Oblique Shock Chart
Oblique Shock Chart - Supersonic flow encounters a wedge and is uniformly deflected forming an oblique shock. Web oblique shock wave data table. A shock wave is most commonly associated with fast military aircraft or spacecraft when they move faster than the speed of sound. Oblique shock charts γ = 1.4. Web consider infinitely thin body m1>1. The oblique shock charts are from naca report 1135, equations, tables, and charts. Mach number behind the shock, pressure ratio, derivation of flow, and angle of shock are presented on charts. Infinitessimal wave μ = sin− ( 1 /m ) oblique shock. The mach waves from a gradual compression deflection will intersect forming a. Get aircraft propulsion, 2nd edition now with the o’reilly learning platform. Β = oblique shock wave angle, (deg) m 2 = mach number of flow behind the shock wave. Input m 1 value and select an input variable by using the choice button and then type in the value of the selected variable. These calculations are presented in tabular form and include values. Oblique shock charts γ = 1.4. The red. Web oblique shocks chart ¶. Same approach as for normal shocks. The required input is the mach number of the upstream flow and the wedge angle. The red line separates the strong and weak solutions. We start with the oblique shock. Get aircraft propulsion, 2nd edition now with the o’reilly learning platform. Draws a chart displaying the possible combinations of deflection and shock wave angle for several values of incident mach number. Β = oblique shock wave angle, (deg) m 2 = mach number of flow behind the shock wave. This form calculates properties of air flow through an oblique shock. Web when a shock wave is inclined to the flow direction it is called an oblique shock. Supersonic flow encounters a wedge and is uniformly deflected forming an oblique shock. Figure 1 depicts a large compression deflection and clearly demonstrates why this is different from a large expansion deflection. Flow must undergo compression to turn. ¶ using a chart like. The red line separates the strong and weak solutions. A shock wave is most commonly associated with fast military aircraft or spacecraft when they move faster than the speed of sound. The mach waves from a gradual compression deflection will intersect forming a. The gas is assumed to be ideal air. Web oblique shock and expansion waves. Web the normal shock analysis dictates that after the shock, the flow is always subsonic. Web oblique shocks chart ¶. The formation of mach waves is described. The oblique shock charts are from naca report 1135, equations, tables, and charts. Web this oblique shock calculator will help determine the fluid flow properties for an oblique shock wave. The mach wave angle is dependent on the free stream mach number. Web oblique shocks commonly occur when a supersonic flow is deflected by a concave corner and is forced to turn onto itself. Figure 1 depicts a large compression deflection and clearly demonstrates why this is different from a large expansion deflection. Flow must undergo compression to turn θ. Return to oblique shock, or normal shock page. Web the normal shock analysis dictates that after the shock, the flow is always subsonic. Same approach as for normal shocks. Values are also included for density ratio and change in entropy. The mach wave angle is dependent on the free stream mach number. Return to oblique shock, or normal shock page. A body of finite thickness, however, will generate oblique waves of finite. Shock angle from a simple mach wave to a normal shock. Θ = wedge deflection angle, (deg) m 1 = mach number of flow upstream of shock wave. On this slide we have listed the equations which describe the change. Web if the shock wave is inclined to the flow direction it is called an oblique shock. The mach waves from a gradual compression deflection will intersect forming a. These calculations are presented in tabular form and include values. The required input is the mach number of the upstream flow and the wedge angle. Same approach as for normal shocks. Web if the shock wave is inclined to the flow direction it is called an oblique shock. Mach number behind the shock, pressure ratio, derivation of flow, and angle of shock are presented on charts. Return to oblique shock, or normal shock page. ( γ = 7/5) notation : Β = oblique shock wave angle, (deg) m 2 = mach number of flow behind the shock wave. For compressible flow, ames research staff, 1953. The formation of mach waves is described. Get aircraft propulsion, 2nd edition now with the o’reilly learning platform. Oblique waves may eventually coalesce and form oblique shocks or spread out to form an expansion wave. Web oblique shock and expansion waves. Infinitessimal wave μ = sin− ( 1 /m ) oblique shock. Pressure, mach number and wave angle changes through oblique shock waves. Mach number in front of the shock from 1.05 to h.0 and for a range of. The total flow after the oblique shock can also be supersonic, which depends on the boundary layer and the deflection angle. ⇒ oblique shock at angle θ m 1>1. The gas is assumed to be ideal air.
Oblique shock waves — Gas Dynamics notes
Oblique Shock Chart

Oblique Shock Chart
Tables and charts of flow parameters across oblique shocks Page 7 of
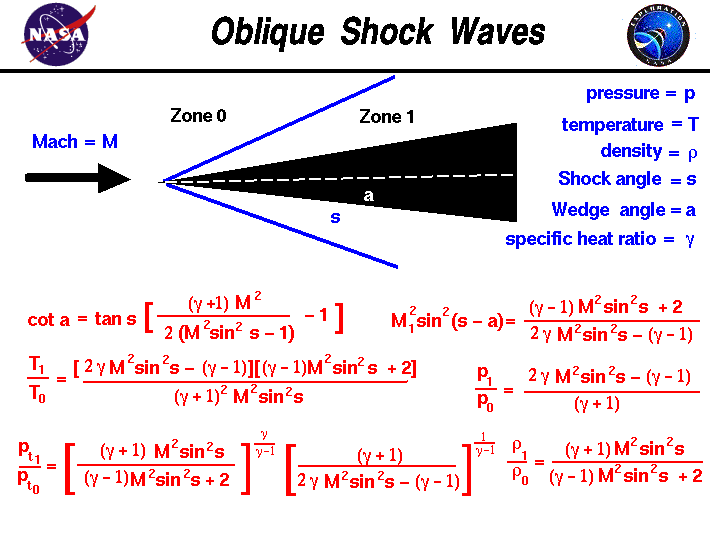
Oblique Shock Waves

Tables and charts of flow parameters across oblique shocks Page 20 of
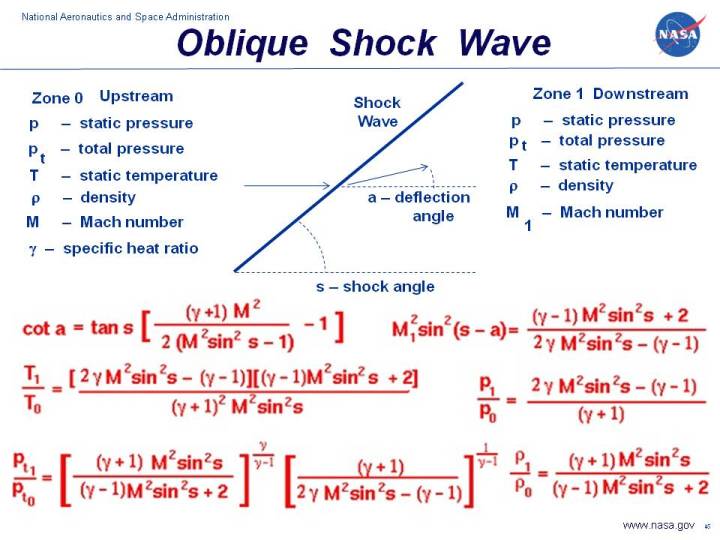
Oblique Shock Waves

Oblique Shock Chart

Tables and charts of flow parameters across oblique shocks Page 14 of
Tables and charts of flow parameters across oblique shocks Page 15 of
Draws A Chart Displaying The Possible Combinations Of Deflection And Shock Wave Angle For Several Values Of Incident Mach Number.
The Red Line Separates The Strong And Weak Solutions.
Θ = Wedge Deflection Angle, (Deg) M 1 = Mach Number Of Flow Upstream Of Shock Wave.
Web The Normal Shock Analysis Dictates That After The Shock, The Flow Is Always Subsonic.
Related Post: