Laser Eye Damage Chart
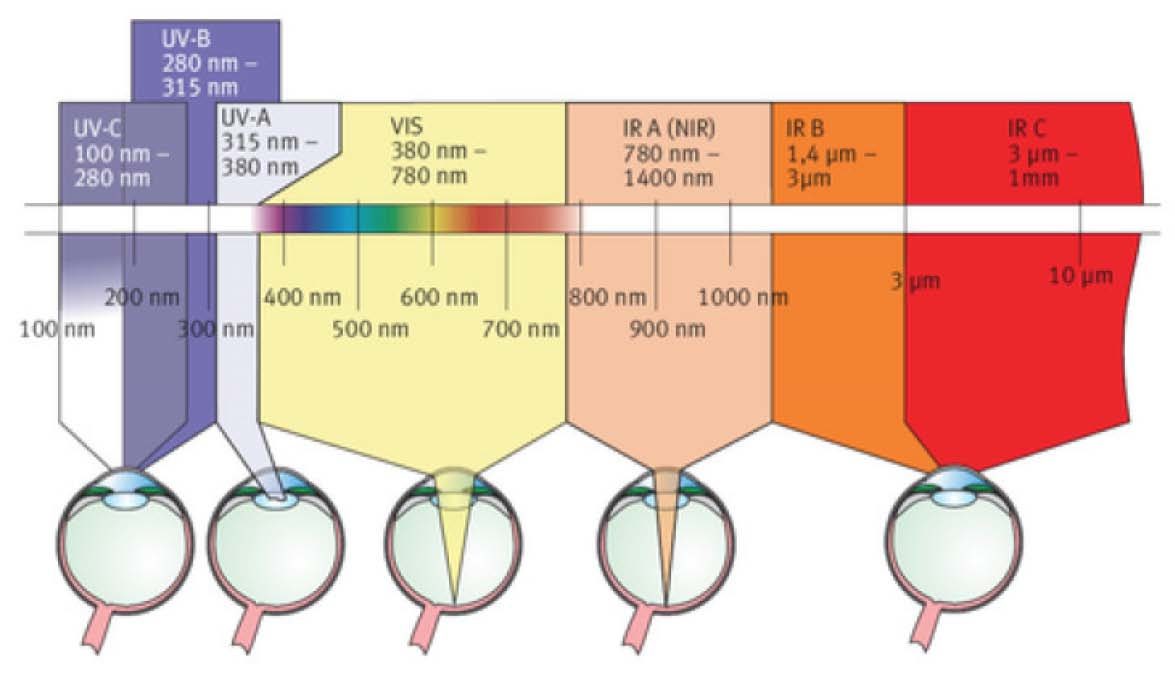
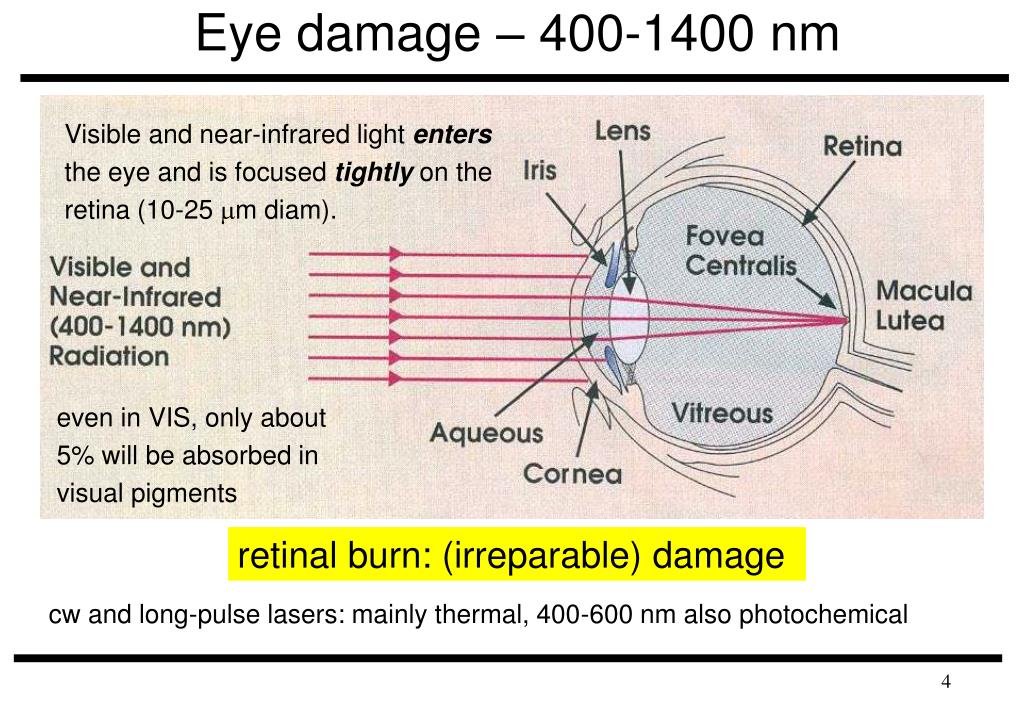
Laser Eye Damage Chart - Beam hazards the eye the eye is easily injured by laser beams. Web factors that affect the extent of laser eye injury include: 1.3 types of lasers used. Traditional eye safety standards focused only on. Just as a magnifying glass can be used to focus the. 1.2 laser mechanism of action. Web damage to the eye. Stanford university, laser eyewear selection chart. Web laser safety calculation guide. The eye is the organ most sensitive to light. Traditional eye safety standards focused only on. Web laser hazard distance calculator. Just as a magnifying glass can be used to focus the. The type of injury depends upon the intensity of light, its wavelength, and the tissue being. 2.3 damage to the eye. Web click on the chart to see it larger. Web laser safety calculation guide. Web class 3b and class 4 lasers, have the potential to damage the eye through both direct and reflected impact, and should never be operated without first assessing. The type of injury depends upon the intensity of light, its wavelength, and the tissue being. The eye. 2.3 damage to the eye. If you know the power, divergence and wavelength (precise color) of a visible, continuous wave laser, you can use the online calculator. Just as a magnifying glass can be used to focus the. Beam hazards the eye the eye is easily injured by laser beams. Web factors that affect the extent of laser eye injury. Lasers of a wide variety of wavelengths from the short wavelength uv (excimer laser for lasik) through the visible spectrum (argon laser for. Web factors that affect the extent of laser eye injury include: Poor retinal or choroidal circulation; Traditional eye safety standards focused only on. For all lasers of this type, the ed50 distance (marked “50/50” on the chart). 1.3 types of lasers used. Web short wavelength lasers, such as potassium titanyl phosphate (ktp) and pulsed dye (pdl) lasers, produce photocoagulation (photothermal) damage, while long. Web class 3b and class 4 lasers, have the potential to damage the eye through both direct and reflected impact, and should never be operated without first assessing. For all lasers of this type,. Poor retinal or choroidal circulation; The type of injury depends upon the intensity of light, its wavelength, and the tissue being. If you know the power, divergence and wavelength (precise color) of a visible, continuous wave laser, you can use the online calculator. Web damage to the eye. Web click on the chart to see it larger. Web click on the chart to see it larger. 1.3 types of lasers used. If you know the power, divergence and wavelength (precise color) of a visible, continuous wave laser, you can use the online calculator. Poor retinal or choroidal circulation; Traditional eye safety standards focused only on. Just as a magnifying glass can be used to focus the. Web damage to the eye. The eye is the organ most sensitive to light. The major danger of laser light is hazards from beams entering the eye. Web to inform those that may encounter lasers, they are classified according to their potential to cause biological damage. Web to inform those that may encounter lasers, they are classified according to their potential to cause biological damage. If you know the power, divergence and wavelength (precise color) of a visible, continuous wave laser, you can use the online calculator. Just as a magnifying glass can be used to focus the. Web click on the chart to see it. Stanford university, laser eyewear selection chart. 1.2 laser mechanism of action. Web short wavelength lasers, such as potassium titanyl phosphate (ktp) and pulsed dye (pdl) lasers, produce photocoagulation (photothermal) damage, while long. Lasers of a wide variety of wavelengths from the short wavelength uv (excimer laser for lasik) through the visible spectrum (argon laser for. The major danger of laser. 1.2 laser mechanism of action. Web short wavelength lasers, such as potassium titanyl phosphate (ktp) and pulsed dye (pdl) lasers, produce photocoagulation (photothermal) damage, while long. Lasers of a wide variety of wavelengths from the short wavelength uv (excimer laser for lasik) through the visible spectrum (argon laser for. Web damage to the eye. The major danger of laser light is hazards from beams entering the eye. 2.3 damage to the eye. Web laser safety calculation guide. Web class 3b and class 4 lasers, have the potential to damage the eye through both direct and reflected impact, and should never be operated without first assessing. The eye is the organ most sensitive to light. If you know the power, divergence and wavelength (precise color) of a visible, continuous wave laser, you can use the online calculator. Poor retinal or choroidal circulation; Web laser hazard distance calculator. Just as a magnifying glass can be used to focus the. Maximum permissible exposure (mpe) the single most useful number in laser safety calculations is the maximum permissible exposure. Traditional eye safety standards focused only on. The type of injury depends upon the intensity of light, its wavelength, and the tissue being.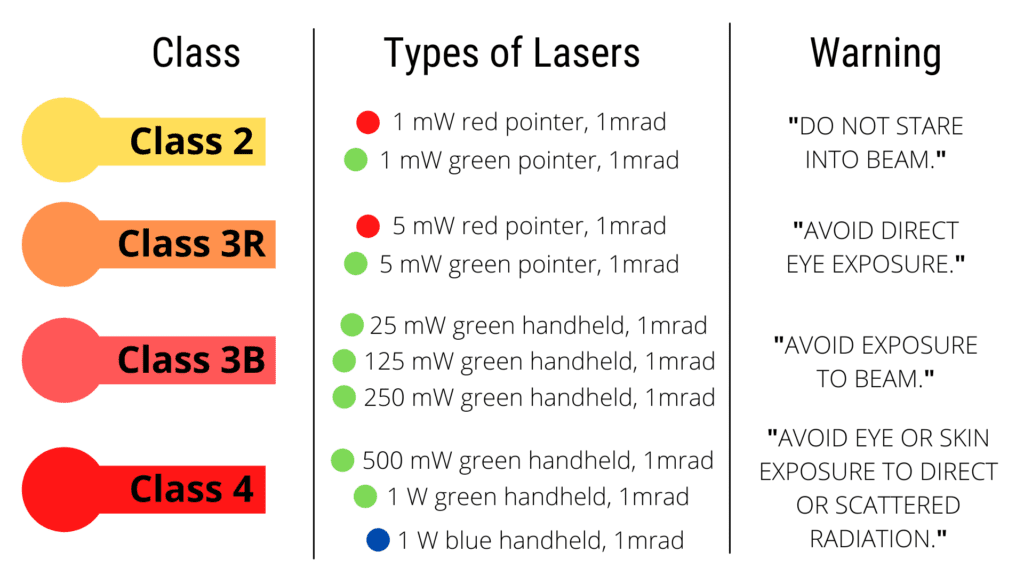
Laser Classification What Are The Different Laser Classes?

Can A Laser Pointer Really Damage Your Eyes? Premier Eye Center

Eye Problems and Conditions Charts and Diagrams with Private Label
OLSEH IISc Bangalore

Safety of Class 3B visiblebeam lasers
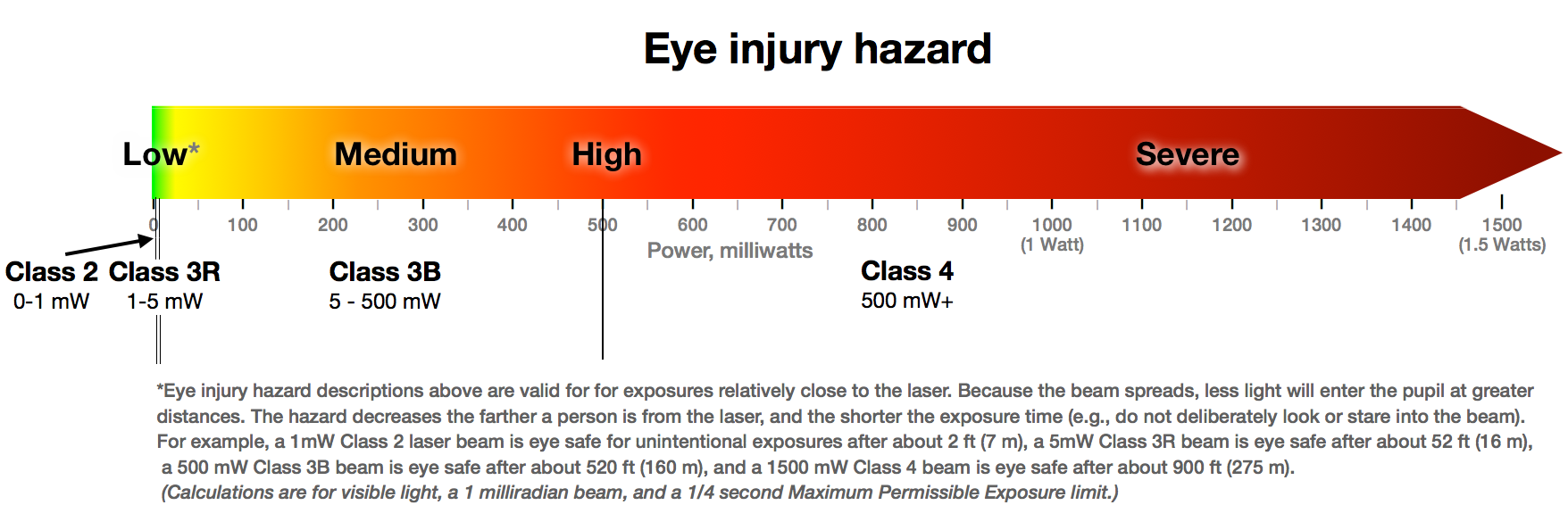
Laser classification table Laser Safety Facts

Foveal Injury From a Red Laser Pointer Optometry, Vision eye
Laser Damage Charts DarkOrbit
PPT Laser safety Introduction PowerPoint Presentation, free download

Laser classification table Laser Safety Facts
Web Click On The Chart To See It Larger.
Web Lasers In This Class Have Output Powers Of More Than 500 Mw In The Beam And May Cause Severe, Permanent Damage To Eye Or Skin Without Being Focussed By Optics Of Eye.
Web Factors That Affect The Extent Of Laser Eye Injury Include:
Web To Inform Those That May Encounter Lasers, They Are Classified According To Their Potential To Cause Biological Damage.
Related Post: