Igneous Rock Flow Chart
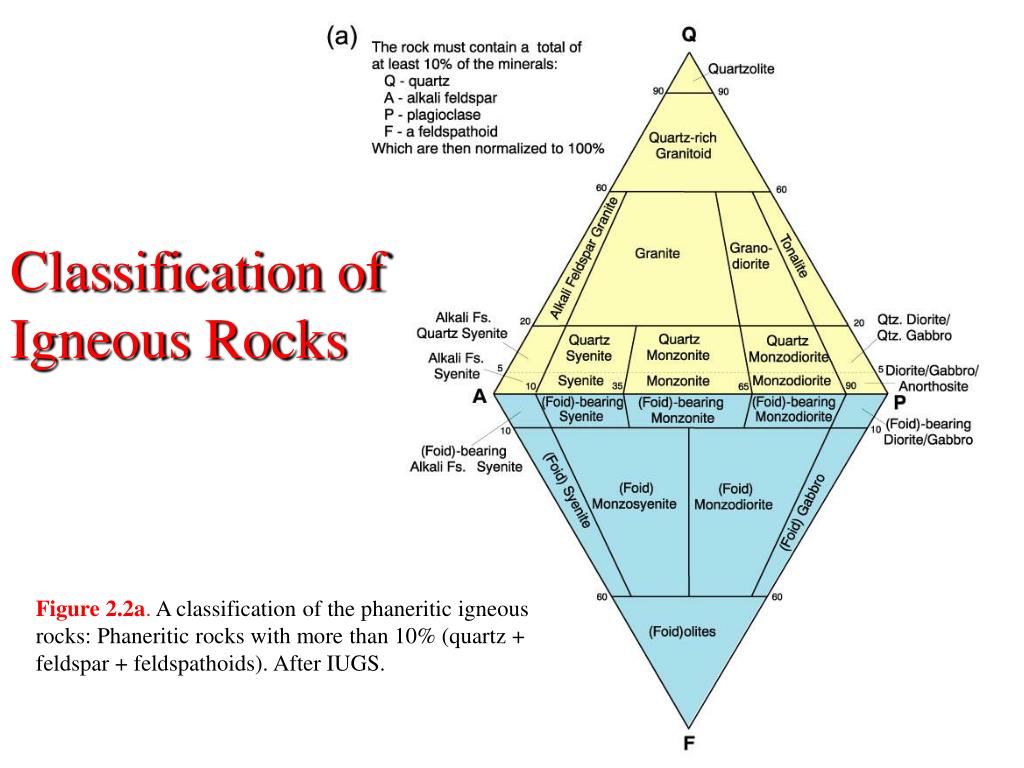
Igneous Rock Flow Chart - Formed from magmas that reached the surface and cooled quickly (co. When magma finds its way to the surface through cracks or volcanoes, it is called lava. They are categorized based on their origin, texture, and mineral composition. Mci = mafic color index, high % = mafic rock *igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of magma (just heat)* intrusive: Web igneous rock flow chart/concept map by earth science educational resources. These charts include many rocks and minerals and will help you identify the samples in your mini me geology kits and those commonly found in nature. Web a colour diagram showing the mineral breakdown of common igneous rocks, including photographs of the common types of rocks in each of the compositional categories (i.e., ultramafic, mafic, intermediate, felsic). Web igneous rock composition refers to what is in the rock (the chemical composition or the minerals that are present), and the word texture refers to the features that we see in the rock such as the mineral sizes or the presence of glass, fragmented material, or vesicles (holes) in the igneous rock. Web let’s explores the nature of igneous rocks, their types, formation processes, properties, classification, and textures. Igneous rocks form from the solidification of molten rock material. Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Web flow charts or, dichotomous keys, are a great tool for identifying rocks and minerals when you are learning about the different sample properties. This relates to the cooling history of. Web igneous rocks are classified based on texture and composition. Web there are two main types of igneous rocks: These characteristics, in turn, signify a particular environment of formation. Web igneous rock composition refers to what is in the rock (the chemical composition or the minerals that are present), and the word texture refers to the features that we see. You are a true mini me geologist! These characteristics, in turn, signify a particular environment of formation. Web an igneous rock can be represented as a vertical line drawn through the diagram, and the vertical scale used to break down the proportion of each mineral it contains. For example, the arrows in the mafic field of the diagram represent a. For example, the arrows in the mafic field of the diagram represent a rock containing 48% pyroxene and 52% plagioclase feldspar. Sand on a beach) mix of many different sizes? Web igneous rocks (fiery rocks) are made when molten material inside or outside the earth cools and becomes solid. Igneous rocks form from the solidification of molten rock material. Web. Web igneous rocks (fiery rocks) are made when molten material inside or outside the earth cools and becomes solid. Are the grains mostly the same size or a. Web flow charts or, dichotomous keys, are a great tool for identifying rocks and minerals when you are learning about the different sample properties. Web an igneous rock can be represented as. Web examples include basalt, rhyolite, and andesite. They are categorized based on their origin, texture, and mineral composition. You are a true mini me geologist! Is its hardness 8 or higher? Earth is composed predominantly of a large mass of igneous rock with a very thin veneer of weathered material—namely, sedimentary rock. For example, the arrows in the mafic field of the diagram represent a rock containing 48% pyroxene and 52% plagioclase feldspar. Web flow charts or, dichotomous keys, are a great tool for identifying rocks and minerals when you are learning about the different sample properties. This melted rock is called magma when it is inside the earth. Properties and characteristics. Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the earth or while the melted rock is still inside the crust. Are the grains mostly the same size or a. You did a great job identifying your new igneous rocks. Properties and characteristics of igneous rocks. They are categorized based on. Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Formed from magmas that cooled and solidified within the crust (basically formed in the ground), very visible crystals extrusive: You did a great job identifying your new igneous rocks. All magma. 4.4 (5 ratings) 1,188 downloads. Sand on a beach) mix of many different sizes? Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. For example, the arrows in the mafic field of the diagram represent a rock containing 48% pyroxene. Web flow charts or, dichotomous keys, are a great tool for identifying rocks and minerals when you are learning about the different sample properties. This relates to the cooling history of the molten magma from which it came. Web a colour diagram showing the mineral breakdown of common igneous rocks, including photographs of the common types of rocks in each of the compositional categories (i.e., ultramafic, mafic, intermediate, felsic). In the mafic field, the arrows represent a rock containing 60% pyroxene and 40% olivine. All magma develops underground, in the lower crust or upper mantle ,. These characteristics, in turn, signify a particular environment of formation. Igneous rocks are typically hard and dense, resistant to weathering, and often exhibit a crystalline structure. Print an igneous identification flow chart or igneous rock dichotomous to use with mini me geology igneous rock kits. This melted rock is called magma when it is inside the earth. They are categorized based on their origin, texture, and mineral composition. Properties and characteristics of igneous rocks. Formed from magmas that cooled and solidified within the crust (basically formed in the ground), very visible crystals extrusive: (a) lava flows and (b) tephra (pyroclastic material). Web igneous rock identification flow chart contains mostly (more than half) dark crystals and only a few light crystals has about half dark crystals and half light crystals (looks more dark) syenite mostly fine grained, a few larger crystals may be seen light gray, pink, red, yellow, tan monzonite diorite lots of quartz in rock (samples in mini me. Web examples include basalt, rhyolite, and andesite. These characteristics, in turn, signify a particular environment of formation.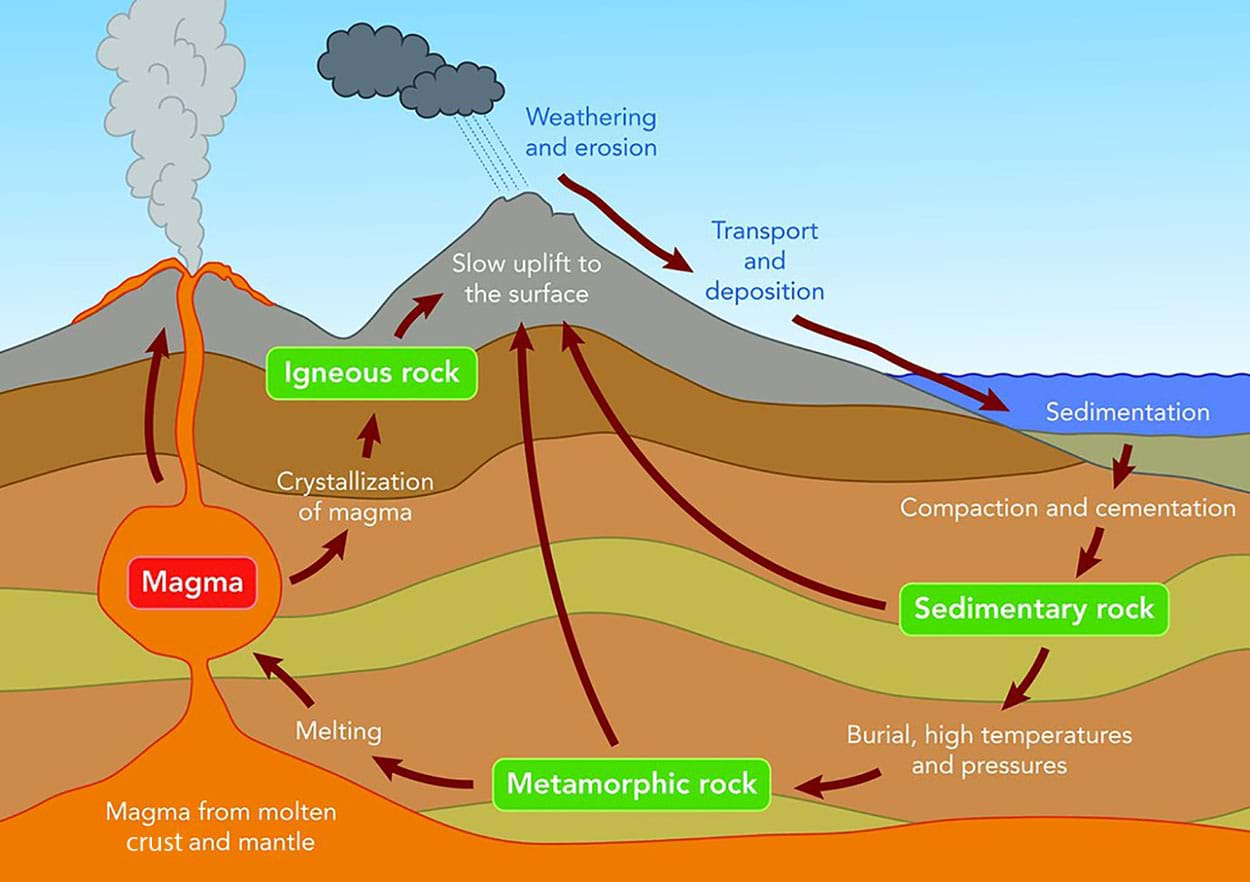
Rocks, Rocks, Rocks Test, Identify Properties & Classify Activity
Igneous Rock Flow Chart
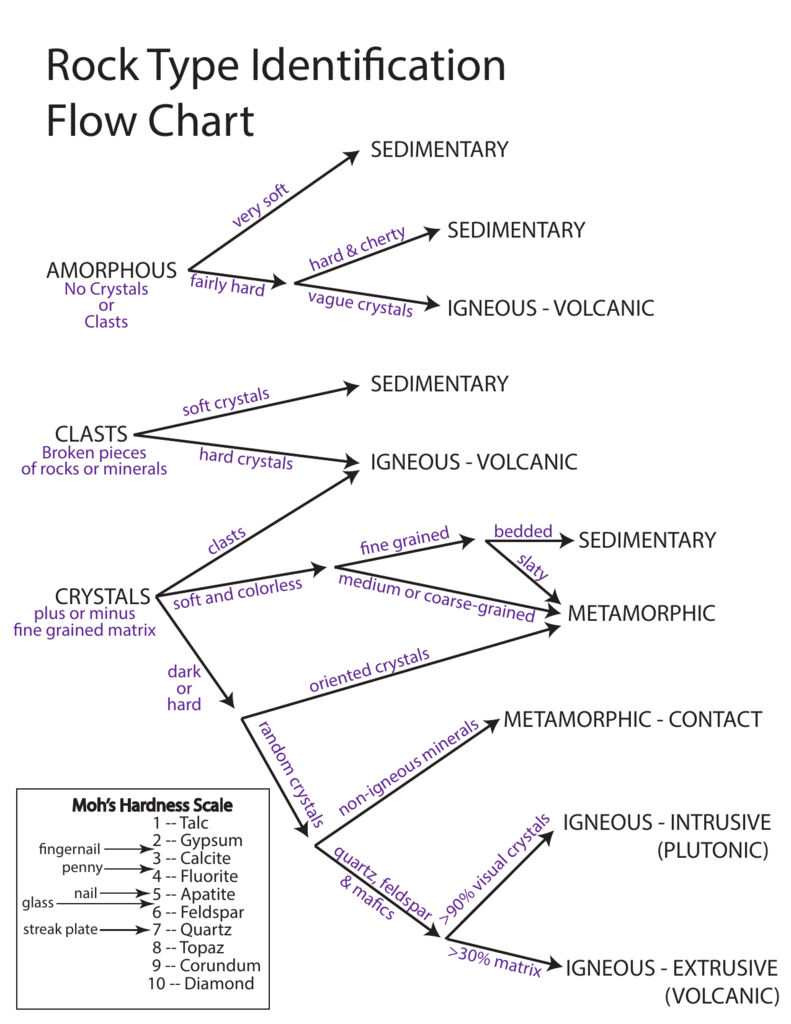
Rock Type Identification Flow Chart
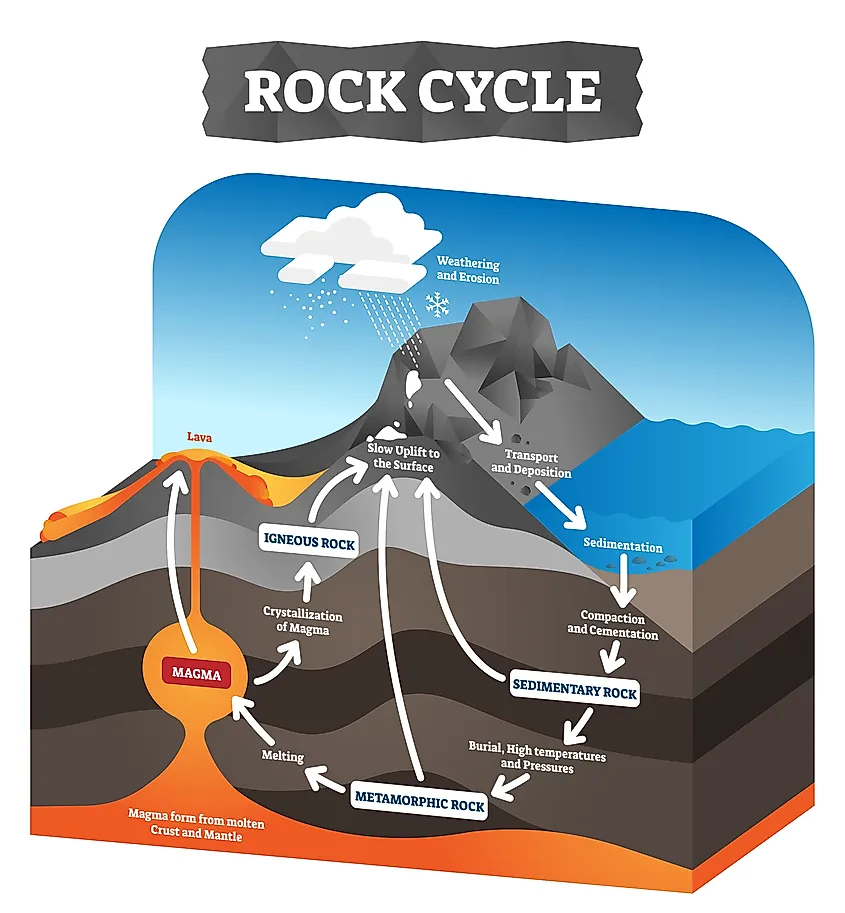
How Are Igneous Rocks Formed? WorldAtlas

Igneous Rock Flow Chart Resources Geology Pinterest
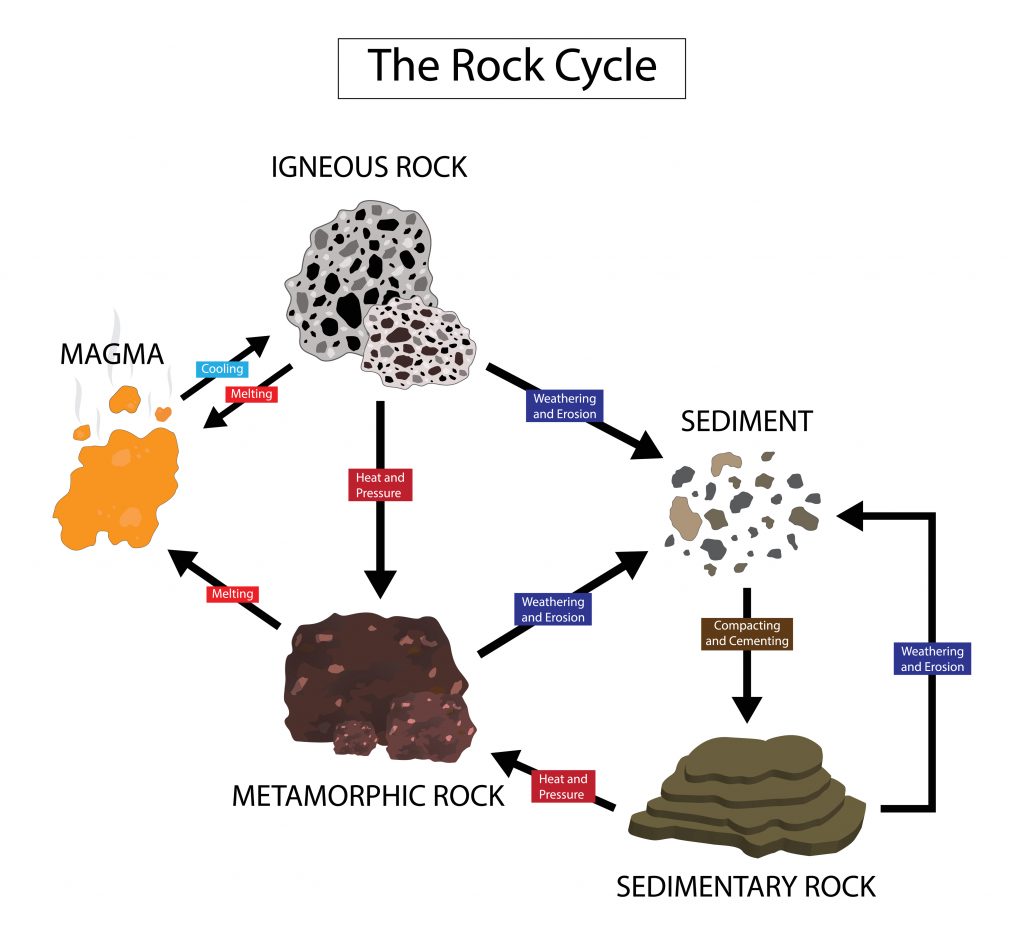
A Beginner's Guide to Types of Rock Igneous, Sedimentary, and

ü Lab 5, IgneousRock Analysis Flow Chart 1 , IgneousRock Analysis Flow
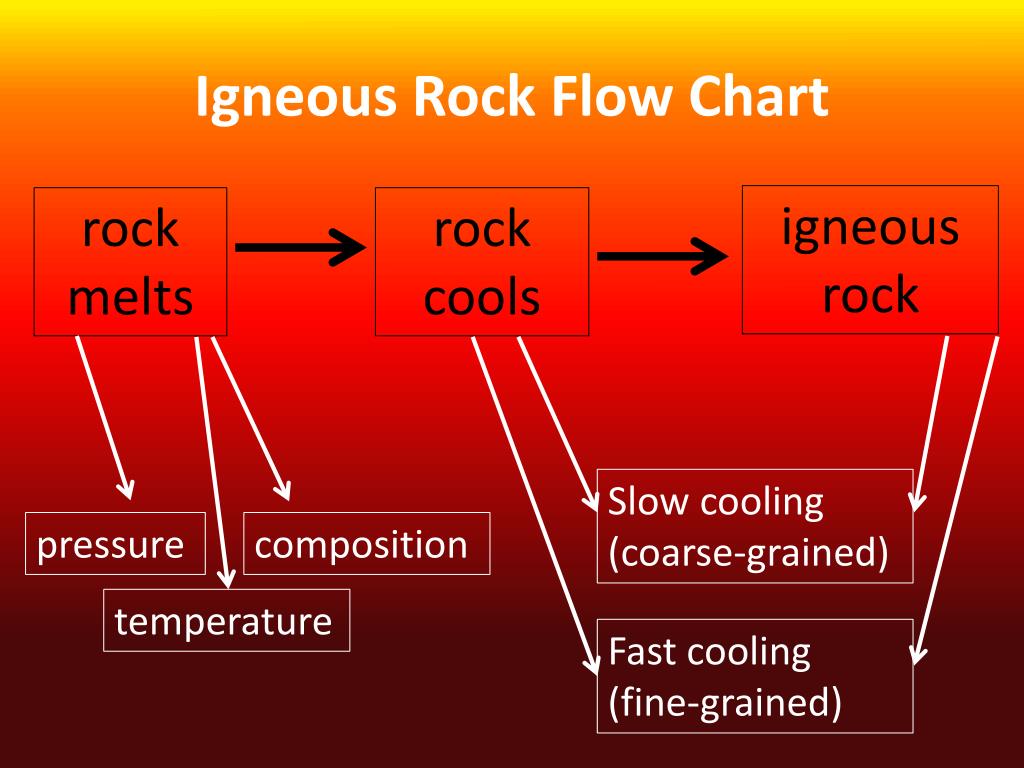
Igneous Rock Identification Flow Chart

Reference Tools for Igneous Rocks Laboratory Manual for Earth Science

Igneous rock concept map
Volcanic Rocks Break Down Into Two More Categories:
Web There Are Two Main Types Of Igneous Rocks:
This Lab Constitutes Four Parts.
Web Let’s Explores The Nature Of Igneous Rocks, Their Types, Formation Processes, Properties, Classification, And Textures.
Related Post: