Osha Minimum Approach Distance Chart
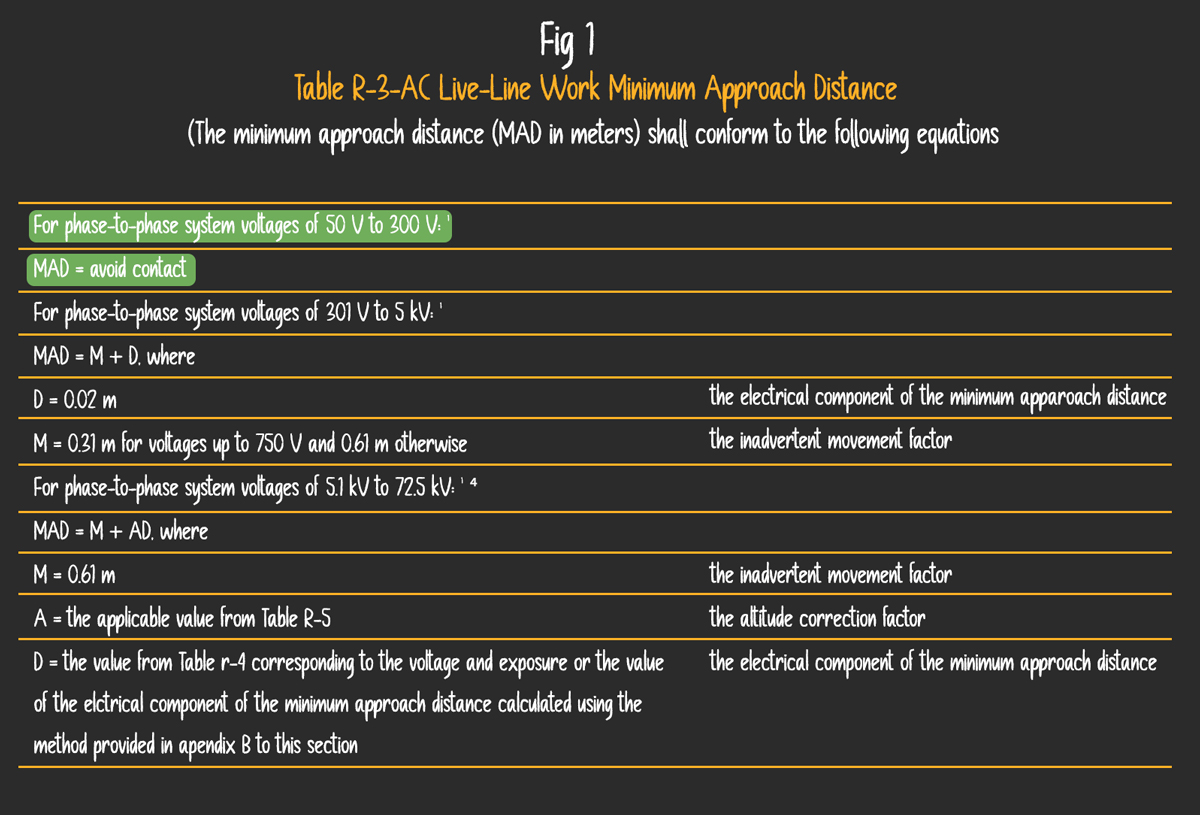
Osha Minimum Approach Distance Chart - Web osha refers to mad as “the closest distance a qualified employee may approach an energized conductor or object.” osha mad requirements in 2014, osha updated the 29 cfr 1910.269 and 1926 subpart v standards with requirements for all employers to establish mads. Minimum approach distances ensure that workers do not approach or take any conductive object closer to the energized parts. 1910.269(a)(2)(ii)(e) 1926.950(b)(2)(v) training new added the recognition of electrical hazards according to exposure and the skills and techniques * for nominal voltages not listed use the next higher voltage in the table. Find out how mads are calculated, what factors affect them and what working rules to follow. Web it is a central element of osha’s standard for electric power. Web osha table a minimum approach distances* *used only after aps has clarified specific voltage. Over 2 kv, not over 15 kv: Required encroachment prevention precautions— see osha 1408(b) you must do all of the following: Web for example, if the conductors are energized at 13.2 kv phase to phase, the minimum approach distance is 2 feet 3 inches and the worker’s arm reach is 3 feet, the worker must position their body 5 feet 3 inches from the energized conductor or device until they have donned rated rubber gloves. Web osha refers to mad as “the closest distance a qualified employee may approach an energized conductor or object.” osha mad requirements in 2014, osha updated the 29 cfr 1910.269 and 1926 subpart v standards with requirements for all employers to establish mads. Web minimum approach distances * category: Over 37 kv, not over 87.5 kv: Over 87.5 kv, not. Web for example, if the conductors are energized at 13.2 kv phase to phase, the minimum approach distance is 2 feet 3 inches and the worker’s arm reach is 3 feet, the worker must position their body 5 feet 3 inches from the energized conductor or device until they have donned rated rubber gloves. Web if employees will be working. Allen smith, manager, safety date published/rev. Web for example, if the conductors are energized at 13.2 kv phase to phase, the minimum approach distance is 2 feet 3 inches and the worker’s arm reach is 3 feet, the worker must position their body 5 feet 3 inches from the energized conductor or device until they have donned rated rubber gloves.. (3) until october 1, 2018, employers may utilize the minimum approach distances specified in appendix a, table 6 or tables 10 to 13. Web osha explains the minimum approach distance (mad) requirements for temporary protective grounds under 1910.269 when installing equipment on energized lines and equipment. Osha 29 cfr 1910.269 3.2. Web if employees will be working at elevations greater. Web if employees will be working at elevations greater than 900 meters (3,000 feet) above mean sea level, the employer shall determine minimum approach distances by multiplying the distances in this table by the correction factor in table r. 1910.269(a)(2)(ii)(e) 1926.950(b)(2)(v) training new added the recognition of electrical hazards according to exposure and the skills and techniques The safe work. The safe work practices required to ensure mad distances are maintained. Web for example, if the conductors are energized at 13.2 kv phase to phase, the minimum approach distance is 2 feet 3 inches and the worker’s arm reach is 3 feet, the worker must position their body 5 feet 3 inches from the energized conductor or device until they. Over 750v not over 2 kv: Web this web page explains the requirements for equipment operations near power lines up to 350 kv in construction. Voltage range (phase to phase, rms) approach distance (inches) 300 v and less (1) over 300v, not over 750v: Over 87.5 kv, not over. Required encroachment prevention precautions— see osha 1408(b) you must do all. Minimum approach distances ensure that workers do not approach or take any conductive object closer to the energized parts. See equations, tables, and references from 29 cfr 1926.960 and 29 cfr 1910.269. Over 37 kv, not over 87.5 kv: Over 15 kv, not over 37 kv: Nfpa 70e table 130.4 (c) (a) It includes a table of minimum approach distances based on voltage and a range of options to prevent encroachment and electrocution. The lab and rab vary depending on voltage present. Over 15 kv, not over 37 kv: Web for example, if the conductors are energized at 13.2 kv phase to phase, the minimum approach distance is 2 feet 3 inches. Switching surge analysis to determine the maximum anticipated Minimum approach distances ensure that workers do not approach or take any conductive object closer to the energized parts. The following table provides minimum approach distances grouped by nominal voltages. Osha 29 cfr 1910.269 3.2. Web osha explains the minimum approach distance (mad) requirements for temporary protective grounds under 1910.269 when installing. It includes a table of minimum approach distances based on voltage and a range of options to prevent encroachment and electrocution. 1910.269(a)(2)(ii)(e) 1926.950(b)(2)(v) training new added the recognition of electrical hazards according to exposure and the skills and techniques * for nominal voltages not listed use the next higher voltage in the table. The nfpa 70e and csa z462 standards provide guidance on the minimum distances that should be maintained between energized electrical equipment and workers based on the incident energy levels. Voltage range (phase to phase, rms) approach distance (inches) 300 v and less (1) over 300v, not over 750v: Find out how mads are calculated, what factors affect them and what working rules to follow. Table 2 — mad chart for incidental line clearance. Web the arc flash boundary is the minimum safe distance from the energized equipment that an unqualified worker can approach without wearing ppe. Over 2 kv, not over 15 kv: Web osha table a minimum approach distances* *used only after aps has clarified specific voltage. Minimum approach distances ensure that workers do not approach or take any conductive object closer to the energized parts. Allen smith, manager, safety date published/rev. Over 87.5 kv, not over. Altitude correction factor for minimum approach distances. Over 15 kv, not over 37 kv: Web osha explains the minimum approach distance (mad) requirements for temporary protective grounds under 1910.269 when installing equipment on energized lines and equipment.)
California Code of Regulations, Title 8, Section 2940.2. Minimum
)
California Code of Regulations, Title 8, Section 2940.2. Minimum
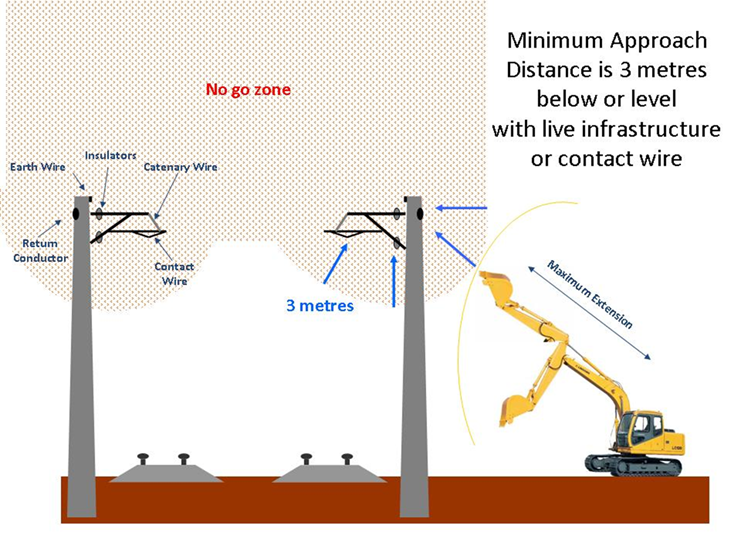
Electrical Safety Department for Infrastructure and Transport South
What is the OSHA? Occupational Safety & Health Association
)
California Code of Regulations, Title 8, Section 2940.2. Minimum

Workplace Safety Limits of Approach Always Look Up Electrical

OSHA Minimum Approach Distances Fact Sheet — State and Federal Poster
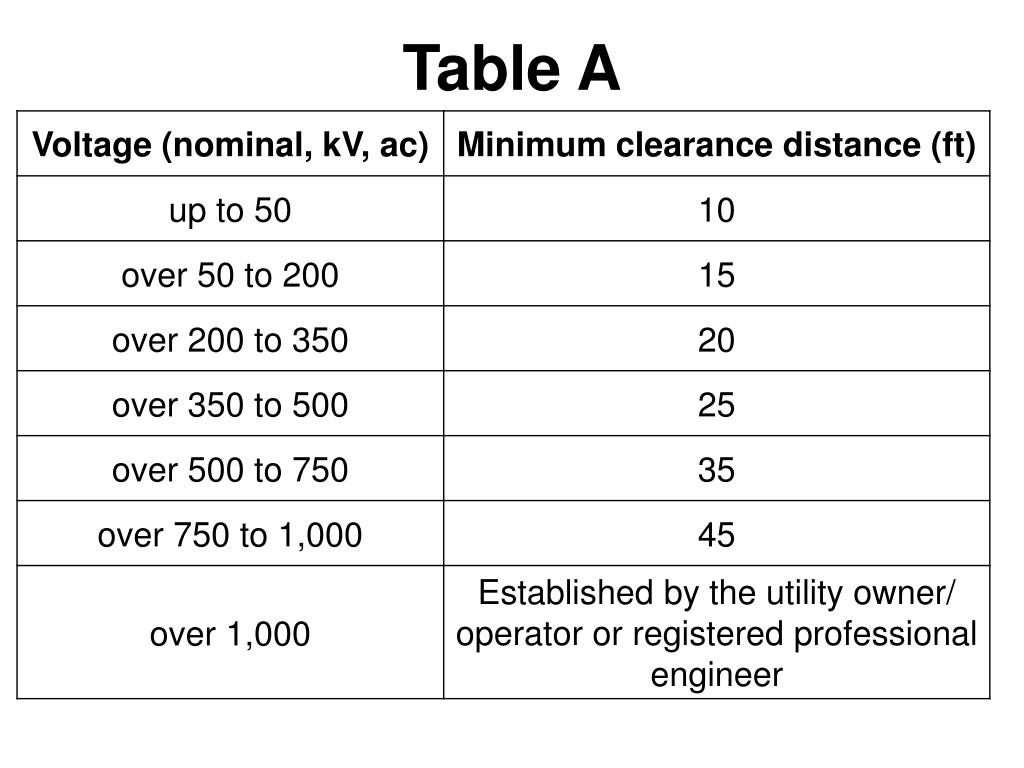
Minimum Approach Distance Chart
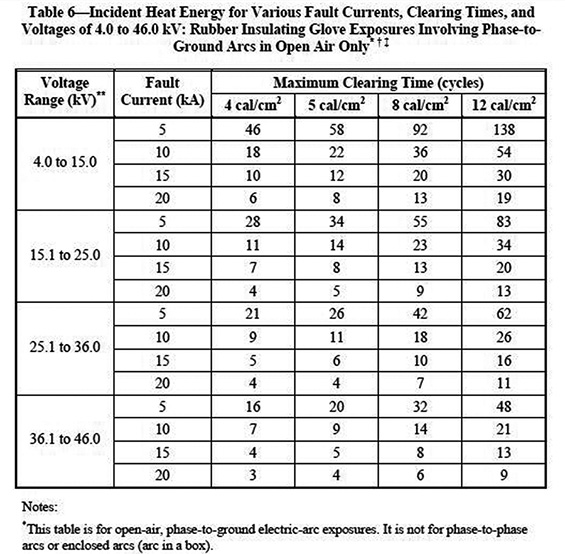
The Bigger Picture Electric Power Generation, Transmission, and

OSHA Minimum Approach Distances Fact Sheet — State and Federal Poster
Web Osha Refers To Mad As “The Closest Distance A Qualified Employee May Approach An Energized Conductor Or Object.” Osha Mad Requirements In 2014, Osha Updated The 29 Cfr 1910.269 And 1926 Subpart V Standards With Requirements For All Employers To Establish Mads.
Best Practice Is To Keep Any Unqualified Person 10’ Or More Away From The Hazard.
Required Encroachment Prevention Precautions— See Osha 1408(B) You Must Do All Of The Following:
Table 3 — Mad Chart For Utility Line Clearance.
Related Post: