web glycols are heavy,. Mixing the two lowers the freezing point of water, allowing it to run through a chiller system at. Web glycol / water specific gravity chart. After placing a sample of the glycol in the beaker, check the reading on the hydrometer and match it to the appropriate chart to accurately determine the glycol to water weight percentage. Do not mix. Web freezing point of aqueous solutions. Web the use of an industrial inhibited glycol and water mixture is recommended in most water chiller systems. Modified on 20 december 2017. Web ethylene glycol heat transfer fluid freeze point chart freezing point °f freezing point °c boiling point °f/760 mm/hg boiling point °c@ 0.96 / barr Web glycols are heavy, syrup like. Web specific heat, viscosity and specific weight of a water and ethylene glycol solution vary significantly with the percent of ethylene glycol and the temperature of the fluid. The end uses for ethylene glycol are numerous (see table 1). Mixing the two lowers the freezing point of water, allowing it to run through a chiller system at. The highest yields. ¤ propylene glycol ¤ inhibitor package & water ¤ color ¤ ph of solution @ 50% glycol ¤ specific gravity @ 60/60 f ¤ reserve alkalinity (min) 95% 5% colorless. Web learn about the chemical and physical properties of ethylene glycol/water mixtures, on our blog. Web andreas volk pointed out that the density calculation can be made more accurate by. Specific gravity is referenced to water at 15.6 °c. Web the conversion charts below are to be used with the ppe precision specific gravity hydrometer and beaker. Fill in all white input fields and click ‘calculate’. Thus, to achieve the same heat exchange inside the heat exchanger , requires more surface area or a larger heat exchanger. Water freezes at. Freeze protection and burst protection. Web glycol / water specific gravity chart. Thus, to achieve the same heat exchange inside the heat exchanger , requires more surface area or a larger heat exchanger. The required concentration of inhibited glycol needed in your system depends on the kind of cold weather protection that is needed. The charts are based on different. The required concentration of inhibited glycol needed in your system depends on the kind of cold weather protection that is needed. After placing a sample of the glycol in the beaker, check the reading on the hydrometer and match it to the appropriate chart to accurately determine the glycol to water weight percentage. ¤ propylene glycol ¤ inhibitor package &. Web see the charts below for help determining what percentage of glycol your system needs. Web skip to glycol concentration chart. There are two basic protection points: ¤ propylene glycol ¤ inhibitor package & water ¤ color ¤ ph of solution @ 50% glycol ¤ specific gravity @ 60/60 f ¤ reserve alkalinity (min) 95% 5% colorless. (ii) adjusting the fit for the density of pure glycerine as a function of temperature. Under these conditions, ethylene glycol yields of 90% can be achieved. Select one variable as fixed by checking appropriate box on the left. Entering the following values in the ac6/ac7’s “specific gravity” menu option will adjust the displayed readings for various water/glycol mixtures. Thus, to achieve the same heat exchange inside the heat exchanger , requires more surface area or a larger heat exchanger. Table obtained from lange's handbook of chemistry, 10th ed. Web ethylene glycol heat transfer fluid freeze point chart freezing point °f freezing point °c boiling point °f/760 mm/hg boiling point °c@ 0.96 / barr However, glycol freezes at 9° f. Mixing the two lowers the freezing point of water, allowing it to run through a chiller system at. Ethylene and propylene are the two standard types of inhibited glycols commonly used. Properties differs so much from clean water that heat transfer systems with ethylene glycol should be calculated thoroughly for actual temperature and solution. Web the use of an industrial inhibited glycol and water mixture is recommended in most water chiller systems.
Ethylene Glycol Temperature Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart

Ethylene Glycol Water Mixture Density Table

Table 6 from Ethylene Glycol and Its Mixtures with Water and
Ethylene Glycol Water Mixture Density Table

Propylene Glycol To Water Ratio Chart

Ethylene Glycol Freeze Chart
![[PDF] Ethylene Glycol and Its Mixtures with Water and Electrolytes](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/b802f6702e8678ea6b78b956f251743775579bf2/14-Figure15-1.png)
[PDF] Ethylene Glycol and Its Mixtures with Water and Electrolytes

Ethylene Glycol Water Mixture Density Table

WaterGlycol mixture measurement Baker Hughes
Ethylene Glycol Water Mixture Density Table
Web C2H4O + H2O → Ho−Ch2Ch2−Oh.
Fill In All White Input Fields And Click ‘Calculate’.
In Both Cases The Fit Was Chosen To Match Data From Gregory (Table 3 And 7) M3:
After Placing A Sample Of The Glycol In The Beaker, Check The Reading On The Hydrometer And Match It To The Appropriate Chart To Accurately Determine The Glycol To Water Weight Percentage.
Related Post: