Ohm Pie Chart
Ohm Pie Chart - And r is the proportionality constant, called as resistance which is measured in ohms. Volts volts = watts / amperes volts = amperes x ohms volts = watts x ohms v = p / i v = i * r v = p * r p = power unit of measure: P = e * i. Voltage is the electrical potential difference and is the driving force that pushes the current through a circuit. V is the voltage applied across the circuit and it is measured in volts. E = p / i. 𝑉 = 𝐼 × 𝑅; To better understand the relationship between various parameters, we can take all the equations used to find the voltage, current, resistance and power, and condense them into a simple ohm’s law pie chart as shown below. Or to find out how much power your circuit uses. 120 volt 60 watt light bulb circuit. Web ohm’s law pie chart. Web the 12 most important formulas: 120 volt 60 watt light bulb circuit. The purpose of electronic circuits is to control the flow of electric currents. 𝐼 = 𝑉 × 𝑅 description: Voltage v = i × r = p / i = √ ( p × r) in volts v current i = v / r = p / v = √ ( p / r) in amperes a. To better understand the relationship between various parameters, we can take all the equations used to find the voltage, current, resistance and. I = e / r. The slope of the line is the resistance, or the voltage divided by the current. In algebraic form, v∝ i. These variables are what we don’t know, what we are trying to find: Web surprised by an ohm’s law pie chart. E = i * r. Web the ohm’s law chart is divided into four main quarters. • ohm's law calculators and formulas. Ohms watts = amperes2 x ohms watts = volts x amperes p =. Volts volts = watts / amperes volts = amperes x ohms volts = watts x ohms v = p / i v = i *. Current is the rate of flow of electric charge. 12 volt 60 watt light bulb circuit. E = i * r. For this purpose we will be accompanied by a resistor, the simplest passive element. Web the three basic principles for this tutorial can be explained using electrons, or more specifically, the charge they create: These variables are what we don’t know, what we are trying to find: Resistance r = v / i = p / i2 = v2 / p in ohms ω power p = v × i = r × i2 = v2 / r in watts w. Web ohm’s law pie chart. Formulas, ohm's law pie chart & calculator. Power. Ohms watts = amperes2 x ohms watts = volts x amperes p =. Ohm's law defines the relationships between (p) power, (e) voltage, (i) current, and (r) resistance. I = p / e. What is ohm’s law actually? • when the voltage is decreased the current decreases proportionately. Web ohm’s law pie formula chart. Web ohm’s law pie chart components of the pie chart: Power is measured in watts and is defined as: The purpose of electronic circuits is to control the flow of electric currents. Current is the rate at which charge is flowing. Resistance r = v / i = p / i2 = v2 / p in ohms ω power p = v × i = r × i2 = v2 / r in watts w. V = i × r. To help us understand the the relationship between the various values a little further, we can take all of the ohm’s. I = e / r. Web the chart below right shows the relationship between power, voltage, and current. And r is the proportionality constant, called as resistance which is measured in ohms. I is the current flowing through the circuit and it is measured in amps. The rate at which work is done when one ampere (a) of current flows. I is the current flowing through the circuit and it is measured in amps. Ohms watts = amperes2 x ohms watts = volts x amperes p =. To help us understand the the relationship between the various values a little further, we can take all of the ohm’s law equations from above for finding voltage, current, resistance and of course power and condense them into a simple ohms law pie chart for use in ac and dc circuits and calculations as shown. And r is the proportionality constant, called as resistance which is measured in ohms. In this video, we look at the 12 math equations on the ohms law wheel and show you how you can easily remember every. Under the condition that all physical parameters and temperatures remain constant, ohm’s law states that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it. Volts volts = watts / amperes volts = amperes x ohms volts = watts x ohms v = p / i v = i * r v = p * r p = power unit of measure: 120 volt 100 watt light bulb circuit. This is one of the few formulas in electronics that you’ll use on a regular basis. Web the chart below right shows the relationship between power, voltage, and current. Or to find out how much power your circuit uses. The formula wheel of acoustics (audio) the big power formulas. Web the current through the resistor and the voltage across the resistor are measured. E = p / i. Web ohm’s law formula chart. The purpose of electronic circuits is to control the flow of electric currents.
Orange County Electricity

Ohms Law Pie Chart
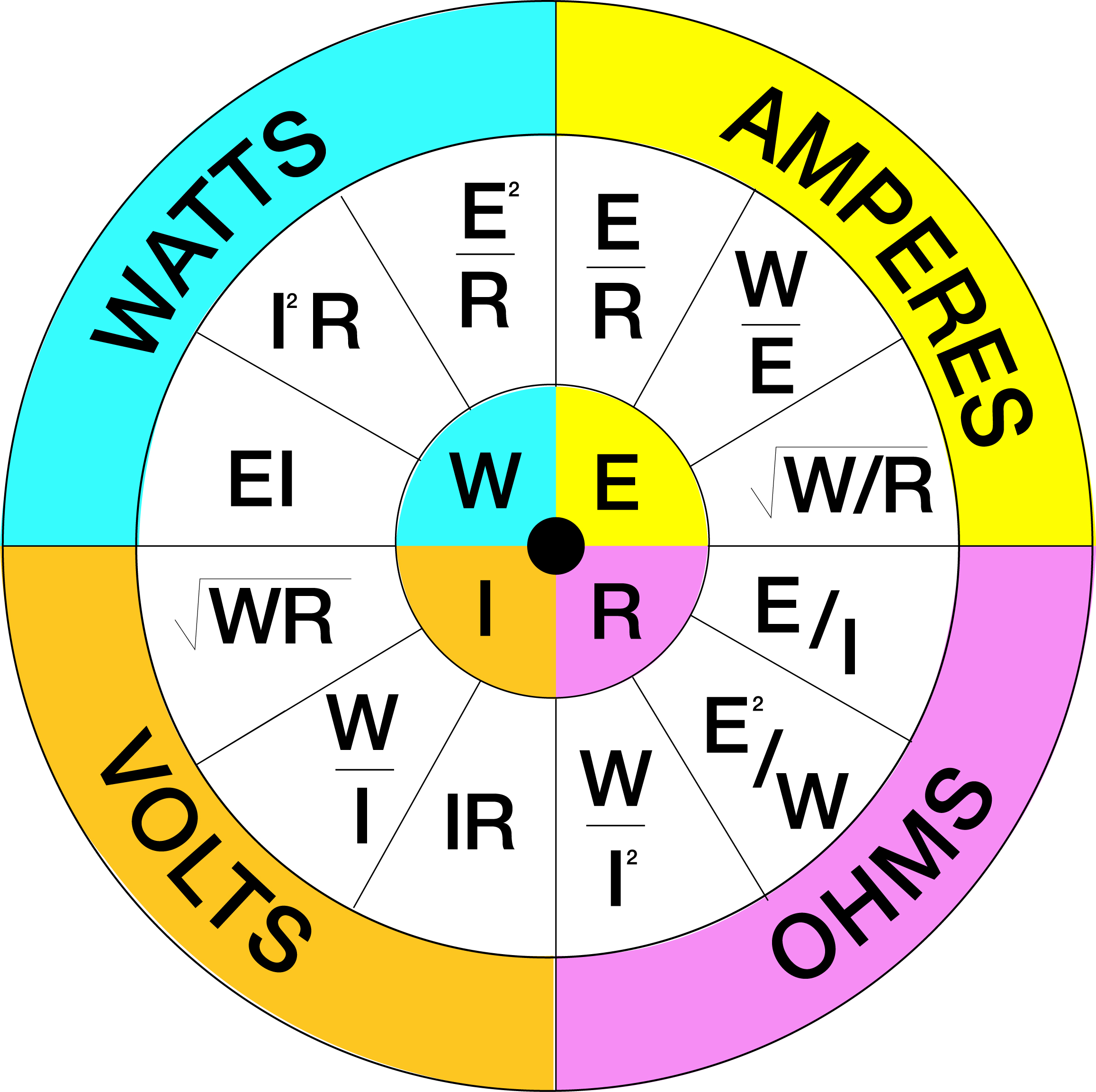
Understanding Ohms Law Pie Chart Poster sites.unimi.it
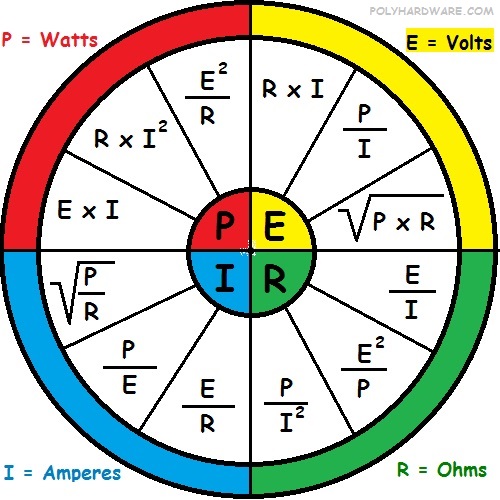
Ohm’s Law Pie Chart Quick and Easy POLYHARDWARE
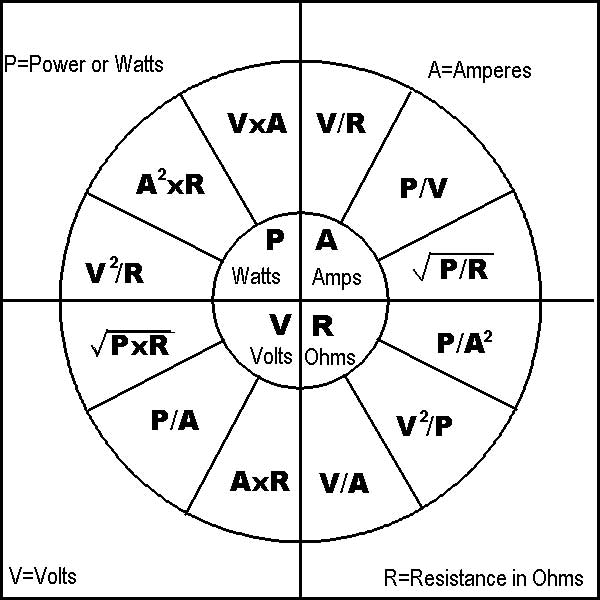
Ohm's Law Pie Chart Hi Tech Controls

Understanding the Basics of Ohm's Law EAHQ

Printable Ohms Law Wheel
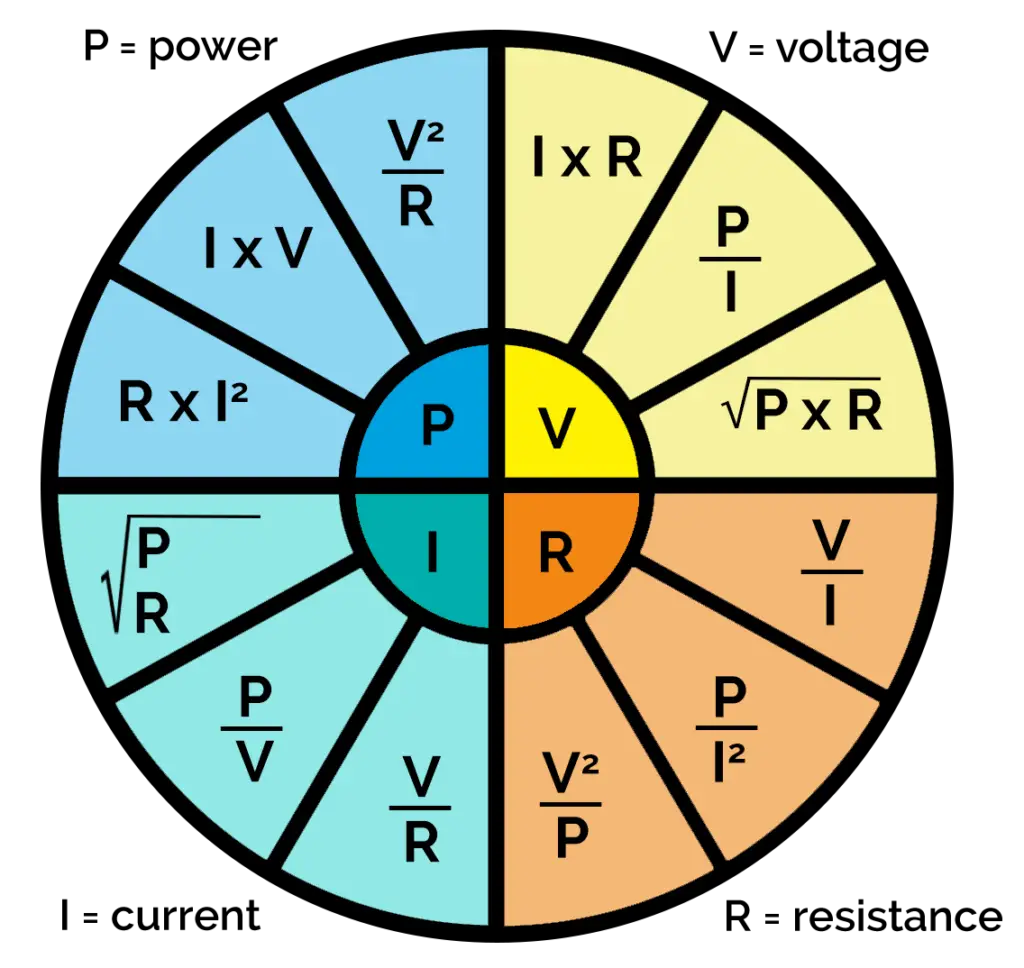
Ohms Law Tutorial And Power In Electrical Circuits 7E0
ELEFU Power and Energy

Ohm's Law Statement, Formula, Derivation, Applications, Limitations
Web Ohms Law Pie Chart.
• When The Voltage Is Decreased The Current Decreases Proportionately.
By Max Maxfield | Friday, February 9, 2018.
Understanding This Law Will Greatly Help Us In Understanding How An Electrical Circuit Works.
Related Post: