Phosphorus Cycle Drawing
Phosphorus Cycle Drawing - Web the phosphorus cycle represents an essential method for freeing phosphorus bound to inorganic materials, such as rocks, minerals, and sediments. Web phosphorus moves in a cycle through rocks, water, soil and sediments and organisms. We need phosphorus for dna , rna, and atp, and it is also a limiting macronutrient. Web energy flows through an ecosystem and is dissipated as heat, but chemical elements are recycled. The global phosphorus cycle involves only aquatic and soil compartments. Normally, we find it in phosphate form. It occurs both in organic (nucleic acids, nucleoproteins, phospholipids, etc.) and inorganic (phosphate) forms in the living organisms. Weathering of rocks and volcanic activity releases phosphate into the soil, water, and air, where it becomes available to terrestrial food webs. The phosphorus cycle, unlike those of carbon and nitrogen cycles lacks an atmospheric component. Web describe the phosphorus cycle and the effects of phosphorus on the environment phosphorus is an essential nutrient for living processes. It is a major component of nucleic acid, both dna and rna; Web this illustration shows the phosphorus cycle. Web the phosphorus cycle is the process by which phosphorus moves through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. Of all the elements recycled in the biosphere, phosphorus is the scarcest and therefore the one most limiting in any given ecological system. Web. And, as calcium phosphate, makes up the supportive components of. A simplified drawing of the phosphorus cycle. Web 2 min read • december 25, 2022 s sumi vora phosphorus cycle phosphorus is really similar to nitrogen. So we're gonna talk about the phosphorous cycle. Of all the elements recycled in the biosphere, phosphorus is the scarcest and therefore the one. And, as calcium phosphate, makes up the supportive components of our bones. In nature, phosphorus exists as the phosphate ion (po 4 3−). Web the phosphorus cycle is the process by which phosphorus moves through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. Of phospholipids, the major component of cell membranes; It is indispensable to life, being intimately involved in energy transfer and. It is a major component of nucleic acids, both dna and rna; A simplified drawing of the phosphorus cycle. It instead cycles between land and water. Phosphorus is essential for plant and animal growth, as well as the health of microbes inhabiting the soil, but is gradually depleted from the soil over time. Web the phosphorus cycle represents an essential. The global phosphorus cycle involves only aquatic and soil compartments. In nature, phosphorus exists as the phosphate ion (po 4 3−). Biogeochemical process showing the movement of phosphorus and its different forms in nature with the help of living organisms is called the phosphorus cycle. Of all the elements recycled in the biosphere, phosphorus is the scarcest and therefore the. They are also an important component. Web after passing through biological via the food chain, phosphorus is eventually returned to the soil and then into systems, where it ultimately becomes sediment and can move back into the geological part of the cycle (figure 4). So we're gonna talk about the phosphorous cycle. Web phosphorus cycle (with diagram) article shared by. (ii) physical erosion and chemical weathering of rocks producing soils and providing dissolved and particulate phosphorus to rivers; The phosphorus cycle, unlike those of carbon and nitrogen cycles lacks an atmospheric component. Web phosphorus, crops and the environment. Web the global phosphorus cycle has four major components: It occurs both in organic (nucleic acids, nucleoproteins, phospholipids, etc.) and inorganic (phosphate). Web google classroom review your understanding of the phosphorus cycle in this free article aligned to ap standards. (iii) riverine transport of phosphorus to lakes and the ocean; It’s a building block of nucleic acids, like dna, and phospholipids that form our cell membranes. It is a major component of nucleic acids, both dna and rna; Key points phosphorus is. Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for living organisms. Of all the elements recycled in the biosphere, phosphorus is the scarcest and therefore the one most limiting in any given ecological system. It is a major component of nucleic acids, both dna and rna; Weathering of rocks and volcanic activity releases phosphate into the soil, water, and air, where it becomes. Some of the phosphorus from terrestrial food webs dissolves in streams and lakes, and the remainder enters the soil. Atmospheric deposition of phosphorus over some tropical forests and oceans is estimated to be greater than the flux from rock weathering [2]. It occurs both in organic (nucleic acids, nucleoproteins, phospholipids, etc.) and inorganic (phosphate) forms in the living organisms. Web. It is a major component of nucleic acid, both dna and rna; Atmospheric deposition of phosphorus over some tropical forests and oceans is estimated to be greater than the flux from rock weathering [2]. The phosphorus cycle, unlike those of carbon and nitrogen cycles lacks an atmospheric component. First, it's important to appreciate that phosphorous is a very reactive element, so it's seldom found by itself. Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for living processes. Some of the phosphorus from terrestrial food webs dissolves in streams and lakes, and the remainder enters the soil. Web after passing through biological via the food chain, phosphorus is eventually returned to the soil and then into systems, where it ultimately becomes sediment and can move back into the geological part of the cycle (figure 4). Web the phosphorus cycle is the biogeochemical cycle that describes the movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. This agronomy fact sheet provides a brief overview of the important components of the phosphorus (p) cycle. Normally, we find it in phosphate form. Phosphorus is often the limiting nutrient in ecosystems. Another source of phosphorus is fertilizers. Rocks, water, soil, and sediments constitute the primary nonliving sources of phosphorus, whereas plants and animals. A simplified drawing of the phosphorus cycle. Weathering of rocks and volcanic activity releases phosphate into the soil, water, and air, where it becomes available to terrestrial food webs. Web “phosphorus cycle is a biogeochemical process that involves the movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere.” what is phosphorus cycle?
Phosphorus Cycle BioNinja
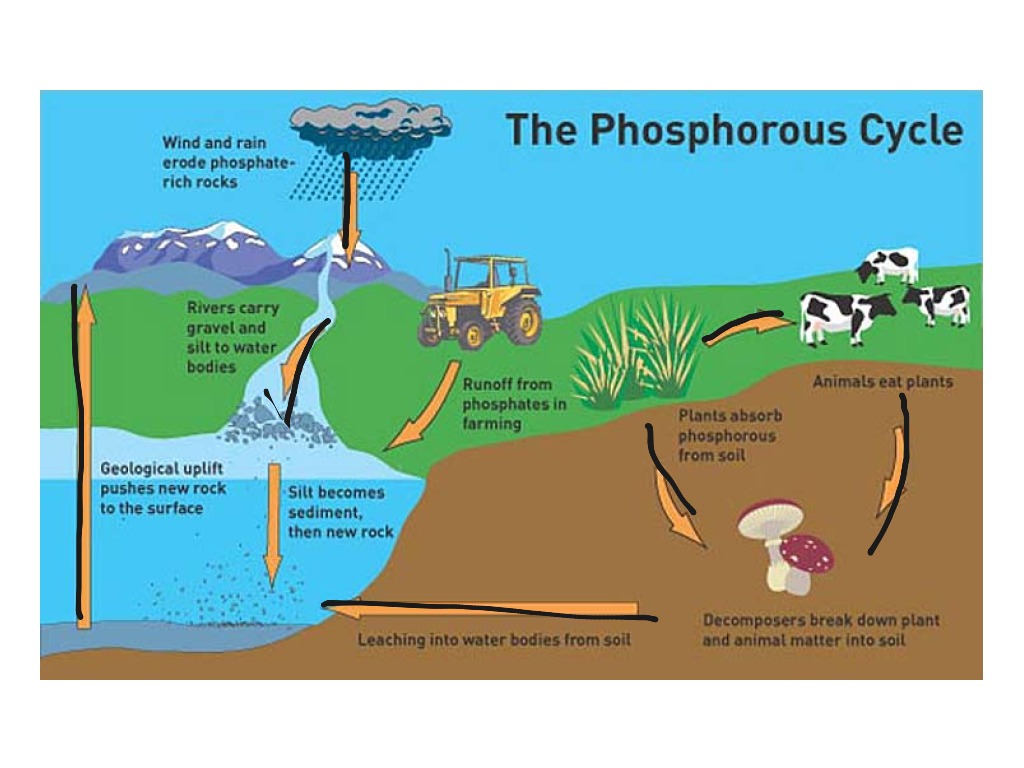
Phosphorus Cycle Science ShowMe
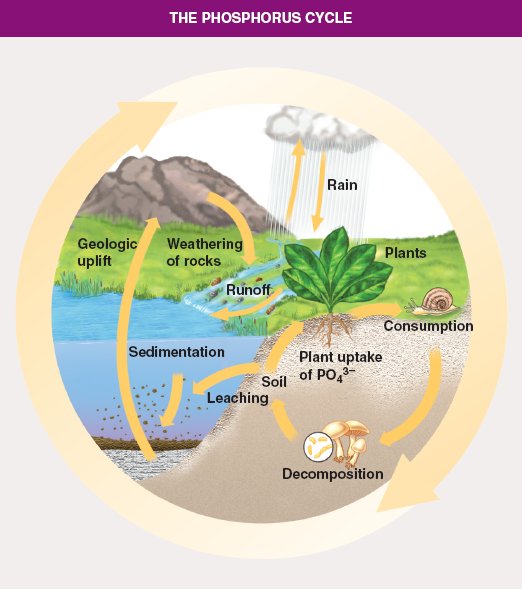
Phosphorus Cycle EFHS Biology 1 (Mr. Harrison) Biogeochemical Cycles

The Phosphorus Cycle (Courtesy International Plant Nutrition Institute
The Phosphorus Cycle Stock Illustration Download Image Now iStock

Schematic figure of the phosphorus cycle. Download Scientific Diagram
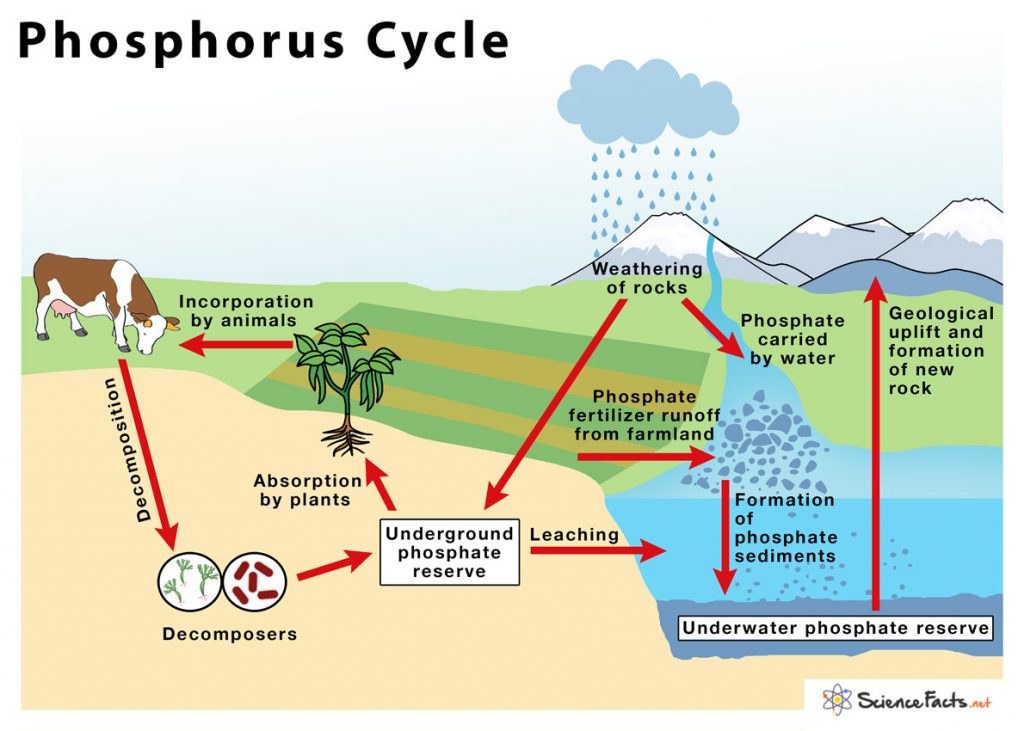
Phosphorus Cycle Definition, Steps, Importance, With Diagram
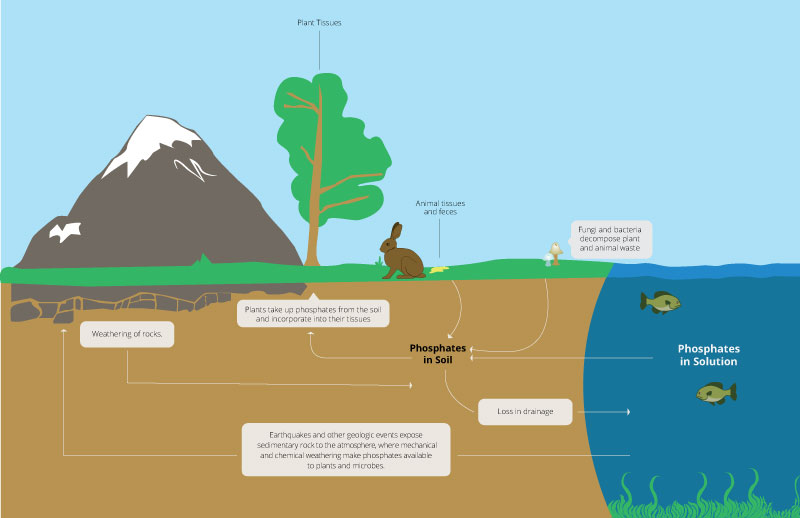
The Phosphorus Cycle Earth Science Visionlearning

Phosphorus Cycle Definition, Steps, Importance and It's Impact
The Phosphorus Cycle
In Nature, Phosphorus Exists As The Phosphate Ion (Po 4 3−).
It Is A Major Component Of Nucleic Acids, Both Dna And Rna;
Animals Possessing Bones Have Large Amount Of Phosphorus In Its Inorganic Form.
Of All The Elements Recycled In The Biosphere, Phosphorus Is The Scarcest And Therefore The One Most Limiting In Any Given Ecological System.
Related Post:

