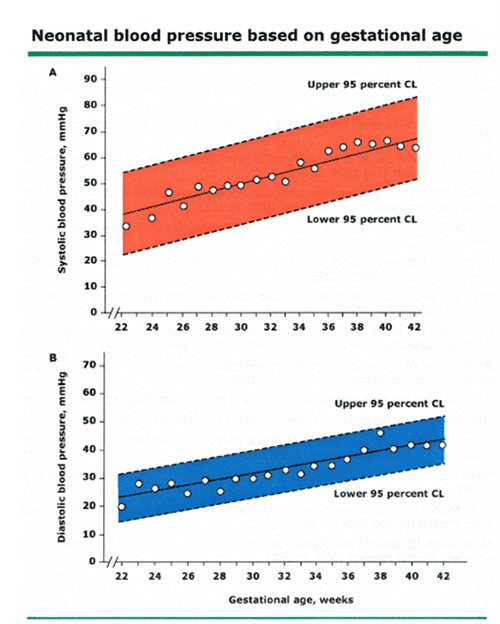
Neonatal Bp Chart
Neonatal Bp Chart - Bp values may reflect perfusion, fluid status,. Web the strongest determinants of neonatal bp are the infant factors of gestational age at birth, birth weight, and postmenstrual age. Hypertension — the diagnosis of hypertension in neonates may be considered when there are persistent systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure. Web measurement of neonatal blood pressure. Healthcare providers check these during exams to get a snapshot of your child’s overall. Web bp by age and height centile tables: Observed bp values for infants born at term over the first 4 days after birth. A child's vital signs change. Understanding the expected pattern of bp. Web based neonatal bp values beyond the first postnatal week for preterm infants born 28 to 36 weeks ga. A child's vital signs change. Observed bp values for infants born at term over the first 4 days after birth. Severe hypertension requires urgent consultation and management. Web therapy of neonatal hypertension should be tailored to the severity of the blood pressure elevation, and to the underlying cause of hypertension as appropriate. Web bp by age and height centile tables: Published bp nomograms demonstrate a rise in bp following delivery in healthy infants at all gestational ages (ga). Web this topic reviews the management of hypertension in neonates and infants, including a suggested approach for initiating pharmacologic therapy. Severe hypertension requires urgent consultation and management. Overview of pediatric vital signs. Web the systolic and diastolic bps are of equal importance. Web based neonatal bp values beyond the first postnatal week for preterm infants born 28 to 36 weeks ga. Severe hypertension requires urgent consultation and management. Web neonatal hypertension is increasingly recognized as dramatic improvements in neonatal intensive care, advancements in our understanding of neonatal physiology, and. Observed bp values for infants born at term over the first 4 days. Web neonatal hypertension is defined as systolic blood pressure (bp) of at least the 95th percentile for gestational age, birthweight, and sex on 3 separate occasions. Web neonatal hypertension is increasingly recognized as dramatic improvements in neonatal intensive care, advancements in our understanding of neonatal physiology, and. Understanding the expected pattern of bp. Web this topic reviews the management of. Web bp by age and height centile tables: Web blood pressure (bp) is routinely measured in newborn infants. Overview of pediatric vital signs. Web based neonatal bp values beyond the first postnatal week for preterm infants born 28 to 36 weeks ga. Web significant changes in these guidelines include (1) the replacement of the term “prehypertension” with the term “elevated. Published bp nomograms demonstrate a rise in bp following delivery in healthy infants at all gestational ages (ga). A child's vital signs change. Observed bp values for infants born at term over the first 4 days after birth. Overview of pediatric vital signs. Patterns of change in physiological variables are as. Understanding the expected pattern of bp. Web therapy of neonatal hypertension should be tailored to the severity of the blood pressure elevation, and to the underlying cause of hypertension as appropriate. Patterns of change in physiological variables are as. Hypertension associated with encephalopathy is. In the past few decades, as neonatal intensive care technology has advanced, so has. Hypertension — the diagnosis of hypertension in neonates may be considered when there are persistent systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure. Patterns of change in physiological variables are as. Web this topic reviews the management of hypertension in neonates and infants, including a suggested approach for initiating pharmacologic therapy. Hypertension associated with encephalopathy is. Understanding the expected pattern of bp. A child's vital signs change. Web therapy of neonatal hypertension should be tailored to the severity of the blood pressure elevation, and to the underlying cause of hypertension as appropriate. Published bp nomograms demonstrate a rise in bp following delivery in healthy infants at all gestational ages (ga). Web this topic reviews the management of hypertension in neonates and infants,. Severe hypertension requires urgent consultation and management. Healthcare providers check these during exams to get a snapshot of your child’s overall. Published bp nomograms demonstrate a rise in bp following delivery in healthy infants at all gestational ages (ga). Web based neonatal bp values beyond the first postnatal week for preterm infants born 28 to 36 weeks ga. Web the. Whilst many infants are not sufficiently. Web the systolic and diastolic bps are of equal importance in determining the following bp categories (see definition and diagnosis of hypertension in children and. Web bp by age and height centile tables: Web based neonatal bp values beyond the first postnatal week for preterm infants born 28 to 36 weeks ga. Bp values may reflect perfusion, fluid status,. Hypertension — the diagnosis of hypertension in neonates may be considered when there are persistent systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure. Web neonatal hypertension is increasingly recognized as dramatic improvements in neonatal intensive care, advancements in our understanding of neonatal physiology, and. In the past few decades, as neonatal intensive care technology has advanced, so has. Web interpret blood pressure measurements using centile charts for age and height (sections 4, 10,11 (neonatal)) repeated blood pressure measurements are required to diagnose. Web blood pressure (bp) is routinely measured in newborn infants. Web the strongest determinants of neonatal bp are the infant factors of gestational age at birth, birth weight, and postmenstrual age. The table below provides acceptable ranges for systolic bp, heart rate and respiratory rate for unwell children. Severe hypertension requires urgent consultation and management. Roper measurement of blood pressure (bp) in neonates and infants can be technically challenging. Patterns of change in physiological variables are as. Systolic and diastolic blood pressures (mean and 95%.Blood pressure hypertension in neonates
![[PDF] Managing Hypertension in the Newborn Infants Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/e0c5981a80e62928f3f7ee5980fb43caf74bbe30/3-Table1-1.png)
[PDF] Managing Hypertension in the Newborn Infants Semantic Scholar
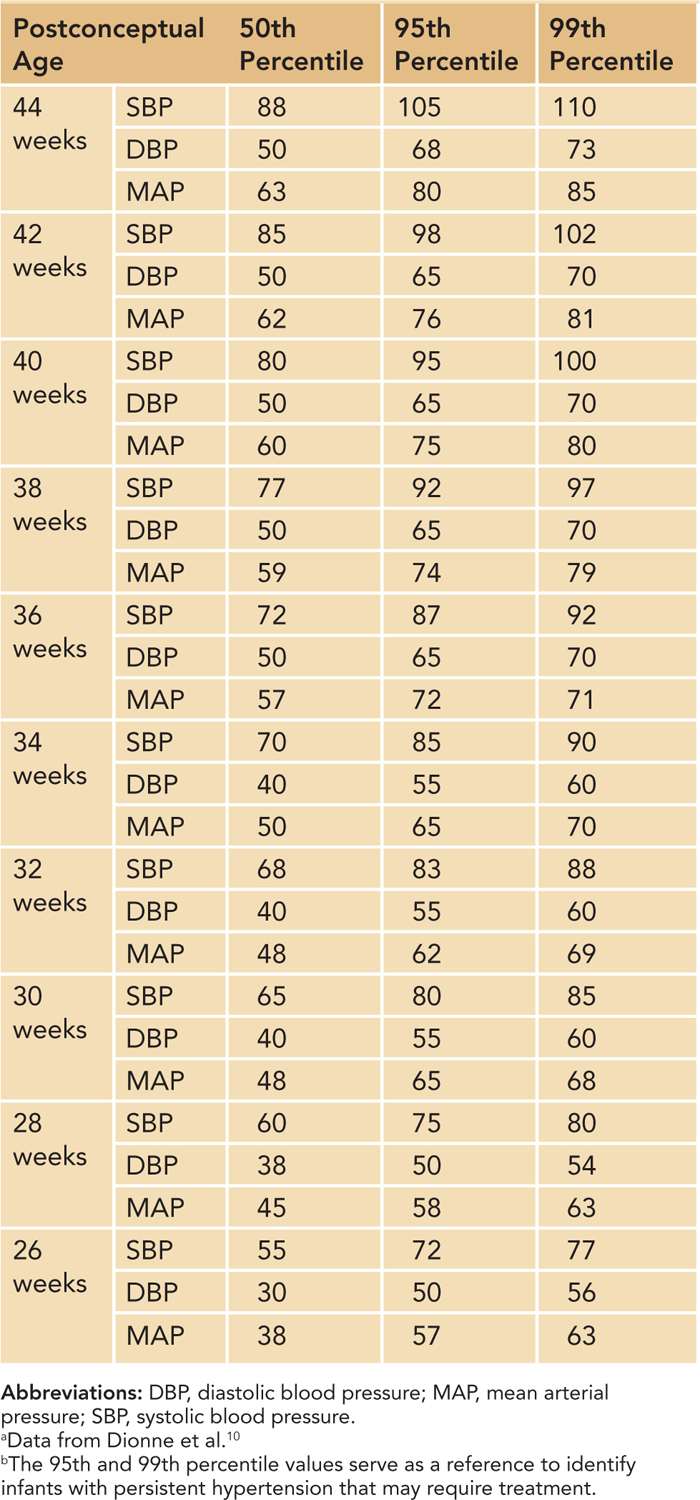
Neonatal Hypertension Obgyn Key

Normal values for neonatal blood pressure Obgyn Key

Blood pressure charts for pediatrics Atlas of Science
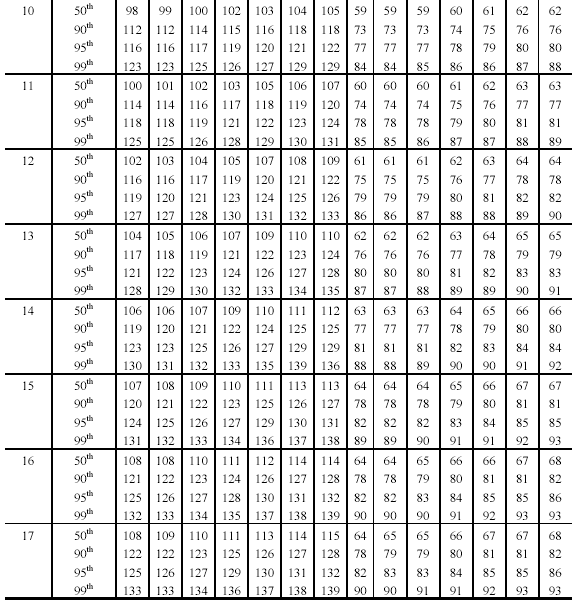
Neonatal blood pressure chart caqwepc

Neonatal Vital Sign Chart
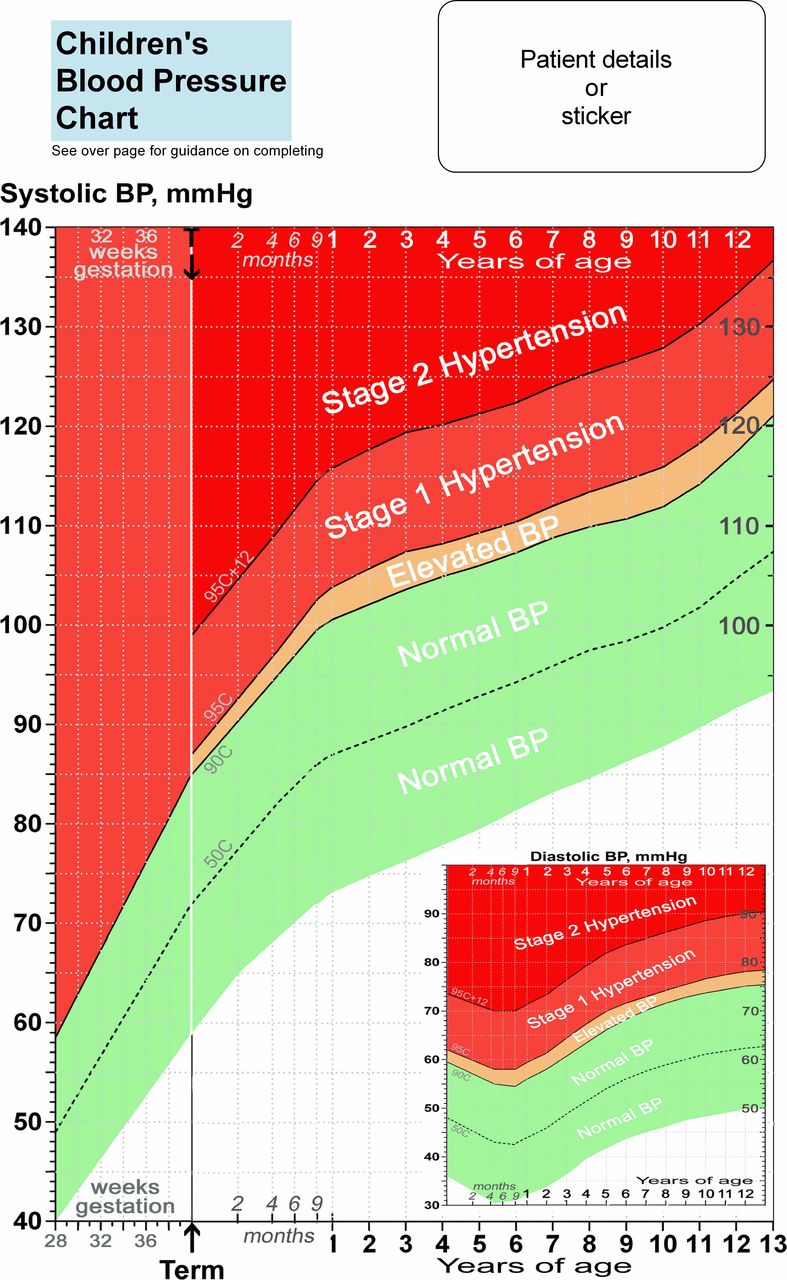
Blood Pressure Chart For Children
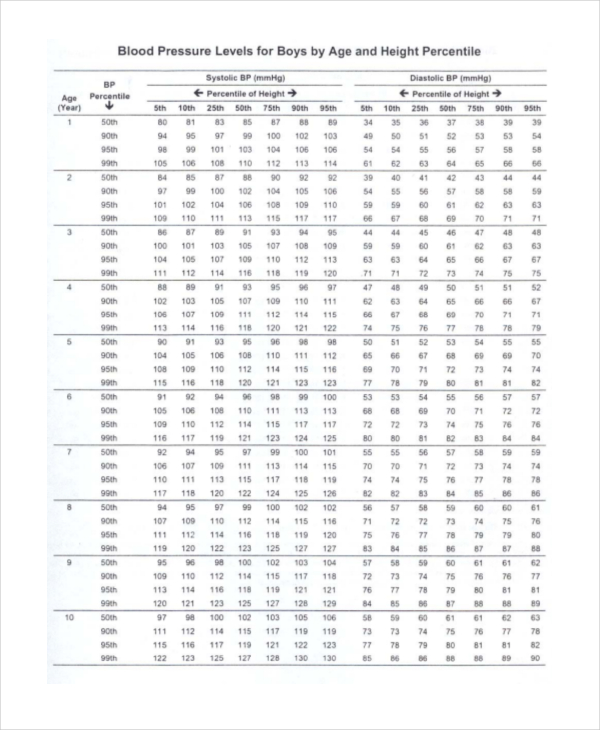
Printable Pediatric Blood Pressure Chart Customize and Print

Systolic blood pressure in babies of less than 32 weeks gestation in
Healthcare Providers Check These During Exams To Get A Snapshot Of Your Child’s Overall.
Overview Of Pediatric Vital Signs.
Web Significant Changes In These Guidelines Include (1) The Replacement Of The Term “Prehypertension” With The Term “Elevated Blood Pressure,” (2) New Normative.
Published Bp Nomograms Demonstrate A Rise In Bp Following Delivery In Healthy Infants At All Gestational Ages (Ga).
Related Post: