Pathway Of Air Flow Chart
Pathway Of Air Flow Chart - The upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. The entrance to the larynx is covered by a small flap of tissue, the epiglottis, that automatically closes. Web the respiratory system. Nose/mouth pharynx glottis trachea bronchi bronchioles alveoli The air pressure within the alveoli, called alveolar pressure ( palv ); Web the pathway of air through the respiratory system. And the pressure within the pleural cavity, called intrapleural pressure ( pip ). Breathing is the process that brings oxygen in the air into your lungs and moves oxygen and through your body. Three in the right lung and two in the left lung. Each lung is divided into sections (lobes): Changes to the volume and air pressure in the lungs trigger pulmonary ventilation. Included in the upper respiratory tract are the nostrils, nasal cavities, pharynx, epiglottis, and the larynx. Web this activity has students create a flow chart that outlines this sequence and describes any changes that occurs to the composition of the air itself. It moves through the pharynx,. Air, a mix of oxygen and other gases, is inhaled. Web the respiratory tract is the path of air from the nose to the lungs. Your lungs are on each side of your heart, inside your chest cavity. Nose/mouth pharynx glottis trachea bronchi bronchioles alveoli Each bronchus divides into smaller bronchi, and again into even smaller tubes called bronchioles. It is divided into two sections: Upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. Web tiny air sacs that allow diffusion of oxygen out of lungs and into the blood, and the carbon dioxide out of blood and into the lungs. Air enters the respiratory system through the nose and mouth and passes down the throat (pharynx) and through the. The air pressure within the alveoli, called alveolar pressure ( palv ); Web in breathing, we take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide. Air, a mix of oxygen and other gases, is inhaled. The taking in of oxygen rich air is called inhalation and expelling air rich in carbon dioxide is called exhalation. Large surface area of alveoli; Identification of the pathway of air (limited to): Web in pulmonary ventilation, air is inhaled through the nasal and oral cavities (the nose and mouth). Large surface area of alveoli; Web the respiratory system starts at the nose and mouth and continues through the airways and the lungs. Web while in the capillaries, the blood moves carbon dioxide into the. The respiratory tract has two major divisions: The trachea branches into two bronchi , each leading into a lung. Each lung is divided into sections (lobes): Web the major mechanisms that drive pulmonary ventilation are atmospheric pressure ( patm ); Web use a flow chart with arrows to describe the path of air flow from the nose to the alveoli. The upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. Web while in the capillaries, the blood moves carbon dioxide into the alveoli and takes up oxygen from the air in the alveoli. Web this activity has students create a flow chart that outlines this sequence and describes any changes that occurs to the composition of the air itself. Nose/mouth pharynx. Changes to the volume and air pressure in the lungs trigger pulmonary ventilation. Web the respiratory system starts at the nose and mouth and continues through the airways and the lungs. Air enters the respiratory system through the nose and mouth and passes down the throat (pharynx) and through the voice box, or larynx. Nose/mouth pharynx glottis trachea bronchi bronchioles. Three in the right lung and two in the left lung. Identification of the pathway of air (limited to): Breathing is the process that brings oxygen in the air into your lungs and moves oxygen and through your body. Passage of air into the lungs. The upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. Web the respiratory system starts at the nose and mouth and continues through the airways and the lungs. It moves through the pharynx, larynx, and trachea into the lungs. Web this activity has students create a flow chart that outlines this sequence and describes any changes that occurs to the composition of the air itself. Web the pathway of air.. Epiglottis, a flap like structure controls the movement of food and air towards respective passage. Web the pathway of air through the respiratory system. Nose/mouth pharynx glottis trachea bronchi bronchioles alveoli Web the respiratory system starts at the nose and mouth and continues through the airways and the lungs. They are the main organs of the respiratory system. The thoracic cage and walls enclose this cavity and its structures, and play an essential role in pulmonary ventilation. The respiratory tract has two major divisions: Included in the upper respiratory tract are the nostrils, nasal cavities, pharynx, epiglottis, and the larynx. Web the organs of the respiratory system form a continuous system of passages called the respiratory tract, through which air flows into and out of the body. Large surface area of alveoli; Web the respiratory system. The entrance to the larynx is covered by a small flap of tissue, the epiglottis, that automatically closes. Web the trachea (windpipe) is the largest airway. It moves through the pharynx, larynx, and trachea into the lungs. Breathing is the process that brings oxygen in the air into your lungs and moves oxygen and through your body. The left and right mainstem [or main] bronchi.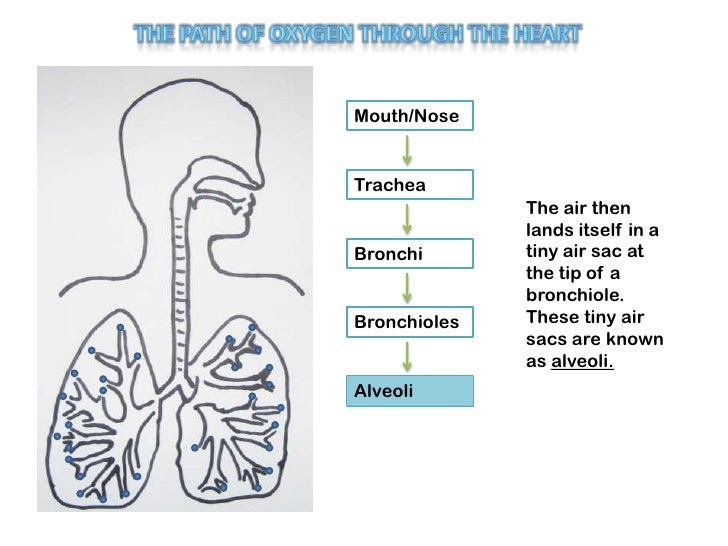
Respiratory System Pathway Of Air

Respiratory System

The Respiratory Pathway hubpages
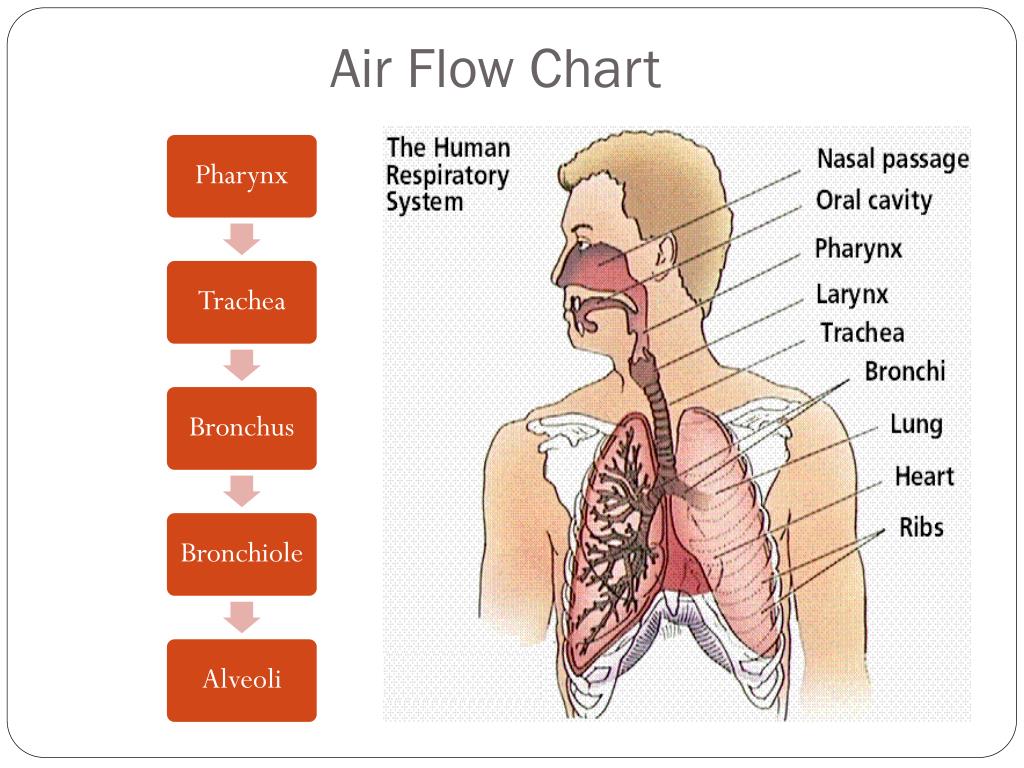
PPT The Respiratory System PowerPoint Presentation, free download

Ventilation (Clinical Essentials) (Paramedic Care) Part 1
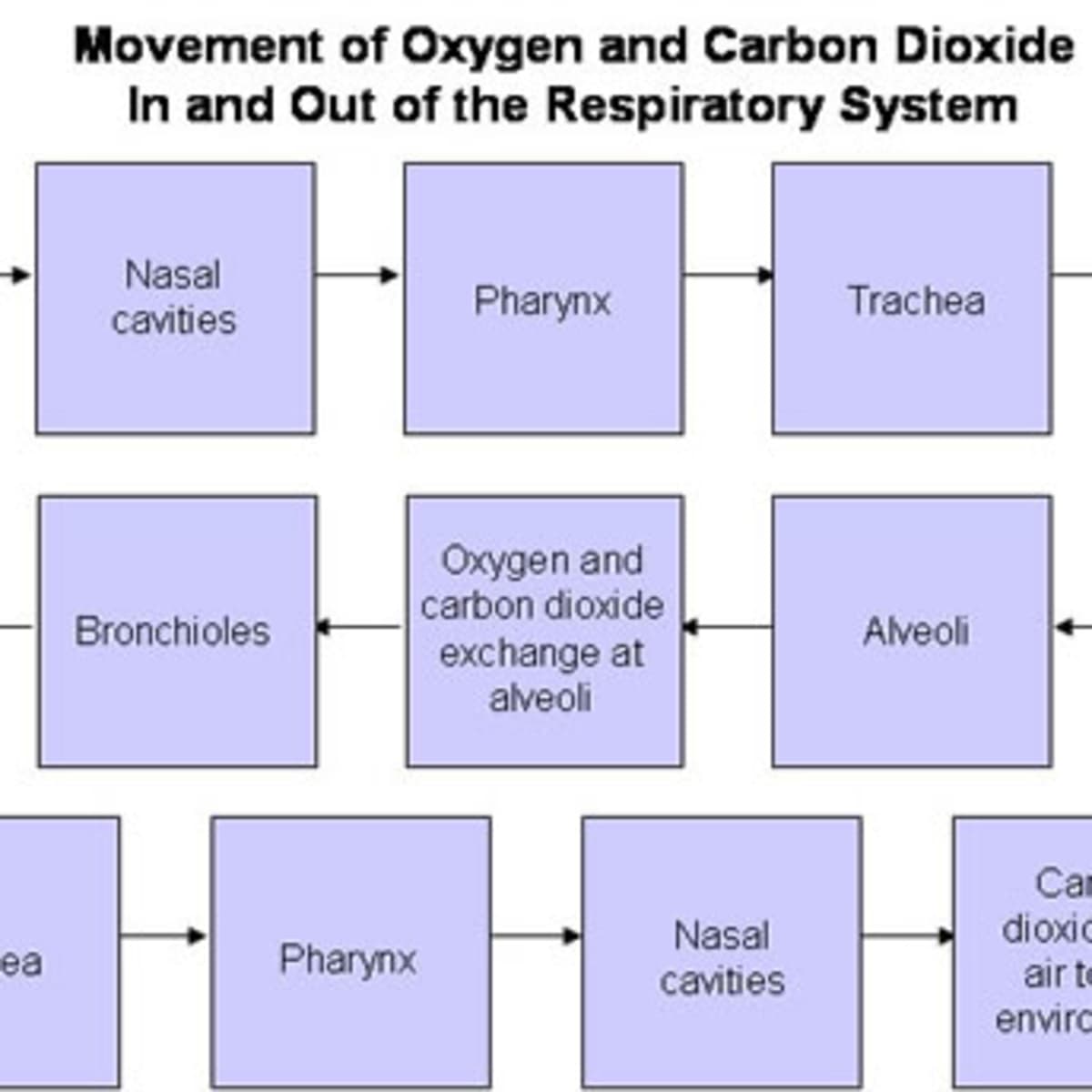
Pathway Of Oxygen Through The Respiratory System aromapic

Human Respiratory System Diagram + Flow Chart Teachoo
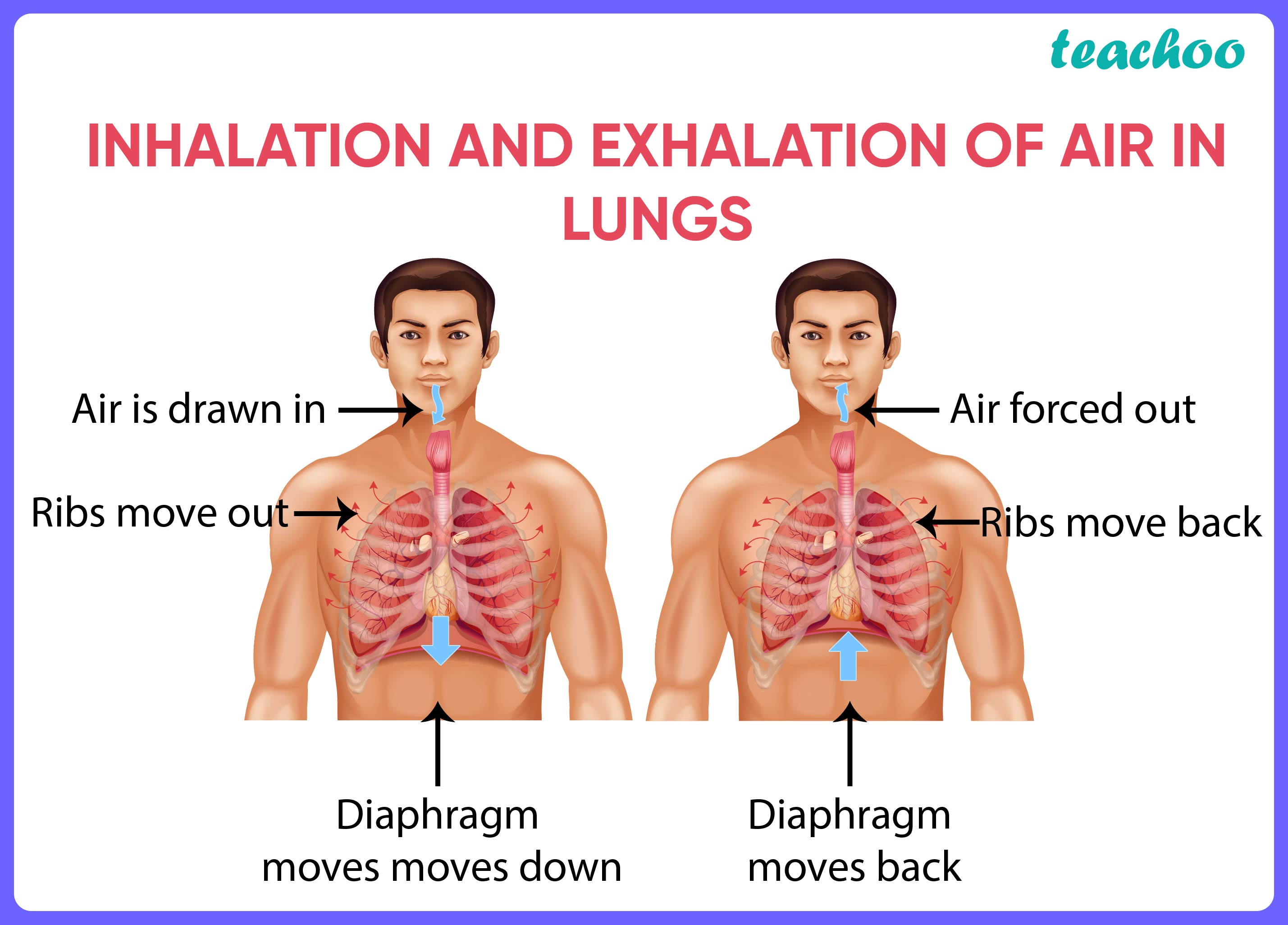
Human Respiratory System Diagram + Flow Chart Teachoo

Draw the flow chart for passing of air in the human respiratorysystem

Pathway Of Air Flow Chart
Web The Gas Exchange Process Is Performed By The Lungs And Respiratory System.
One Breath = 1 Inhalation + 1 Exhalation.
Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like Nose, Pharynx, Larynx And More.
Respiratory System Structure And Function.
Related Post: