Ocean Acidification Drawing
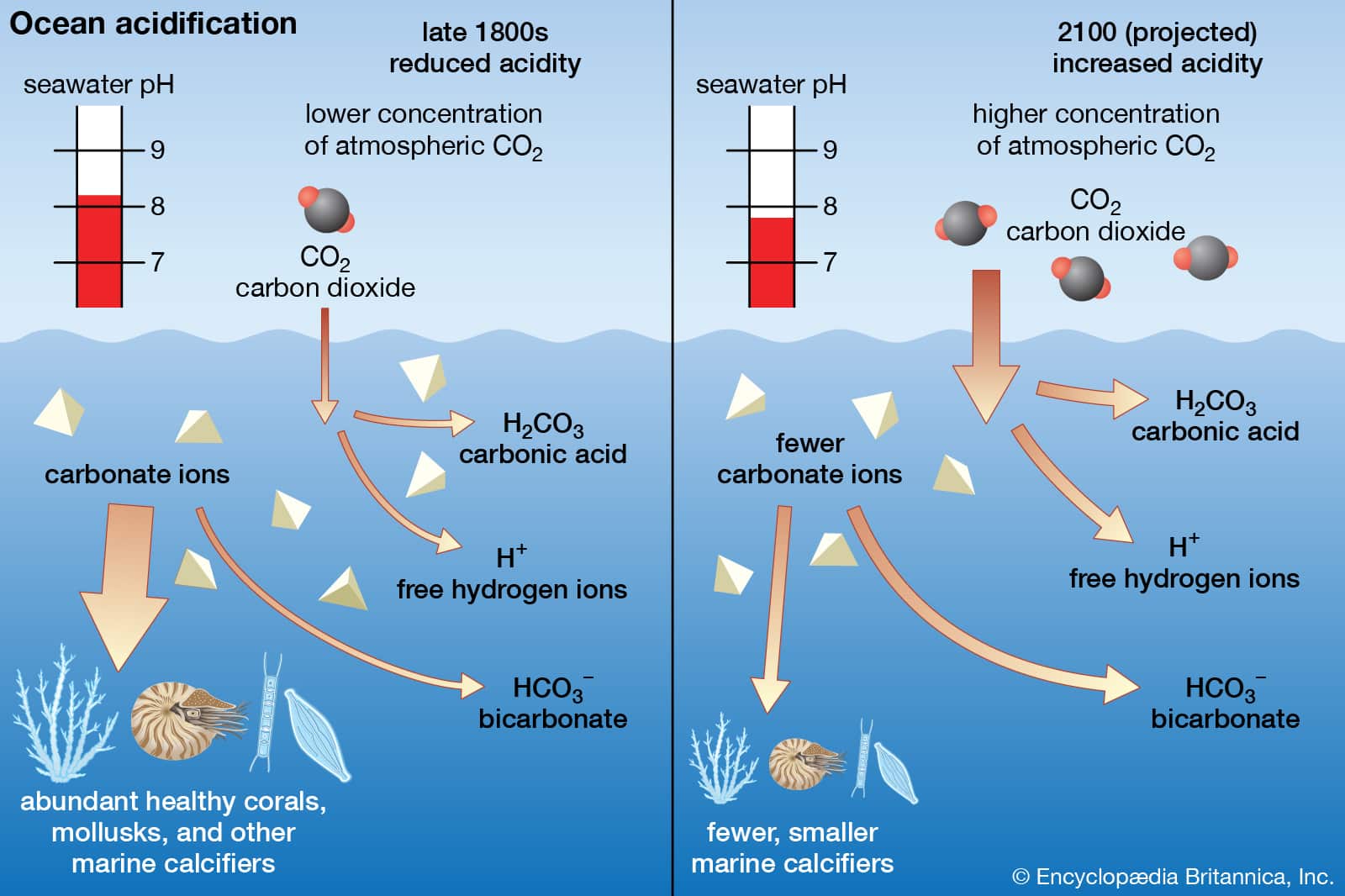
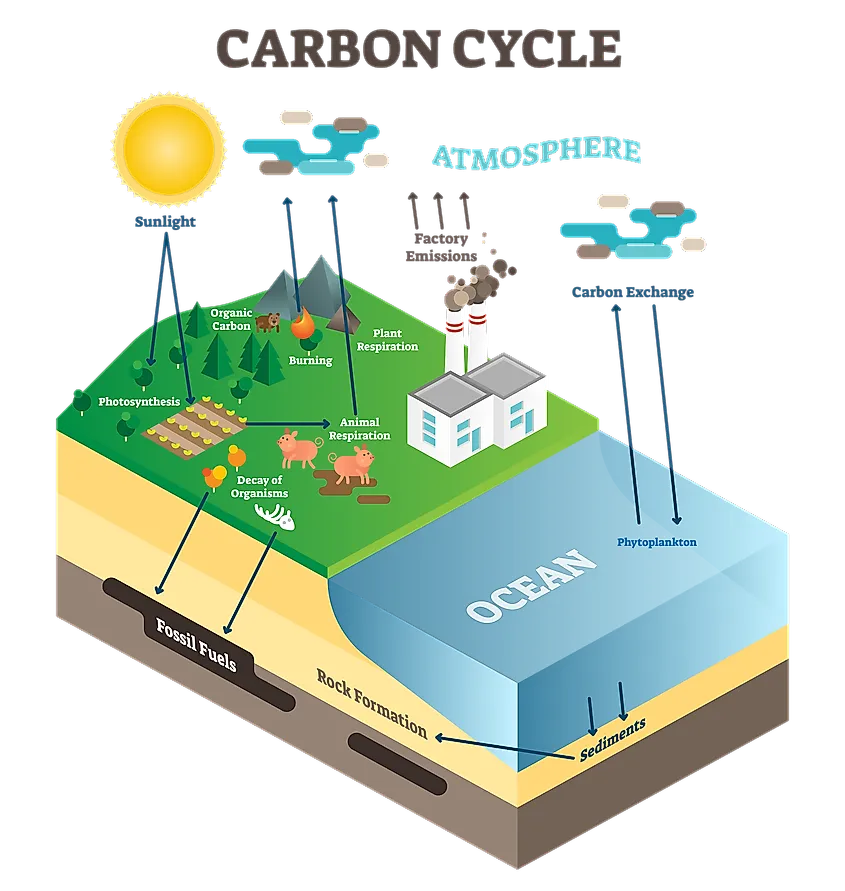
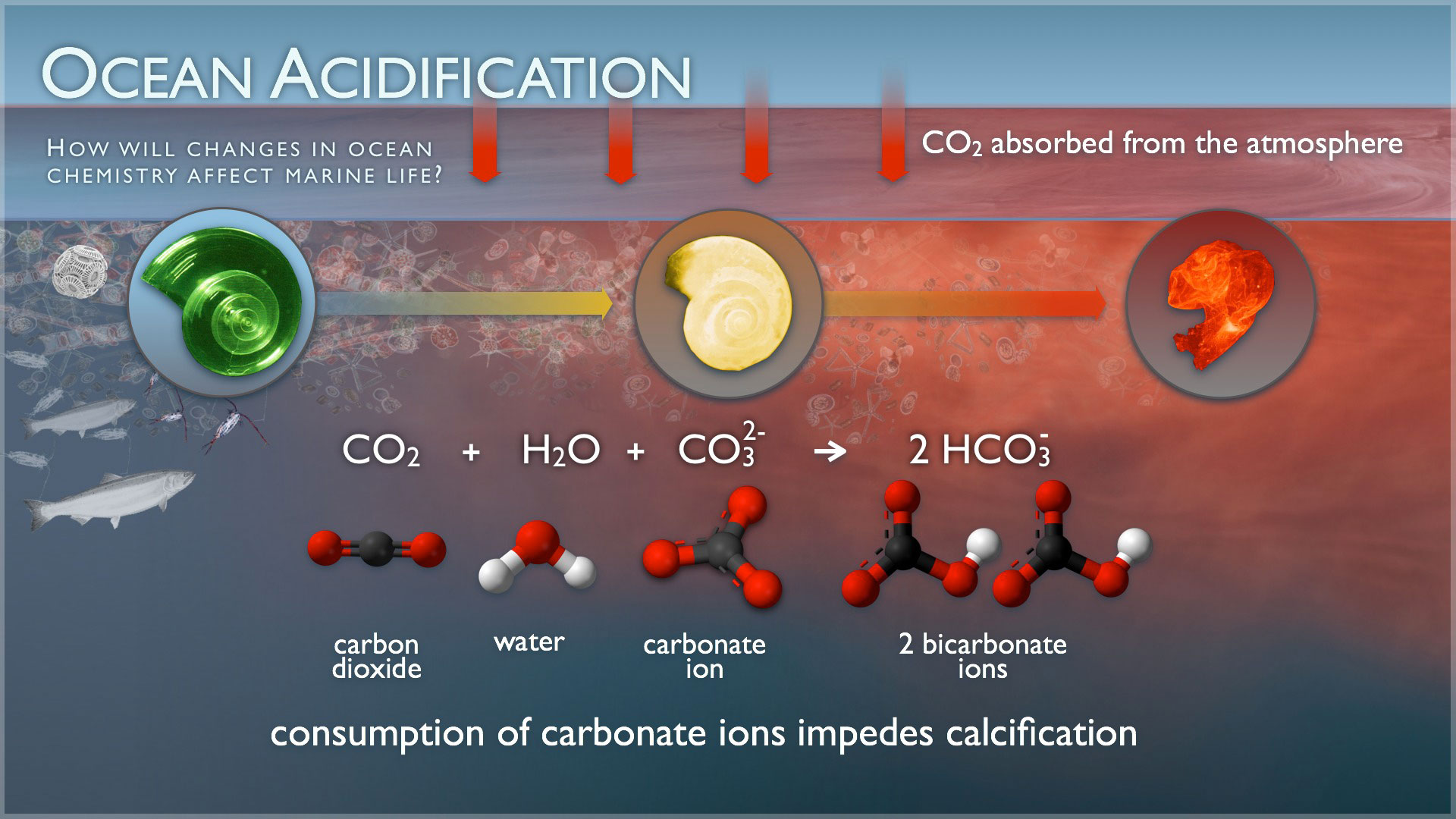
Ocean Acidification Drawing - Columbia university researchers showed that when carbon dioxide levels rise, ocean ph plummets and corals and other calcareous organisms perish. Web the short answer: Web like global warming, this phenomenon, which is known as ocean acidification, is a direct consequence of increasing levels of carbon dioxide (co 2) in earth’s atmosphere. (noaa pmel carbon program ( link )) how do we know ocean carbon dioxide levels are rising and ph is decreasing? Ocean acidification is largely the result of loading earth’s atmosphere with large quantities of co 2, produced by vehicles and industrial and agricultural processes. Web during this era, biosphere 2’s artificial sea became an extraordinary model for the effects of ocean acidification. About a quarter of the carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere from the burning of fossil fuels, ends up in our ocean. Prior to industrialization, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere was 280 parts per million (ppm). Acidification can be measured by testing for acid neutralizing capacity (anc), which is the ability of a water body to reduce the effect of a strong acid. Ocean acidification is the decrease in the ph of the earth's ocean. It's a significant and harmful consequence of excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere that we don't see or feel because its effects are happening underwater. Prior to industrialization, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere was 280 parts per million (ppm). This is called ocean acidification. Web ocean acidification is sometimes called “climate change’s equally evil twin,” and for. In the last 200 years, the ocean has taken up around 30% of all co2 emissions and this absorption has altered the production of calcium carbonate in oceanic waters, causing the phenomenon known as ocean acidification (oa). Web the ocean carbon and acidification data system (ocads) is a data management system at the national oceanic and atmospheric administration (noaa) national. Web ocean acidification refers to a reduction in the ph of the ocean over an extended period of time, caused primarily by uptake of carbon dioxide (co 2) from the atmosphere. • assess environmental problems caused by humans and predict future consequences and describe how these problems can be solved. Scientists have observed that the ocean is becoming more acidic. It's a significant and harmful consequence of excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere that we don't see or feel because its effects are happening underwater. Ocean acidification is simply a sustained fall in the average ph of seawater in the world’s oceans. There are also indirect and potentially adverse. Ocean acidification is largely the result of loading earth’s atmosphere with. Scientists often use “tropical cyclone” as a generic term, while “hurricane,” “typhoon,” and “cyclone” are regional terms. Web most living organisms, especially aquatic life, function at the optimal ph range of 6.5 to 8.5. Ocean acidification is the decrease in the ph of the earth's ocean. Prior to industrialization, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere was 280 parts. Ph and the ocean’s balance. Ocean waves off the coast of new zealand. There are also indirect and potentially adverse. Ocean acidification is the decrease in the ph of the earth's ocean. Ocean acidification is fundamentally changing the chemistry of the world’s oceans and threatening our marine resources. Click to view notes from our reviewers Web ocean acidification means that the average ocean ph value is dropping over time. (noaa pmel carbon program ( link )) how do we know ocean carbon dioxide levels are rising and ph is decreasing? Web • analyze the effects of ocean acidification on coral reefs by collecting data from a model and. The ocean absorbs around 30% of carbon dioxide (co 2) released to the atmosphere as a result of human activities. Ocean waves off the coast of new zealand. Web like global warming, this phenomenon, which is known as ocean acidification, is a direct consequence of increasing levels of carbon dioxide (co 2) in earth’s atmosphere. Scientists have observed that the. Click to view notes from our reviewers Sufficient anc in surface waters will prevent ph levels from straying outside the range in. Acidification can be measured by testing for acid neutralizing capacity (anc), which is the ability of a water body to reduce the effect of a strong acid. Columbia university researchers showed that when carbon dioxide levels rise, ocean. Web when carbon dioxide (co 2) is absorbed by seawater, chemical reactions occur that reduce seawater ph, carbonate ion concentration, and saturation states of biologically important calcium carbonate minerals. • assess environmental problems caused by humans and predict future consequences and describe how these problems can be solved. Ocean acidification is the decrease in the ph of the earth's ocean.. Ocean acidification is the decrease in the ph of the earth's ocean. Web what is ocean acidification? Web • analyze the effects of ocean acidification on coral reefs by collecting data from a model and drawing conclusions. Web the ocean carbon and acidification data system (ocads) is a data management system at the national oceanic and atmospheric administration (noaa) national centers for environmental information (ncei). Web the short answer: Web ocean acidification describes the lowering of seawater ph and carbonate saturation that result from increasing atmospheric co 2 concentrations. The ocean absorbs around 30% of carbon dioxide (co 2) released to the atmosphere as a result of human activities. • assess environmental problems caused by humans and predict future consequences and describe how these problems can be solved. Between 1950 and 2020, the average ph of the ocean surface fell from approximately 8.15 to 8.05. Web ocean acidification refers to a reduction in the ph of the ocean over an extended period of time, caused primarily by uptake of carbon dioxide (co 2) from the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is an “acid gas” and causes the ocean to increase in. Web most living organisms, especially aquatic life, function at the optimal ph range of 6.5 to 8.5. Web some scientists continue trying to pinpoint the critical threshold for ocean acidification — when ph sinks so low it threatens the ocean’s ability to function, putting the entire earth. Watch our video for a quick overview. In this article, “hurricane” will be used as an umbrella term to refer to them no matter where they are. Web ocean acidification is sometimes called “climate change’s equally evil twin,” and for good reason: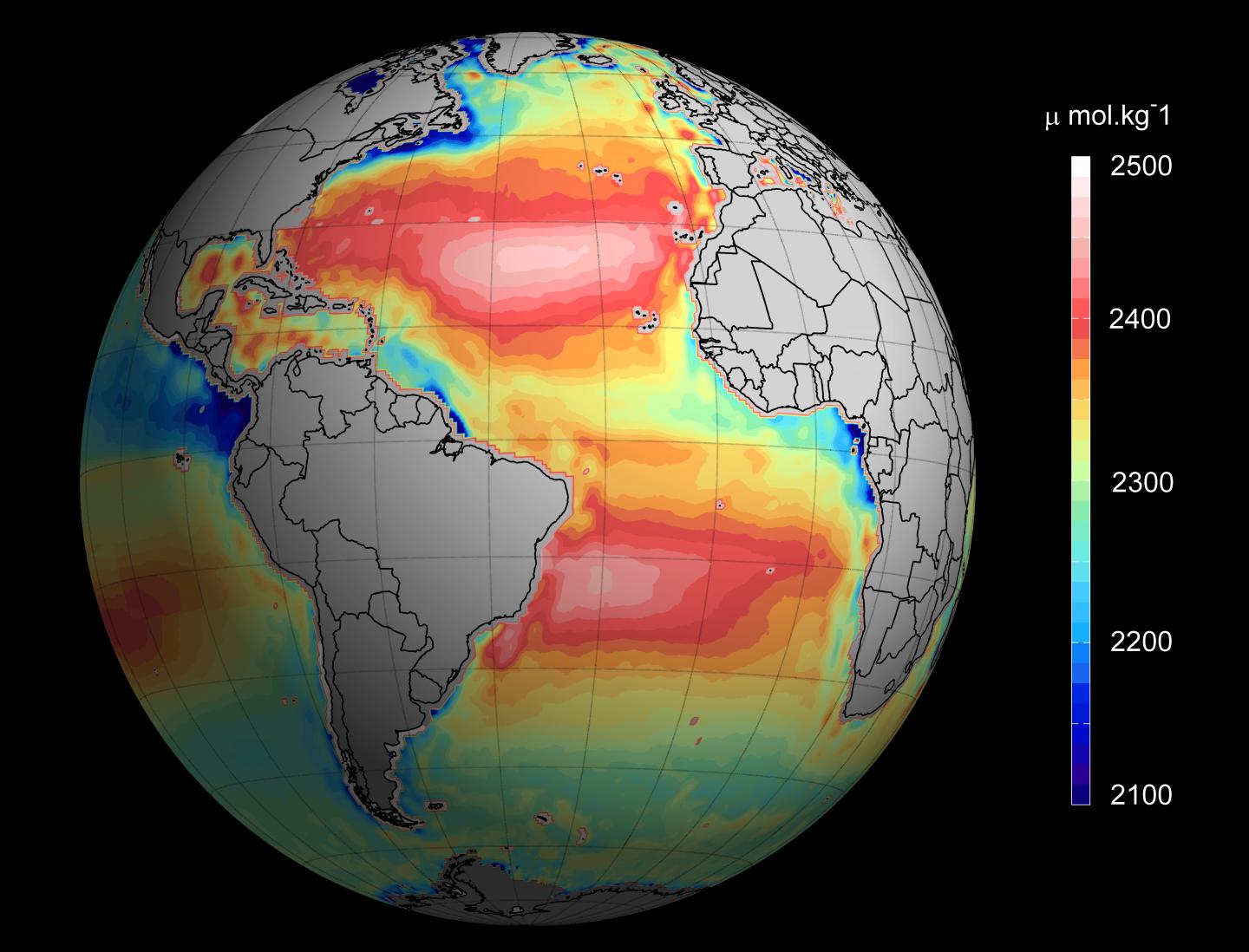
Global Ocean Acidity Revealed in New Maps Live Science

Exploring Ocean Acidification Easily and Affordably Vernier
Ocean Acidification Causes & Its Effects UPSC

Understanding the Science of Ocean and Coastal Acidification Ocean
Ocean Acidification WorldAtlas
Ocean Acidification Illustration
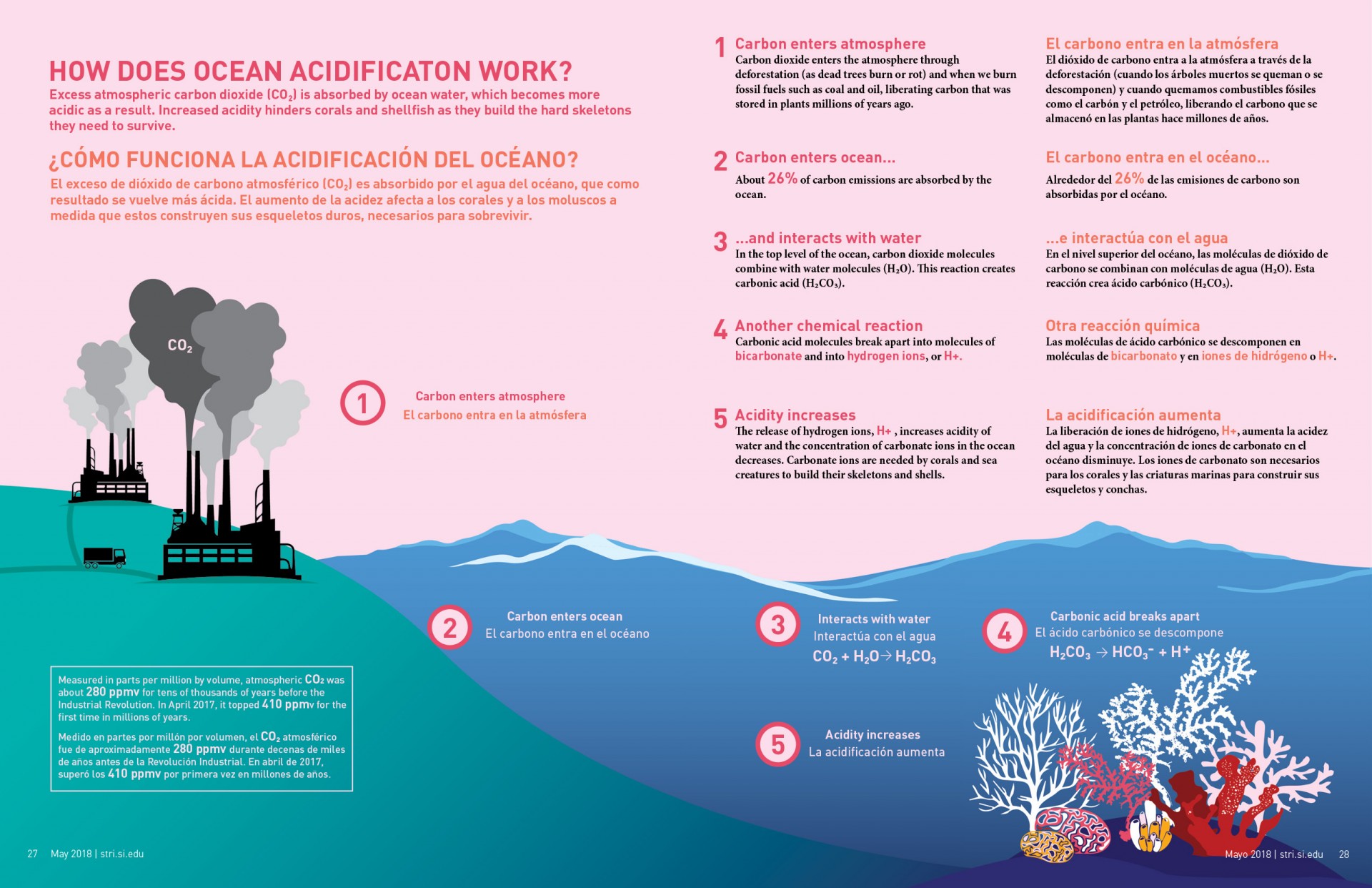
Ocean acidification and reefs Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute

Ocean Acidification Process Climate Central

Effects of Ocean and Coastal Acidification on Ecosystems US EPA

OCEAN ACIDIFICATION ‘Causes and Impacts’ IMA
Web The Reason For The Three Names Is That These Storms Are Called Different Things In Different Places.
Ocean Acidification Is Simply A Sustained Fall In The Average Ph Of Seawater In The World’s Oceans.
Web This Applet Is An Ocean Acidification Grapher That Allows User To Plot Changes In Atmospheric C02 Against Ocean Ph, From 1988 To 2009, In The Central North Pacific.
Ocean Acidification Is Fundamentally Changing The Chemistry Of The World’s Oceans And Threatening Our Marine Resources.
Related Post: