Kingdoms Of Living Things Chart
Kingdoms Of Living Things Chart - Web list the main features used to place all organisms into one of the five kingdoms: The protists are predominantly unicellular, microscopic, nonvascular organisms that do not generally form tissues. Web the six kingdoms are: Regnum animale ('animal kingdom') and regnum vegetabile ('vegetable kingdom', for plants). Exhibiting all modes of nutrition, protists are frequently motile organisms, primarily using flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia. Web one system uses five main groups: Either they were placed in a separate category called chaos or, in some cases, they were classified with plants or animals. List the main features used to place organisms into groups within the plant kingdom, limited to ferns and flowering plants (dicotyledons and monocotyledons) Web a graphic that shows that living organisms are separated into 5 kingdoms bacteria protists fungi plants and animals with pictured examples in each kingdom. All organisms are classified into one of the following 6 kingdoms. Web uniting the characteristics that make up the two previous classifications, whittaker classified all living beings into five kingdoms: Web 6 kingdoms of life. Kingdoms are divided into subgroups at various levels. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. Look at the sky, the soil, trees, plants, people, animals. Their existence was not discovered until the 1980s. Archaebacteria are the most recent addition to the kingdoms of organisms. Web most scientists classify living things into one of the following six kingdoms. Regnum animale ('animal kingdom') and regnum vegetabile ('vegetable kingdom', for plants). Web 6 kingdoms of life. These groups are called kingdoms. Web scientists classify living things into categories based on their physical and genetic similarities. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. The plantae kingdom is broken down even further to include divisions. Regnum animale ('animal kingdom') and regnum vegetabile ('vegetable kingdom', for plants). Web the five kingdom classification system is a system of classifying living things based on what they have in common and how they differ. The protists are predominantly unicellular, microscopic, nonvascular organisms that do not generally form tissues. Kingdoms are divided into subgroups at various levels. While kingdoms are. Web in his classification scheme, linnaeus recognized only two kingdoms of living things: Web uniting the characteristics that make up the two previous classifications, whittaker classified all living beings into five kingdoms: Kingdoms are divided into subgroups at various levels. Web there are six kingdoms which include eubacteria, archaebacteria, plantae, animalia, fungi, and protista. Animals (all multicellular animals) plants (all. Animal, plant, fungus, prokaryote, protoctist. However, archaebacteria are the oldest known living organisms. Web one system uses five main groups: Wikipedia) browse more topics under diversity. Count how many living things you can see. Web a graphic that shows that living organisms are separated into 5 kingdoms bacteria protists fungi plants and animals with pictured examples in each kingdom. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. The following flowchart shows the hierarchy of classification. Web uniting the characteristics that make up the two previous classifications, whittaker classified all. Web find out what a kingdom is in biology and how living things are classified into 5 kingdoms, as well as their characteristics and different examples of each one. The following flowchart shows the hierarchy of classification. Web a graphic that shows that living organisms are separated into 5 kingdoms bacteria protists fungi plants and animals with pictured examples in. Web in his classification scheme, linnaeus recognized only two kingdoms of living things: At the time, microscopic organisms had not been studied in detail. Web the six kingdoms are: The protists are predominantly unicellular, microscopic, nonvascular organisms that do not generally form tissues. Linnaeus also included minerals in his classification system, placing them in a third kingdom, regnum lapideum. Kingdom → phylum → class → order → family → genus → species. While kingdoms are a little more specific, it should still be relatively easy to categorize a living organism based on the kingdom. Their existence was not discovered until the 1980s. Regnum animale ('animal kingdom') and regnum vegetabile ('vegetable kingdom', for plants). Web the 5 kingdoms of life. Web a graphic that shows that living organisms are separated into 5 kingdoms bacteria protists fungi plants and animals with pictured examples in each kingdom. The protists are predominantly unicellular, microscopic, nonvascular organisms that do not generally form tissues. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. Web the first division of living things in the classification system is to put them into one of five kingdoms. While kingdoms are a little more specific, it should still be relatively easy to categorize a living organism based on the kingdom. In the 1960s, american biologist robert whittaker proposed a classification system based on five kingdoms: Kingdom → phylum → class → order → family → genus → species. Web list the main features used to place all organisms into one of the five kingdoms: Nature is all around you if you have the eyes to see it. Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics like cell type, nutrient acquisition, and reproduction. Web the six kingdoms are: Animals (all multicellular animals) plants (all green plants). Web the five kingdom classification system is a system of classifying living things based on what they have in common and how they differ. Web find out what a kingdom is in biology and how living things are classified into 5 kingdoms, as well as their characteristics and different examples of each one. Monerans, protists, fungi, plants, and animals. Web uniting the characteristics that make up the two previous classifications, whittaker classified all living beings into five kingdoms:
Biology 5 Kingdoms of Living Things Classification Iberdrola in 2021
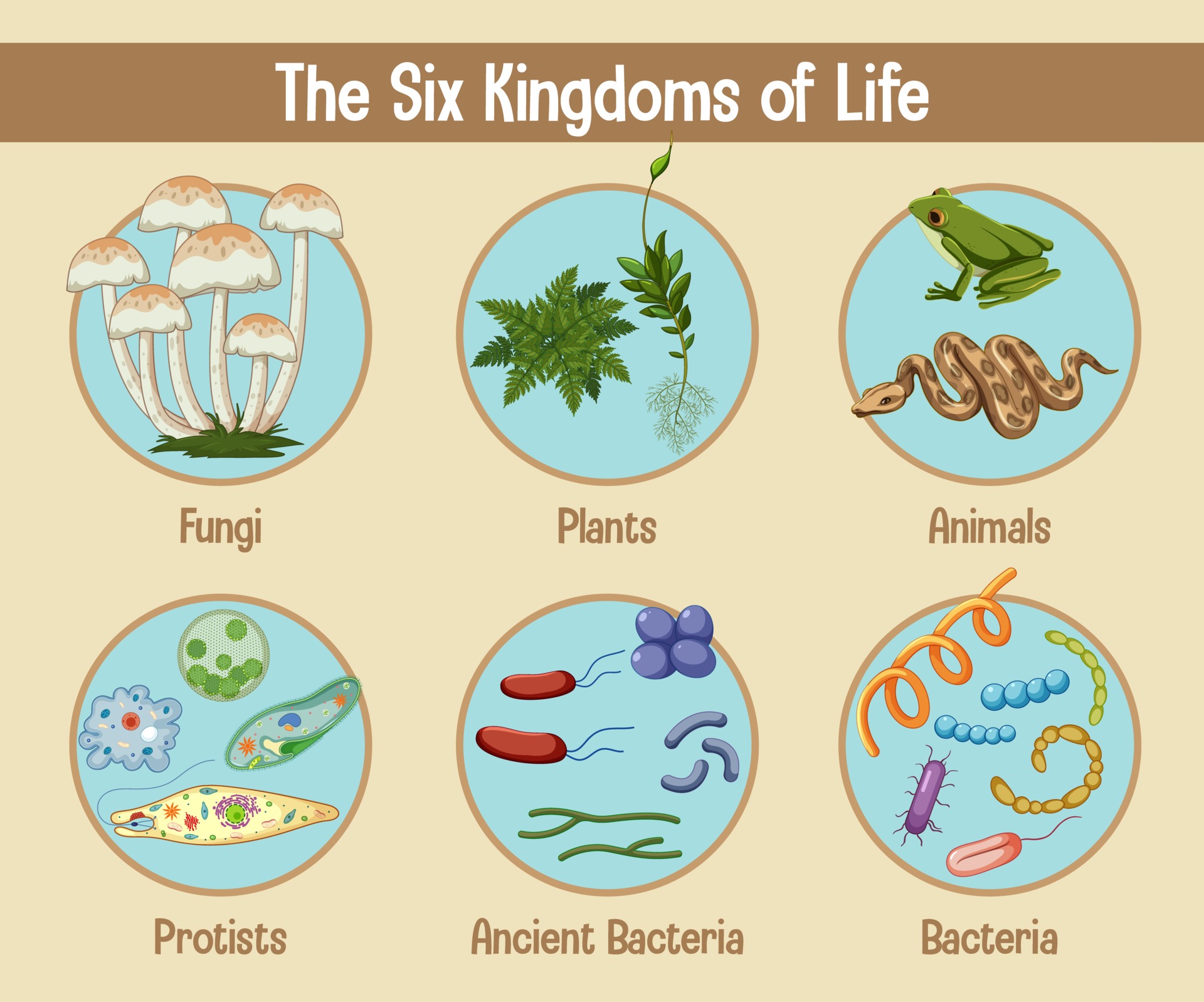
Science poster of six kingdoms of life 2906732 Vector Art at Vecteezy
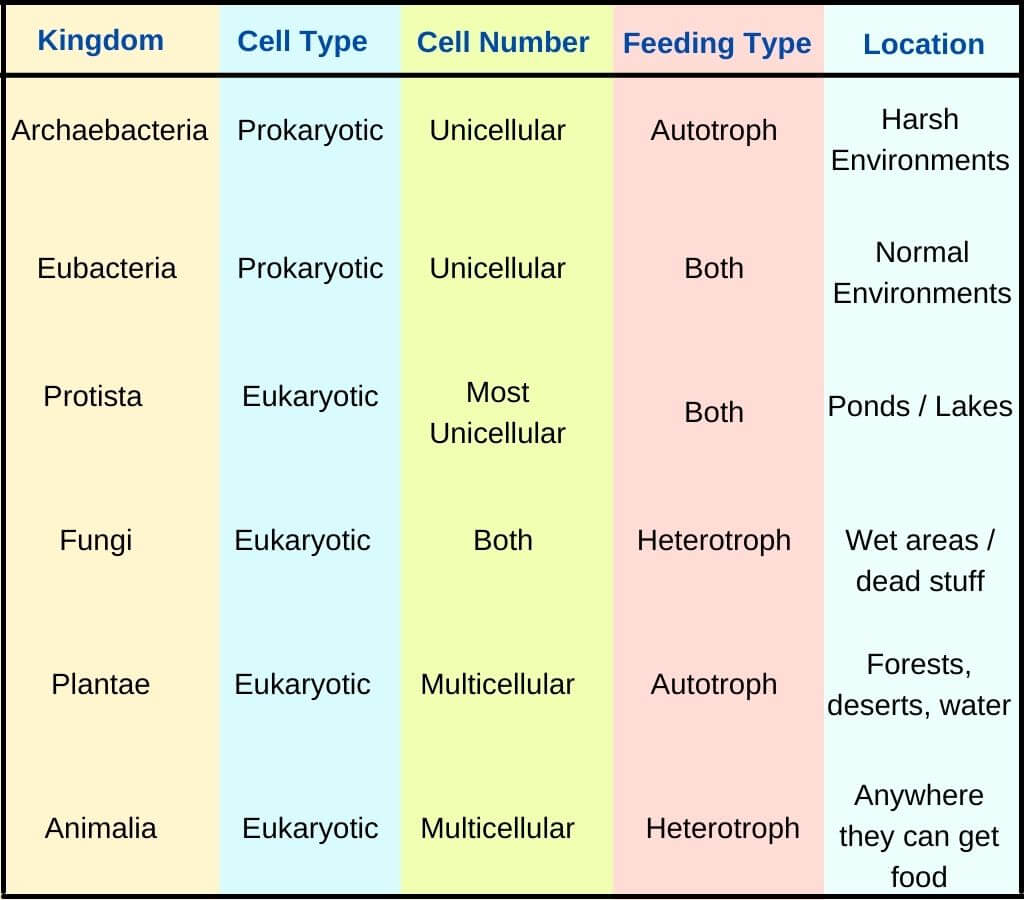
A Simple Explanation of the 6 Kingdoms of Life
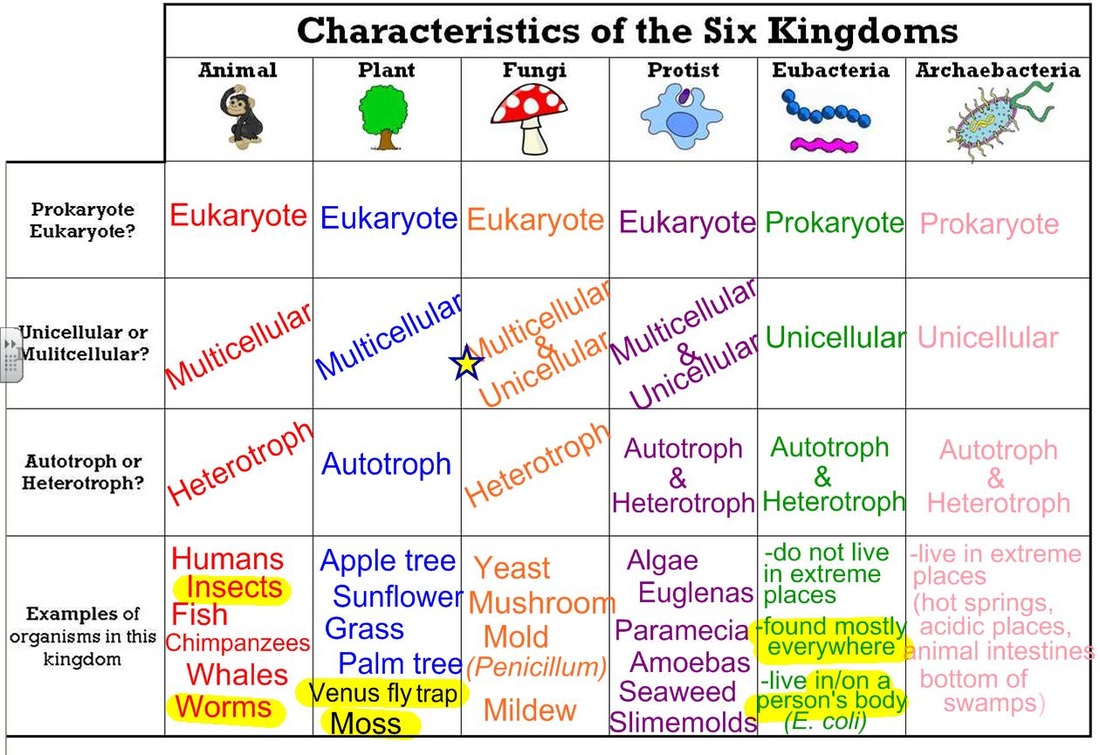
Classification of Organisms Rumney Marsh Academy Science Revere

Chart showing the five kingdoms of living things

Biology 5 Kingdoms of Living Things Classification Iberdrola

Kingdoms Of Living Things Chart
/six-kingdoms-of-life-373414-Final1-5c538e2446e0fb00013faa3c.png)
How Many Living Things Are On Earth Right Now The Earth Images

Montessori Materials The Six Kingdoms Chart with Cards
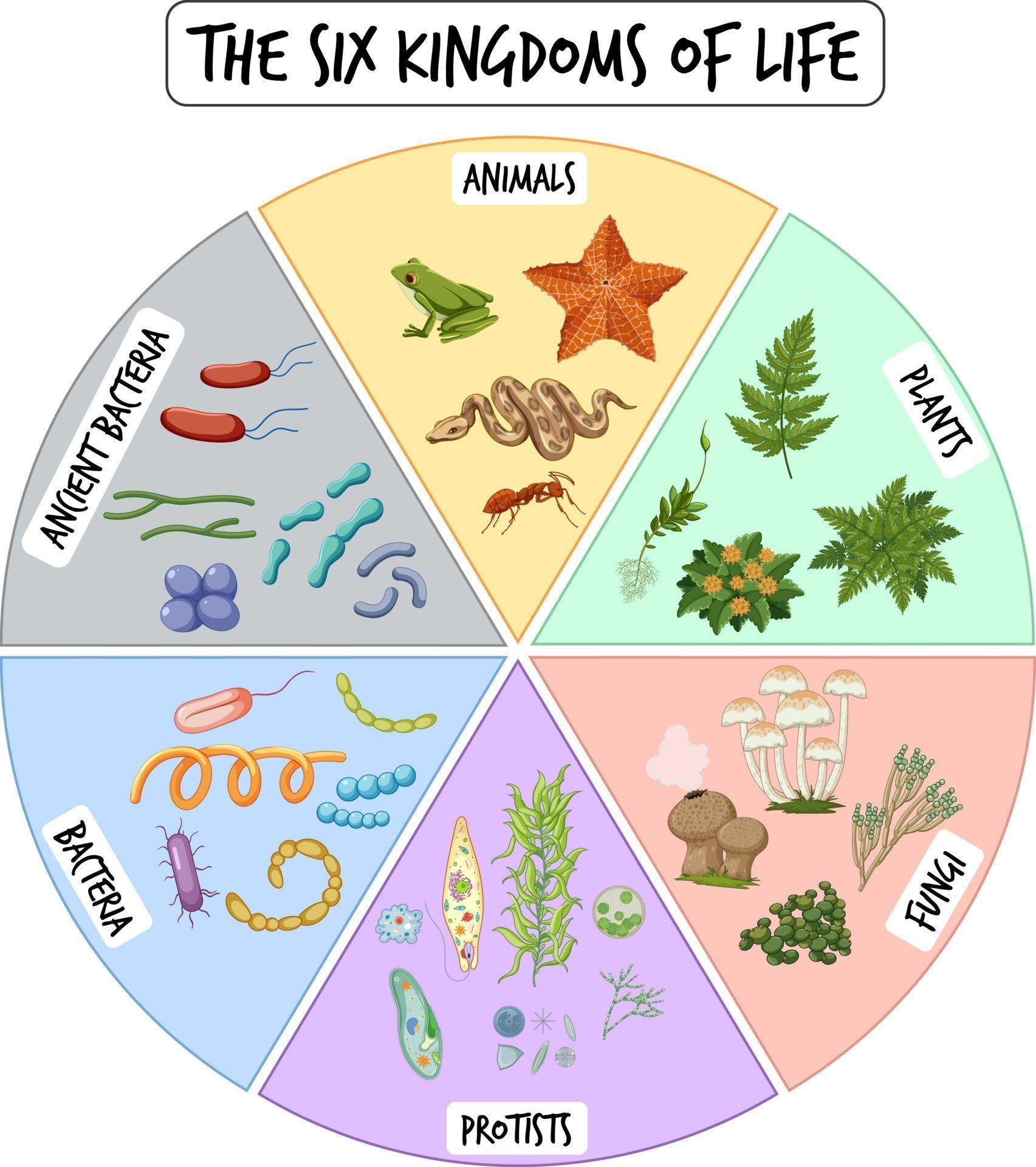
Information poster of six kingdoms of life 2906704 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Regnum Animale ('Animal Kingdom') And Regnum Vegetabile ('Vegetable Kingdom', For Plants).
The Plantae Kingdom Is Broken Down Even Further To Include Divisions.
Count How Many Living Things You Can See.
Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae And Animalia.
Related Post: