Negligence Flow Chart
Negligence Flow Chart - P's act was a failure to exercise reasonable care, and his negligence is the superseding cause. [1] the defendant owed a legal duty of care to the plaintiff; Web the document summarizes the key elements of the tort of negligence in english law. Dual intent = (1) & (2) the intent to contact is satisfied if the defendant either: Causation (p must show connection between breach. Web explanation of negligence concept map 1. Web a flowchart summarising the principles that a court will consider when determining a damages award in a tort action, including causation, mitigation, contributory negligence and remoteness. Cla s 5d(1) covers common law causation (‘factual causation’) and remoteness (‘scope of liability’). Web the amount of travel fell by 75 percent in 2020; However, travel is on its way to a full recovery by the end of 2024. P's act was a failure to exercise reasonable care, and his negligence is the superseding cause. Web the amount of travel fell by 75 percent in 2020; Web identify relevant risk of harm and negligence. Of care (issue for the judge; For more information on the negligence analysis, see our flow charts on proximate cause and landowner liability. Web this document analyzes whether negligence occurred in a legal case. It does not address the concepts of contributory negligence or proportionate liability. Web four requirements for liability of negligence 1. When p did x, he voluntarily and knowingly assumed the risk of doing so. Causation (p must show connection between breach. Knows with substantial certainty that the contact will occur. [2] the defendant breached that duty through an act or omission; Single intent = (1) only; He didn't know of risk. Everyone owes everyone a general duty of due care to not subject others to unreasonable risks of harm. Everyone owes everyone a general duty of due care to not subject others to unreasonable risks of harm. What is the standard of care? If d’s negligence is not established as a necessary condition of p’s loss, it may still be sufficient to establish liability: Dual intent = (1) & (2) the intent to contact is satisfied if the defendant. Welcome to studocu sign in to access the best study resources. Courts demand a higher standard where the foreseeable harm includes bodily injury, especially specific injuries. Palsgraf andrews / cardozo anyone/zone of danger. Knows with substantial certainty that the contact will occur. Causation (p must show connection between breach. If d’s negligence is not established as a necessary condition of p’s loss, it may still be sufficient to establish liability: What is the standard of care? Web four requirements for liability of negligence 1. Single intent = (1) only; Welcome to studocu sign in to access the best study resources. Who is the reasonable person? [2] the defendant breached that duty through an act or omission; Web using flowcharts to show the key principles and cases. Tort tort means civil wrongs, that is where one person is harmed by the actions of another (not arising from contract). He didn't know of risk. Web identify relevant risk of harm and negligence. The flowchart also sets out the types of damages that may be awarded. Web flowchart negligence flow chart duty of care reasonably reasonably foreseeable foreseeable class class of of persons persons (chapman (chapman vv hearse) hearse. If d’s negligence is not established as a necessary condition of p’s loss, it may still. Web the document summarizes the key elements of the tort of negligence in english law. However, travel is on its way to a full recovery by the end of 2024. Who is the reasonable person? More regional trips, an emerging population of new travelers, and a fresh set of destinations are powering steady spending in tourism. [3] the breach was. Definition negligence means the failure of a person to take care which leads to injury (or pure economic loss) to another. Note, businesses owe a higher duty of care. Web four requirements for liability of negligence 1. Everyone owes everyone a general duty of due care to not subject others to unreasonable risks of harm. Web does anyone have a. General duty of due care: Web “negligence is the omission to do something which a reasonable man, guided upon those considerations which ordinarily regulate the conduct of human affairs, would do, or doing something which a prudent and reasonable man would not do.” For each section, it outlines the legal tests and principles used to determine if there is negligence. When p did x, he voluntarily and knowingly assumed the risk of doing so. Knows with substantial certainty that the contact will occur. Web does anyone have a good flowchart that i could use to help me navigate negligence for my torts final? Analogous cases caparo as interpreted in robinson chief police constable for west yorkshire. P can argue if no other options = not voluntary; Web a flowchart summarising the principles that a court will consider when determining a damages award in a tort action, including causation, mitigation, contributory negligence and remoteness. Note, businesses owe a higher duty of care. However, travel is on its way to a full recovery by the end of 2024. An unintentional breach of duty that results in harm to step. Web does a statute such as the good samaritan act raise the standard of care to gross negligence? It breaks down the elements that must be proven for negligence: For more information on the negligence analysis, see our flow charts on proximate cause and landowner liability. What is the standard of care?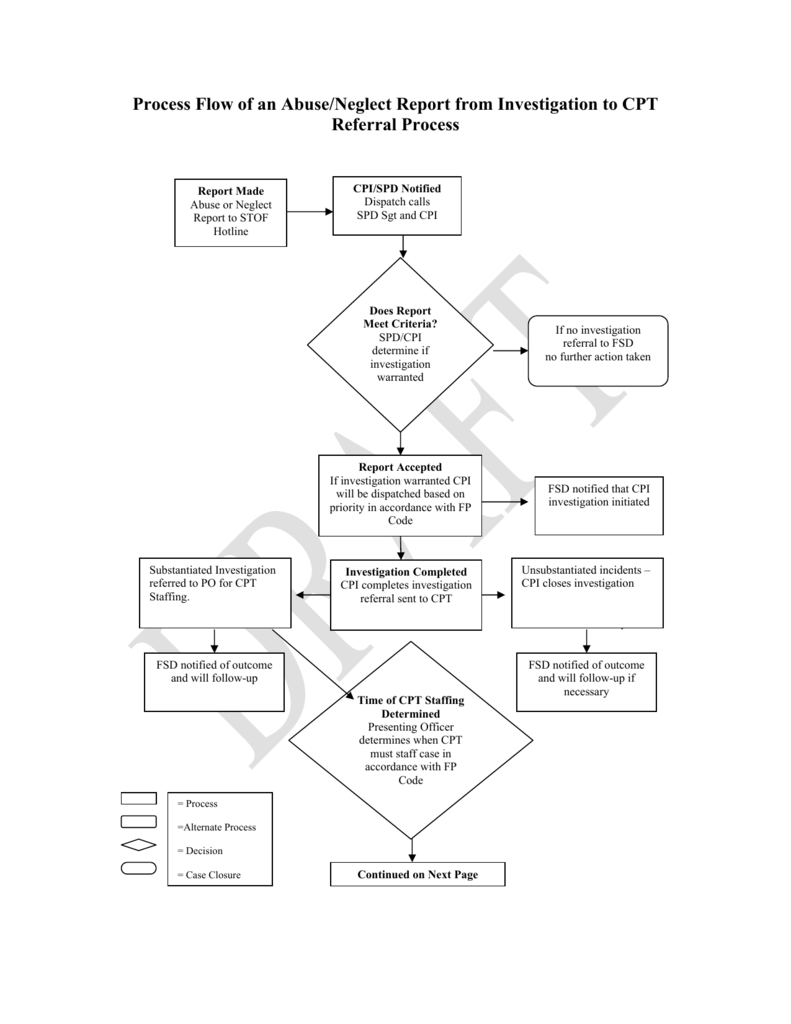
Process Flow Chart of Abuse and Neglect Referrals
Torts Flow Chart PDF Causation (Law) Negligence
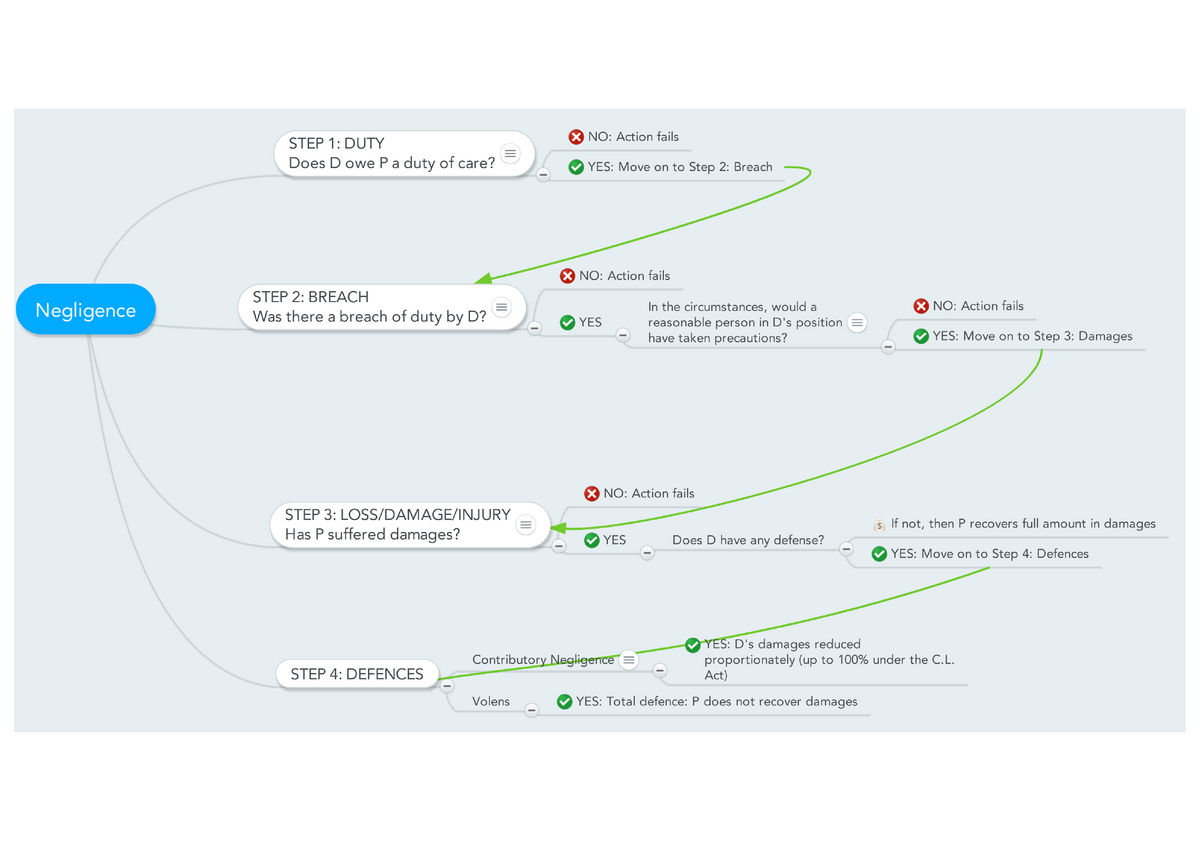
Negligence flow chart w notes STEP DUTY Does owe duty of care Was it
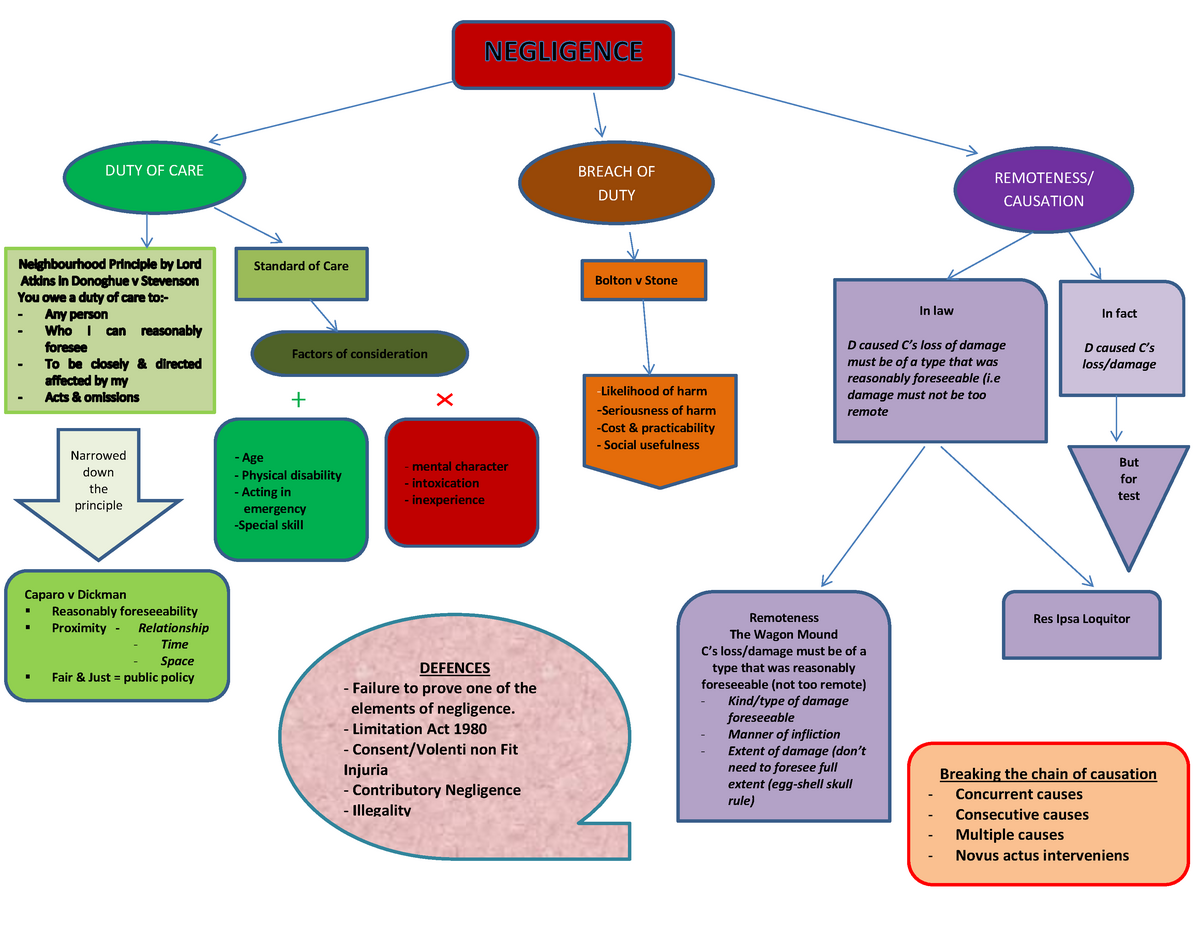
Negligence chart Well prepared slides DUTY OF CARE BREACH OF DUTY
Negligence Flow Chart
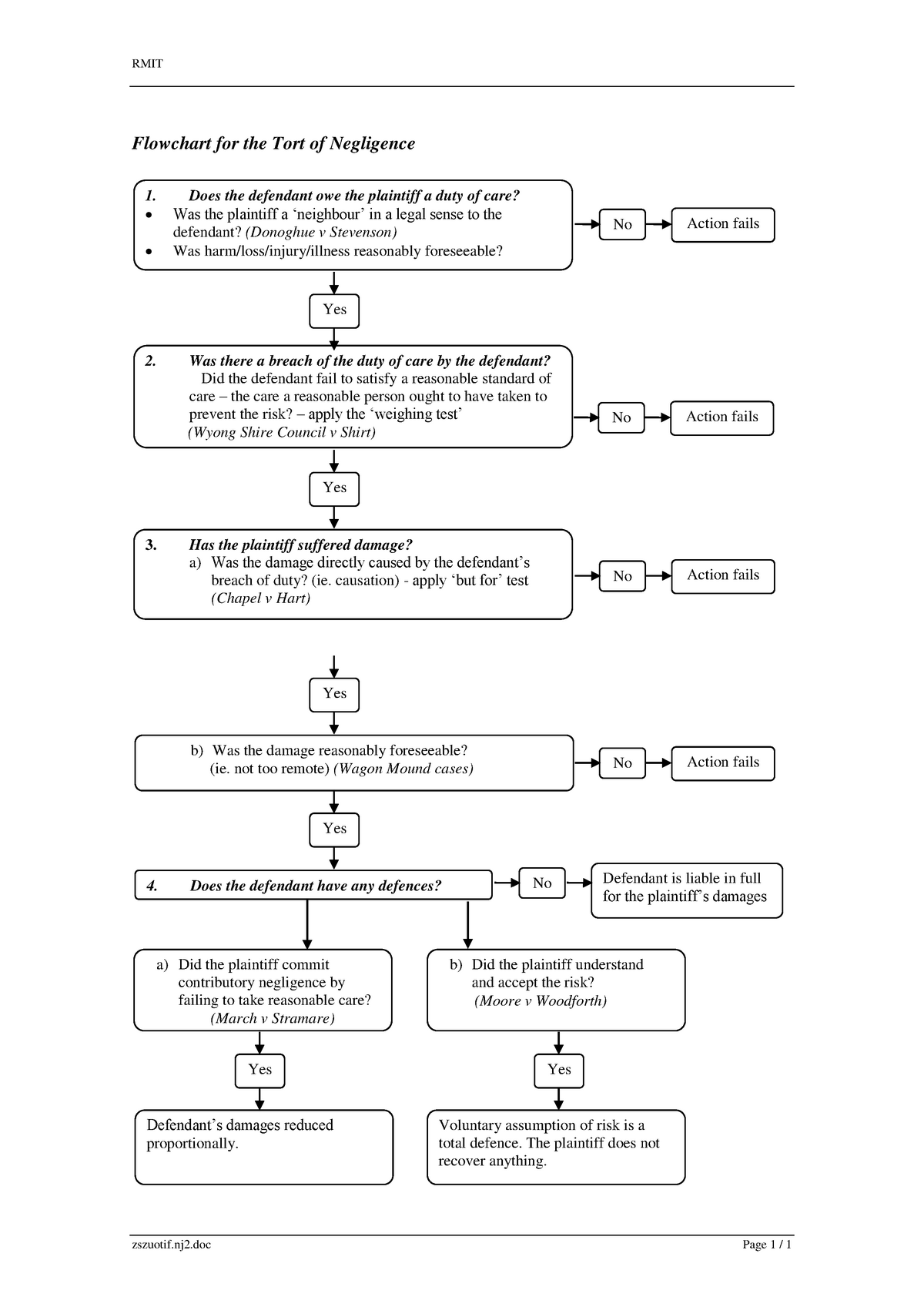
Week 2 Negligence Flow Chart RMIT Flowchart for the Tort of
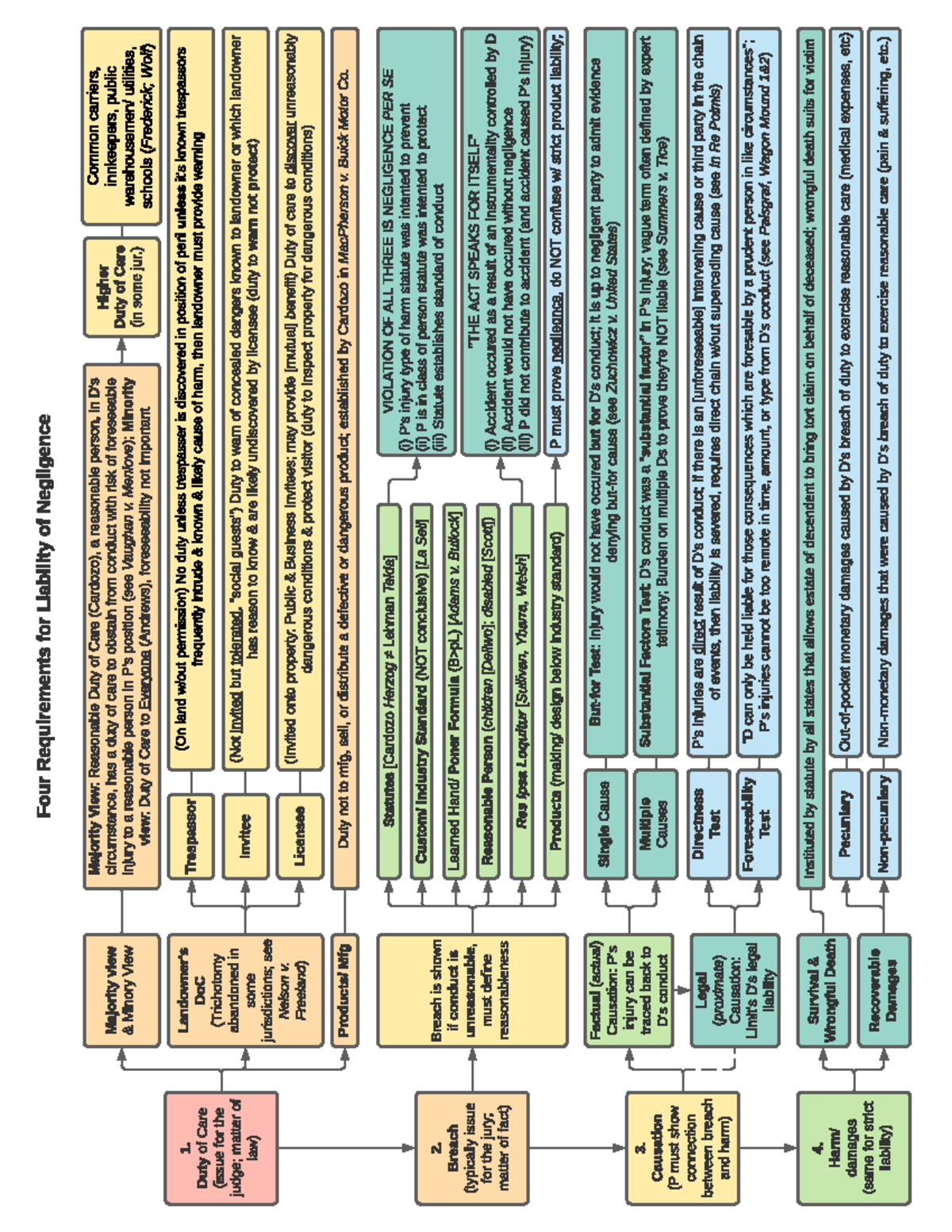
Liability of Negligence Flowchart Four Requirements for Liability of

Negligence Flow Chart LAWS1061 Torts UNSW Thinkswap
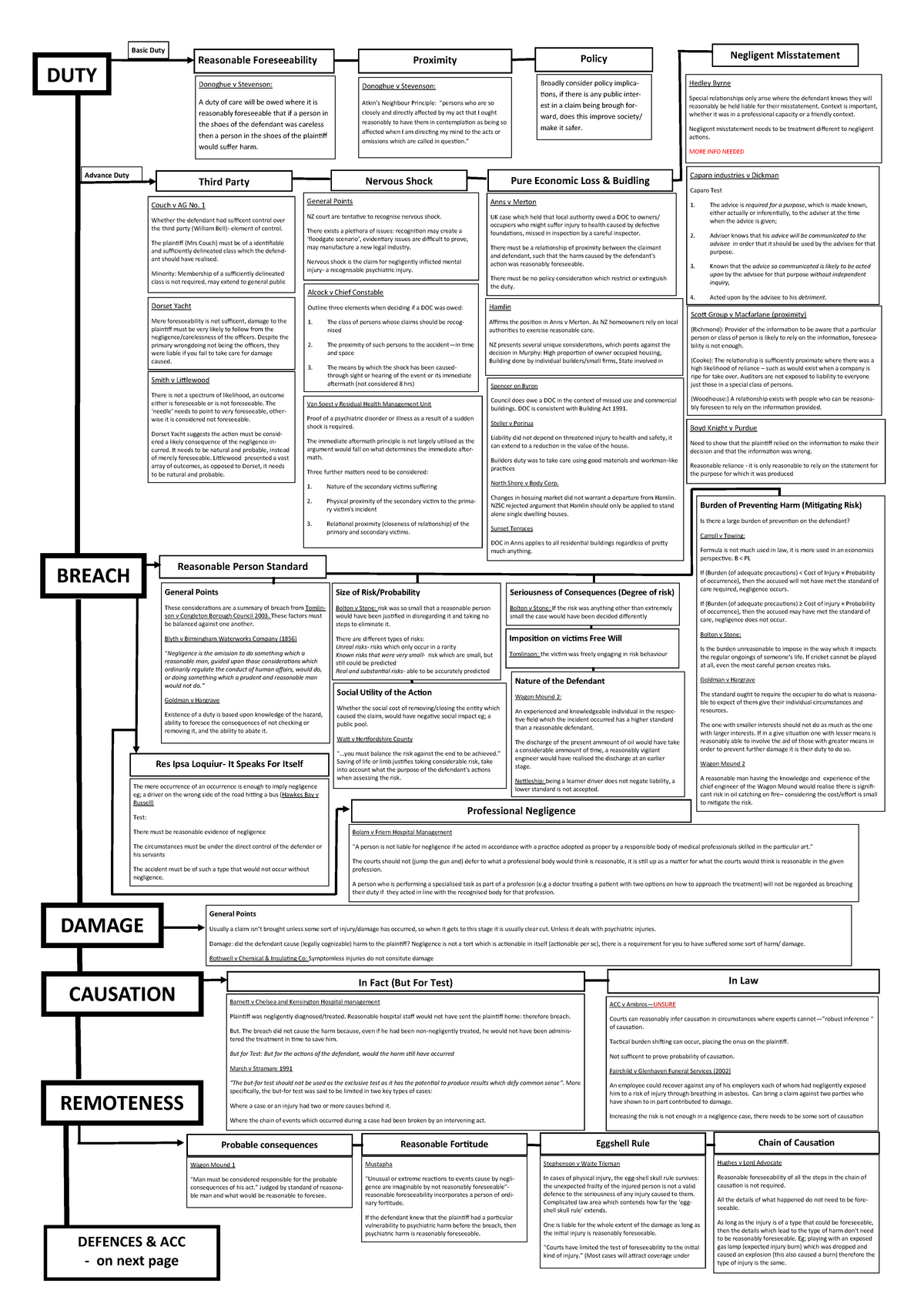
Negligence flow chart a3 DUTY Reasonable Foreseeability Proximity
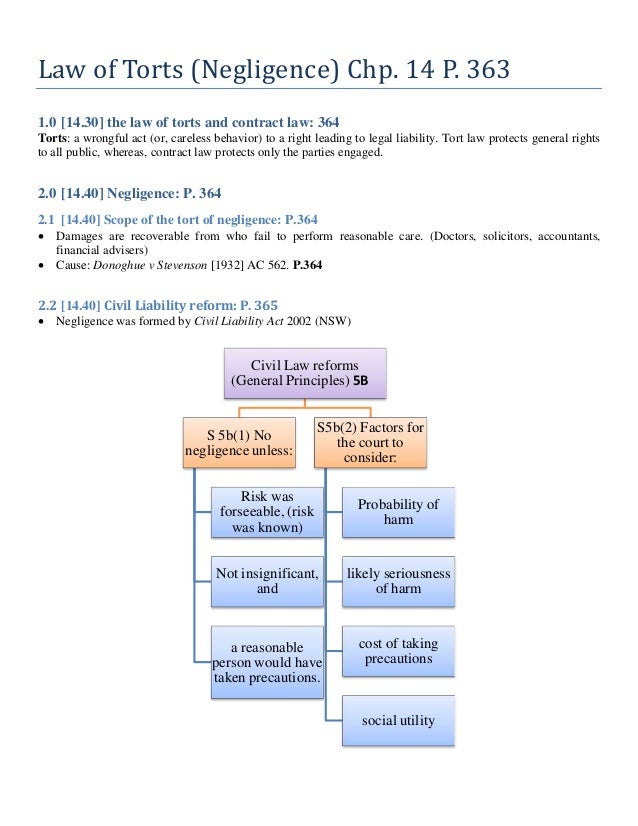
Law of torts, Negligence
Defendant Must Intend To (1) Cause A Contact With The Plaintiff (2) That Is Harmful Or Offensive.
He Didn't Know Of Risk.
Web Using Flowcharts To Show The Key Principles And Cases.
More Regional Trips, An Emerging Population Of New Travelers, And A Fresh Set Of Destinations Are Powering Steady Spending In Tourism.
Related Post:

