Microscope Draw Tube
Microscope Draw Tube - Stage control/stage height adjustment 16. The finished drawing will be embellished with a tad bit of color making it a drawing you will be proud to. For the arm, just simply draw a long curve line from the right side of the rectangle to the bottom then go up. What is body tube definition? It is the tube that carries the eyepiece. The drawing in figure 1 illustrates the optical path (the red line) defining the mechanical tube length for a typical. Outline the slide platform 1.6 step 6: The upper part of the arm of the microscope comprises a hollow and tubular structure known as the body tube. Web 1.1 step 1: Web this short video discuss the expectations of a microscope observation and drawings and also provides examples of errors to watch out for.teachers: The upper part of the arm of the microscope comprises a hollow and tubular structure known as the body tube. For the passage of light rays through the body tube, there is a pathway. Shape the microscope head 1.3 step 3: Brings the specimen into general focus. The microscope has an arm wherein we use this part as we are. Shape the illuminator 1.8 step 8: In the past, adjustable graduated drawtubes were offered as an. Fine tunes the focus and increases the detail of the specimen. Do it with a light hand, as you will erase this later. Web connects ocular tube and base. Begin with the eyepiece 1.2 step 2: Continue follow my channel and like, share,comment also. The drawtube (if present) carries the ocular, it can be adjusted to control tube length and so effect corrections for the objective lens. It is the smaller knob, which is used for sharp and fine focusing of the object. Do it with a light hand,. Stage and stage clips 7. Forming a cone of all the dispersed light rays from the illuminator: It is also called a body tube or eyepiece tube. Continue follow my channel and like, share,comment also. For accurate and sharp focusing, this knob can. Web what is the main function of the draw tube on a microscope? For the passage of light rays through the body tube, there is a pathway. The drawtube (if present) carries the ocular, it can be adjusted to control tube length and so effect corrections for the objective lens. Supports the tube and connects it to the base. Forming. Draw the objective lenses 1.5 step 5: There are three structural parts of the microscope i.e. Web to draw a microscope, begin by mapping out its structure in three dimensions, start adding in the characteristic details, and shade one side of it to give it. Provides support to help microscope stand upright: The rectangle should be as tall as you. The lens at the top that you look through, usually 10x or 15x power. Web to draw a microscope, begin by mapping out its structure in three dimensions, start adding in the characteristic details, and shade one side of it to give it. Brings the specimen into general focus. The rectangle should be as tall as you want the microscope. The body tube can be shifted down and up using the adjustment knobs. It is the smaller knob, which is used for sharp and fine focusing of the object. Stage and stage clips 7. The arm connects the body tube to the base of the microscope. The bottom of the microscope, used for support. You can change how close the objective lens is to the object using a knob. Outline the slide platform 1.6 step 6: For accurate and sharp focusing, this knob can. Draw the base of the microscope sketch 1.7 step 7: Web connects ocular tube and base. Supports the tube and connects it to the base. Draw the base of the microscope sketch 1.7 step 7: Diaphragm (iris) controls the intensity of. There are three structural parts of the microscope i.e. Brings the specimen into general focus. These lenses come together and are not far apart in a tube. A rotating turret that houses the objective lenses. On and off switch 17. Web a draw tube is one of two tubes that is in a monocular microscope. Shape the microscope head 1.3 step 3: The drawtube (if present) carries the ocular, it can be adjusted to control tube length and so effect corrections for the objective lens. There are three structural parts of the microscope i.e. Microscopy) the smaller of the two tubes on a monocular microscope. The body tube connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses. For the arm, just simply draw a long curve line from the right side of the rectangle to the bottom then go up. Shape the illuminator 1.8 step 8: Web to draw a microscope, begin by mapping out its structure in three dimensions, start adding in the characteristic details, and shade one side of it to give it. Stage and stage clips 7. For the passage of light rays through the body tube, there is a pathway. Fine tunes the focus and increases the detail of the specimen. Web the mechanical tube length of an optical microscope is defined as the distance from the nosepiece opening, where the objective is mounted, to the top edge of the observation tubes where the eyepieces (oculars) are inserted.
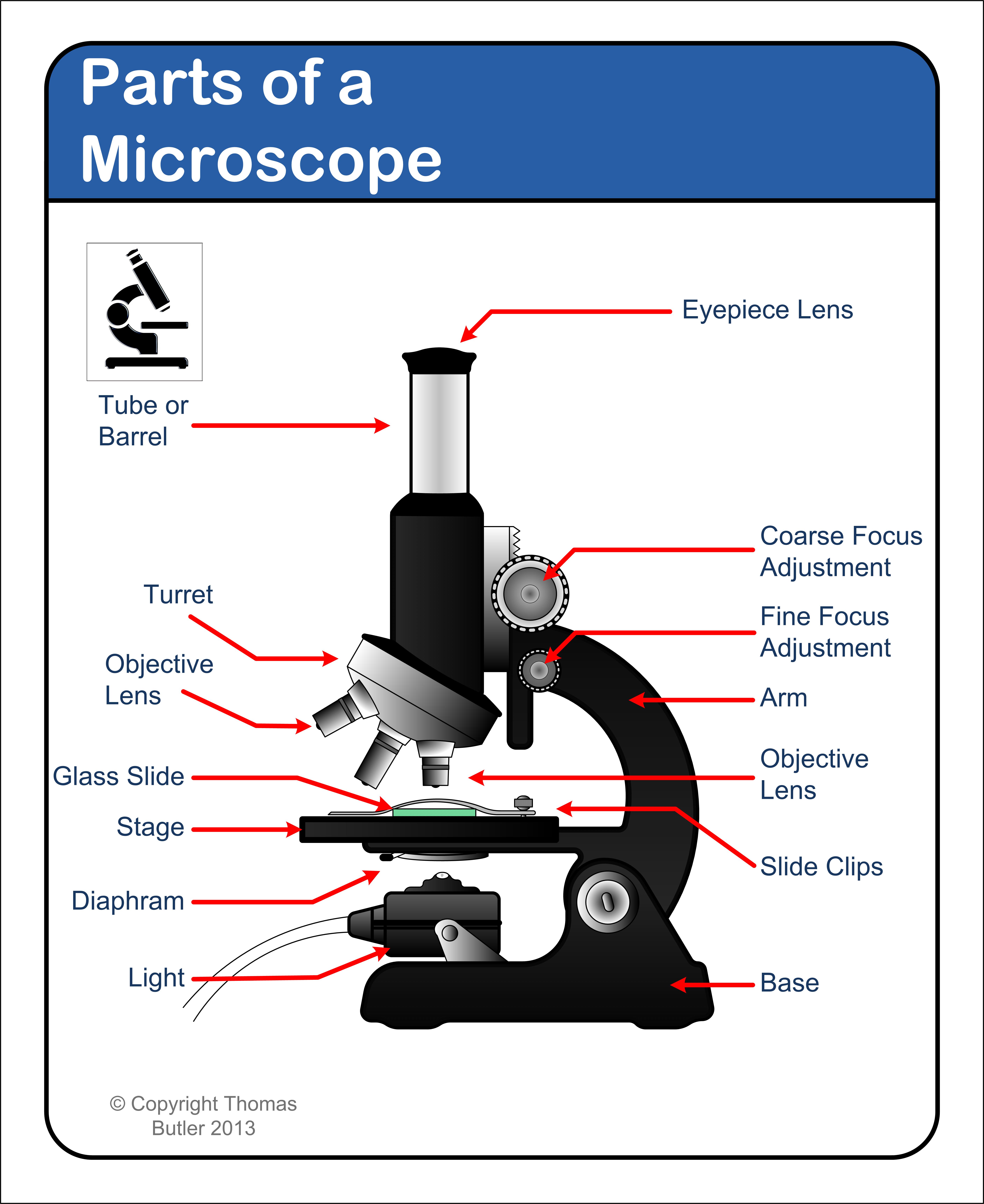
Parts of a microscope with functions and labeled diagram
Simple Microscope Drawing at GetDrawings Free download

DRAWING TUBE Munday Scientific Instruments

Lab 4271

Easy Microscope Drawing 2019 Microscopic images, Simple doodles

Mention the Function of Each Microscope Part BYJU'S Biology

How to draw Microscope diagram for beginners step by step YouTube

Showing the Compound microscope with drawing tube (camera lucida
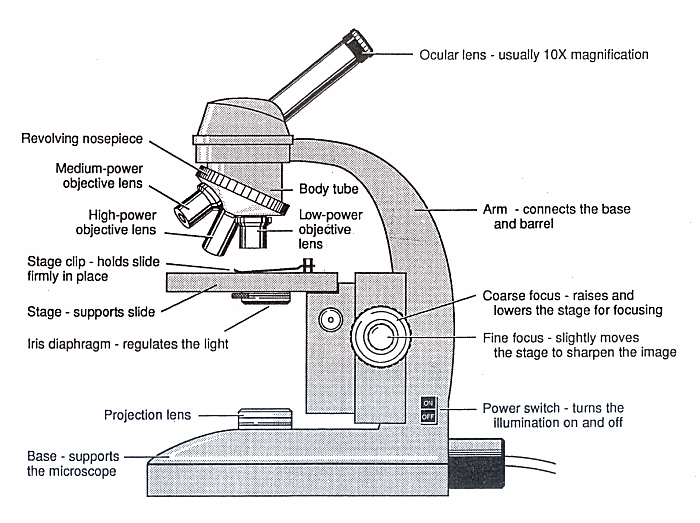
Diagram of a Microscope Guide to using a microscope

How to Draw a Microscope Really Easy Drawing Tutorial
Knobs (Fine And Coarse) 6.
Brings The Specimen Into General Focus.
Web The End Where The Ocular Lens Is Present Is Known As The Head While The End Where The Objective Lens Is Placed Is Known As The Nose Piece.
What Are The Common Mechanical Parts Of The Microscope?
Related Post: