Insulin Sensitivity Factor Chart
Insulin Sensitivity Factor Chart - Duration of insulin action (dia) insulin on. Since the human body is so complex, not all people will process. See an example of how to apply the insulin sensitivity. Web learn how to use the correction factor tool to find out how much extra mealtime insulin you need to lower your blood sugar. Web insulin sensitivity factors. Web for example, a correction factor of 2 means that 1 unit of insulin should lower your bgl by 2mmol/l. Web learn how to calculate and test your insulin sensitivity factor, also known as your correction factor or correction bolus, to adjust your insulin dosage. Web an insulin sensitivity factor (isf) or correction factor describes how much one unit of rapid or regular insulin will lower blood glucose. Web high insulin sensitivity is when your cells respond normally to insulin, facilitating glucose uptake, keeping your blood sugar levels stable, and reducing the. Web insulin plays a pertinent role in maintaining the glucose levels in the brain. Novorapid, humalog or apidra ) will lower blood. 1 unit of bolus insulin lowers. For example, a ratio of 1:2 means that one. Since the human body is so complex, not all people will process. Web learn how to use the correction factor tool to find out how much extra mealtime insulin you need to lower your blood sugar. Duration of insulin action (dia) insulin on. Web insulin to carbohydrate ratio: Your isf is the number of mmol/l that one unit of insulin will lower your blood glucose level by. Web learn how to measure how much insulin can lower blood sugar levels and adjust your insulin dose accordingly. 1 unit of bolus insulin lowers glucose by 1 mmol/l; Web some people may need 1 unit of insulin to lower blood glucose by 50 mg/dl and someone else may need 1 unit of insulin to lower blood glucose by 25 mg/dl. 1 unit of bolus insulin lowers glucose by 1 mmol/l; The inability of insulin to bind to the insulin receptors due to the downregulation of the. Web learn. See an example of how to apply the insulin sensitivity. Web insulin sensitivity factors. Web some people may need 1 unit of insulin to lower blood glucose by 50 mg/dl and someone else may need 1 unit of insulin to lower blood glucose by 25 mg/dl. Web insulin plays a pertinent role in maintaining the glucose levels in the brain.. 1 unit to 10g cho total amount of carbs in the meal: Web insulin to carbohydrate ratio: Web insulin resistance, also known as impaired insulin sensitivity, happens when cells in your muscles, fat and liver don’t respond as they should to insulin, a hormone. Web target blood glucose / range. So if your bgl is 9mmol/l and you give 1. Web insulin plays a pertinent role in maintaining the glucose levels in the brain. Web in general, 1 unit of insulin lowers your blood sugar by about 50 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl). 1 unit to 10g cho total amount of carbs in the meal: Web learn how to use the correction factor tool to find out how much extra mealtime. Web insulin plays a pertinent role in maintaining the glucose levels in the brain. Since the human body is so complex, not all people will process. Web learn how to measure how much insulin can lower blood sugar levels and adjust your insulin dose accordingly. Web a correction factor (sometimes referred to as insulin sensitivity factor or isf) is the. Web insulin to carbohydrate ratio: Novorapid, humalog or apidra ) will lower blood. Web learn how to calculate and test your insulin sensitivity factor, also known as your correction factor or correction bolus, to adjust your insulin dosage. Since the human body is so complex, not all people will process. Web an insulin sensitivity factor (isf) or correction factor describes. Find formulas, examples and factors that affect. Find examples, tips and a chart to help you. Web for example, a correction factor of 2 means that 1 unit of insulin should lower your bgl by 2mmol/l. 1 unit of bolus insulin lowers glucose by 1 mmol/l; So if your bgl is 9mmol/l and you give 1 unit of insulin, your. Find out how to use the 1800 rule, the 500 rule,. Web insulin to carbohydrate ratio: Web high insulin sensitivity is when your cells respond normally to insulin, facilitating glucose uptake, keeping your blood sugar levels stable, and reducing the. Web learn what the insulin sensitivity factor is and how it helps you determine the right dose of insulin for. Web learn how to measure how much insulin can lower blood sugar levels and adjust your insulin dose accordingly. Web learn how to calculate your insulin doses for carbohydrate coverage, high blood sugar correction and total mealtime dose. Web high insulin sensitivity is when your cells respond normally to insulin, facilitating glucose uptake, keeping your blood sugar levels stable, and reducing the. Web an insulin sensitivity factor (isf) or correction factor describes how much one unit of rapid or regular insulin will lower blood glucose. Web learn how to use the correction factor tool to find out how much extra mealtime insulin you need to lower your blood sugar. Your isf is the number of mmol/l that one unit of insulin will lower your blood glucose level by. Web some people may need 1 unit of insulin to lower blood glucose by 50 mg/dl and someone else may need 1 unit of insulin to lower blood glucose by 25 mg/dl. Find formulas, examples and factors that affect. For example, a ratio of 1:2 means that one. Web insulin resistance, also known as impaired insulin sensitivity, happens when cells in your muscles, fat and liver don’t respond as they should to insulin, a hormone. See an example of how to apply the insulin sensitivity. Find out how to use the 1800 rule, the 500 rule,. 1 unit to 10g cho total amount of carbs in the meal: Find examples, tips and a chart to help you. Web a correction factor (sometimes referred to as insulin sensitivity factor or isf) is the amount that 1 unit of rapid acting insulin (e.g. Web target blood glucose / range.
Frontiers Diurnal Variation of RealLife Insulin Sensitivity Factor
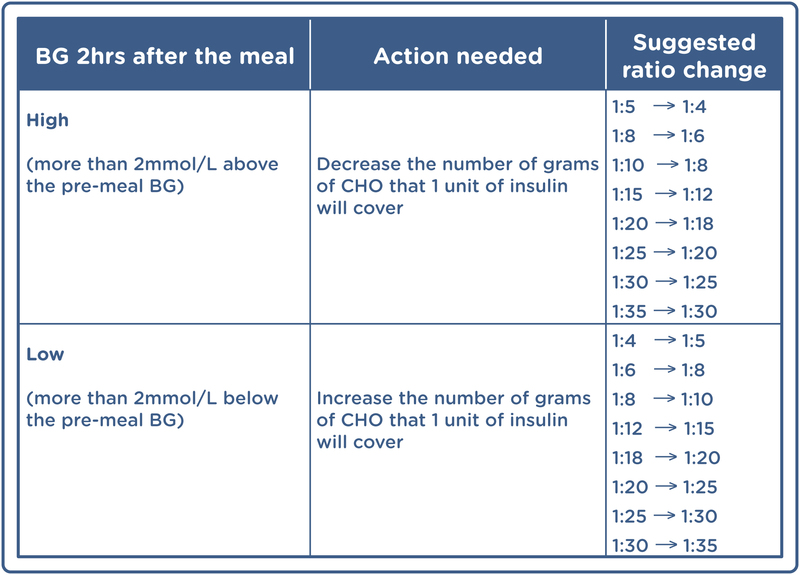
Insulin Sliding Scale Chart In Mmol L Best Picture Of Chart

Infographics The Muscle PhD
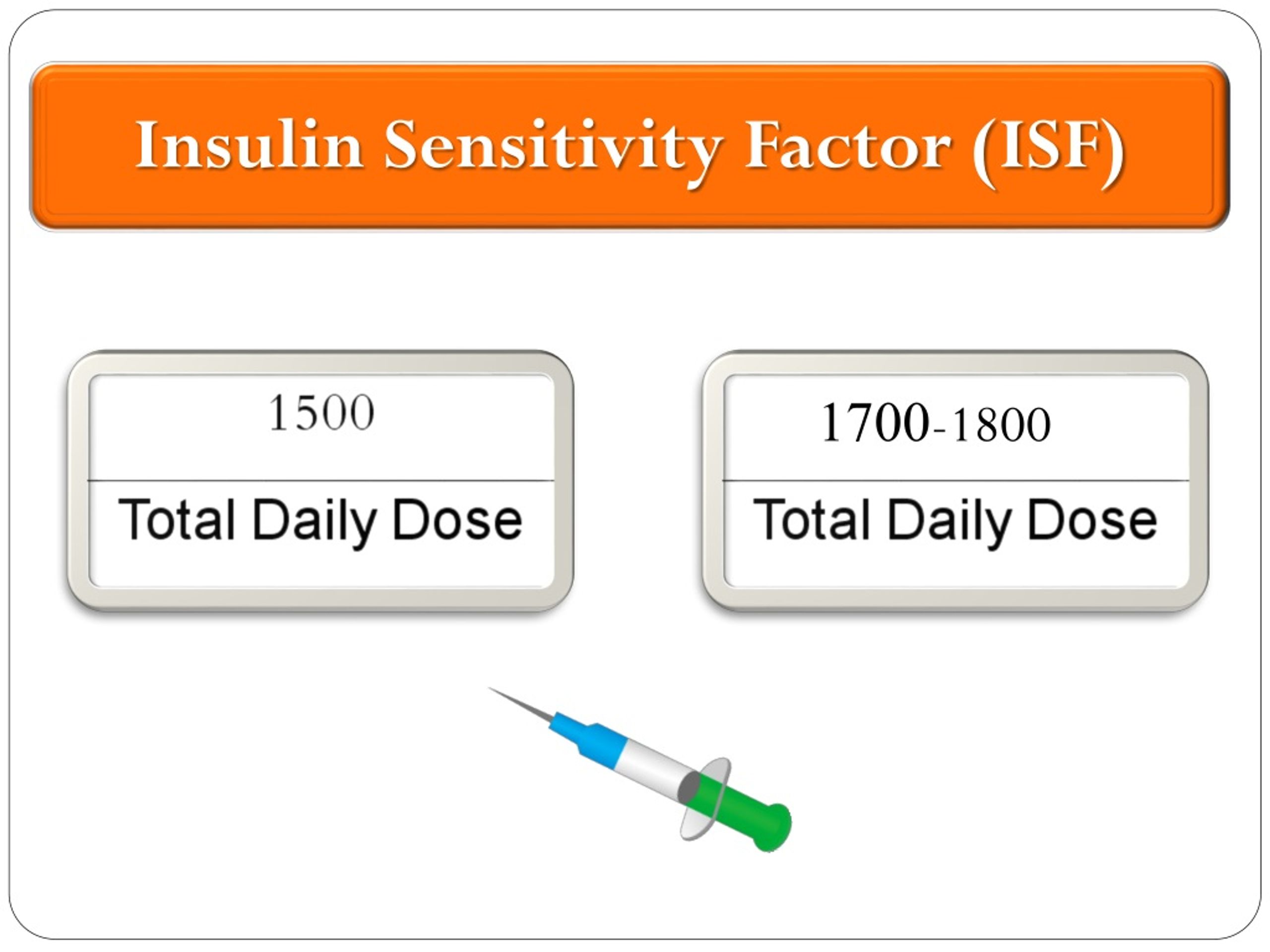
PPT Medical nutrition therapy Diabetes (2) PowerPoint Presentation

Equations and references of insulin sensitivity indices derived from
Insulin Sensitivity Factor Calculation Insulin Choices

Let's talk about your insulin pump data Tidepool blog
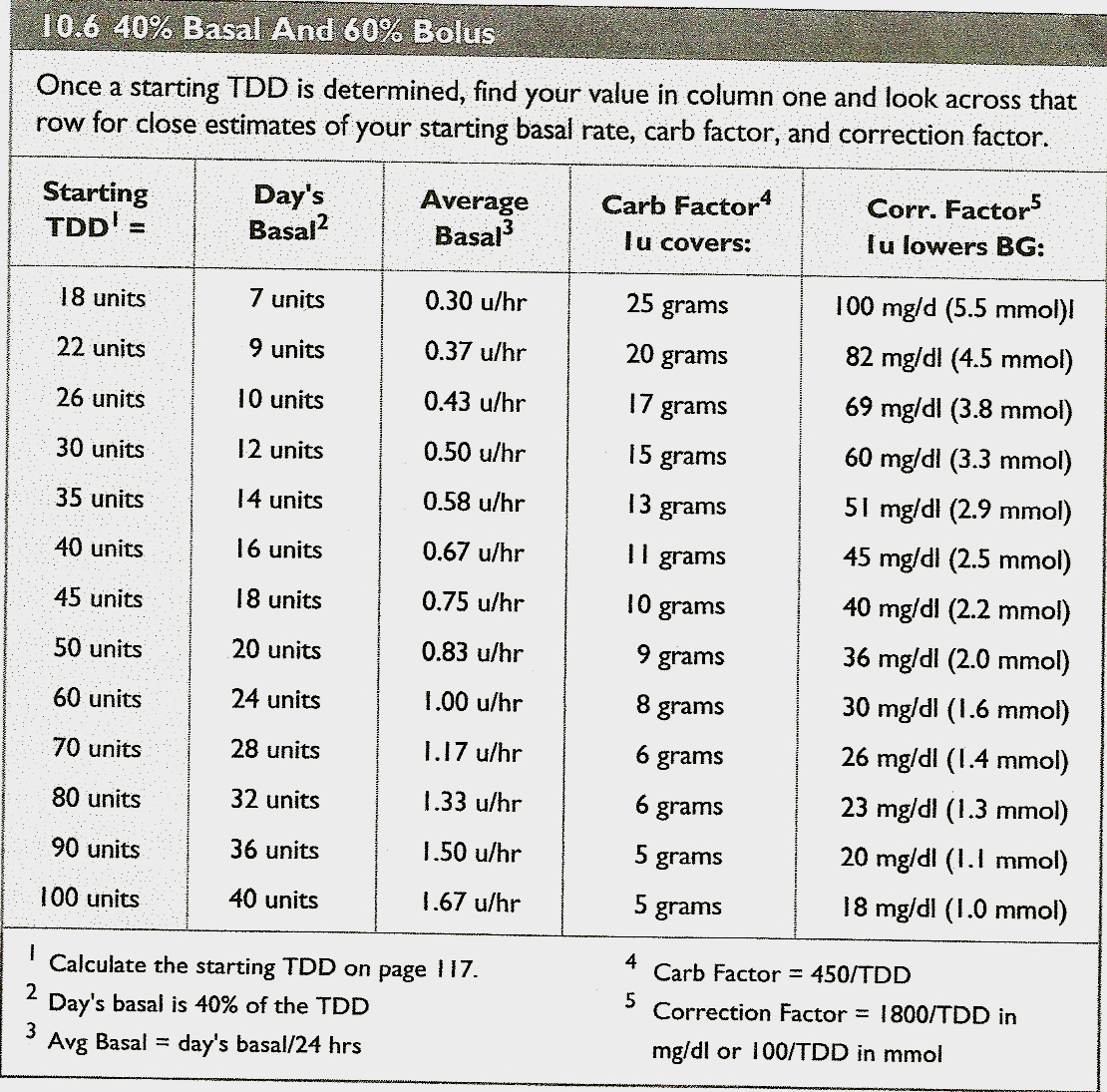
A Sweet Grace Insulin sensitivity
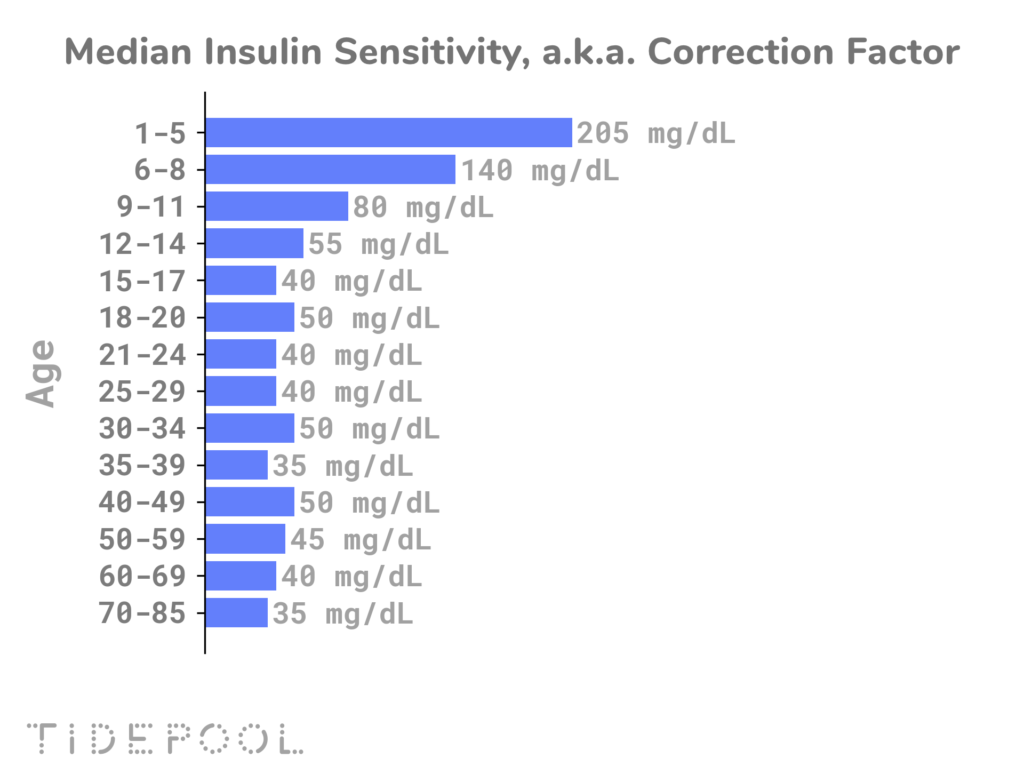
Insulin Sensitivity Factor Chart

Printable Sliding Scale Insulin Chart Download
1 Unit Of Bolus Insulin Lowers.
Novorapid, Humalog Or Apidra ) Will Lower Blood.
1 Unit Of Bolus Insulin Lowers Glucose By 1 Mmol/L;
Web In General, 1 Unit Of Insulin Lowers Your Blood Sugar By About 50 Milligrams Per Deciliter (Mg/Dl).
Related Post: