How To Draw Alpha Helix
How To Draw Alpha Helix - Will always return you to this original view. The alpha means that if you look down the length of the spring, the coiling is happening in a clockwise direction as it goes away from you. Web an alpha helix with a coiled flat arrow. Alpha helices and beta sheets. One of them is an alpha helix, in which a long chain of peptides coils up like a phone cord (go to a museum if you don't know what a phone cord looks like). There are a number of possible macromolecular structures that peptides and proteins can adopt. Web one of these conformations, proposed first by pauling and in fact observed prominently in protein tertiary structure, is the α helix (alpha helix, model at right). Tertiary structure describes the folding of the polypeptide chain to assemble the different secondary structure elements in a particular arrangement. • amino and carboxy groups of amino acid residues (the backbone of the polypeptide chain) form hydrogen bonds to create secondary structure. Web lesson summary faqs activities what is alpha helix structure? [23] each of these can be visualized with. Web these helices are formed when the carbonyl o of the i th amino acid h bonds to the amide h of the i th +4 aa (4 amino acids away). An alpha helix structure is a type of secondary structure in a protein. Web draw glutamic acid and predict the overall. • amino and carboxy groups of amino acid residues (the backbone of the polypeptide chain) form hydrogen bonds to create secondary structure. Alpha helices and beta sheets. This coil is held together by hydrogen bonds between the oxygen of c=o. The alpha means that if you look down the length of the spring, the coiling is happening in a clockwise. Web these helices are formed when the carbonyl o of the i th amino acid h bonds to the amide h of the i th +4 aa (4 amino acids away). There are a number of possible macromolecular structures that peptides and proteins can adopt. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid. There are a number of possible macromolecular structures that peptides and proteins can adopt. • amino and carboxy groups of amino acid residues (the backbone of the polypeptide chain) form hydrogen bonds to create secondary structure. Web this illustration may be a combination of two images, or simply a program i don't know about. They both are shaped by hydrogen. Molecular graphics image of 16 residues of poly gly in the α helix conformation. Web this illustration may be a combination of two images, or simply a program i don't know about. Transparent background) and then combine the illustration with something else, e.g. One of them is an alpha helix, in which a long chain of peptides coils up like. Web lesson summary faqs activities what is alpha helix structure? Web this illustration may be a combination of two images, or simply a program i don't know about. Molecular graphics image of 16 residues of poly gly in the α helix conformation. This coil is held together by hydrogen bonds between the oxygen of c=o. An alpha helix structure is. Transparent background) and then combine the illustration with something else, e.g. Web 15.9k subscribers subscribe 25k views 8 years ago h2 chem hacks the secondary structure of proteins are held together by hydrogen bonds between peptide linkages at regular intervals. In an alpha helix the polypeptide chain twists like a. Alpha helices and beta sheets. Web this illustration may be. There are a number of possible macromolecular structures that peptides and proteins can adopt. • amino and carboxy groups of amino acid residues (the backbone of the polypeptide chain) form hydrogen bonds to create secondary structure. Tertiary structure describes the folding of the polypeptide chain to assemble the different secondary structure elements in a particular arrangement. Web draw glutamic acid. Web how to draw alpha helix and beta sheet? An alpha helix structure is a type of secondary structure in a protein. The alpha means that if you look down the length of the spring, the coiling is happening in a clockwise direction as it goes away from you. Web 15.9k subscribers subscribe 25k views 8 years ago h2 chem. • amino and carboxy groups of amino acid residues (the backbone of the polypeptide chain) form hydrogen bonds to create secondary structure. Web this illustration may be a combination of two images, or simply a program i don't know about. Web draw glutamic acid and predict the overall charge state of the amino acid at ph = 1, ph =. Will always return you to this original view. Web lesson summary faqs activities what is alpha helix structure? Web 15.9k subscribers subscribe 25k views 8 years ago h2 chem hacks the secondary structure of proteins are held together by hydrogen bonds between peptide linkages at regular intervals. Web • secondary structure includes: Web the two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Alpha helices and beta sheets. Transparent background) and then combine the illustration with something else, e.g. In an alpha helix the polypeptide chain twists like a. • amino and carboxy groups of amino acid residues (the backbone of the polypeptide chain) form hydrogen bonds to create secondary structure. One of them is an alpha helix, in which a long chain of peptides coils up like a phone cord (go to a museum if you don't know what a phone cord looks like). Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary structure. Web draw glutamic acid and predict the overall charge state of the amino acid at ph = 1, ph = 3, ph = 7, and ph = 12. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. 3d structure generation) into a single prediction pipeline. This coil is held together by hydrogen bonds between the oxygen of c=o. An alpha helix structure is a type of secondary structure in a protein.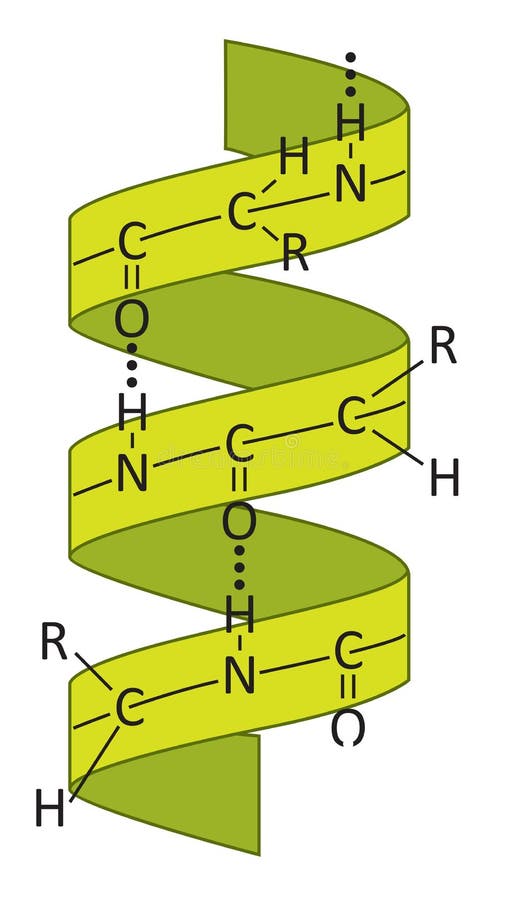
Alpha helix stock vector. Illustration of amino, helical 174067513

Proteins Microbiology

Draw the Structure of alpha helix Chemistry Biomolecules 12894141
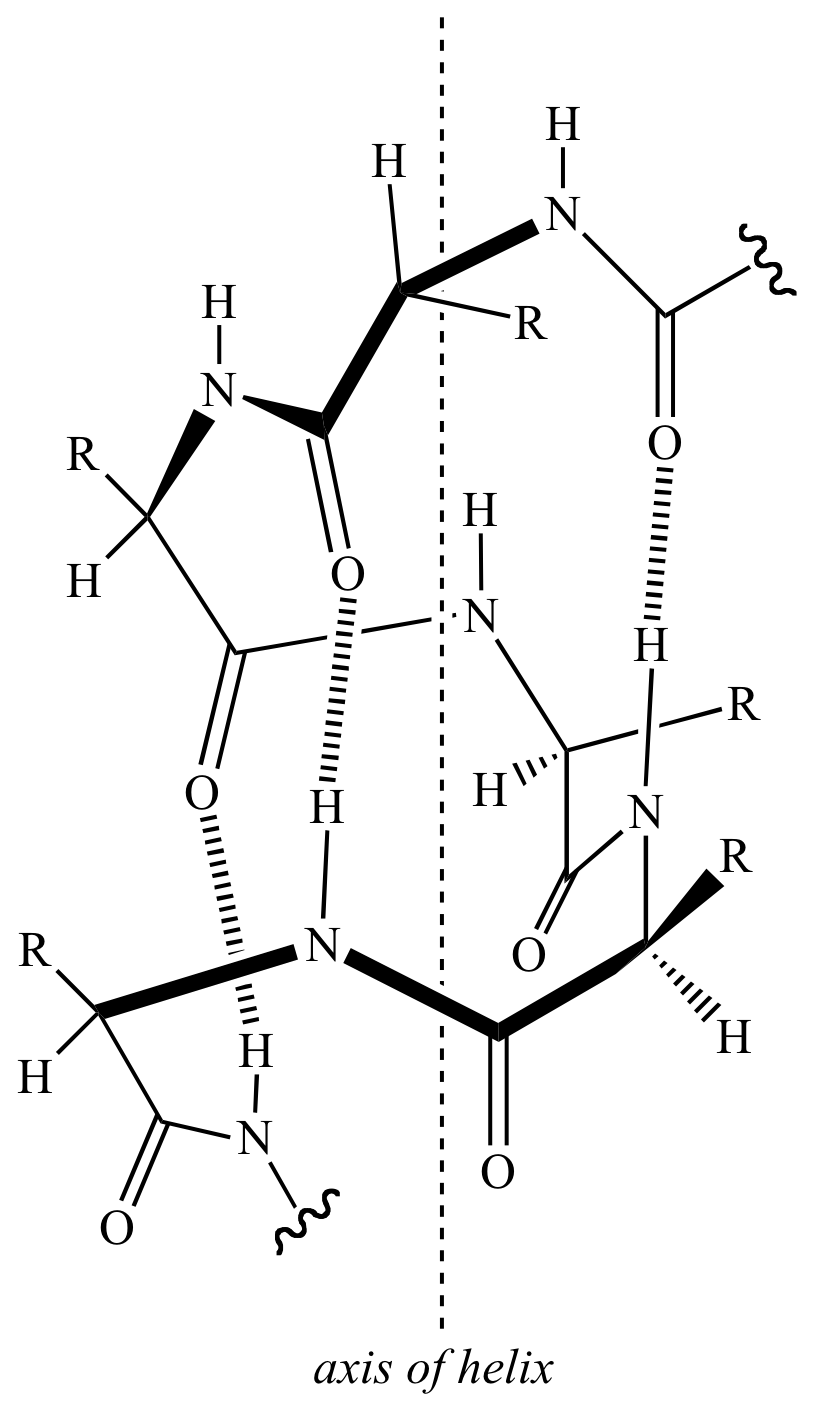
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Alphahelix
![[Solved] How can I draw alpha helices in ChemDraw? 9to5Science](https://i.stack.imgur.com/gaLg9.png)
[Solved] How can I draw alpha helices in ChemDraw? 9to5Science

Biochemistry Fundamentals Secondary Structure 1 The Alpha Helix

Alpha helix secondary structure of protein YouTube
![[Solved] How can I draw alpha helices in ChemDraw? 9to5Science](https://i.stack.imgur.com/2F9WZ.jpg)
[Solved] How can I draw alpha helices in ChemDraw? 9to5Science
23 2D representation of the structure of a typical alphahelix. While

How to draw Alpha Helix for Secondary Structure of Proteins
Rotate The Structure And Look Down The Axis Of Each Helix.
[23] Each Of These Can Be Visualized With.
The Alpha Means That If You Look Down The Length Of The Spring, The Coiling Is Happening In A Clockwise Direction As It Goes Away From You.
This Section Will Discuss The Protein, Types Of Protein, And The Primary And Secondary Protein Structures, I.e.
Related Post: