Meiosis And Mitosis Comparison Chart
Meiosis And Mitosis Comparison Chart - Both mitosis and meiosis involve: In eukaryotic cells, the production of new cells occurs as a result of mitosis and meiosis. Web mitosis and meiosis: Facts explained through comparison chart with differences & similarities between their stages, along with venn diagram & picture Stages of interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Web mitosis produces two genetically identical “daughter” cells from a single “parent” cell, whereas meiosis produces cells that are genetically unique from the parent and contain only half as much dna. A type of cellular reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced by half through the separation of homologous chromosomes, producing two haploid cells. Web 10 key differences between mitosis and meiosis. Web there are two types of cell division: Meiosis, by beverly biology (2014) on youtube, which compares and contrasts mitosis and meiosis. In meiosis i, the homologous chromosome pairs become associated with each other and are bound together with the synaptonemal complex. The nuclei resulting from a mitotic division. Web take a look at the following video, mitosis vs. Stages of interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Web mitosis produces two genetically identical “daughter” cells from a single “parent” cell, whereas meiosis. Web mitosis forms diploid cells that have the same number of chromosomes as the parent, whereas meiosis forms haploid cells with half the original number of chromosomes. In meiosis i, the homologous chromosome pairs become associated with each other and are bound together with the synaptonemal complex. Web here, we outline the differences between mitosis and meiosis in humans (diploid. These two nuclear division processes are similar but distinct. Mitosis and meiosis, which are both forms of division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells, share some similarities, but also exhibit distinct differences that lead to their very different outcomes. In meiosis, the new cells have half the genetic material of the parent cell and is the process by which egg. Most of the time, when a cell in our bodies divides, each new cell carries a complete set of chromosomes. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and results in two identical daughter cells with a diploid (2n) number of chromosomes. Getting mitosis and meiosis confused on a biology exam can cost you a lot of points, so it's important to keep. The cells involved with human reproduction, however, carry only half after division. Knowing the differences between these fundamental cell processes is an important foundation in your understanding of genetics for the rest of the course. Stages of interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and results in two identical daughter cells with a diploid (2n) number. Web 10 key differences between mitosis and meiosis. Below we highlight the key differences and similarities between the two types of cell division. A type of cellular reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced by half through the separation of homologous chromosomes, producing two haploid cells. These two nuclear division processes are similar but distinct. Difference between mitosis. The nuclei resulting from a mitotic division. Web updated on may 12, 2024. Web mitosis results in two identical daughter cells, whereas meiosis results in four sex cells. Mitosis is the process by which body cells divide and create copies of themselves for growth and repair. Dna replication produces identical sister chromatids. This process is essential for growth and repair in the body. In meiosis, the new cells have half the genetic material of the parent cell and is the process by which egg and sperm cells are formed. These two nuclear division processes are similar but distinct. Chiasmata develop and crossover occurs between homologous chromosomes, which then line up along the. Below we highlight the key differences and similarities between the two types of cell division. Chiasmata develop and crossover occurs between homologous chromosomes, which then line up along the metaphase plate in tetrads with. Knowing the differences between these fundamental cell processes is an important foundation in your understanding of genetics for the rest of the course. Crossing over, meiosis. Both mitosis and meiosis start with a diploid parent cell that splits into daughter cells. Web here, we outline the differences between mitosis and meiosis in humans (diploid #46). Web mitosis and meiosis, which are both forms of division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells, share some similarities, but also exhibit distinct differences that lead to their very different outcomes.. Web 10 key differences between mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and results in two identical daughter cells with a diploid (2n) number of chromosomes. The nuclei resulting from a mitotic division. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. Chiasmata develop and crossover occurs between homologous chromosomes, which then line up along the metaphase plate in tetrads with. The diploid number results from the fact that each cell includes one copy of each chromosome (numbered one through 22 in humans, plus one sex chromosome) from the organism's mother and one from the father. Web mitosis produces two genetically identical “daughter” cells from a single “parent” cell, whereas meiosis produces cells that are genetically unique from the parent and contain only half as much dna. Most of the time, when a cell in our bodies divides, each new cell carries a complete set of chromosomes. A type of cellular reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced by half through the separation of homologous chromosomes, producing two haploid cells. For example egg or sperm cells. In meiosis, the new cells have half the genetic material of the parent cell and is the process by which egg and sperm cells are formed. In mitosis the daughter cells are identical to the parent as well as to each other. Mitosis is the process by which body cells divide and create copies of themselves for growth and repair. In meiosis i, the homologous chromosome pairs become associated with each other and are bound together with the synaptonemal complex. Web here, we outline the differences between mitosis and meiosis in humans (diploid #46). In meiosis homologous chromosomes separate leading to daughter cells that are not genetically identical.
COMPARE AND CONTRAST the phases of mitosis and meiosis with this
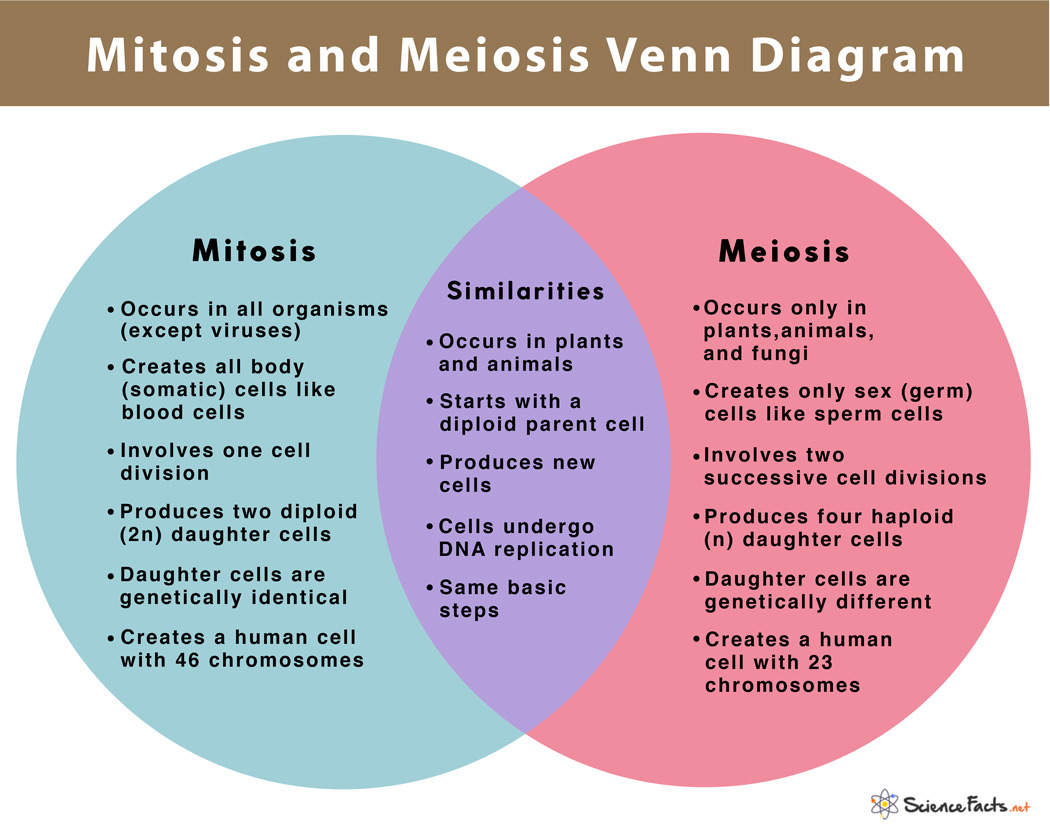
Mitosis vs Meiosis 14 Main Differences Along With Similarities
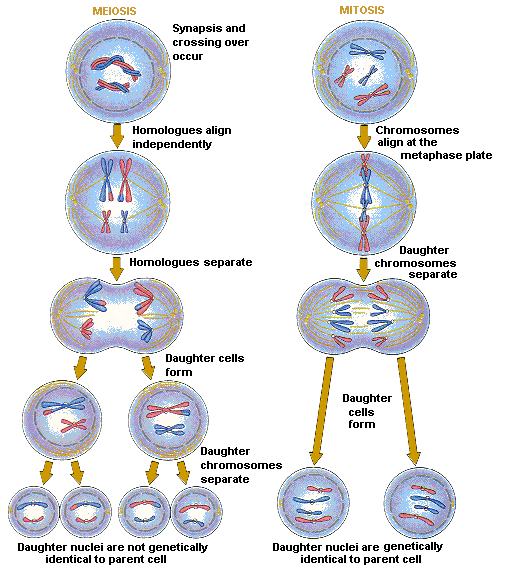
AP Biology for Dummies Mitosis VS

Meiosis vs Mitosis Difference and Comparison Diffen

Meiosis vs. Mitosis Comparison SchoolWorkHelper

A Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis
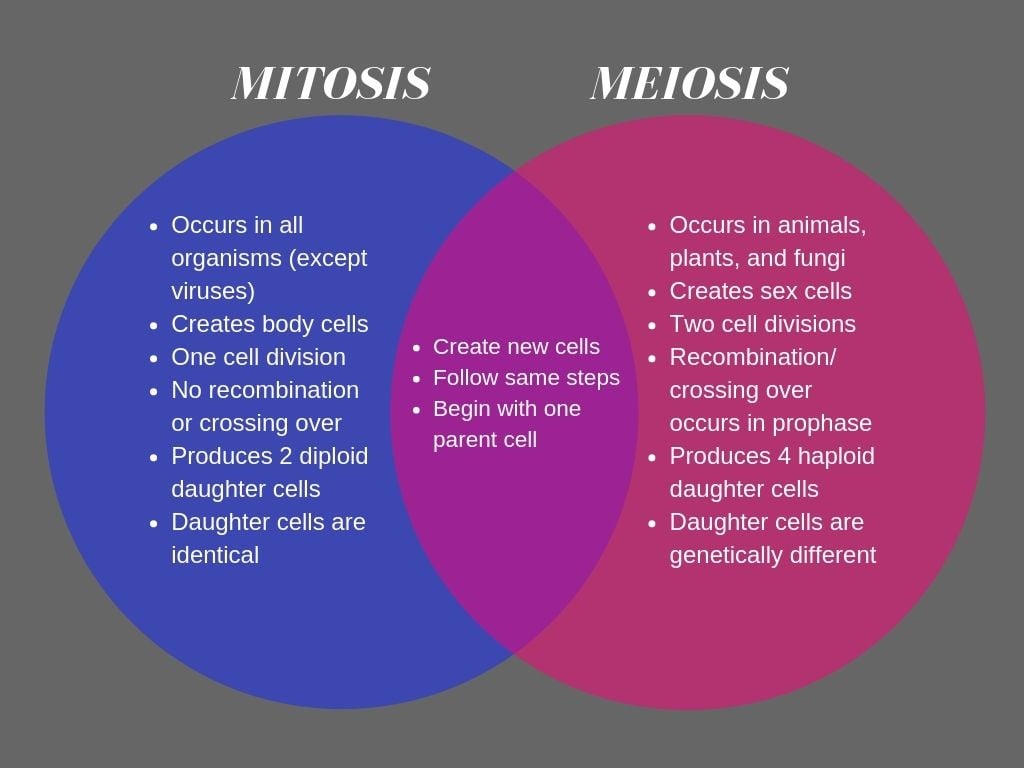
10 Key Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
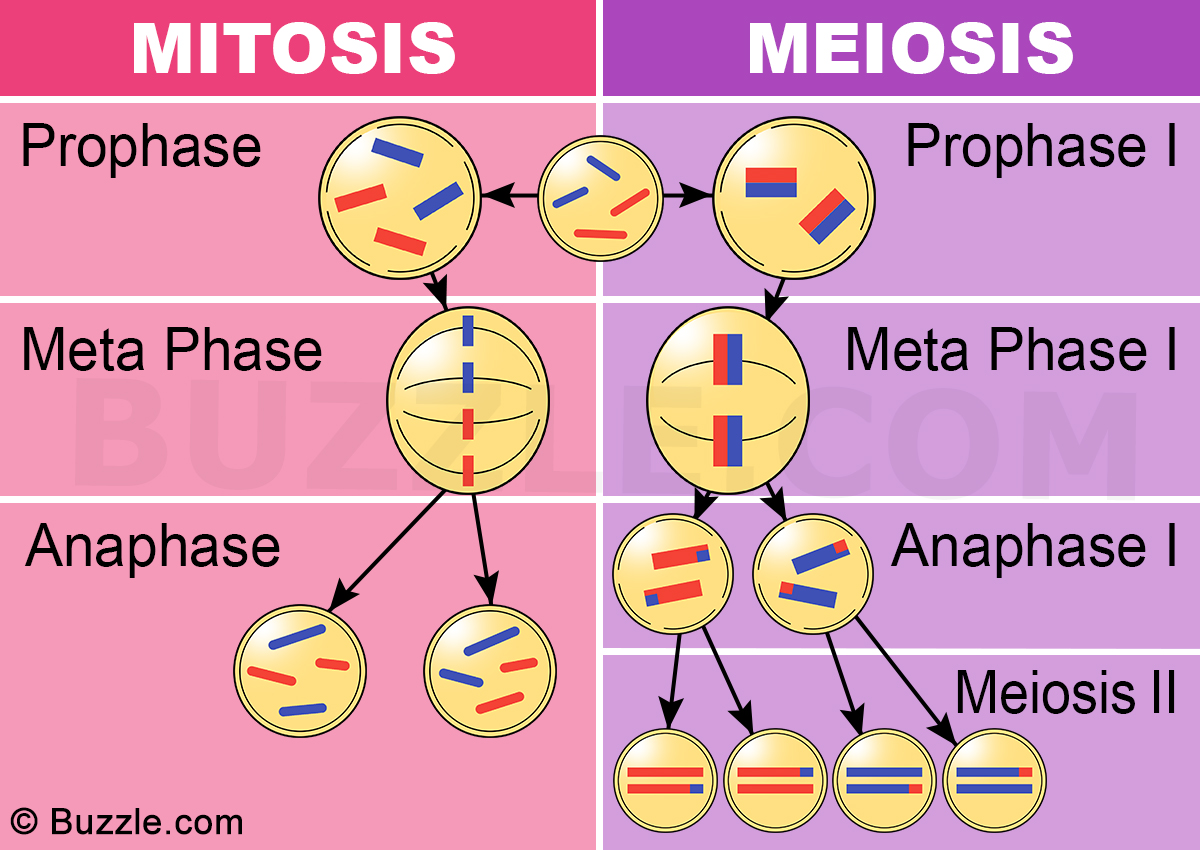
Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis Online Science Notes

Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis Laney Lee

Difference Between Mitosis and Meiosis Chart
Mitosis Is A Single Nuclear Division That Results In Two Nuclei, Usually Partitioned Into Two New Cells.
Mitosis And Meiosis, Which Are Both Forms Of Division Of The Nucleus In Eukaryotic Cells, Share Some Similarities, But Also Exhibit Distinct Differences That Lead To Their Very Different Outcomes.
Meiosis, By Beverly Biology (2014) On Youtube, Which Compares And Contrasts Mitosis And Meiosis.
Both Mitosis And Meiosis Start With A Diploid Parent Cell That Splits Into Daughter Cells.
Related Post: