Plasticity Index Chart
Plasticity Index Chart - Therefore, the lower bound of the chart is defined by the ll = pi boundary. Web plasticity chart used with the unified soil classification system (astm 2011). Web however, in general, the plasticity index of clay minerals ranges from about 5 to 50. Plasticity index (pi or i p) is calculated as the plastic limit subtracted from the liquid limit and is an important value when classifying soil types. Web vardanega et al. Web plasticity index (pi) is the numerical difference between liquid limit and plastic limit. Web plasticity chart, developed by arthur casagrande (1932) is a plot of the plasticity index (pi) versus the liquid limit (ll) of soils. Soils with a high pi tend to be clay, those with a lower pi tend to be. Therefore, the lower bound of the chart is defined by the ll = pi boundary A definition as to whether soil groups form a continuum between clay and silt or whether they are subsets of them. The pi is defined as the range of moisture contents over which the soil deforms plastically. Web vardanega et al. The plasticity index must be ≥0; Determine which type of soil is located on the left side of the boundary line and which type is located on the right side of the boundary line. Web a recommended plasticity chart that. I.e., (2.19) the pi thus is a measure of the plasticity of a soil. Plasticity index (pi or i p) is calculated as the plastic limit subtracted from the liquid limit and is an important value when classifying soil types. Web plasticity index (pi) is the numerical difference between liquid limit and plastic limit. It is necessary to adopt a. Usually plasticity index depends on the amount of clay present in the soil. Web current state of soil. A definition as to whether soil groups form a continuum between clay and silt or whether they are subsets of them. Web among the index parameters, atterberg limits (atterberg 1911a, 1911b) (including the liquid limit ( ll) and plastic limit ( pl. Pi indicates the range of water contents over which a soil behaves as a plastic material. Determine which type of soil is located on the left side of the boundary line and which type is located on the right side of the boundary line. I.e., (2.19) the pi thus is a measure of the plasticity of a soil. The plasticity. Web plasticity chart used with the unified soil classification system (astm 2011). Web a recommended plasticity chart that defines low, medium and high plasticity. 34k views 3 years ago soil mechanics tutorials. Web the plasticity index (pi) quantifies the plastic behavior of soil, differentiating moisture content levels where soil retains plasticity, and is calculated by subtracting the plastic limit (pl). In particular, the dilatancy or plasticity characteristics of soils such as clayey silt should be clearly defined. Web current state of soil. Plasticity index (pi or i p) is calculated as the plastic limit subtracted from the liquid limit and is an important value when classifying soil types. I.e., (2.19) the pi thus is a measure of the plasticity of. Web the plasticity index (pi) is a measure of the plasticity of a soil. Begin by locating the boundary between the two main soil categories, which is indicated by a dashed line on the graph. It is necessary to adopt a formal system of soil description and classification in order to describe the various materials found in ground investigation. The. A definition as to whether soil groups form a continuum between clay and silt or whether they are subsets of them. Soils with a high pi tend to be clay, those with a lower pi tend to be silt, and. 34k views 3 years ago soil mechanics tutorials. I.e., (2.19) the pi thus is a measure of the plasticity of. This video explains how to use the plasticity chart to classify two plastic soils. Web the plasticity index (pi) is a measure of the plasticity of a soil. The plasticity index is defined as the difference between the liquid limit and the plastic limit. The plasticity index is the size of the range of water contents where the soil exhibits. Web the plasticity index (pi) is a measure of the plasticity of a soil. 34k views 3 years ago soil mechanics tutorials. The plasticity index is the size of the range of water contents where the soil exhibits plastic properties. It is necessary to adopt a formal system of soil description and classification in order to describe the various materials. Therefore, the lower bound of the chart is defined by the ll = pi boundary. The pi is defined as the range of moisture contents over which the soil deforms plastically. A high value of pi indicates an excess of clay in. The chart is used for the classification of fine grained soils (or fine grained fraction of coarse grained soils) based on their plasticity. Web the plasticity index (pi) is a measure of the plasticity of a soil. Usually plasticity index depends on the amount of clay present in the soil. In particular, the dilatancy or plasticity characteristics of soils such as clayey silt should be clearly defined. Web plasticity chart, developed by arthur casagrande (1932) is a plot of the plasticity index (pi) versus the liquid limit (ll) of soils. Web the plasticity index (pi) quantifies the plastic behavior of soil, differentiating moisture content levels where soil retains plasticity, and is calculated by subtracting the plastic limit (pl) from the liquid limit (ll), providing crucial insights into soil behavior for engineering applications. Web plasticity index (pi) is the numerical difference between liquid limit and plastic limit. Web the plasticity index (pi) is a measure of the plasticity of a soil. Pi indicates the range of water contents over which a soil behaves as a plastic material. Web vardanega et al. The pi is thus defined to be the difference between the ll and the pl; The plasticity index is defined as the difference between the liquid limit and the plastic limit. Web plasticity chart used with the unified soil classification system (astm 2011).Liquid Limit and Plasticity Index Chart PDF Solid Mechanics

Plasticity Index
Plasticity Index

Plasticity chart for the classification of finegrained soil (A

Fine Soil Classification Part 3 Determination Plasticity Index and the

Plasticity Index Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Plasticity Chart from ASTM Standard D 248793 Classification for

Plasticity indices and liquid limits of residual soils represented in
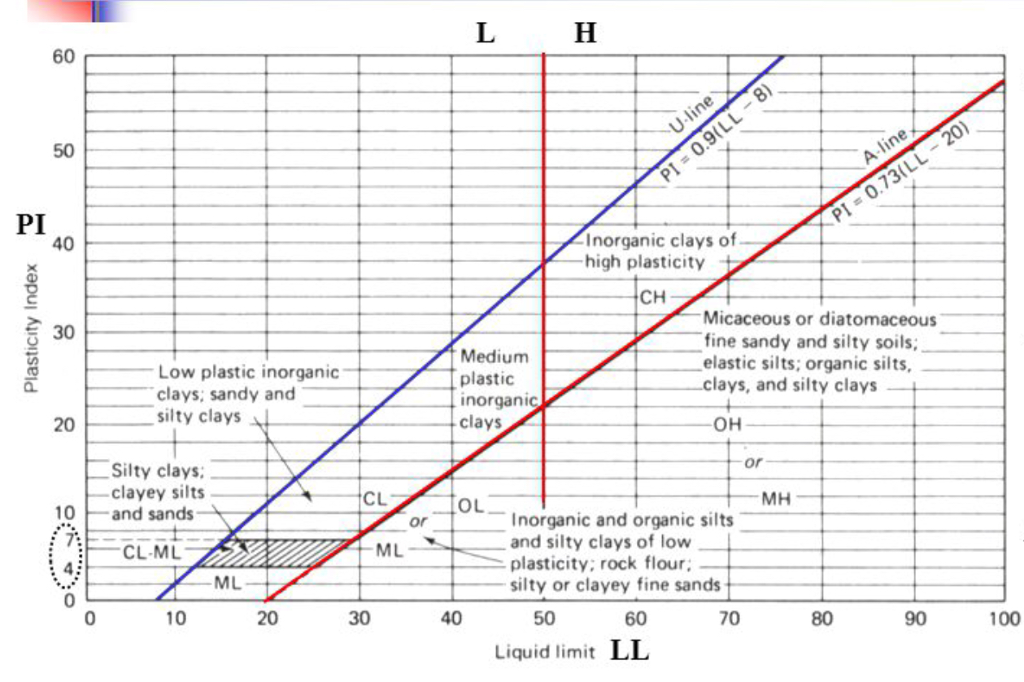
Solved Determine plasticity index and classify soil using
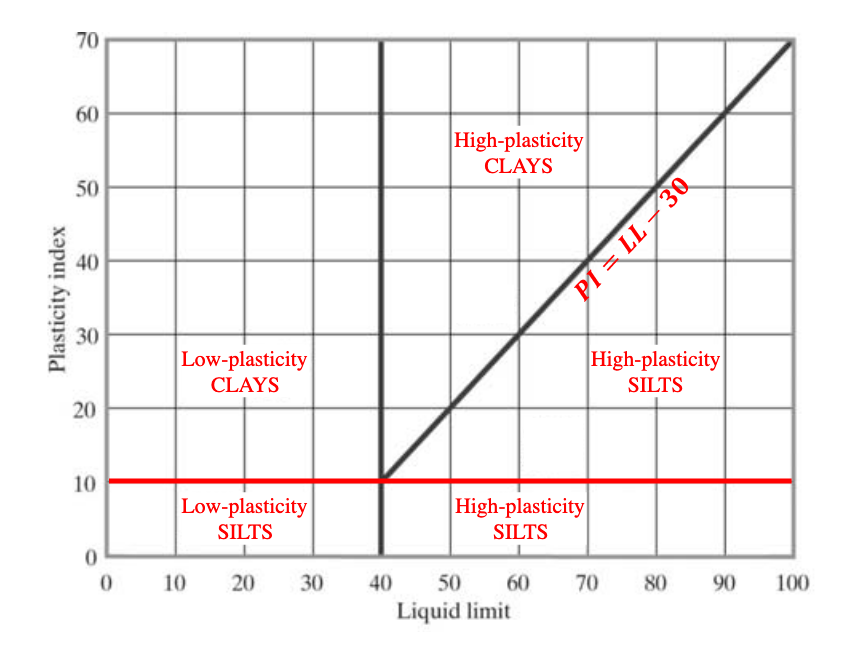
AASHTO Soil Classification System AASHTO Chart
Web The Liquid Limit And Plasticity Index In The Unified Soil Classification System Are Determined And Plotted On The Plasticity Chart.
Plasticity Index (Pi Or I P) Is Calculated As The Plastic Limit Subtracted From The Liquid Limit And Is An Important Value When Classifying Soil Types.
Web However, In General, The Plasticity Index Of Clay Minerals Ranges From About 5 To 50.
Web Among The Index Parameters, Atterberg Limits (Atterberg 1911A, 1911B) (Including The Liquid Limit ( Ll) And Plastic Limit ( Pl )) Are Some Of The Oldest Tests For The Fine Grained Soils, Yet They Are Frequently Used.
Related Post:
