How To Draw Conjugate Acid
How To Draw Conjugate Acid - Web draw the conjugate bases and several resonance structures of each. Atoms first 2e | openstax™️. Vocabulary for finding the conjugate of an. Web in order to find the conjugate acid of nh3 we must first understand the bronsted lowery definitions for acids and bases. Web steps to find the conjugate of an acid. Pka trends for carbonyl systems: This is because acids are proton donors (h is considered the proton because h has one proton). Using their conjugate bases, explain the pka differences using hückel mo diagrams. The other pair consists of (ch 3) 3 n and (ch 3) 3 nh +, where (ch 3) 3 nh + is the conjugate acid (it has an additional proton) and (ch 3) 3 n is the conjugate base. Draw the conjugate bases for each acid below. By contrast, a conjugate base is the species formed after an acid donates its proton. Draw the conjugate bases for each acid below. Suppose our analyte is hydrochloric acid hcl (strong acid) and the titrant is sodium hydroxide naoh (strong base). Using their conjugate bases, explain the pka differences using hückel mo diagrams. Remove a hydrogen atom from the acid. And we've shown the movement of electrons using curved arrows. Web one pair is h 2 o and oh −, where h 2 o has one more h + and is the conjugate acid, while oh − has one less h + and is the conjugate base. Web draw the conjugate bases and several resonance structures of each. Let bh. Suppose our analyte is hydrochloric acid hcl (strong acid) and the titrant is sodium hydroxide naoh (strong base). Web (b) draw the structure of each conjugate acid that can be formed. What is the conjugate base of. Let bh + be the conjugate acid of a base. Web it's basically the same way as any other molecule. (c) mark with an asterisk any structure that can show amphiprotic behavior in aqueous solution. how do i go about solving this? A conjugate acid contains one more h atom and one more + charge than the base that formed it. Web so on the right, this right here must be the conjugate acid. Draw the conjugate bases for each. The expression for the acidic constant ka for the conjugate acid. And here's another way to look at it. Draw the conjugate bases for each acid below. Atoms first 2e | openstax™️. Web draw the conjugate acid of each of the following: Web steps to find the conjugate of an acid. And we've shown the movement of electrons using curved arrows. I don't understand why the protons are accepted at the ns and not the os. A conjugate acid is formed when a proton is added to a base, and a conjugate base is formed when a proton is removed from an. Bh + = b + h +. Atoms first 2e | openstax™️. Web in order to find the conjugate acid of nh3 we must first understand the bronsted lowery definitions for acids and bases. Pka trends for carbonyl systems: (c) mark with an asterisk any structure that can show amphiprotic behavior in aqueous solution. how do i go about solving. Web in order to find the conjugate acid of nh3 we must first understand the bronsted lowery definitions for acids and bases. Web draw the conjugate bases and several resonance structures of each. By contrast, a conjugate base is the species formed after an acid donates its proton. Bh + = b + h +. Ka = [b][h +] [bh. Let bh + be the conjugate acid of a base. Acids and bases acids and bases. Also, how do you draw a conjugate acid? So this is the conjugate acid on the right. In the base dissociation equilibrium above the conjugate acid of base b is hb +. Bh + = b + h +. What is the conjugate acid of each of the following? Web draw the conjugate base of any one of the following strong acids: Let’s attempt to draw some titration curves now. Nitric acid, perchloric acid, sulfuric acid. Web one pair is h 2 o and oh −, where h 2 o has one more h + and is the conjugate acid, while oh − has one less h + and is the conjugate base. Remove a hydrogen atom from the acid given. By contrast, a conjugate base is the species formed after an acid donates its proton. And we've shown the movement of electrons using curved arrows. Also, how do you draw a conjugate acid? Nitric acid, perchloric acid, sulfuric acid. I don't understand why the protons are accepted at the ns and not the os. Web 📗 need help with chemistry? This is because acids are proton donors (h is considered the proton because h has one proton). 1) titration of a strong acid with a strong base. What is the conjugate acid of each of the following? For a given acid or base, these equilibria are linked by the water dissociation equilibrium: Pka trends for carbonyl systems: Let bh + be the conjugate acid of a base. (c) mark with an asterisk any structure that can show amphiprotic behavior in aqueous solution. how do i go about solving this? A conjugate acid is formed when a proton is added to a base, and a conjugate base is formed when a proton is removed from an acid.
How to typset/draw conjugate acids and bases

Chapter 10 Exercises 3 and 4 Drawing Conjugate Acids and Conjugate
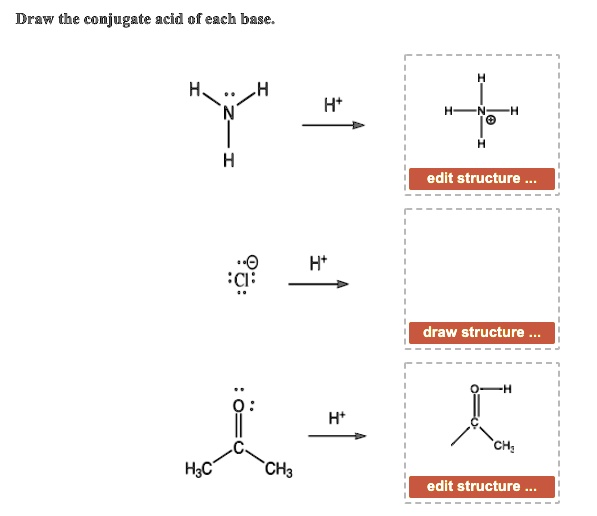
SOLVED Draw the conjugate acid of each base A H N" H2N edit structure
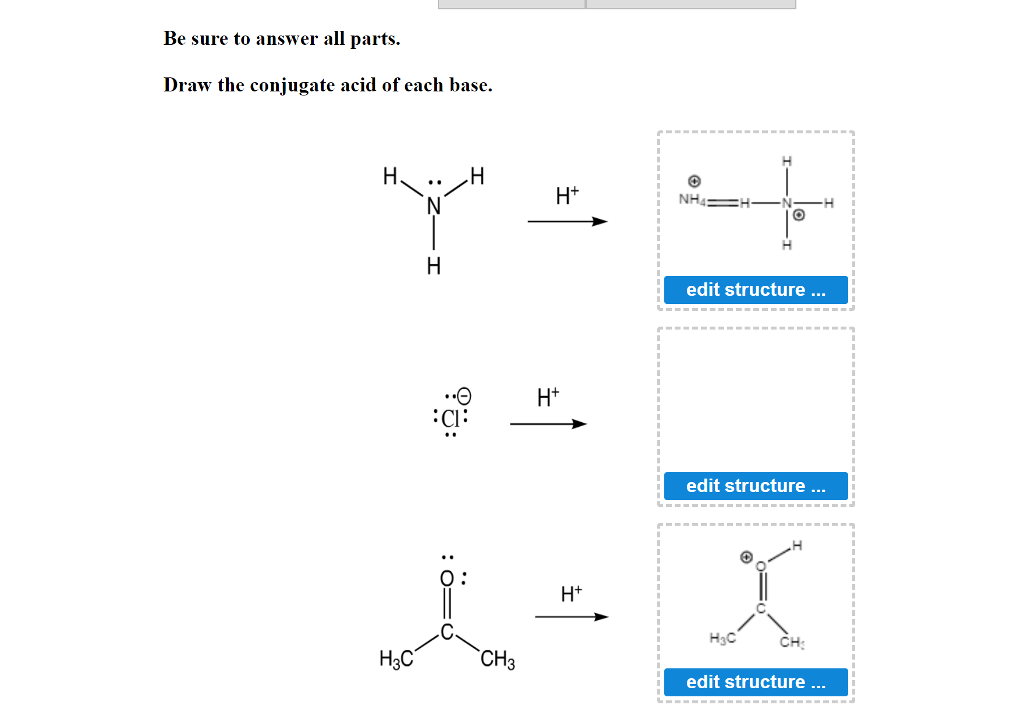
Solved Be sure to answer all parts. Draw the conjugate acid
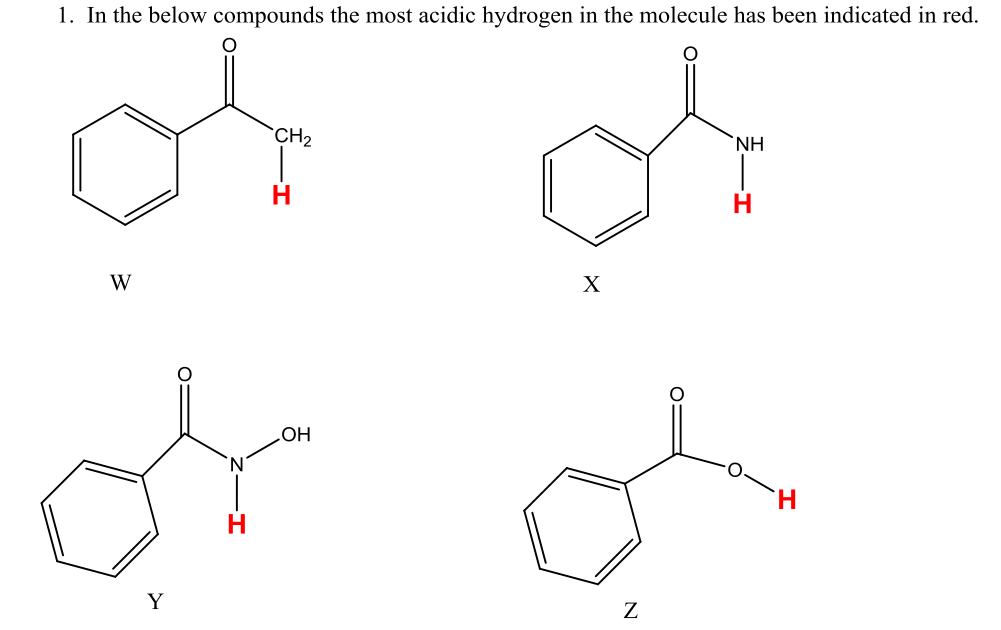
Solved A. Draw the conjugate base of each acid, including

Draw the Lewis Structure for the Conjugate Acid of Ammonia En
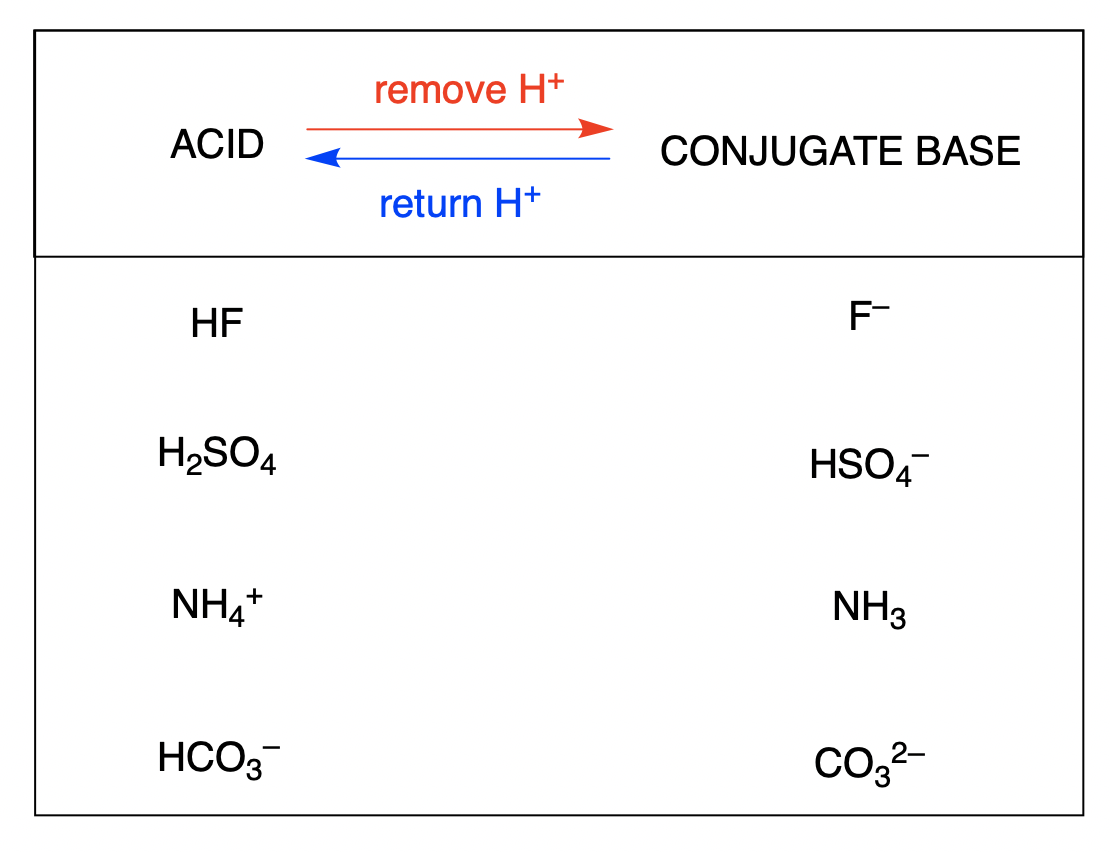
Write the Formula for the Conjugate Acid of Each Base
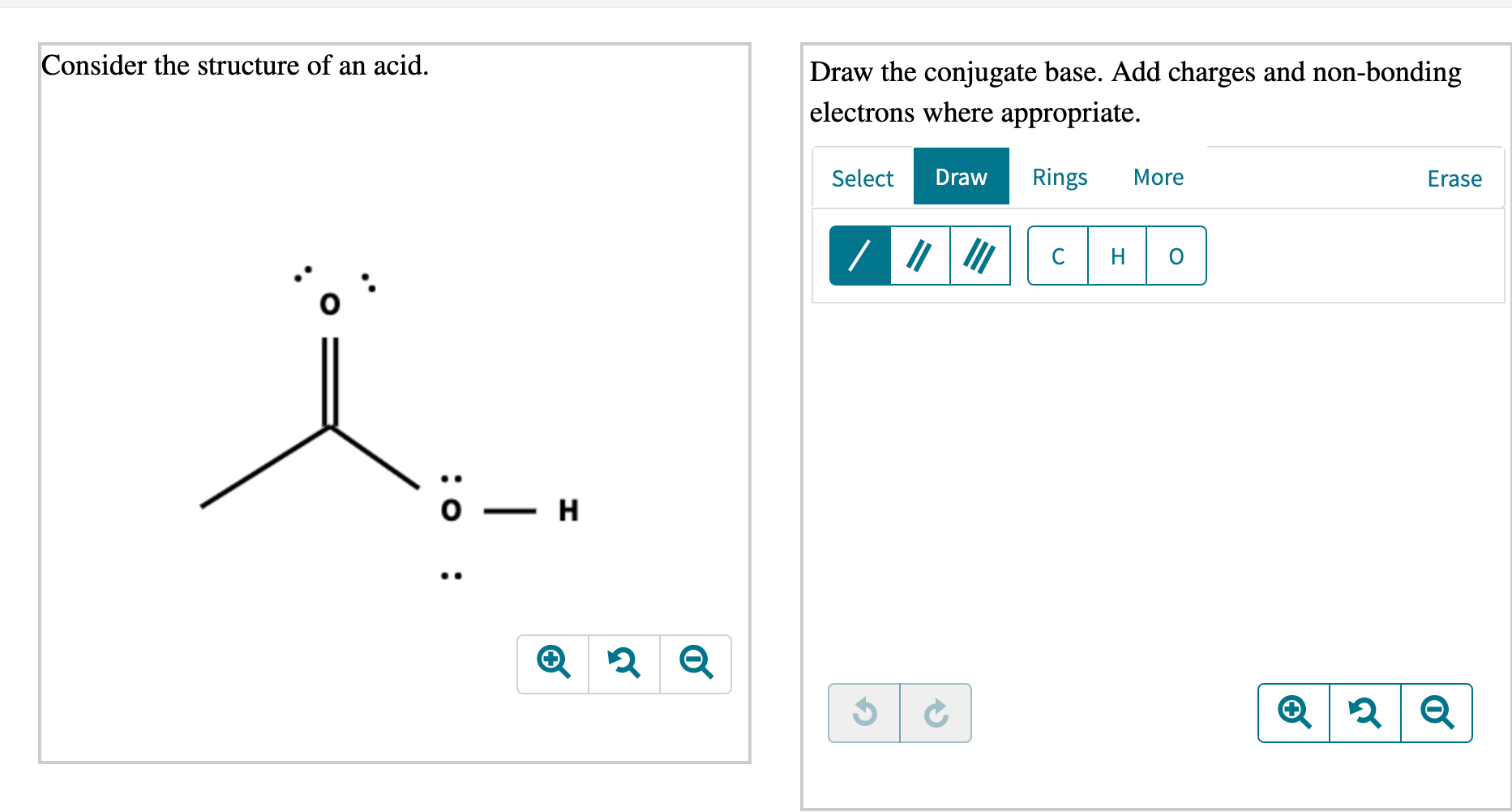
Solved Consider the structure of an acid. Draw the conjugate

CHEM112 5 6 drawing conjugate acids and bases YouTube
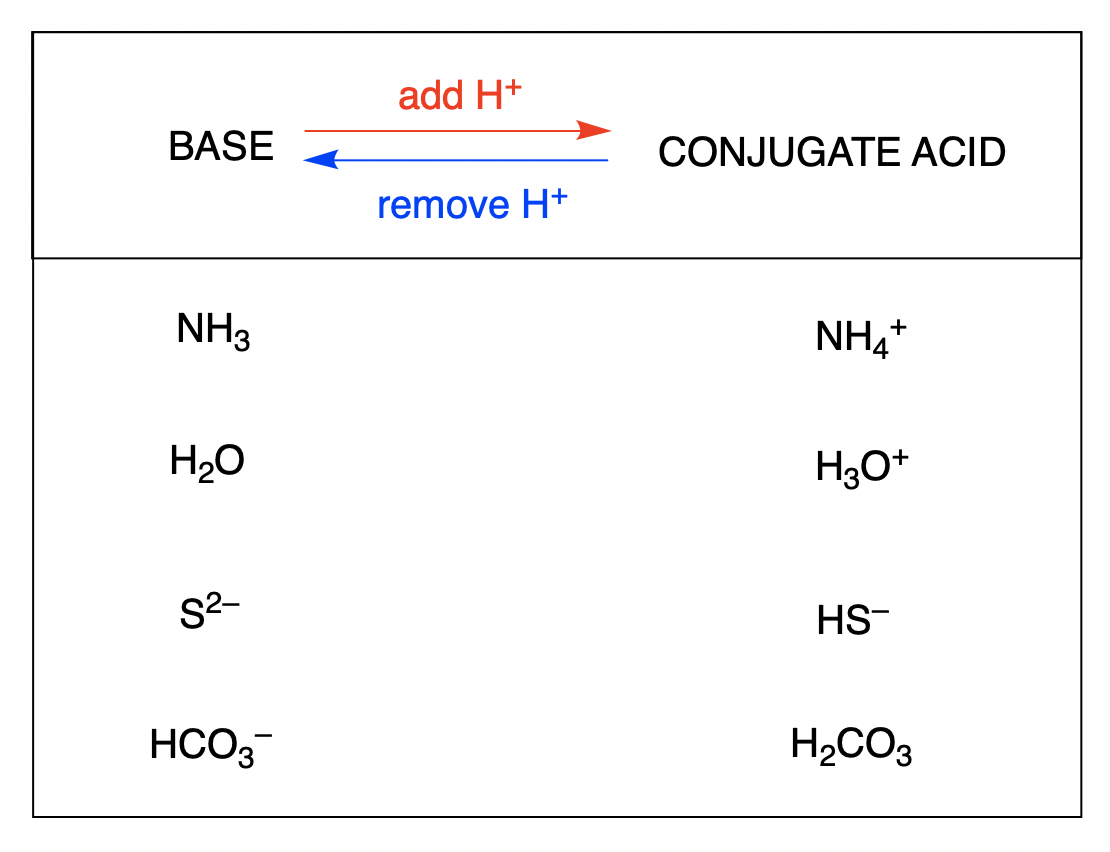
Enter the Conjugate Base for Each Acid.
For Example (D), Also Identify The Conjugate Acid And The Conjugate Base In The Reverse Reaction.
So This Is The Conjugate Acid On The Right.
Web It's Basically The Same Way As Any Other Molecule.
2.5K Views 1 Year Ago Chapter 14 | Solution Manual For Chemistry:
Related Post: